Surface-Controlled CdS/Ti3C2 MXene Schottky Junction for Highly Selective and Active Photocatalytic Dehydrogenation-Reductive Amination
Graphical Abstract
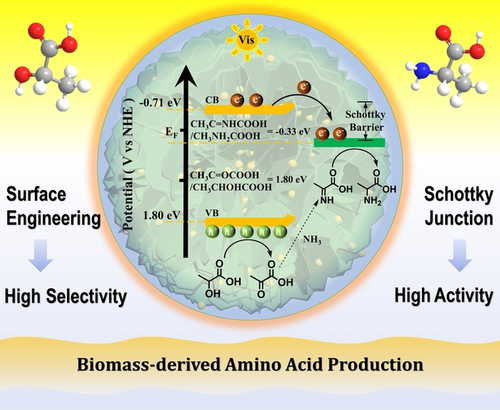
The novel hierarchical flower-like CdS/Ti3C2 Schottky junction, synthesized by crystal orientation control and heterostructure construction, shows unprecedented selectivity, activity, and stability for photocatalytic dehydrogenation-reductive amination under ambient conditions. Using the presented protocol, a wide range of biomass-derived hydroxyl acids can be successfully converted into the corresponding amino acids.
Abstract
Photocatalytic valorization and selective transformation of biomass-derived platform compounds offer great opportunities for efficient utilization of renewable resources under mild conditions. Here, the novel three-dimensional hierarchical flower-like CdS/Ti3C2 Schottky junction (MCdS) composed of surface-controlled CdS and pretreated Ti3C2 MXene is created for photocatalytic dehydrogenation-reductive amination of biomass-derived amino acid production under ambient temperature with unprecedented activity and selectivity. Schottky junction efficiently promotes photoexcited charge migration and separation and inhibits photogenerated electron-hole recombination, which results in a super-high activity. Meanwhile, CdS with the reduced surface energy supplies sufficient hydrogen sources for imine reduction and induces the preferential orientation of alanine, thus contributing superior selectivity. Moreover, a wide range of hydroxyl acids are successfully converted into corresponding amino acids and even one-pot conversion of glucose to alanine is easily achieved over MCdS. This work illustrates the mechanism of crystal orientation control and heterojunction construction in controlling catalytic behavior of photocatalytic nanoreactor, providing a paradigm for construction of MXene-based heterostructure.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Open Research
Data Availability Statement
The data that support the findings of this study are available in the supplementary material of this article.