Polydimethylsiloxane-Driven Microdroplet Systems: Propelling Forces in Advancing Chemical and Materials Innovation
Chao Liu
Centre for Molecular Systems and Organic Devices, State Key Laboratory of Flexible Electronics (LoFE) & Institute of Advanced Materials (IAM), Nanjing University of Posts & Telecommunications, 9 Wenyuan Road, Nanjing, Jiangsu, 210023 China
Search for more papers by this authorXin Chen
Centre for Molecular Systems and Organic Devices, State Key Laboratory of Flexible Electronics (LoFE) & Institute of Advanced Materials (IAM), Nanjing University of Posts & Telecommunications, 9 Wenyuan Road, Nanjing, Jiangsu, 210023 China
Search for more papers by this authorShuangyi Li
Centre for Molecular Systems and Organic Devices, State Key Laboratory of Flexible Electronics (LoFE) & Institute of Advanced Materials (IAM), Nanjing University of Posts & Telecommunications, 9 Wenyuan Road, Nanjing, Jiangsu, 210023 China
Search for more papers by this authorHaodi Zhu
Centre for Molecular Systems and Organic Devices, State Key Laboratory of Flexible Electronics (LoFE) & Institute of Advanced Materials (IAM), Nanjing University of Posts & Telecommunications, 9 Wenyuan Road, Nanjing, Jiangsu, 210023 China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Ying Wei
Centre for Molecular Systems and Organic Devices, State Key Laboratory of Flexible Electronics (LoFE) & Institute of Advanced Materials (IAM), Nanjing University of Posts & Telecommunications, 9 Wenyuan Road, Nanjing, Jiangsu, 210023 China
E-mail: [email protected]; [email protected]; [email protected]Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Shasha Wang
Centre for Molecular Systems and Organic Devices, State Key Laboratory of Flexible Electronics (LoFE) & Institute of Advanced Materials (IAM), Nanjing University of Posts & Telecommunications, 9 Wenyuan Road, Nanjing, Jiangsu, 210023 China
E-mail: [email protected]; [email protected]; [email protected]Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Linghai Xie
Centre for Molecular Systems and Organic Devices, State Key Laboratory of Flexible Electronics (LoFE) & Institute of Advanced Materials (IAM), Nanjing University of Posts & Telecommunications, 9 Wenyuan Road, Nanjing, Jiangsu, 210023 China
E-mail: [email protected]; [email protected]; [email protected]Search for more papers by this authorChao Liu
Centre for Molecular Systems and Organic Devices, State Key Laboratory of Flexible Electronics (LoFE) & Institute of Advanced Materials (IAM), Nanjing University of Posts & Telecommunications, 9 Wenyuan Road, Nanjing, Jiangsu, 210023 China
Search for more papers by this authorXin Chen
Centre for Molecular Systems and Organic Devices, State Key Laboratory of Flexible Electronics (LoFE) & Institute of Advanced Materials (IAM), Nanjing University of Posts & Telecommunications, 9 Wenyuan Road, Nanjing, Jiangsu, 210023 China
Search for more papers by this authorShuangyi Li
