Alcohol Activation by Benzodithiolylium for Deoxygenative Alkylation Driven by Photocatalytic Energy Transfer
Bin-Qing He
Hubei Key Laboratory of Bioinorganic Chemistry & Materia Medica, School of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan, 430074 P.R. China
Both authors contributed equally to this work.
Search for more papers by this authorLu Zhao
Hubei Key Laboratory of Bioinorganic Chemistry & Materia Medica, School of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan, 430074 P.R. China
Both authors contributed equally to this work.
Search for more papers by this authorJun Zhang
Hubei Key Laboratory of Bioinorganic Chemistry & Materia Medica, School of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan, 430074 P.R. China
Search for more papers by this authorWen-Hui Bao
Hubei Key Laboratory of Bioinorganic Chemistry & Materia Medica, School of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan, 430074 P.R. China
Search for more papers by this authorMingjun Yang
Computational R&D, Shenzhen Jingtai Technology Co., Ltd. (XtalPi), Shenzhen, 518000 P.R. China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Xuesong Wu
Hubei Key Laboratory of Bioinorganic Chemistry & Materia Medica, School of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan, 430074 P.R. China
E-mail: [email protected]
Search for more papers by this authorBin-Qing He
Hubei Key Laboratory of Bioinorganic Chemistry & Materia Medica, School of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan, 430074 P.R. China
Both authors contributed equally to this work.
Search for more papers by this authorLu Zhao
Hubei Key Laboratory of Bioinorganic Chemistry & Materia Medica, School of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan, 430074 P.R. China
Both authors contributed equally to this work.
Search for more papers by this authorJun Zhang
Hubei Key Laboratory of Bioinorganic Chemistry & Materia Medica, School of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan, 430074 P.R. China
Search for more papers by this authorWen-Hui Bao
Hubei Key Laboratory of Bioinorganic Chemistry & Materia Medica, School of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan, 430074 P.R. China
Search for more papers by this authorMingjun Yang
Computational R&D, Shenzhen Jingtai Technology Co., Ltd. (XtalPi), Shenzhen, 518000 P.R. China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Xuesong Wu
Hubei Key Laboratory of Bioinorganic Chemistry & Materia Medica, School of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan, 430074 P.R. China
E-mail: [email protected]
Search for more papers by this authorGraphical Abstract
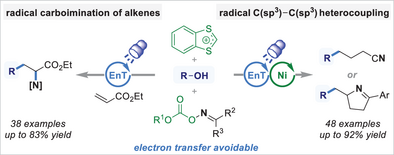
1,3-Benzodithiolylium cation was identified as an alcohol-activating reagent for energy-transfer-driven deoxygenative radical alkylation, avoiding electron transfer. Photocatalytic deoxygenative coupling reactions of alcohols with diverse oxime carbonates involving selective C(sp3)─C(sp3) bond construction are presented, including energy-transfer-driven carboimination of alkenes, energy transfer (EnT)/nickel dual-catalyzed ring-opening cross-coupling, and cyclization cross-coupling.
Abstract
The 1,3-benzodithiolylium (BDT) cation was identified as an efficient hydroxyl-activating reagent for the photocatalytic deoxygenative radical functionalization of alcohols in the absence of any electron transfer process. A series of unprecedented photocatalytic energy transfer (EnT)-driven deoxygenative radical coupling reactions of alcohols with bifunctional oxime carbonates have been developed based on the activation by BDT. Nickel-catalyzed radical sorting followed by C(sp3)─C(sp3) bond construction facilitates the heteroselective cross-coupling of two distinct alkyl radicals originating from parallel radical relays. These reactions allow the versatile synthesis of diverse nitrogen-containing molecules, including amino acid derivatives, imines, nitriles, and pyrrolines, by using ubiquitous alcohols as regiodefined alkyl building blocks.
Conflict of Interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Open Research
Data Availability Statement
The data that support the findings of this study are available in the supplementary material of this article.
