Selective Leaflet-Anchored DNA Nanoprobes for Simultaneous Monitoring of Juxta-Plasma Membrane Environments
Yao He
Molecular Science and Biomedicine Laboratory (MBL), State Key Laboratory of Chemo/Biosensing and Chemometrics, College of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering College of Biology, Aptamer Engineering Center of Hunan Province, Hunan University, Changsha, Hunan, 410082 China
Search for more papers by this authorJie Lin
Molecular Science and Biomedicine Laboratory (MBL), State Key Laboratory of Chemo/Biosensing and Chemometrics, College of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering College of Biology, Aptamer Engineering Center of Hunan Province, Hunan University, Changsha, Hunan, 410082 China
Search for more papers by this authorFandi Wu
Molecular Science and Biomedicine Laboratory (MBL), State Key Laboratory of Chemo/Biosensing and Chemometrics, College of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering College of Biology, Aptamer Engineering Center of Hunan Province, Hunan University, Changsha, Hunan, 410082 China
Search for more papers by this authorYong-Hao Ma
Molecular Science and Biomedicine Laboratory (MBL), State Key Laboratory of Chemo/Biosensing and Chemometrics, College of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering College of Biology, Aptamer Engineering Center of Hunan Province, Hunan University, Changsha, Hunan, 410082 China
Search for more papers by this authorZhaoyang Wang
Molecular Science and Biomedicine Laboratory (MBL), State Key Laboratory of Chemo/Biosensing and Chemometrics, College of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering College of Biology, Aptamer Engineering Center of Hunan Province, Hunan University, Changsha, Hunan, 410082 China
Search for more papers by this authorHui Wu
The Key Laboratory of Zhejiang Province for Aptamers and Theranostics Zhejiang Cancer Hospital, Hangzhou Institute of Medicine (HIM), Chinese Academy of Sciences, Hangzhou, Zhejiang, 310022 China
Search for more papers by this authorZhimin Wang
Molecular Science and Biomedicine Laboratory (MBL), State Key Laboratory of Chemo/Biosensing and Chemometrics, College of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering College of Biology, Aptamer Engineering Center of Hunan Province, Hunan University, Changsha, Hunan, 410082 China
Search for more papers by this authorNachuan Wen
Molecular Science and Biomedicine Laboratory (MBL), State Key Laboratory of Chemo/Biosensing and Chemometrics, College of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering College of Biology, Aptamer Engineering Center of Hunan Province, Hunan University, Changsha, Hunan, 410082 China
The Key Laboratory of Zhejiang Province for Aptamers and Theranostics Zhejiang Cancer Hospital, Hangzhou Institute of Medicine (HIM), Chinese Academy of Sciences, Hangzhou, Zhejiang, 310022 China
Search for more papers by this authorYutong Zhang
Molecular Science and Biomedicine Laboratory (MBL), State Key Laboratory of Chemo/Biosensing and Chemometrics, College of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering College of Biology, Aptamer Engineering Center of Hunan Province, Hunan University, Changsha, Hunan, 410082 China
The Key Laboratory of Zhejiang Province for Aptamers and Theranostics Zhejiang Cancer Hospital, Hangzhou Institute of Medicine (HIM), Chinese Academy of Sciences, Hangzhou, Zhejiang, 310022 China
Search for more papers by this authorWenfei Guo
Molecular Science and Biomedicine Laboratory (MBL), State Key Laboratory of Chemo/Biosensing and Chemometrics, College of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering College of Biology, Aptamer Engineering Center of Hunan Province, Hunan University, Changsha, Hunan, 410082 China
The Key Laboratory of Zhejiang Province for Aptamers and Theranostics Zhejiang Cancer Hospital, Hangzhou Institute of Medicine (HIM), Chinese Academy of Sciences, Hangzhou, Zhejiang, 310022 China
Search for more papers by this authorYulin Du
The Key Laboratory of Zhejiang Province for Aptamers and Theranostics Zhejiang Cancer Hospital, Hangzhou Institute of Medicine (HIM), Chinese Academy of Sciences, Hangzhou, Zhejiang, 310022 China
Search for more papers by this authorWeihong Tan
Molecular Science and Biomedicine Laboratory (MBL), State Key Laboratory of Chemo/Biosensing and Chemometrics, College of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering College of Biology, Aptamer Engineering Center of Hunan Province, Hunan University, Changsha, Hunan, 410082 China
