Dynamic Covalent and Noncovalent Bonds Based Self-assembled Biomaterials: From Construction to Biomedical Applications
Chengfei Liu
Shaanxi Key Laboratory of Macromolecular Science and Technology, Xi’an Key Laboratory of Hybrid Luminescent Materials and Photonic Device, MOE Key Laboratory of Material Physics and Chemistry under Extraordinary Conditions, School of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Northwestern Polytechnical University, Xi’an, Shaanxi, 710072 China
C. F. Liu and Y. F. Jin contributed equally to this work.
Search for more papers by this authorYifan Jin
Shaanxi Key Laboratory of Macromolecular Science and Technology, Xi’an Key Laboratory of Hybrid Luminescent Materials and Photonic Device, MOE Key Laboratory of Material Physics and Chemistry under Extraordinary Conditions, School of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Northwestern Polytechnical University, Xi’an, Shaanxi, 710072 China
C. F. Liu and Y. F. Jin contributed equally to this work.
Search for more papers by this authorJiaqi Li
Shaanxi Key Laboratory of Macromolecular Science and Technology, Xi’an Key Laboratory of Hybrid Luminescent Materials and Photonic Device, MOE Key Laboratory of Material Physics and Chemistry under Extraordinary Conditions, School of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Northwestern Polytechnical University, Xi’an, Shaanxi, 710072 China
Search for more papers by this authorZeyi Wang
Shaanxi Key Laboratory of Macromolecular Science and Technology, Xi’an Key Laboratory of Hybrid Luminescent Materials and Photonic Device, MOE Key Laboratory of Material Physics and Chemistry under Extraordinary Conditions, School of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Northwestern Polytechnical University, Xi’an, Shaanxi, 710072 China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Jingxia Wang
Shaanxi Key Laboratory of Macromolecular Science and Technology, Xi’an Key Laboratory of Hybrid Luminescent Materials and Photonic Device, MOE Key Laboratory of Material Physics and Chemistry under Extraordinary Conditions, School of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Northwestern Polytechnical University, Xi’an, Shaanxi, 710072 China
E-mail: [email protected]; [email protected]Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Wei Tian
Shaanxi Key Laboratory of Macromolecular Science and Technology, Xi’an Key Laboratory of Hybrid Luminescent Materials and Photonic Device, MOE Key Laboratory of Material Physics and Chemistry under Extraordinary Conditions, School of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Northwestern Polytechnical University, Xi’an, Shaanxi, 710072 China
E-mail: [email protected]; [email protected]Search for more papers by this authorChengfei Liu
Shaanxi Key Laboratory of Macromolecular Science and Technology, Xi’an Key Laboratory of Hybrid Luminescent Materials and Photonic Device, MOE Key Laboratory of Material Physics and Chemistry under Extraordinary Conditions, School of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Northwestern Polytechnical University, Xi’an, Shaanxi, 710072 China
C. F. Liu and Y. F. Jin contributed equally to this work.
Search for more papers by this authorYifan Jin
Shaanxi Key Laboratory of Macromolecular Science and Technology, Xi’an Key Laboratory of Hybrid Luminescent Materials and Photonic Device, MOE Key Laboratory of Material Physics and Chemistry under Extraordinary Conditions, School of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Northwestern Polytechnical University, Xi’an, Shaanxi, 710072 China
