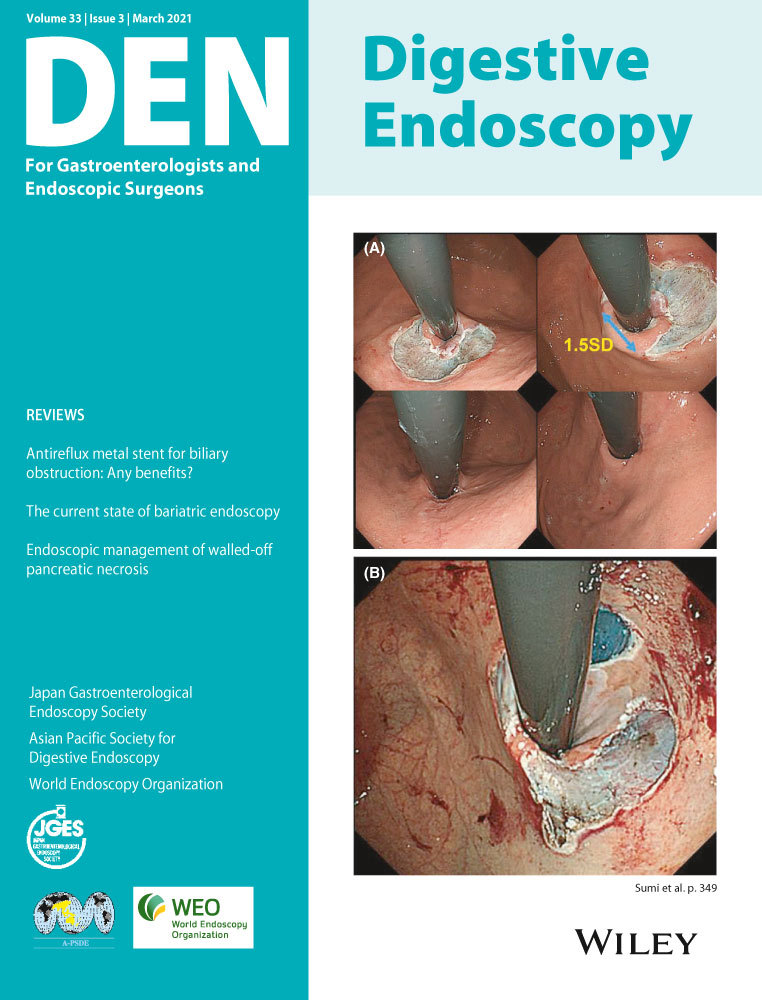
Endoscopic treatment of proton pump inhibitor-refractory gastroesophageal reflux disease with anti-reflux mucosectomy: Experience of 109 cases
Abstract
Objectives
Some patients with gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) are refractory to proton pump inhibitor (PPI) therapy. Anti-reflux mucosectomy (ARMS) is a minimally invasive endoscopic procedure for treatment of GERD. In this study, we retrospectively evaluated the outcomes of ARMS performed in patients with PPI-refractory GERD at our institution.
Methods
A total of 109 patients with PPI-refractory GERD who underwent ARMS were retrospectively reviewed. Pre- and post-ARMS questionnaire scores, acid exposure time (AET), DeMeester score, proximal extent, and PPI discontinuation rate were compared.
Results
There was a significant improvement in the symptom score (P < 0.01) and 40–50% of patients were able to discontinue PPI after ARMS. In patients who were followed up for 3 years, sustained improvement in subjective symptoms was observed. AET and DeMeester score significantly improved after ARMS (P < 0.01); however, there was no significant improvement in proximal extent (P = 0.0846).
Conclusions
Anti-reflux mucosectomy is an effective minimally invasive therapy for patients with PPI-refractory GERD. The therapeutic efficacy is attributable to suppression of acid backflow due to contraction of the scar tissue in cardia.
Conflict of Interests
Dr. Inoue H. is an advisor and received educational grants from Olympus Medical Systems Corporation; he also received educational grants from the Takeda Pharmaceutical Company and is an advisor for the Top Corporation. All other authors have no conflict of interests to declare.