Centre for Molecular Systems and Organic Devices, State Key Laboratory of Flexible Electronics (LoFE) & Institute of Advanced Materials (IAM), Nanjing University of Posts & Telecommunications, 9 Wenyuan Road, Nanjing, Jiangsu, 210023 China
Search for more papers by this authorHaodi Zhu
Centre for Molecular Systems and Organic Devices, State Key Laboratory of Flexible Electronics (LoFE) & Institute of Advanced Materials (IAM), Nanjing University of Posts & Telecommunications, 9 Wenyuan Road, Nanjing, Jiangsu, 210023 China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Ying Wei
Centre for Molecular Systems and Organic Devices, State Key Laboratory of Flexible Electronics (LoFE) & Institute of Advanced Materials (IAM), Nanjing University of Posts & Telecommunications, 9 Wenyuan Road, Nanjing, Jiangsu, 210023 China
E-mail: [email protected]; [email protected]; [email protected]Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Shasha Wang
Centre for Molecular Systems and Organic Devices, State Key Laboratory of Flexible Electronics (LoFE) & Institute of Advanced Materials (IAM), Nanjing University of Posts & Telecommunications, 9 Wenyuan Road, Nanjing, Jiangsu, 210023 China
E-mail: [email protected]; [email protected]; [email protected]Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Linghai Xie
Centre for Molecular Systems and Organic Devices, State Key Laboratory of Flexible Electronics (LoFE) & Institute of Advanced Materials (IAM), Nanjing University of Posts & Telecommunications, 9 Wenyuan Road, Nanjing, Jiangsu, 210023 China
E-mail: [email protected]; [email protected]; [email protected]Search for more papers by this authorComprehensive Summary
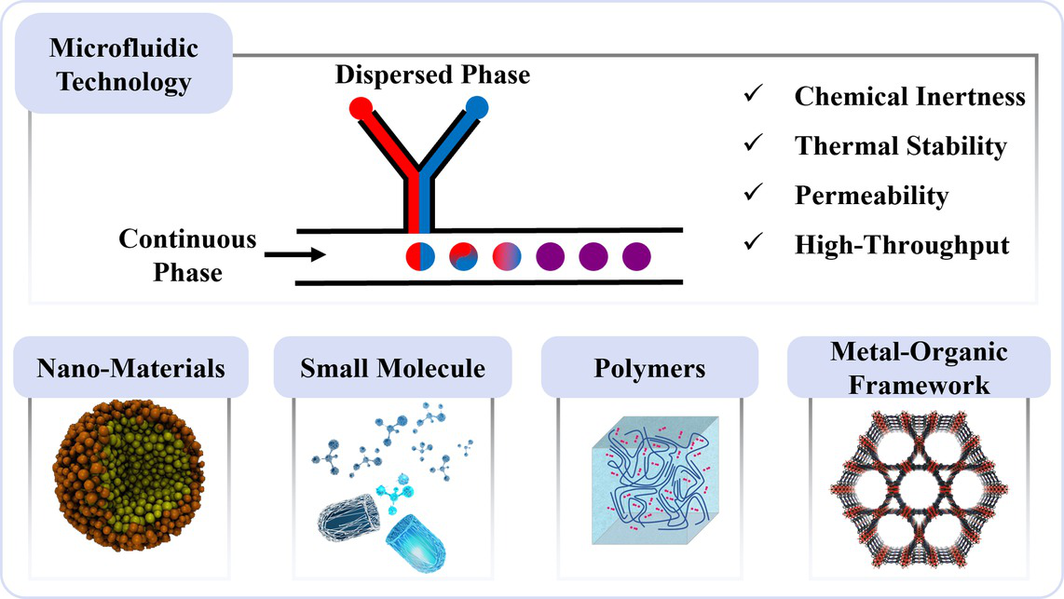
Microfluidic technology is an emerging arena that manipulates tiny fluids through the use of microchannels, which typically range in dimensions from tens to hundreds of micrometers. This technology has been widely applied in chemical analysis, biological detection, and materials synthesis due to its precise processing and manipulation of tiny fluids. Moreover, droplet microfluidics with polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) devices is one of the most famous ways to carry out some applications or investigations that were not previously possible using conventional techniques. This review covers the mechanisms of droplet formation, innovative applications in synthesis, and potential integration with advanced techniques. Precise control over microfluidic channels, excellent efficiency, product consistency, and high-throughput screening capabilities are highlighted. In this respect, employing this technology in the synthesis of nanomaterials, small molecules, and polymers is discussed, as well as facilitating the development of novel materials. Additionally, we discuss future prospects, including optimizing device design, integrating with cutting-edge technologies, and advancing precision medicine. Despite challenges related to device complexity and fabrication costs, the potential for resolution through new materials and methods underscores the critical role of droplet microfluidics in scientific innovation.