C. F. Liu and Y. F. Jin contributed equally to this work.
Search for more papers by this authorJiaqi Li
Shaanxi Key Laboratory of Macromolecular Science and Technology, Xi’an Key Laboratory of Hybrid Luminescent Materials and Photonic Device, MOE Key Laboratory of Material Physics and Chemistry under Extraordinary Conditions, School of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Northwestern Polytechnical University, Xi’an, Shaanxi, 710072 China
Search for more papers by this authorZeyi Wang
Shaanxi Key Laboratory of Macromolecular Science and Technology, Xi’an Key Laboratory of Hybrid Luminescent Materials and Photonic Device, MOE Key Laboratory of Material Physics and Chemistry under Extraordinary Conditions, School of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Northwestern Polytechnical University, Xi’an, Shaanxi, 710072 China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Jingxia Wang
Shaanxi Key Laboratory of Macromolecular Science and Technology, Xi’an Key Laboratory of Hybrid Luminescent Materials and Photonic Device, MOE Key Laboratory of Material Physics and Chemistry under Extraordinary Conditions, School of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Northwestern Polytechnical University, Xi’an, Shaanxi, 710072 China
E-mail: [email protected]; [email protected]Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Wei Tian
Shaanxi Key Laboratory of Macromolecular Science and Technology, Xi’an Key Laboratory of Hybrid Luminescent Materials and Photonic Device, MOE Key Laboratory of Material Physics and Chemistry under Extraordinary Conditions, School of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Northwestern Polytechnical University, Xi’an, Shaanxi, 710072 China
E-mail: [email protected]; [email protected]Search for more papers by this authorComprehensive Summary
Self-assembly processes are ubiquitous in biological systems, playing essential roles in sustaining life activities. The exploration of self-assembled biomaterials (SABMs) holds great potential for advancing various fields, particularly in biomedicine and materials science. Because of the unique reversibility and responsiveness to stimuli, dynamic covalent bonds (DCBs) and noncovalent bonds (NCBs) endow SABMs with self-healing properties, stimuli responsiveness and controllable degradation, making them highly versatile for a wide range of biomedical applications. In this article, recent advances and future trends for SABMs based on DCBs and NCBs are thoroughly reviewed. We begin by introducing the molecular principles and characteristics of DCBs and NCBs that govern the formation of SABMs. We also explore the responsive and functional features of these materials in detail. Finally, we summarize the perspectives and challenges associated with the development of SABMs in biomedical applications. We aim for this review to offer a comprehensive overview of SABMs, serving as a valuable resource for chemists and materials scientists striving to further advance the design of SABMs in biological applications.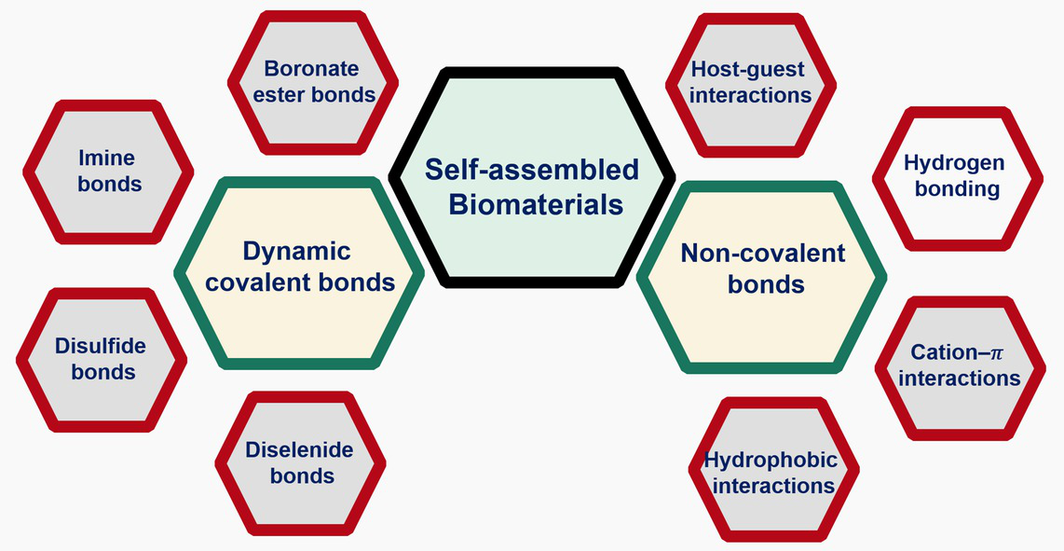
Key Scientists

References
- 1 Liu, Q.; Song, L.; Chen, S.; Gao, J.; Zhao, P.; Du, J. A superparamagnetic polymersome with extremely high T2 relaxivity for MRI and cancer-targeted drug delivery. Biomaterials 2017, 114, 23–33.
- 2 Yang, X.; Cao, Z.; Lu, H.; Wang, H. In Situ Construction of Functional Assemblies in Living Cells for Cancer Therapy. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2021, 10, 2100381.
- 3 Mignani, S.; Rodrigues, J.; Tomas, H.; Zablocka, M.; Shi, X.; Caminade, A.-M.; Majoral, J.-P. Dendrimers in Combination with Natural Products and Analogues as Anti-cancer Agents. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2018, 47, 514–532.
- 4 Wang, X.; Zhang, M.; Li, Y.; Cong, H.; Yu, B.; Shen, Y. Research Status of Dendrimer Micelles in Tumor Therapy for Drug Delivery. Small 2023, 19, 2304006.
- 5 Chakraborty, P.; Roy, N.; Biswas, P.; Biswas, D.; Datta, H.; Dutta, A.; Dastidar, P. Exploiting Urea-Carboxylate Synthon for Designing Supramolecular Topical Hydrogel via Simple Organic Salt Formation: Synthesis, Crystal Structures, and Anticancer Behavior against MelanomaB16–F10 Cells. Chem. Mater. 2024, 36, 7317–7331.
- 6 Zhang, J.; Wu, T.; Li, C.; Du, J. A glycopolymersome strategy for ‘drug-free’ treatment of diabetic nephropathy. J. Controlled Release 2024, 372, 347–361.