Supporting Information
| Filename | Description |
|---|---|
| anie202423795-sup-0001-SuppMat.pdf28 MB | Supporting Information |
Please note: The publisher is not responsible for the content or functionality of any supporting information supplied by the authors. Any queries (other than missing content) should be directed to the corresponding author for the article.
References
- 1J. A. Milligan, J. P. Phelan, S. O. Badir, G. A. Molander, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2019, 58, 6152–6163.
- 2A. L. G. Kanegusuku, J. L. Roizen, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2021, 60, 21116–21149.
- 3A. Y. Chan, I. B. Perry, N. B. Bissonnette, B. F. Buksh, G. A. Edwards, L. I. Frye, O. L. Garry, M. N. Lavagnino, B. X. Li, Y. Liang, E. Mao, A. Millet, J. V. Oakley, N. L. Reed, H. A. Sakai, C. P. Seath, D. W. C. MacMillan, Chem. Rev. 2022, 122, 1485–1542.
- 4R. Kranthikumar, Organometallics 2022, 41, 667–679.
- 5S. Dongbang, Organometallics 2024, 43, 1662–1681.
- 6K. Anwar, K. Merkens, F. J. A. Troyano, A. Gómez-Suárez, Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2022, 2022, e202200330.
- 7A. Cook, S. G. Newman, Chem. Rev. 2024, 124, 6078–6144.
- 8T. Mandal, S. Mallick, M. Islam, S. D. Sarkar, ACS Catal. 2024, 14, 13451–13496.
- 9For representative examples of C(sp3)–C(sp3) bond formation, see: G. L. Lackner, K. W. Quasdorf, L. E. Overman, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 15342–15345.
- 10G. L. Lackner, K. W. Quasdorf, G. Pratsch, L. E. Overman, J. Org. Chem. 2015, 80, 6012–6024.
- 11C. C. Nawrat, C. R. Jamison, Y. Slutskyy, D. W. C. MacMillan, L. E. Overman, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2015, 137, 11270–11273.
- 12S. Y. Abbas, P. Zhao, L. E. Overman, Org. Lett. 2018, 20, 868–871.
- 13L. Guo, H.-Y. Tu, S. Zhu, L. Chu, Org. Lett. 2019, 21, 4771–4776.
- 14For representative examples of C(sp3)–C(sp3) bond formation, see: Z.-Y. Liu, S. P. Cook, Org. Lett. 2021, 23, 808–813.
- 15H.-M. Guo, X. Wu, Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 5365.
- 16T. Nanjo, T. Matsugasako, Y. Maruo, Y. Takemoto, Org. Lett. 2022, 24, 359–363.
- 17H.-M. Guo, B.-Q. He, X. Wu, Org. Lett. 2022, 24, 3199–3204.
- 18W. Zhang, X. Wu, Chem. Commun. 2022, 58, 12843–12846.
- 19P. R. Chheda, N. Simmons, D. P. Schuman, Z. Shi, Org. Lett. 2022, 24, 9514–9519.
- 20For representative examples of C(sp3)–C(sp3) bond formation, see: E. Speckmeier, P. J. W. Fuchs, K. Zeitler, Chem. Sci. 2018, 9, 7096–7103.
- 21Y. Wei, B. Ben-zvi, T. Diao, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2021, 60, 9433–9438.
- 22C.-K. Ran, Y.-N. Niu, L. Song, M.-K. Wei, Y.-F. Cao, S.-P. Luo, Y.-M. Yu, L.-L. Liao, D.-G. Yu, ACS Catal. 2022, 12, 18–24.
- 23O. P. Williams, A. F. Chmiel, M. Mikhael, D. M. Bates, C. S. Yeung, Z. K. Wickens, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2023, 62, e202300178.
- 24A. Chen, S. Zhao, Y. Han, Z. Zhou, B. Yang, L.-G. Xie, M. A. Walczak, F. Zhu, Chem. Sci. 2023, 14, 7569–7580.
- 25W. Xu, C. Fan, X. Hu, T. Xu, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2024, 63, e202401575.