The Key Laboratory of Zhejiang Province for Aptamers and Theranostics Zhejiang Cancer Hospital, Hangzhou Institute of Medicine (HIM), Chinese Academy of Sciences, Hangzhou, Zhejiang, 310022 China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Liping Qiu
Molecular Science and Biomedicine Laboratory (MBL), State Key Laboratory of Chemo/Biosensing and Chemometrics, College of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering College of Biology, Aptamer Engineering Center of Hunan Province, Hunan University, Changsha, Hunan, 410082 China
The Key Laboratory of Zhejiang Province for Aptamers and Theranostics Zhejiang Cancer Hospital, Hangzhou Institute of Medicine (HIM), Chinese Academy of Sciences, Hangzhou, Zhejiang, 310022 China
E-mail: [email protected]
Search for more papers by this authorYao He
Molecular Science and Biomedicine Laboratory (MBL), State Key Laboratory of Chemo/Biosensing and Chemometrics, College of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering College of Biology, Aptamer Engineering Center of Hunan Province, Hunan University, Changsha, Hunan, 410082 China
Search for more papers by this authorJie Lin
Molecular Science and Biomedicine Laboratory (MBL), State Key Laboratory of Chemo/Biosensing and Chemometrics, College of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering College of Biology, Aptamer Engineering Center of Hunan Province, Hunan University, Changsha, Hunan, 410082 China
Search for more papers by this authorFandi Wu
Molecular Science and Biomedicine Laboratory (MBL), State Key Laboratory of Chemo/Biosensing and Chemometrics, College of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering College of Biology, Aptamer Engineering Center of Hunan Province, Hunan University, Changsha, Hunan, 410082 China
Search for more papers by this authorYong-Hao Ma
Molecular Science and Biomedicine Laboratory (MBL), State Key Laboratory of Chemo/Biosensing and Chemometrics, College of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering College of Biology, Aptamer Engineering Center of Hunan Province, Hunan University, Changsha, Hunan, 410082 China
Search for more papers by this authorZhaoyang Wang
Molecular Science and Biomedicine Laboratory (MBL), State Key Laboratory of Chemo/Biosensing and Chemometrics, College of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering College of Biology, Aptamer Engineering Center of Hunan Province, Hunan University, Changsha, Hunan, 410082 China
Search for more papers by this authorHui Wu
The Key Laboratory of Zhejiang Province for Aptamers and Theranostics Zhejiang Cancer Hospital, Hangzhou Institute of Medicine (HIM), Chinese Academy of Sciences, Hangzhou, Zhejiang, 310022 China
Search for more papers by this authorZhimin Wang
Molecular Science and Biomedicine Laboratory (MBL), State Key Laboratory of Chemo/Biosensing and Chemometrics, College of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering College of Biology, Aptamer Engineering Center of Hunan Province, Hunan University, Changsha, Hunan, 410082 China
Search for more papers by this authorNachuan Wen
Molecular Science and Biomedicine Laboratory (MBL), State Key Laboratory of Chemo/Biosensing and Chemometrics, College of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering College of Biology, Aptamer Engineering Center of Hunan Province, Hunan University, Changsha, Hunan, 410082 China
The Key Laboratory of Zhejiang Province for Aptamers and Theranostics Zhejiang Cancer Hospital, Hangzhou Institute of Medicine (HIM), Chinese Academy of Sciences, Hangzhou, Zhejiang, 310022 China
Search for more papers by this authorYutong Zhang
Molecular Science and Biomedicine Laboratory (MBL), State Key Laboratory of Chemo/Biosensing and Chemometrics, College of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering College of Biology, Aptamer Engineering Center of Hunan Province, Hunan University, Changsha, Hunan, 410082 China
The Key Laboratory of Zhejiang Province for Aptamers and Theranostics Zhejiang Cancer Hospital, Hangzhou Institute of Medicine (HIM), Chinese Academy of Sciences, Hangzhou, Zhejiang, 310022 China
Search for more papers by this authorWenfei Guo
Molecular Science and Biomedicine Laboratory (MBL), State Key Laboratory of Chemo/Biosensing and Chemometrics, College of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering College of Biology, Aptamer Engineering Center of Hunan Province, Hunan University, Changsha, Hunan, 410082 China
The Key Laboratory of Zhejiang Province for Aptamers and Theranostics Zhejiang Cancer Hospital, Hangzhou Institute of Medicine (HIM), Chinese Academy of Sciences, Hangzhou, Zhejiang, 310022 China
Search for more papers by this authorYulin Du