- 7 Qin, Y.; Chen, L.-J.; Dong, F.; Jiang, S.-T.; Yin, G.-Q.; Li, X.; Tian, Y.; Yang, H.-B. Light-Controlled Generation of Singlet Oxygen within a Discrete Dual-Stage Metallacycle for Cancer Therapy. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2019, 141, 8943–8950.
- 8 Dutta, D.; Zhou, Q.; Mukerabigwi, J. F.; Lu, N.; Ge, Z. Hypoxia-Responsive Polyprodrug Nanocarriers for Near-Infrared Light-Boosted Photodynamic Chemotherapy. Biomacromolecules 2021, 22, 4857–4870.
- 9 Cao, Y.; Si, J.; Zheng, M.; Zhou, Q.; Ge, Z. X-ray-responsive prodrugs and polymeric nanocarriers for multimodal cancer therapy. Chem. Commun. 2023, 59, 8323–8331.
- 10 Sun, X.; Dong, Y.; Liu, Y.; Song, N.; Li, F.; Yang, D. Self-assembly of artificial architectures in living cells-design and applications. Sci. China Chem. 2022, 65, 31–47.
- 11
Xianyu, B.; Xu, H. Dynamic covalent bond-based materials: From construction to biomedical applications. Supramol. Mater. 2024, 3, 100070.
10.1016/j.supmat.2024.100070 Google Scholar
- 12 Chen, L.-J.; Yang, H. B. Construction of Stimuli-Responsive Functional Materials via Hierarchical Self-Assembly Involving Coordination Interactions. Acc. Chem. Res. 2018, 51, 2699–2710.
- 13 Jiang, W.-L.; Huang, B.; Zhao, X.-L.; Shi, X.; Yang, H. B. Strong Halide Anion Binding within the Cavity of a Conformation-adaptive Phenazine-based Pd2L4 Cage. Chem 2023, 9, 2655–2668.
- 14 Liu, Y.; Wang, L.; Zhao, L.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Z.-T.; Huang, F. Multiple Hydrogen bonding Driven Supramolecular Architectures and Their Biomedical Applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2024, 53, 1592–1623.
- 15 Zhu, H.; Chen, L.; Sun, B.; Wang, M.; Li, H.; Stoddart, J. F.; Huang, F. Applications of Macrocycle-based Solid-state Host–guest Chemistry. Nat. Rev. Chem. 2023, 7, 768–782.
- 16 Dai, Y.; Li, T.; Zhang, Z.; Tan, Y.; Pan, S.; Zhang, L.; Xu, H.; Oxidative Polymerization in Living Cells. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2021, 143, 10709.
- 17 Wang, D.; Liu, B.; Ma, Y.; Wu, C.; Mou, Q.; Deng, H.; Wang, R.; Yan, D.; Zhang, C.; Zhu, X. A molecular recognition approach to synthesize nucleoside analogue based multifunctional nanoparticles for targeted cancer therapy. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2017, 139, 14021–14024.
- 18 Cui, J.; Du, L.; Meng, Z.; Gao, J.; Tan, A.; Jin, X.; Zhu, X. Ingenious Structure Engineering to Enhance Piezoelectricity in Poly(vinylidene fluoride) for Biomedical Applications. Biomacromolecules 2024, 25, 5541–5591.
- 19 Xie, M.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Lu, R.; Zhai, Z.; Huang, Y.; Wang, F.; Xin, C.; Rong, G.; Zhao, C.; Jiang, K.; Zhou, X.; Zhou, X.; Zhu, X.; Hong, J.; Zhang, C. Membrane Fusion-Mediated Loading of Therapeutic siRNA into Exosome for Tissue-Specific Application. Adv. Mater. 2024, 36, 2403935.
- 20 Zhang, W.; Ge, Z.; Xiao, Y.; Liu, D.; Du, J. Antioxidant and Immunomodulatory Polymer Vesicles for Effective Diabetic Wound Treatment through ROS Scavenging and Immune Modulating. Nano Lett. 2024, 24, 9494–9504.
- 21 Yan, M.; Wu, S.; Wang, Y.; Liang, M.; Wang, M.; Hu, W.; Yu, G.; Mao, Z.; Huang, F.; Zhou, J. Recent Progress of Supramolecular Chemotherapy Based on Host–Guest Interactions. Adv. Mater. 2024, 36, 2304249.
- 22 Wang, Q.; Serda, M.; Li, Q.; Sun, T. Recent Advancements on Self-Immolative System Based on Dynamic Covalent Bonds for Delivering Heterogeneous Payloads. Adv. Healthcare Mater. 2023, 12, 2300138.