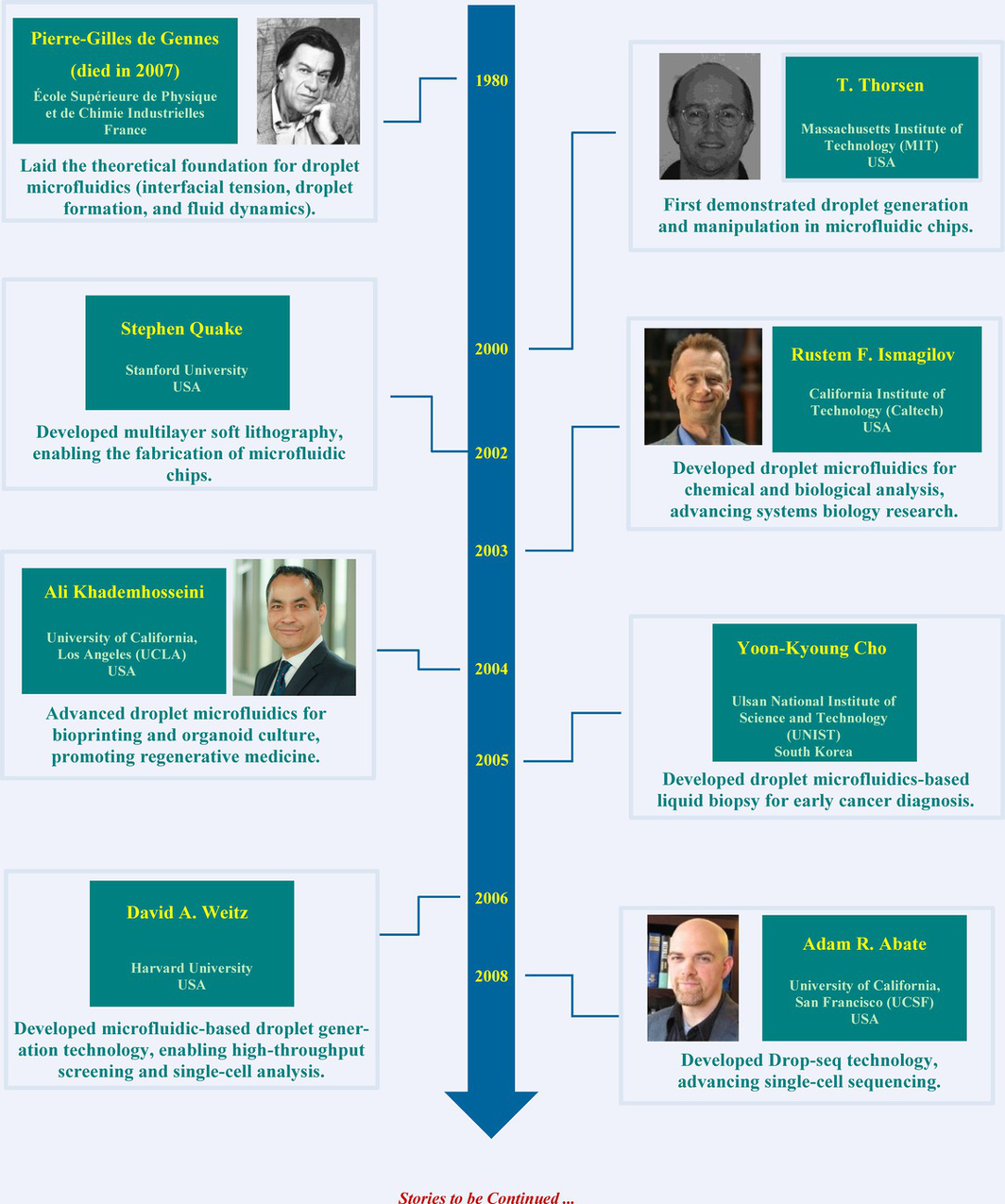
Key Scientists
References
- 1 Thorsen, T.; Maerkl, S. J.; Quake, S. R. Microfluidic Large-Scale Integration. Science 2002, 298, 580–584.
- 2 Lai, H.; Folch, A. Design and dynamic characterization of “single- stroke” peristaltic PDMS micropumps. Lab Chip 2011, 11, 336–342.
- 3 Sánchez-Ferrer, A.; Fischl, T.; Stubenrauch, M.; Albrecht, A.; Wurmus, H.; Hoffmann, M.; Finkelmann, H. Liquid-Crystalline Elastomer Microvalve for Microfluidics. Adv. Mater. 2011, 23, 4526–4530.
- 4 Murakami, Y.; Araki, K.; Ohashi, R.; Honma, H.; Misawa, N.; Takahashi, K.; Sawada, K.; Ishida, M. Mems mixer as an example of a novel construction method of microfluidics by discrete microparts. Sens. Actuators, B 2014, 194, 528–533.
- 5 Zhang, J.; Coulston, R. J.; Jones, S. T.; Geng, J.; Scherman, O. A.; Abell, C. One-Step Fabrication of Supramolecular Microcapsules from Microfluidic Droplets. Science 2012, 335, 690–694.