The Key Laboratory of Zhejiang Province for Aptamers and Theranostics Zhejiang Cancer Hospital, Hangzhou Institute of Medicine (HIM), Chinese Academy of Sciences, Hangzhou, Zhejiang, 310022 China
Search for more papers by this authorWeihong Tan
Molecular Science and Biomedicine Laboratory (MBL), State Key Laboratory of Chemo/Biosensing and Chemometrics, College of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering College of Biology, Aptamer Engineering Center of Hunan Province, Hunan University, Changsha, Hunan, 410082 China
The Key Laboratory of Zhejiang Province for Aptamers and Theranostics Zhejiang Cancer Hospital, Hangzhou Institute of Medicine (HIM), Chinese Academy of Sciences, Hangzhou, Zhejiang, 310022 China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Liping Qiu
Molecular Science and Biomedicine Laboratory (MBL), State Key Laboratory of Chemo/Biosensing and Chemometrics, College of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering College of Biology, Aptamer Engineering Center of Hunan Province, Hunan University, Changsha, Hunan, 410082 China
The Key Laboratory of Zhejiang Province for Aptamers and Theranostics Zhejiang Cancer Hospital, Hangzhou Institute of Medicine (HIM), Chinese Academy of Sciences, Hangzhou, Zhejiang, 310022 China
E-mail: [email protected]
Search for more papers by this authorGraphical Abstract
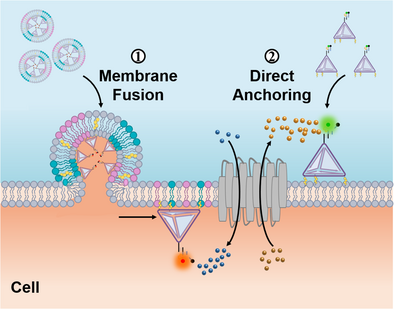
Fusogenic nanoliposomes were developed to effectively anchor amphiphilic DNA tetrahedral probes onto the inner leaflet of the cell membrane. By combining this strategy with the direct anchoring of amphiphilic probes on the outer leaflet, precise functionalization of both membrane leaflets could be achieved, thereby enabling simultaneous monitoring of both the inner and outer juxta-plasma membrane environments.
Abstract
The cell membrane functions as a bidirectional interface that coordinates the selective transport of substances and information between the interior and exterior of the cell. Simultaneous monitoring of both the inner and outer local environments surrounding this lipid bilayer is crucial for elucidating various cellular activities but significantly challenged by the lack of technologies capable of precisely engineering biosensing probes on both membrane leaflets. In this work, by developing fusogenic nanoliposomes with high cell fusion efficiency, we successfully anchored amphiphilic DNA tetrahedral probes onto the inner leaflet of the plasma membrane. By integrating this with the direct anchoring of amphiphilic probes on the outer leaflet, we achieved precise functionalization of both leaflets of the cell membrane, thus enabling simultaneous monitoring of localized targets within their respective juxta-plasma membrane environments, avoiding signal contamination caused by the optical diffraction limit. Using selectively dual-leaflet-anchored tetrahedral DNAzyme probes, we revealed that the transmembrane ion channel SLC41A1 synergistically modulated the influx of Na+ and the efflux of Mg2+ in live cells. With a modular design, this membrane-anchored DNA nanoplatform can be readily extended for the study of bilateral interface-dominant cellular processes, shifting the paradigm toward a more localized and subtle perspective.
Conflict of Interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Open Research
Data Availability Statement
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
Supporting Information
| Filename | Description |
|---|---|
| anie202425335-sup-0001-SuppMat.docx50.8 MB | Supporting Information |
Please note: The publisher is not responsible for the content or functionality of any supporting information supplied by the authors. Any queries (other than missing content) should be directed to the corresponding author for the article.
References
- 1H. E. Grecco, M. Schmick, P. I. H. Bastiaens, Cell 2011, 144, 897–909.
- 2S. E. Anton, C. Kayser, I. Maiellaro, K. Nemec, J. Möller, A. Koschinski, M. Zaccolo, P. Annibale, M. Falcke, M. J. Lohse, A. Bock, Cell 2022, 185, 1130–1142.
- 3A. C. Newton, M. D. Bootman, J. D. Scott, Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2016, 8, a005926.
- 4Y. Bagheri, F. Shafiei, S. Chedid, B. Zhao, M. You, Supramol. Chem. 2019, 31, 532–544.
- 5Y. Chen, T. Wu, S. Xie, Y. Bai, H. Xing, Sci. Adv. 2023, 9, eadg2583.
- 6M. J. Lin, Y. Y. Chen, S. S. Zhao, R. Tang, Z. Nie, H. Xing, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2022, 61, e202111647.
- 7A. Csiszár, N. Hersch, S. Dieluweit, R. Biehl, R. Merkel, B. Hoffmann, Bioconjugate Chem. 2010, 21, 537–543.
- 8M. C. Smith, R. M. Crist, J. D. Clogston, S. E. McNeil, Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2017, 409, 5779–5787.