- 23 Huang, W.; Yang, Y.; Ye, D. Recent Advances in Activatable Probes for Molecular Imaging by Stimuli-Controlled Disassembly. Chin. J. Chem. 2023, 41, 2382–2399.
- 24 Li, T.; Pan, S.; Gao, S.; Xiang, W.; Sun, C.; Cao, W.; Xu, H. Diselenide-Pemetrexed Assemblies for Combined Cancer Immuno-, Radio-, and Chemotherapies. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2020, 59, 2700–2704.
- 25 Li, T.; Pan, S.; Zhuang, H.; Gao, S.; Xu, H. Selenium-Containing Carrier- Free Assemblies with Aggregation-Induced Emission Property Combine Cancer Radiotherapy with Chemotherapy. ACS Appl. Bio Mater. 2020, 3, 1283–1292.
- 26 Sun, C.; Tan, Y.; Xu, H. From Selenite to Diselenide-Containing Drug Delivery Systems. ACS Mater. Lett. 2020, 2, 1173–1177.
- 27 Yang, J.; Pan, S.; Gao, S.; Li, T.; Xu, H. CO/chemosensitization/antiangiogenesis synergistic therapy with H2O2-responsive diselenide-containing polymer. Biomaterials 2021, 271, 120721.
- 28 Gao, S.; Li, T.; Guo, Y.; Sun, C.; Xianyu, B.; Xu, H. Selenium-Containing Nanoparticles Combine the NK Cells Mediated Immunotherapy with Radiotherapy and Chemotherapy. Adv. Mater. 2020, 32, 1907568.
- 29 Pan, S.; Guan, J.; Xianyu, B.; Tan, Y.; Li, T.; Xu, H. A Nanotherapeutic Strategy to Reverse NK Cell Exhaustion. Adv. Mater. 2023, 35, 2211370.
- 30 Xianyu, B.; Pan, S.; Gao, S.; Xu, H.; Li, T. Selenium-Containing Nanocomplexes Achieve Dual Immune Checkpoint Blockade for NK Cell Reinvigoration. Small 2024, 20, 2306225.
- 31 Zhang, H.; Liu, T.; Sun, Y.; Wang, S.; Wang, W.; Kuang, Z.; Duan, M.; Du, T.; Liu, M.; Wu, L.; et al. Carbon-Spaced Tandem-Disulfide Bond Bridge Design Addresses Limitations of Homodimer Prodrug Nanoassemblies: Enhancing Both Stability and Activatability. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2024, 146, 22675–22688.
- 32 Wu, J.; Zhao, L.; Xu, X.; Bertrand, N.; Choi, W. I.; Yameen, B.; Shi, J.; Shah, V.; Mulvale, M.; MacLean, J. L.; Farokhzad, O. C. Hydrophobic Cysteine Poly(disulfide)-based Redox-Hypersensitive Nanoparticle Platform for Cancer Theranostics. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2015, 54, 9218–9223.
- 33 Zhang, F.; Ni, Q.; Jacobson, O.; Cheng, S.; Liao, A.; Wang, Z.; He, Z.; Yu, G.; Song, J.; Ma, Y.; et al. Polymeric Nanoparticles with a Glutathione-Sensitive Heterodimeric Multifunctional Prodrug for In Vivo Drug Monitoring and Synergistic Cancer Therapy. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2018, 57, 7066–7070.
- 34 Zhou, Z.; Du, C.; Zhang, Q.; Yu, G.; Zhang, F.; Chen, X. Exquisite Vesicular Nanomedicine by Paclitaxel Mediated Co-assembly with Camptothecin Prodrug. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2021, 60, 21033–21039.
- 35 Liu, C.; Li, H.; Li, P.; Liu, C.; Bai, Y.; Pang, J.; Wang, J.; Tian, W. A Dual Drug-based Hyperbranched Polymer with Methotrexate and Chlorambucil Moieties for Synergistic Cancer Chemotherapy. Polym. Chem. 2020, 11, 5810–5818.
- 36 Fleige, E.; Achazi, K.; Schaletzki, K.; Triemer, T.; Haag, R. pH-Responsive Dendritic Core–Multishell Nanocarriers. J. Control. Release 2014, 185, 99–108.
- 37 Yan, M.; Guo, Y.; Zhao, W. Cross-Linked but Self-Healing and Entirely Degradable Poly-Schiff Base Metal Complex Materials for Potential Anti-Biofouling. Adv. Mater. Interfaces 2022, 9, 2101920.
- 38 Zhang, P.; Zhang, Y.; Ding, X.; Shen, W.; Li, M.; Wagner, E.; Xiao, C.; Chen. X. A Multistage Cooperative NanoplatformEnables Intracellular Co-Delivery of Proteinsand Chemotherapeutics for Cancer Therapy. Adv. Mater. 2020, 32, 2000013.