- 6 Zhang, P. F.; Abate, A. R. High-Definition Single-Cell Printing: Cell-by-Cell Fabrication of Biological Structures. Adv. Mater. 2020, 32, 2005346.
- 7 Atencia, J.; Beebe, D. J. Controlled microfluidic interface. Nature 2005, 437, 648–655.
- 8 DeMello, A. J. Control and detection of chemical reactions in microfluidic systems. Nature 2006, 442, 394–402.
- 9 Nan, L.; Zhang, H. D.; Weitz, D. A.; Shum, H. C. Development and future of droplet microfluidics. Lab Chip 2024, 24, 1135–1153.
- 10 Yan, W. J.; Yang, L. K.; Chen, J. N.; Wu, Y. Q.; Wang, P. J.; Li, Z. P. In Situ Two-Step Photoreduced SERS Materials for On-Chip Single-Molecule Spectroscopy with High Reproducibility. Adv. Mater. 2017, 29, 1702893.
- 11 Xiong, Q. R.; Lim, C. Y.; Ren, J. H.; Zhou, J. J.; Pu, K. Y.; Chan-Park, M. B.; Mao, H.; Lam, Y. C.; Duan, H. W. Magnetic nanochain integrated microfluidic biochips. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 1743.
- 12 Morelli, L.; Serioli, L.; Centorbi, F. A.; Jendresen, C. B.; Matteucci, M.; Ilchenko, O.; Demarchi, D.; Nielsen, A. T.; Zor, K.; Boisen, A. Injection molded lab-on-a-disc platform for screening of genetically modified E. coli using liquid–liquid extraction and surface enhanced Raman scattering. Lab Chip 2018, 18, 869–877.
- 13 Park, S.; Jeon, C. S.; Choi, N.; Moon, J.; Lee, K. M.; Pyun, S. H.; Kang, T.; Choo, J. Sensitive and reproducible detection of SARS-CoV-2 using SERS-based microdroplet sensor. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 446, 137085.
- 14 Oliveira, K.; Teixeira, A.; Fernandes, J. M.; Lopes, C.; Chícharo, A.; Piairo, P.; Wu, L.; Rodríguez-Lorenzo, L.; Diéguez, L.; Abalde-Cela, S. Multiplex SERS Phenotyping of Single Cancer Cells in Microdroplets. Adv. Optical Mater. 2023, 11, 2201500.
- 15 Li, M. S.; Dyett, B.; Yu, H. T.; Bansal, V.; Zhang, X. H. Functional Femtoliter Droplets for Ultrafast Nanoextraction and Supersensitive Online Microanalysis. Small 2019, 15, 1804683.
- 16 Liu, W.; Wang, Z. H.; Liu, Z. P.; Chen, J. X.; Shi, L. Y.; Huang, L. J.; Liu, Y.; Cui, S.; He, X. Utilizing an Automated SERS-Digital Microfluidic System for High-Throughput Detection of Explosives. ACS Sens. 2023, 8, 1733–1741.
- 17 Das, A.; Fehse, S.; Polack, M.; Panneerselvam, R.; Belder, D. Surface- Enhanced Raman Spectroscopic Probing in Digital Microfluidics through a Microspray Hole. Anal. Chem. 2023, 95, 1262–1272.
- 18 Yu, X. D.; Park, S.; Lee, S.; Joo, S. W.; Choo, J. Microfluidics for disease diagnostics based on surface-enhanced raman scattering detection. Nano Converg. 2024, 11, 17.
- 19 Shah, R. K.; Kim, J. W.; Weitz, D. A. Janus Supraparticles by Induced Phase Separation of Nanoparticles in Droplets. Adv. Mater. 2009, 21, 194 9–1953.
- 20 Kang, H. M.; Subramaniam, M.; Targ, S.; Nguyen, M.; Maliskova, L.; McCarthy, E.; Wan, E.; Wong, S.; Byrnes, L.; Lanata, C.; Gate, R.; Mostafavi, S.; Marson, A.; Zaitlen, N.; Criswell, L. A.; Ye, C. J. Multiplexed droplet single-cell RNA-sequencing using natural genetic variation. Nat. Biotechnol. 2018, 36, 89–94.
- 21 Niu, M. C.; Cao, W. J.; Wang, Y. C.; Zhu, Q. Y.; Luo, J. Y.; Wang, B. P.; Zheng, H.; Weitz, D. A.; Zong, C. H. Droplet-based transcriptome profiling of individual synapses. Nat. Biotechnol. 2023, 41, 1332–1344.