- 26For representative examples of C(sp3)–C(sp3) bond formation, see: H. A. Sakai, D. W. C. MacMillan, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2022, 144, 6185–6192.
- 27J. Z. Wang, H. A. Sakai, D. W. C. MacMillan, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2022, 61, e202207150.
- 28N. E. Intermaggio, A. Millet, D. L. Davis, D. W. C. MacMillan, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2022, 144, 11961–11968.
- 29W. L. Lyon, D. W. C. MacMillan, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2023, 145, 7736–7742.
- 30C. A. Gould, A. L. Pace, D. W. C. MacMillan, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2023, 145, 16330–16336.
- 31E. Mao, C. N. P. Kullmer, H. A. Sakai, D. W. C. MacMillan, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2024, 146, 5067–5073.
- 32J. Z. Wang, W. L. Lyon, D. W. C. MacMillan, Nature 2024, 628, 104–109.
- 33R. Chen, N. E. Intermaggio, J. Xie, J. A. Rossi-Ashton, C. A. Gould, R. T. Martin, J. Alcázar, D. W. C. MacMillan, Science 2024, 383, 1350–1357.
- 34Q. Cai, I. M. McWhinnie, N. W. Dow, A. Y. Chan, D. W. C. MacMillan, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2024, 146, 12300–12309.
- 35E. E. Stache, A. B. Ertel, T. Rovis, A. G. Doyle, ACS Catal. 2018, 8, 11134–11139.
- 36Z.-Z. Xie, Y. Zheng, C.-P. Yuan, J.-P. Guan, Z.-P. Ye, J.-A. Xiao, H.-Y. Xiang, K. Chen, X.-Q. Chen, H. Yang, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2022, 61, e202211035.
- 37W.-D. Li, Y. Wu, S.-J. Li, Y.-Q. Jiang, Y.-L. Li, Y. Lan, J.-B. Xia, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2022, 144, 8551–8559.
- 38W. Xu, J. Ma, X.-A. Yuan, J. Dai, J. Xie, C. Zhu, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2018, 57, 10357–10361.
- 39S. K. Kariofillis, B. J. Shields, M. A. Tekle-Smith, M. J. Zacuto, A. G. Doyle, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2020, 142, 7683–7689.
- 40S. K. Kariofillis, S. Jiang, A. M. Żurański, S. S. Gandhi, J. I. M. Alvarado, A. G. Doyle, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2022, 144, 1045–1055.
- 41C. Romano, L. Talavera, E. Gómez-Bengoa, R. Martin, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2022, 144, 11558–11563.
- 42S. Dongbang, A. G. Doyle, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2022, 144, 20067–20077.
- 43W. Xiong, T. Kang, F. Li, H. Liao, Y. Yan, J. Dong, G. Li, D. Xue, ACS Catal. 2024, 14, 14089–14097.
- 44Q.-Q. Zhou, Y.-Q. Zou, L.-Q. Lu, W.-J. Xiao, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2019, 58, 1586–1604.
- 45F. Strieth-Kalthoff, M. J. James, M. Teders, L. Pitzer, F. Glorius, Chem. Soc. Rev. 2018, 47, 7190–7202.
- 46F. Strieth-Kalthoff, F. Glorius, Chem 2020, 6, 1888–1903.
- 47S. Dutta, J. E. Erchinger, F. Strieth-Kalthoff, R. Kleinmans, F. Glorius, Chem. Soc. Rev. 2024, 53, 1068–1089.
- 48J. Davies, S. P. Morcillo, J. J. Douglas, D. Leonori, Chem. - Eur. J. 2018, 24, 12154–12163.
- 49W. Yin, X. Wang, New J. Chem. 2019, 43, 3254–3264.
- 50X.-Y. Yu, Q.-Q. Zhao, J. Chen, W.-J. Xiao, J.-R. Chen, Acc. Chem. Res. 2020, 53, 1066–1083.