- 39 Yi, M.; Nguyen, T.; Liu, H.; Liu, Y.; Xiong, S.; Wang, Y. A Boronate Ester Driven Rechargeable Antibacterial Membrane for Fast Molecular Sieving. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2023, 33, 2213471.
- 40 Pan, S.; Yang, J.; Ji, S.; Li, T.; Gao, S.; Sun, C.; Xu, H. Cancer Therapy by Targeting Thioredoxin Reductase Based on Selenium-Containing Dynamic Covalent Bond. CCS Chem. 2020, 2, 225–235.
- 41 Liu, C.; Xianyu, B.; Dai, Y.; Pan, S.; Li, T.; Xu, H. Intracellular Hyperbranched Polymerization for Circumventing Cancer Drug Resistance. ACS Nano 2023, 17, 11905–11913.
- 42 Liu, C.; Si, J.; Cao, M.; Zhao, P.; Dai, Y.; Xu, H. Visualizing Chain Growth of Polytelluoxane via Polymerization Induced Emission. Adv. Sci. 2023, 10, 2304518.
- 43 Geng, W.-C.; Jiang, Z.-T.; Chen, S.-L.; Guo, D.-S. Supramolecular Interaction in the Action of Drug Delivery Systems. Chem. Sci. 2024, 15, 7811–7823.
- 44 Zhang, H.; Pan, Y.; Li, Y.; Li, C.; Wang, Y.; Jiang, W.; Xu, F.; Mai, Y.; Zhou, Y. Hierarchical Self-Assembly of Hyperbranched Polymer-Based Topological Supramolecular Amphiphiles. Chem. Eur. J. 2024, 30, e202402231.
- 45 Jin, H. B.; Huang, W.; Zhu, X. Y.; Zhou, Y. F.; Yan, D. Y. Biocompatible or biodegradable hyperbranched polymers: from self-assembly to cytomimetic applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2012, 41, 5986.
- 46 Shen, Y.; Jin, E. Prodrugs Forming High Drug Loading Multifunctional Nanocapsules for Intracellular Cancer Drug Delivery. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 132, 4259–4265.
- 47 Huang, P.; Wang, D.; Su, Y.; Huang, W.; Zhou, Y.; Cui, D.; Zhu, X.; Yan, D. Combination of Small Molecule Prodrug and Nanodrug Delivery: Amphiphilic Drug–Drug Conjugate for Cancer Therapy. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2014, 136, 11748–11756.
- 48 Liang, X.; Gao, C.; Cui, L.; Wang, S.; Wang, J.; Dai, Z. Self-Assembly of an Amphiphilic Janus Camptothecin–Floxuridine Conjugate into Liposome-Like Nanocapsules for More Efficacious Combination Chemotherapy in Cancer. Adv. Mater. 2017, 29, 1703135.
- 49 Wang, H.; Xue, K.-F.; Yang, Y.; Hu, H.; Xu, J.-F.; Zhang, X. In Situ Hypoxia-Induced Supramolecular Perylene Diimide Radical Anions in Tumors for Photothermal Therapy with Improved Specificity. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2022, 144, 2360–2367.
- 50 Zhang, T.-X.; Zhang, Z.-Z.; Yue, Y.-X.; Hu, X.-Y.; Huang, F.; Shi, L.; Liu, Y.; Guo, D.-S. A General Hypoxia-Responsive Molecular Container for Tumor-Targeted Therapy. Adv. Mater. 2020, 32, 1908435.
- 51 Zhang, Y.-M.; Liu, Y.-H.; Liu, Y. Cyclodextrin-Based Multistimuli-Responsive Supramolecular Assemblies and Their Biological Functions. Adv. Mater. 2020, 32, 1806158.
- 52 Li, X.; Shen, M.; Yang, J.; Liu, L.; Yang, Y.-W. Pillararene-Based Stimuli- Responsive Supramolecular Delivery Systems for Cancer Therapy. Adv. Mater. 2024, 36, 2313317.
- 53 Yang, L.; Tan, X.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, X. Supramolecular Polymers: Historical Development, Preparation, Characterization, and Functions. Chem. Rev. 2015, 115, 7196–7239.
- 54 Zhu, H.; Wang, H.; Shi, B.; Shangguan, L.; Tong, W.; Yu, G.; Mao, Z.; Huang, F. Supramolecular peptide constructed by molecular Lego allowing programmable self-assembly for photodynamic therapy. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 2412.
- 55 Liu, C.; Li, C.; Pang, C.; Li, M.; Li, H.; Li, P.; Fan, L.; Liu, H.; Tian, W. Supramolecular Drug–Drug Complex Vesicles Enable Sequential Drug Release for Enhanced Combination Therapy. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 27940–27950.