- 22 Haswell, S. J.; Middleton, R. J.; O’Sullivan, B.; Skelton, V.; Wattsa, P.; Styring, P. The application of micro reactors to synthetic chemistry. Chem. Commun. 2001, 5, 391–398.
- 23 Abakumov, A. M.; Aksenov, V. L.; Alyoshin, V. A.; Antipov, E. V.; Balagurov, A. M.; Mikhailova, D. A.; Putilin, S. N.; Rozova, M. G. Effect of Fluorination on the Structure and Superconducting Properties of the Hg-1201 Phase. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1998, 80, 385.
- 24 Brivio, M.; Verboom, W.; Reinhoudt, D. N. Miniaturized continuous flow reaction vessels: influence on chemical reactions. Lab Chip 2006, 6, 329.
- 25 Sart, S.; Ronteix, G.; Jain, S.; Amselem, G.; Baroud, C. N. Cell Culture in Microfluidic Droplets. Chem. Rev. 2022, 122, 7061−7096.
- 26 Kim, T.; Ko, M.; Rha, E.; Kim, H.; Lee, H. Microfluidics-driven high- throughput phenotyping and screening in synthetic biology: from single cells to cell-free systems. Biotechnol. Bioproc. Eng. 2024, 29, 25–33.
- 27 Ma, L.; Zhao, X.; Hou, J. S.; Huang, L.; Yao, Y. L.; Ding, Z. H.; Wei, J. J.; Hao, N. J. Droplet Microfluidic Devices: Working Principles, Fabrication Methods, and Scale-Up Applications. Small Methods 2024, 8, 2301406.
- 28 Shang, Y. T.; Wang, Z. Z.; Xi, L. Q.; Wang, Y. T.; Liu, M. J.; Feng, Y.; Wang, J.; Wu, Q. P.; Xiang, X. R.; Chen, M. T.; Ding, Y. Droplet-based single-cell sequencing: Strategies and applications. Biotechnol. Adv. 2024, 77, 108454.
- 29 Li, H.; Ma, Y. D.; Fu, R. X.; Peng, J. X.; Zhai, Y. B.; Li, J. H.; Xu, W.; Hu, S. Y.; Ma, H. B.; Wheeler, A. R.; Zhang, S. L. Droplet-Based Microfluidics with Mass Spectrometry for Microproteomics. Engineering 2024, 43, 37–53.
- 30 Yan, J. S.; Cheng, J.; Zou, Y. Y.; Guo, J. C.; Guo, J. H. Detection and Analysis of Droplets in Microfluidic Devices: A Review. IEEE Sens. J. 2024, 24, 33881–33902.
- 31 Dong, Q.; Xia, Y. N.; Whitesides, G. M. Soft lithography for micro- and nanoscale patterning. Nat. Protoc. 2010, 5, 491–502.
- 32 Wang, B. L.; Ghaderi, A.; Zhou, H.; Agresti, J.; Weitz, D. A.; Fink, G. R.; Stephanopoulos, G. Microfluidic high-throughput culturing of single cells for selection based on extracellular metabolite production or consumption. Nat. Biotechnol. 2014, 32, 473.
- 33 Bhargava, K. C.; Thompson, B.; Malmstadt, N. Discrete elements for 3D microfluidics. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 2014, 111, 15013–15018.
- 34 Bauer, W. C.; Fischlechner, M.; Abell, C.; Huck, W. T. S. Hydrophilic PDMS microchannels for high-throughput formation of oil-in-water microdroplets and water-in-oil-in-water double emulsions. Lab Chip 2010, 10, 1814–1819.
- 35 Song, Y.; Kumar, C. S. S. R.; Hormes, J. Fabrication of SU-8 based microfluidic reactor on a PEEK substrate sealed by a ’flexible semi-solid transfer’(FST) process. J. Micromech. Microeng. 2004, 14, 932–940.
- 36 Seemann, R.; Brinkmann, M.; Pfohl, T.; Herminghaus, S. Droplet based microfluidics. Rep. Prog. Phys. 2012, 75, 016601.
- 37 Anna, S. L.; Bontoux, N.; Stone, H. A. Formation of dispersions using "flow-focusing" in microchannels. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2003, 82, 364–366.
