Lenalidomide-associated progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy
Abstract
Background
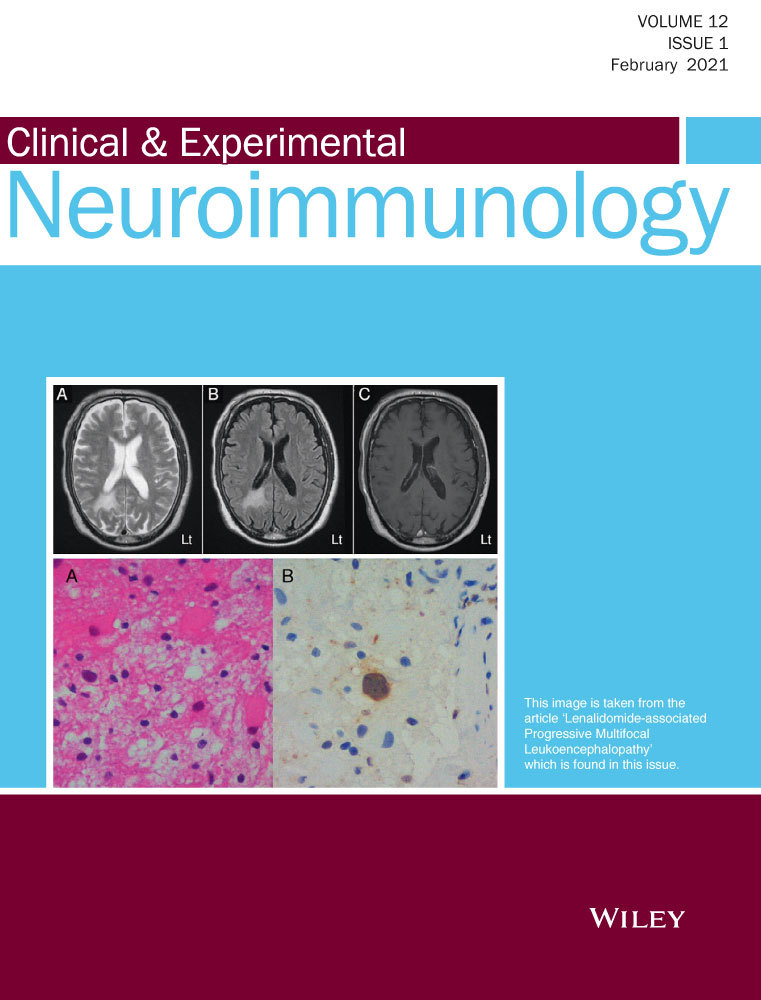
Lenalidomide, an analogue of thalidomide, is frequently used to treat multiple myeloma (MM). Progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy (PML) is an infectious disease of the central nervous system caused by the reactivation of the JC polyomavirus. Only a few reports have described PML in patients receiving lenalidomide therapy.
Case presentation
A 76-year-old man with MM presented progressive visual and cognitive impairment during lenalidomide administration. Magnetic resonance imaging showed a lesion in the right parietal lobe. Brain biopsy confirmed the diagnosis of PML. Lenalidomide therapy was discontinued, and oral mefloquine was commenced. He was alive more than 1 year later with mild neurologic decline.
Conclusions
Although rare, lenalidomide-induced PML should be considered in myeloma patients treated with lenalidomide.
CONFLICT OF INTEREST
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
DISCLOSURE
Informed consent was obtained from the patient and his caregiver.