- 56 Bai, Y.; Liu, C.; Yang, J.; Liu, C.; Shang, Q.; Tian, W. Supramolecular Self-assemblies Based on Water-Soluble Pillar[6]arene and Drug-drug Conjugates for the Combination of Chemotherapy. Colloids Surf. B 2022, 217, 112606.
- 57 Liu, C.; Li, M.; Li, P.; Bai, Y.; Pang, J.; Fan, L.; Tian, W. Ruthenium (II)-Coordinated Supramolecular Metallodrug Complex Realizing Oxygen Self-Supply In Situ for Overcoming Hypoxic Tumors. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2021, 31, 2105837.
- 58 Liu, C.; Li, M.; Liu, C.; Qiu, S.; Bai, Y.; Fan, L.; Tian, W. A Supramolecular Organometallic Drug Complex with H2O2 Self-provision Intensifying Intrcellular Autocatalysis for Chemodynamic Therapy. J. Mater. Chem. B 2022, 10, 8981–8987.
- 59 Zhang, Y.-M.; Liu, Y.-H.; Liu, Y. Cyclodextrin-Based Multistimuli-Responsive Supramolecular Assemblies and Their Biological Functions. Adv. Mater. 2020, 32, 1806158.
- 60 Xiong, Q.; Bai, Y.; Shi, R.; Wang, J.; Xu, W.; Zhang, M.; Song, T. Preferentially Released MiR-122 from Cyclodextrin-based Star Copolymer Nanoparticle Enhances Hepatoma Chemotherapy by Apoptosis Induction and Cytotoxics Efflux Inhibition. Bioact. Mater. 2021, 6, 3744–3755.
- 61 Mu, B.; Gao, Z.; Liu, C.; Xiao, X.; Tian, W. Supramolecular Coassembly: Monomer Pair Design, Morphology Regulation and Functional Application. Chem. Commun. 2023, 59, 5514–5530.
- 62 Bai, Y.; Liu, C.-P.; Chen, D.; Liu, C.-F.; Zhuo, L.-H.; Li, H.; Wang, C.; Bu, H.-T.; Tian, W. β-Cyclodextrin-modified Hyaluronic Acid-based Supramolecular Self-assemblies for pH- and Esterase-dual-responsive Drug Delivery. Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 246, 116654.
- 63 Yao, H.; Qi, M.; Liu, Y.; Tian, W. Host–Guest Binding-Site-Tunable Self-Assembly of Stimuli-Responsive Supramolecular Polymers. Chem. Eur. J. 2016, 22, 8508–8519.
- 64 Yao, H.; Yang, T.; He, J.; Du, G.; Song, X.; Zhang, Y.; Tian, W. Ultrasound and Redox-Triggered Morphology Transitions of Supramolecular Self-assemblies with pH Responsiveness for Triple-Controlled Release. Langmuir 2019, 35, 8045–8051.
- 65 Wu, J.-J.; Chen, F.-Y.; Han, B.-B.; Zhang, H.-Q.; Zhao, L.; Zhang, Z.-R.; Li, J.-J.; Zhang, B.-D.; Zhang, Y.-N.; Yue, Y.-X. Hu, H.-G.; Li, W.-H.; Zhang, B.; Chen, Y.-X.; Guo, D.-S.; Li, Y.-M. CASTING: A Potent Supramolecular Strategy to Cytosolically Deliver STING Agonist for Cancer Immunotherapy and SARS-CoV-2 Vaccination. CCS Chem. 2023, 5, 885–901.
- 66 Yu, H.-J.; Zhou, Q.; Dai, X.; Shen, F.-F.; Zhang, Y.-M.; Xu, X.; Liu, Y. Photooxidation-Driven Purely Organic Room-Temperature Phosphorescent Lysosome-Targeted Imaging. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2021, 143, 13887–13894.
- 67 Jia, F.; Schröder, H.; Yang, L.; Essen, C.; Sobottka, S.; Sarkar, B.; Rissanen, K.; Jiang, W.; Schalley, C. Redox-Responsive Host-Guest Chemistry of a Flexible Cage with Naphthalene Walls. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2020, 142, 3306–3310
- 68 Li, Z.; Chen, S.; Binder, W. H.; Zhu, J. Hydrogen-Bonded Polymer Nanomedicine with AIE Characteristic for Intelligent Cancer Therapy. ACS Macro Lett. 2023, 12, 1384–1388.
- 69 Wang, D.; Yu, C.; Xu, L.; Shi, L.; Tong, G.; Wu, J.; Liu, H.; Yan, D.; Zhu, X. Nucleoside Analogue-Based Supramolecular Nanodrugs Driven by Molecular Recognition for Synergistic Cancer Therapy. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2018, 140, 8797–8806.