- 9Y. Zhuo, Z. Luo, Z. Zhu, J. Wang, X. Li, Z. Zhang, C. Guo, B. Wang, D. Nie, Y. Gan, G. Hu, M. Yu, Nat. Nanotechnol. 2024, 19, 1858–1868.
- 10L. V. Chernomordik, M. M. Kozlov, Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2008, 15, 675–683.
- 11A. H. de Vries, A. E. Mark, S. J. Marrink, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2004, 126, 4488–4489.
- 12R. Ziblat, L. Leiserowitz, L. Addadi, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 132, 9920–9927.
- 13D. H. Johnson, O. H. Kou, N. Bouzos, W. F. Zeno, Trends Biochem. Sci. 2024, 49, 401–416.
- 14M. Sharma, M. Marin, H. Wu, D. Prikryl, G. B. Melikyan, ACS Nano 2023, 17, 17436–17450.
- 15M. Sousa de Almeida, E. Susnik, B. Drasler, P. Taladriz-Blanco, A. Petri-Fink, B. Rothen-Rutishauser, Chem. Soc. Rev. 2021, 50, 5397–5434.
- 16J. J. Rennick, A. P. R. Johnston, R. G. Parton, Nat. Nanotechnol. 2021, 16, 266–276.
- 17J. Yang, A. Bahreman, G. Daudey, J. Bussmann, R. C. L. Olsthoorn, A. Kros, ACS Cent. Sci. 2016, 2, 621–630.
- 18J. P. Leonetti, N. Mechti, G. Degols, C. Gagnor, B. Lebleu, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1991, 88, 2702–2706.
- 19M. M. Mhlanga, D. Y. Vargas, C. W. Fung, F. R. Kramer, S. Tyagi, Nucleic Acids Res. 2005, 33, 1902–1912.
- 20Z. Wang, X. Wang, Y. He, H. Wu, R. Mao, H. Wang, L. Qiu, JACS Au 2024, 4, 4110–4128.
- 21J. Li, K. Xun, K. Pei, X. Liu, X. Peng, Y. Du, L. Qiu, W. Tan, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2019, 141, 18013–18020.
- 22B. Chen, P. Yu, W. N. Chan, F. Xie, Y. Zhang, L. Liang, K. T. Leung, K. W. Lo, J. Yu, G. M. K. Tse, W. Kang, K. F. To, Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2024, 9, 1–41.
- 23J. S. Qi, Y. H. Xing, Y. C. Liu, M. M. Wang, X. Q. Wei, Z. H. Sui, L. Ding, Y. Zhang, C. Lu, Y. H. Fei, N. Liu, R. Chen, M. M. Wu, L. J. Wang, Z. Y. Zhong, T. Wang, Y. F. Liu, Y. Q. Wang, J. M. Liu, H. X. Xu, F. Guo, W. Y. Wang, Autophagy 2021, 17, 4401–4422.
- 24J. Hu, X. Luo, M. J. Panga, C. Appiah, V. Retyunskiy, L. Zhu, Y. Zhao, J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 461, 132575.
- 25T. Nemoto, H. Tagashira, T. Kita, S. Kita, T. Iwamoto, J. Pharmacol. Sci. 2023, 151, 88–92.
- 26Z. Deng, P. Gao, H. Liu, Y. He, S. Zhong, Y. Yang, Anal. Chem. 2021, 93, 16432–16438.
- 27L. Qiu, T. Zhang, J. Jiang, C. Wu, G. Zhu, M. You, X. Chen, L. Zhang, C. Cui, R. Yu, W. Tan, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2014, 136, 13090–13093.
- 28K. Jomova, M. Makova, S. Y. Alomar, S. H. Alwasel, E. Nepovimova, K. Kuca, C. J. Rhodes, M. Valko, Chem. Biol. Interact. 2022, 367, 110173.
- 29X. Wang, G. Kim, J. L. Chu, T. Song, Z. Yang, W. Guo, X. Shao, M. L. Oelze, K. C. Li, Y. Lu, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2022, 144, 5812–5819.
- 30T. E. Fagan, A. Romani, Am. J. Physiol. 2000, 279, G943–G950.
- 31A. Tucci, M. A. Nalls, H. Houlden, T. Revesz, A. B. Singleton, N. W. Wood, J. Hardy, C. Paisán-Ruiz, Eur. J. Hum. Genet. 2010, 18, 1356–1359.
- 32M. Kolisek, A. Nestler, J. Vormann, M. Schweigel-Röntgen, Am. J. Physiol. 2012, 302, C318–C326.
- 33M. Kolisek, G. Sponder, L. Mastrototaro, A. Smorodchenko, P. Launay, J. Vormann, M. Schweigel-Röntgen, PLoS One 2013, 8, e71096.
- 34P. Dalal, A. Romani, Metabolism 2010, 59, 1663–1671.