- 51I. B. Krylov, O. O. Segida, A. S. Budnikov, A. O. Terent'ev, Adv. Synth. Catal. 2021, 363, 2502–2528.
- 52C. Pratley, S. Fenner, J. A. Murphy, Chem. Rev. 2022, 122, 8181–8260.
- 53K. A. Rykaczewski, E. R. Wearing, D. E. Blackmun, C. S. Schindler, Nat. Synth. 2022, 1, 24–36.
- 54V. K. Soni, S. Lee, J. Kang, Y. K. Moon, H. S. Hwang, Y. You, E. J. Cho, ACS Catal. 2019, 9, 10454–10463.
- 55J. Kang, H. S. Hwang, V. K. Soni, E. J. Cho, Org. Lett. 2020, 22, 6112–6116.
- 56T. Patra, P. Bellotti, F. Strieth-Kalthoff, F. Glorius, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2020, 59, 3172–3177.
- 57T. Patra, M. Das, C. G. Daniliuc, F. Glorius, Nat. Catal. 2021, 4, 54–61.
- 58G. Tan, M. Das, H. Keum, P. Bellotti, C. Daniliuc, F. Glorius, Nat. Chem. 2022, 14, 1174–1184.
- 59G. Tan, M. Das, R. Kleinmans, F. Katzenburg, C. Daniliuc, F. Glorius, Nat. Catal. 2022, 5, 1120–1130.
- 60G. Tan, F. Paulus, Á. Rentería-Gómez, R. F. Lalisse, C. G. Daniliuc, O. Gutierrez, F. Glorius, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2022, 144, 21664–21673.
- 61G. Tan, F. Paulus, A. Petti, M.-A. Wiethoff, A. Lauer, C. Daniliuc, F. Glorius, Chem. Sci. 2023, 14, 2447–2454.
- 62F. Paulus, C. Stein, C. Heusel, T. J. Stoffels, C. G. Daniliuc, F. Glorius, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2023, 145, 23814–23823.
- 63R. Laskar, S. Dutta, J. C. Spies, P. Mukherjee, Á. Rentería-Gómez, R. E. Thielemann, C. G. Daniliuc, O. Gutierrez, F. Glorius, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2024, 146, 10899–10907.
- 64For representative examples, see: J. Li, Y. Yuan, X. Bao, T. Sang, J. Yang, C. Huo, Org. Lett. 2021, 23, 3712–3717.
- 65S.-Q. Lai, B.-Y. Wei, J.-W. Wang, W. Yu, B. Han, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2021, 60, 21997–22003.
- 66X. Wang, C. Chen, P. Liang, J.-Q. Chen, J. Wu, Org. Chem. Front. 2022, 9, 4328–4333.
- 67J. Majhi, R. K. Dhungana, Á. Rentería-Gómez, M. Sharique, L. Li, W. Dong, O. Gutierrez, G. A. Molander, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2022, 144, 15871–15878.
- 68Y.-S. Jiang, F. Liu, M.-S. Huang, X.-L. Luo, P.-J. Xia, Org. Lett. 2022, 24, 8019–8024.
- 69Y. Zheng, Z.-J. Wang, Z.-P. Ye, K. Tang, Z.-Z. Xie, J.-A. Xiao, H.-Y. Xiang, K. Chen, X.-Q. Chen, H. Yang, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2022, 61, e202212292.
- 70X.-X. Zhang, H. Zheng, Y.-K. Mei, Y. Liu, Y.-Y. Liu, D.-W. Ji, B. Wan, Q.-A. Chen, Chem. Sci. 2023, 14, 11170–11179.
- 71M. Chen, W. Sun, J. Yang, L. Yuan, J.-Q. Chen, J. Wu, Green Chem. 2023, 25, 3857–3863.
- 72X.-K. Qi, M.-J. Zheng, C. Yang, Y. Zhao, L. Guo, W. Xia, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2023, 145, 16630–16641.