- 70 Pan, S.; Li, T.; Tan, Y.; Xu, H. Selenium-containing Nanoparticles Synergistically Enhance Pemetrexed&NK Cell-based Chemoimmunotherapy. Biomaterials 2022, 280, 121321.
- 71 Mahadevi, A. S.; Sastry, G. N. Cation–π Interaction: Its Role and Relevance in Chemistry, Biology, and Material Science. Chem. Rev. 2013, 113, 2100–2138.
- 72 Tan, G.; Wang, Y.; He, Y.; Miao, G.; Li, Y.; Wang, X. Bioinspired Poly(cation-π) Micelles Drug Delivery Platform for Improving Chemotherapy Efficacy. J. Control. Release 2022, 349, 486–501.
- 73 Liu, C.; Li, M.; Sun, J.; Li, P.; Bai, Y.; Zhang, J.; Qian, Y.; Shi, M.; He, J.; Huo, H.; Pang, J.; Fan, L.; Tian, W. Cation-π Interaction-Mediated Tumour Drug Delivery for Deep Intratumoral Penetration and Treatment. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2022, 32, 2205043.
- 74 Wang, J.; Gu, X.; Zhang, P.; Huang, X.; Zheng, X.; Chen, M.; Feng, H.; Kwok, R.; Lam, J.; Tang, B. Ionization and Anion–π+ Interaction: A New Strategy for StructuralDesign of Aggregation-Induced Emission Luminogens. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2017, 139, 16974–16979.
- 75 Liu, L.; Li, C.; Gong, J.; Zhang, Y.; Ji, W.; Feng, L.; Jiang, G.; Wang, J.; Tang, B. A Highly Water-Soluble Aggregation-Induced Emission Luminogen with Anion-π+ Interactions for Targeted NIR Imaging of Cancer Cells and Type I Photodynamic Therapy. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2023, 62, e202307776.
- 76 Pan, Y.-C.; Tian, J.-H.; Guo, D.-S. Molecular Recognition with Macrocyclic Receptors for Application in Precision Medicine. Acc. Chem. Res. 2023, 56, 3626–3639.
- 77 Wang, H.; Wu, H.; Yi, Y.; Xue, K.-F.; Xu, J.-F.; Wang, H.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, X. Self-Motivated Supramolecular Combination Chemotherapy for Overcoming Drug Resistance Based on Acid-Activated Competition of Host–Guest Interactions. CCS Chem. 2021, 3, 1413–1425.
- 78 Zhou, Z.; Maxeiner, K.; Ng, D. Y. W.; Weil, T. Polymer Chemistry in Living Cells. Acc. Chem. Res. 2022, 55, 2998–3009.
- 79 Liu, C.; Xianyu, B.; He, C.; Cao, M.; Chen, Z.; Li, T.; Xu, H. Intracellular Construction of Topological Polymer Networks to Destruct Organelles. CCS Chem. 2025, 7, 403–415.
- 80 Yao, S.-Y.; Ying, A.-K.; Jiang, Z.-T.; Cheng, Y.-Q.; Geng, W.-C.; Hu, X.-Y.; Cai, K.; Guo, D.-S. Single Molecular Nanomedicines Based on Macrocyclic Carrier-Drug Conjugates for Concentration-Independent Encapsulation and Precise Activation of Drugs. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2024, 146, 14203–14212.
- 81 Liu, C.; Liu, C.; Bai, Y.; Wang, J.; Tian, W. Drug Self-Delivery Systems: Molecule Design, Construction Strategy, and Biological Application. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2023, 12, 2202769.
- 82 Yu, G.; Zhao, X.; Zhou, J.; Mao, Z.; Huang, X.; Wang, Z.; Hua, B.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, F.; He, Z.; Orit, J.; Gao, C.; Wang, W.; Yu, C.; Zhu, X.; Huang, F.; Chen, X. Supramolecular Polymer-Based Nanomedicine: High Therapeutic Performance and Negligible Long-Term Immunotoxicity. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2018, 140, 8005–8019.
- 83 Li, S.; Wang, Y.; Wang, X.; Feng, J.; Guo, D.-S.; Meng, Z.; Liu, Y.; Sun, S.-K.; Zhang, Z. Macrocyclic-Albumin Conjugates for Precise Delivery of Radionuclides and Anticancer Drugs to Tumors. ACS Nano 2023, 17, 22399–22409.
- 84 Ren, Y.; Zhou, Z.; Maxeiner, K.; Kaltbeitzel, A.; Harley, I.; Xing, J.; Wu, Y.; Wagner, M.; Landfester, K.; Lieberwirth, I.; Weil, T.; Ng, D. Supramolecular Assembly in Live Cells Mapped by Real-Time Phasor-Fluorescence Lifetime Imaging. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2024, 146, 11991–11999.