- 38 Umbanhowar, P. B.; Prasad, V.; Weitz, D. A. Monodisperse Emulsion Generation via Drop Break Off in a Coflowing Stream. Langmuir 2000, 16, 347–351.
- 39 Castro-Hernández, E.; Gundabala, V.; Fernández-Nieves, A.; Gordillo, J. M. Scaling the drop size in coflow experiments. New J. Phys. 2009, 11, 075021.
- 40 Song, Y. J.; Li, R. S.; Sun, Q. Q.; Jin, P. Y. Controlled growth of Cu nanoparticles by a tubular microfluidic reactor. Chem. Eng. J. 2011, 168, 477–484.
- 41 Utada, A. S.; Fernandez-Nieves, A.; Gordillo, J. M.; Weitz, D. A. Absolute Instability of a Liquid Jet in a Coflowing Stream. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2008, 100, 014502.
- 42 Guillot, P.; Colin, A.; Utada, A. S.; Ajdari, A. Stability of a Jet in Confined Pressure-Driven Biphasic Flows at Low Reynolds Numbers. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2007, 99, 104502.
- 43 Utada, A. S.; Fernandez-Nieves, A.; Stone, H. A.; Weitz, D. A. Dripping to Jetting Transitions in Coflowing Liquid Streams. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2007, 99, 094502.
- 44 Utada, A. S.; Chu, L. Y.; Fernandez-Nieves, A.; Link, D. R.; Holtze, C.; Weitz, D. A. Dripping, Jetting, Drops, and Wetting: The Magic of Microfluidics. MRS Bull. 2007, 32, 702–708.
- 45 Tice, J. D.; Song, H.; Lyon, A. D.; Ismagilov, R. F. Formation of droplets and mixing in multiphase microfluidics at low values of the Reynolds and the capillary numbers. Langmuir 2003, 19, 9127–9133.
- 46 Pethig, R. R.; Smith, S. Introductory Bioelectronics: For Engineers and Physical Scientists, John Wiley & Sons, 2013.
- 47 Baroud, C. N.; Delville, J. P.; Gallaire, F.; Wunenburger, R. Thermocapillary valve for droplet production and sorting. Phys. Rev. E 2007, 75, 046302.
- 48 Lee, W.; Walker, L. M.; Anna, S. L. Role of geometry and fluid properties in droplet and thread formation processes in planar flow focusing. Phys. Fluids 2009, 21, 032103.
- 49 Fu, T. T.; Wu, Y. N.; Ma, Y. G; Li, H. Z. Droplet formation and breakup dynamics in microfluidic flow-focusing devices: From dripping to jetting. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2012, 84, 207–217.
- 50 Garstecki, P.; Fuerstman, M. J.; Stonec, H. A.; Whitesides, G. M. Formation of droplets and bubbles in a microfluidic T-junction—scaling and mechanism of break-up. Lab Chip 2006, 6, 437–446.
- 51 Tarchichi, N.; Chollet, F.; Manceau, J. New regime of droplet generation in a T-shape microfluidic junction. Microfluid. Nanofluid. 2013, 14, 45–51.
- 52 Pathak, M. Numerical simulation of membrane emulsification: Effect of flow properties in the transition from dripping to jetting. J. Membr. Sci. 2011, 382, 166–176.
- 53 Li, Z.; Leshansky, A. M.; Pismen, L. M.; Tabeling, P. Step-emulsification in a microfluidic device. Lab Chip 2015, 15, 1023–1031.
- 54 Anna, S. L.; Bontoux, N.; Stone, H. A. Formation of dispersions using “flow focusing” in microchannels. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2003, 82, 364–366.
- 55 Dollet, B.; Hoeve, W. V.; Raven, J.; Marmottant, P.; Versluis, M. Role of the Channel Geometry on the Bubble Pinch-Off in Flow-Focusing Devices. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2008, 100, 034504.
- 56 Garstecki, P.; Stone, H. A.; Whitesides, G. M. Mechanism for Flow-Rate Controlled Breakup in Confined Geometries: A Route to Monodisperse Emulsions. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2005, 94, 164501.
- 57 Abate, A. R.; Weitz, D. A. High-Order Multiple Emulsions Formed in Poly(dimethylsiloxane) Microfluidics. Small 2009, 5, 2030–2032.