- 73For representative examples, see: B. Yang,, X.-Y. Wang, X.-T. Huang, Z.-Y. Liu, X. Li, T. Huang, X.-S. Li, L.-Z. Wu, R. Fang, Q. Liu, ACS Catal. 2023, 13, 15331–15339.
- 74L. Geniller, M. Taillefer, F. Jaroschik, A. Prieto, J. Org. Chem. 2024, 89, 656–664.
- 75T. Huang, C. Liu, P.-F. Yuan, T. Wang, B. Yang, Y. Ma, Q. Liu, Green Chem. 2024, 26, 9859–9868.
- 76For representative examples, see: Z. Zhang, D. T. Ngo, D. A. Nagib, ACS Catal. 2021, 11, 3473–3477.
- 77A. F. Prusinowski, H. C. Sise, T. N. Bednar, D. A. Nagib, ACS Catal. 2022, 12, 4327–4332.
- 78S. Kim, H. Oh, W. Dong, J. Majhi, M. Sharique, B. Matsuo, S. Keess, G. A. Molander, ACS Catal. 2023, 13, 9542–9549.
- 79S.-S. Li, Y.-S. Jiang, L.-N. Chen, D.-N. Chen, X.-L. Luo, C.-X. Pan, P.-J. Xia, Org. Lett. 2023, 25, 7009–7013.
- 80M. Salamone, M. Bietti, Acc. Chem. Res. 2015, 48, 2895–2903.
- 81H. Cao, X. Tang, H. Tang, Y. Yuan, J. Wu, Chem. Catal. 2021, 1, 523–598.
- 82X. Wu, C. Zhu, CCS Chem. 2020, 2, 813–828.
- 83G. Schukat, E. Fanghänel, Science of Synthesis, Thieme, Stuttgart, Germany 2002, p. 191.
- 84J. Nakayama, K. Fujiwara, M. Hoshino, Bull. Chem. Soc. Jpn. 1976, 49, 3567–3573.
- 85M. Sekine, T. Hata, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1983, 105, 2044–2049.
- 86M. Sekine, T. Nakanishi, J. Org. Chem. 1989, 54, 5998–6000.
- 87M. Sekine, T. Nakanishi, Nat. Prod. Lett. 1992, 1, 25–28.
- 88J. J. Newton, G. Engüdar, A. J. Brooke, M. B. Nodwell, H. Horngren-Rhodes, R. E. Martin, P. Schaffer, R. Britton, C. M. Friesen, Chem. Eur. J. 2023, 29, e202202862.
- 89Y.-R. Luo, in Comprehensive Handbook of Chemical Bond Energies, CRC Press, Boca Raton, Florida, USA 2007, p. 127.
10.1201/9781420007282 Google Scholar
- 90M. S. Lowry, J. I. Goldsmith, J. D. Slinker, R. Rohl, R. A. Pascal, G. G. Malliaras, S. Bernhard, Chem. Mater. 2005, 17, 5712–5719.
- 91K. Teegardin, J. I. Day, J. Chan, J. Weaver, Org. Process Res. Dev. 2016, 20, 1156–1163.
- 92N. F. Nikitas, P. L. Gkizis, C. G. Kokotos, Org. Biomol. Chem. 2021, 19, 5237–5253.
- 93Y. Zhang, K.-D. Li, H.-M. Huang, ChemCatChem 2024, 16, e202400955.
- 94A. V. Tsymbal, L. D. Bizzini, D. W. C. MacMillan, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2022, 144, 21278–21286.
- 95E. Mao, D. W. C. MacMillan, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2023, 145, 2787–2793.
- 96F. Cong, G.-Q. Sun, S.-H. Ye, R. Hu, W. Rao, M. J. Koh, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2024, 146, 10274–10280.
- 97D. Kreher, M. Cariou, S.-G. Liu, E. Levillain, J. Veciana, C. Rovira, A. Gorgues, P. Hudhomme, J. Mater. Chem. 2002, 12, 2137–2159.
- 98D. Leifert, A. Studer, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2020, 59, 74–108.