- 85 Wang, J.; Li, J.; Li, M.; Ma, K.; Wang, D.; Su, L.; Zhang, X.; Tang, B. Z. Nanolab in a Cell: Crystallization-Induced In Situ Self-Assembly for Cancer Theranostic Amplification. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2022, 144, 14388–14395.
- 86 Wang, L.; Tran, M.; D’Este, E.; Roberti, J.; Koch, B.; Xue, L.; Johnsson, K. A General Strategy to Develop Cell Permeable and Fluorogenic Probes for Multicolour Nanoscopy. Nat. Chem. 2020, 12, 165–172.
- 87 Scipioni, L.; Rossetta, A.; Tedeschi, G.; Gratton, E. Phasor S-FLIM: a new paradigm for fast and robust spectral fluorescence lifetime imaging. Nat. Meth. 2021, 18, 542–550.
- 88 Zhao, X.-X.; Li, L.-L.; Zhao, Y.; An, H.-W.; Cai, Q.; Lang, J.-Y.; Han, X.-X.; Peng, B.; Fei, Y.; Liu, H.; Qin, H.; Nie, G.; Wang, H.; In Situ Self-Assembled Nanofibers Precisely Target Cancer-Associated Fibroblasts for Improved Tumor Imaging. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2019, 58, 15287–15294.
- 89 Hu, R.; Chen, X.; Zhou, T.; Si, H.; He, B.; Kwok, R. T. K.; Qin, A.; Tang, B. Z. Lab-in-cell based on spontaneous amino-yne click polymerization. Sci. China Chem. 2019, 62, 1198–1203.
- 90 Schenkman, L. Second Thoughts About CT Imaging. Science 2011, 331, 1002–1004.
- 91 Lee, N.; Choi, S. H.; Hyeon, T. Nano-Sized CT Contrast Agents. Adv. Mater. 2013, 25, 2641–2660.
- 92 Liu, C.; Li, M.; Li, P.; Chen, W.; Li, H.; Fan, L.; Tian, W. Platinum-Containing Supramolecular Drug Self-Delivery Nanomicelles for Efficient Synergistic Combination Chemotherapy. Biomacromolecules 2021, 22, 2382–2392.
- 93 Kong, L.; Gao, M.; Shi, J.; Zhao, C.; Chen, C. Synthetic Polypeptide Bioadhesive Based on Cation–π Interaction and Secondary Structure. ACS Macro Lett. 2024, 13, 361–367.
- 94 Xiong, J.; Duan, M.; Zou, X.; Gao, S.; Guo, J.; Wang, X.; Li, Q.; Li, W.; Wang, X.; Yan, F. Biocompatible Tough Ionogels with Reversible Supramolecular Adhesion. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2024, 146, 13903–13913.
- 95 Strakosas, X.; Biesmans, H.; Abrahamsson, T.; Hellman, K.; Ejneby, M. S.; Donahue, M. J.; Ekström, P.; Ek, F.; Savvakis, M.; Hjort, M.; Bliman, D.; Linares, M.; Lindholm, C.; Stavrinidou, E.; Gerasimov, J. Y.; Simon, D. T.; Olsson, R.; Berggren, M. Metabolite-induced in vivo fabrication of substrate-free organic bioelectronics. Science 2023, 379, 795–802.
- 96 Liu, J.; Kim, Y. S.; Richardson, C. E.; Tom, A.; Ramakrishnan, C.; Birey, F.; Katsumata, T.; Chen, S.; Wang, C.; Wang, X.; Joubert, L.-M.; Jiang, Y.; Wang, H.; Fenno, L. E.; Tok, J. B.-H.; Pașca, S. P.; Shen, K.; Bao, Z.; Deisseroth, K. Genetically targeted chemical assembly of functional materials in living cells, tissues, and animals. Science 2020, 367, 1372–1376.
- 97 Yang, J.; Pan, S.; Gao, S.; Dai, Y.; Xu, H. Anti-recurrence/metastasis and Chemosensitization Therapy with Thioredoxin Reductase-interfering Drug Delivery System. Biomaterials 2020, 249, 120054.
- 98
Liu, C.; Yang, Z.; Song, X.; Qian, Y.; Huo, H.; He, J.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, Z.; Shi, M.; Pang, J.; Zhang, B.; Tian, W. Light controlled drug-based supramolecular polymer self-assemblies for efficient antibacterial manipulation. Supramolecular Materials 2022, 1, 100014.
10.1016/j.supmat.2022.100014 Google Scholar