- 58
Song, Y.; Cheng, D. J.; Zhao, L. Microfluidics: Fundamental, Devices and Applications, John Wiley & Sons, 2018.
10.1002/9783527800643 Google Scholar
- 59 Thorsen, T.; Roberts, R. W.; Arnold, F. H.; Quake, S. R. Dynamic Pattern Formation in a Vesicle-Generating Microfluidic Device. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2001, 86, 4163.
- 60 Tarchichi, N.; Chollet, F.; Manceau, J. New regime of droplet generation in a T-shape microfluidic junction. Microfluid. Nanofluid. 2013, 14, 45–51.
- 61 De Menech, M.; Garstecki, P.; Jousse, F.; Stone, H. A. Transition from squeezing to dripping in a microfluidic T-shaped junction. J. Fluid Mech. 2008, 595, 141–161.
- 62 Eggersdorfer, M. L.; Seybold, H.; Ofnerc, A.; Weitz, D. A.; Studart, A. R. Wetting controls of droplet formation in step emulsification. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 2018, 115, 9479–9484.
- 63 Ofner, A.; Moore, D. G.; Rühs, P. A.; Schwendimann, P.; Eggersdorfer, M.; Amstad, E.; Weitz, D. A.; Studart, A. R. High-Throughput Step Emulsification for the Production of Functional Materials Using a Glass Microfluidic Device. Macromol. Chem. Phys. 2017, 218, 1600472.
- 64 Amstad, E.; Chemama, M.; Eggersdorfer, M.; Arriaga, L. R.; Brenner, M. P.; Weitz, D. A. Robust scalable high throughput production of monodisperse drops. Lab Chip 2016, 16, 4163–4172.
- 65 Chao, Y. C.; Shum, H. C. Emerging aqueous two-phase systems: from fundamentals of interfaces to biomedical applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2020, 49, 114–142.
- 66 Nan, L.; Cao, Y.; Yuan, S.; Shum, H. C. Oil-mediated high-throughput generation and sorting of water-in-water droplets. Microsyst. Nanoeng. 2020, 6, 70.
- 67 Liu, H. T.; Wang, H.; Wei, W. B.; Liu, H.; Jiang, L.; Qin, J. H. A Microfluidic Strategy for Controllable Generation of Water-in-Water Droplets as Biocompatible Microcarriers. Small 2018, 14, 1801095.
- 68 Shestopalov, I.; Tice, J. D.; Ismagilov, R. F. Multi-step synthesis of nanoparticles performed on millisecond time scale in a microfluidic droplet-based system. Lab Chip 2004, 4, 316–321.
- 69 Song, H.; Ismagilov, R. F. Millisecond kinetics on a microfluidic chip using nanoliters of reagents. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2003, 125, 14613–14619.
- 70 Song, H.; Bringer, M. R.; Tice, J. D.; Gerdts, C. J.; Ismagilov, R. F. Experimental test of scaling of mixing by chaotic advection in droplets moving through microfluidic channels. Appl Phys Lett. 2003, 83, 4664–4666.
- 71 Abolhasani, M.; Oskooei, A.; Klinkova, A.; Kumacheva, E.; Günther, A. Shaken, and stirred: oscillatory segmented flow for controlled size-evolution of colloidal nanomaterials. Lab Chip 2014, 14, 2309–2318.
- 72 Liu, R.; Wu, Q.; Huang, X.; Zhao, X. X.; Chen, X. H.; Chen, Y. G.; Weitz, D. A.; Song, Y. J. Synthesis of nanomedicine hydrogel microcapsules by droplet microfluidic process and their pH and temperature dependent release. RSC Adv. 2021, 11, 37814–37823.
- 73 Kašpar, O.; Koyuncu, A. H.; Pittermannová, A.; Ulbrich, P.; Tokárová, V. Governing factors for preparation of silver nanoparticles using droplet-based microfluidic device. Biomed. Microdevices. 2019, 21, 88.
- 74 Moragues, T.; Mitchell, S.; Akl, D. F.; Pérez-Ramírez, J.; DeMello, A. Droplet-Based Microfluidics Platform for the Synthesis of Single- Atom Heterogeneous Catalysts. Small Struct. 2023, 4, 2200284.
- 75 Koryakina, I.; Bikmetova, S.; Khmelevskaia, D.; Markina, D.; Kuleshova, A.; Logunov, L.; Timin, A. S.; Pushkarev, A.; Makarov, S.; Zyuzin, M. V. Droplet Microfluidic Synthesis of Halide Perovskites Affords Upconversion Lasing in Mie Resonant Cuboids. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2023, 6, 4370−4378.
- 76 Selsouli, Y. A.; Rho, H. S.; Eischen-Loges, M.; Galván-Chacón, V. P.; Stähli, C.; Viecelli, Y.; Döbelin, N.; Bohner, M.; Birgani, Z. T.; Habibović, P. Optimization of a tunable process for rapid production of calcium phosphate microparticles using a droplet-based microfluidic platform. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2024, 12, 1352184.
- 77 Dexter, J. P.; Parker, W. Parallel combinatorial chemical synthesis using single-layer poly(dimethylsiloxane) microfluidic devices. Biomicrofluidics 2009, 3, 034106.
- 78 Song, H.; Tice, J. D.; Ismagilov, R. F. A microfluidic system for controlling reaction networks in time. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2003, 42, 768–772.
- 79 Theberge, A. B.; Mayot, E.; Harrak, A. E.; Kleinschmidt, F.; Huck, W. T. S.; Griffiths, A. D. Microfluidic platform for combinatorial synthesis in picolitre droplets. Lab Chip 2012, 12, 1320–1326.
- 80 Tanaka, D.; Sawai, S.; Hattori, S.; Nozaki, Y.; Yoon, D. H.; Fujita, H.; Sekiguchi, T.; Akitsu, T.; Shoji, S. Microdroplet synthesis of azo compounds with simple microfluidics-based pH control. RSC Adv. 2020, 10, 38900.
- 81 Ruszczak, A.; Jankowski, P.; Vasantham, S. K.; Scheler, O.; Garstecki, P. Physicochemical Properties Predict Retention of Antibiotics in Water-in-Oil Droplets. Anal. Chem. 2023, 95, 1574−1581.
- 82 Kuehne, A. J. C.; Weitz, D. A. Highly monodisperse conjugated polymer particles synthesized with drop-based microfluidics. Chem. Commun. 2011, 47, 12379–12381.
- 83 Ursuegui, S.; Mosser, M.; Wagner, A. Copper-free click chemistry for microdroplet's W/O interface engineering. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 94942–94948.
- 84 Ghosh, S.; Schurtenberger, P. Microfluidic production of snowman- shaped Janus hydrogel particles. Colloids Surf. A 2019, 573, 205–210.
- 85 Chung, C. H. Y.; Lau, C. M. L.; Sin, D. T.; Chung, J. T.; Zhang, Y. Z.; Chau, Y.; Yao, S. H. Droplet-Based Microfluidic Synthesis of Hydrogel Microparticles via Click Chemistry-Based Cross-Linking for the Controlled Release of Proteins. ACS Appl. Bio Mater. 2021, 4, 6186−6194.
- 86 Giannitelli, S. M.; Limiti, E.; Mozetic, P.; Pinelli, F.; Han, X. Y.; Abbruzzese, F.; Basoli, F.; Rio, D. D.; Scialla, S.; Rossi, F.; Trombetta, M.; Rosanò, L.; Gigli, G.; Zhang, Z. J.; Mauri, E.; Rainer, A. Droplet-based microfluidic synthesis of nanogels for controlled drug delivery: tailoring nanomaterial properties via pneumatically actuated flowfocusing junction. Nanoscale 2022, 14, 11415.
- 87 Wu, Q.; Huang, X.; Liu, R.; Yang, X. Z.; Xiao, G.; Jiang, N.; Weitz, D. A.; Song, Y. J. Multichannel Multijunction Droplet Microfluidic Device to Synthesize Hydrogel Microcapsules with Different Core−Shell Structures and Adjustable Core Positions. Langmuir 2024, 40, 1950−1960.
- 88 Zheng, B.; Roach, L. S.; Ismagilov, R. F. Screening of protein crystallization conditions on a microfluidic chip using nanoliter-size droplets. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2003, 125, 11170–11171.
- 89 Faustini, M.; Kim, J.; Jeong, G.; Kim, J. Y.; Moon, H. R.; Ahn, W.; Kim, D. Microfluidic Approach toward Continuous and Ultrafast Synthesis of Metal–Organic Framework Crystals and Hetero Structures in Confined Microdroplets. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 14619–14626.




