Neutral Chalcogen Bonding Enabled Photoinduced Cross-Electrophile C—S/Se Coupling of Aryl Iodides via SRN1 Process
Yong-Liang Tu
School of Chemical Sciences, University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, 100049 China
These authors contribute equally to this work.
Search for more papers by this authorXiang Li
School of Chemical Sciences, University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, 100049 China
These authors contribute equally to this work.
Search for more papers by this authorBei-Bei Zhang
School of Chemical Sciences, University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, 100049 China
Search for more papers by this authorGui-Ying Fu
School of Chemical Sciences, University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, 100049 China
Search for more papers by this authorLing Zhou
School of Materials and Architectural Engineering, Guizhou Normal University, Guiyang, Guizhou, 550025 China
School of Chemical Sciences, University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, 100049 China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Wei Gong
School of Materials and Architectural Engineering, Guizhou Normal University, Guiyang, Guizhou, 550025 China
E-mail: [email protected]; [email protected]Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Xiang-Yu Chen
School of Chemical Sciences, University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, 100049 China
Beijing National Laboratory for Molecular Sciences, Beijing, 100190 China
E-mail: [email protected]; [email protected]Search for more papers by this authorYong-Liang Tu
School of Chemical Sciences, University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, 100049 China
These authors contribute equally to this work.
Search for more papers by this authorXiang Li
School of Chemical Sciences, University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, 100049 China
These authors contribute equally to this work.
Search for more papers by this authorBei-Bei Zhang
School of Chemical Sciences, University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, 100049 China
Search for more papers by this authorGui-Ying Fu
School of Chemical Sciences, University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, 100049 China
Search for more papers by this authorLing Zhou
School of Materials and Architectural Engineering, Guizhou Normal University, Guiyang, Guizhou, 550025 China
School of Chemical Sciences, University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, 100049 China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Wei Gong
School of Materials and Architectural Engineering, Guizhou Normal University, Guiyang, Guizhou, 550025 China
E-mail: [email protected]; [email protected]Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Xiang-Yu Chen
School of Chemical Sciences, University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, 100049 China
Beijing National Laboratory for Molecular Sciences, Beijing, 100190 China
E-mail: [email protected]; [email protected]Search for more papers by this authorComprehensive Summary
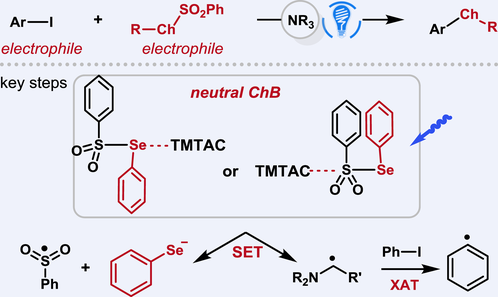
Cross-coupling reactions between aryl halides and thiolates or selenolates typically require transition metals, photocatalysts, strong bases, or/and malodorous thiols/selenols, with various mechanisms proposed. This study aims to leverage a new application of neutral ChB to address these challenges and enable a very simple photoinduced cross-electrophile C—S/Se coupling using readily available chalcogen electrophiles. Mechanistic investigations have revealed the important role of neutral ChB in facilitating single electron transfer processes, thereby enabling the generation of thiolates/selenolates from stable chalcogen electrophiles and α-aminoalkyl radicals, which possess the capability to abstract halogen atoms from aryl iodides. Moreover, the study provided support for the radical nucleophilic substitution mechanism.
Supporting Information
| Filename | Description |
|---|---|
| cjoc202401197-sup-0001-supinfo.pdfPDF document, 10.7 MB |
Appendix S1: Supporting Information |
Please note: The publisher is not responsible for the content or functionality of any supporting information supplied by the authors. Any queries (other than missing content) should be directed to the corresponding author for the article.
References
- 1(a) Iwaoka, M.; Komatsu, H.; Katsuda, T.; Tomoda, S. Nature of Nonbonded Se···O Interactions Characterized by 17O NMR Spectroscopy and NBO and AIM Analyses. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2004, 126, 5309–5317; (b) Bleiholder, C.; Werz, D. B.; Köppel, H.; Gleiter, R. Theoretical Investigations on Chalcogen−Chalcogen Interactions: What Makes These Nonbonded Interactions Bonding? J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2006, 128, 2666–2674; (c) Pascoe, D. J.; Ling, K. B.; Cockroft, S. L. The Origin of Chalcogen-Bonding Interactions. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2017, 139, 15160–15167; (d) Zhou, B.; Gabbaï, F. P. Anion Chelation via Double Chalcogen Bonding: The Case of a Bis-telluronium Dication and Its Application in Electrophilic Catalysis via Metal–Chloride Bond Activation. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2021, 143, 8625–8630; (e) Vogel, L.; Wonner, P.; Huber, S. M. Chalcogen Bonding: An Overview. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2018, 58, 1880–1891; (f) Sekar, G.; Nair, V. V.; Zhu, J. Chalcogen bonding catalysis. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2024, 53, 586–605.
- 2(a) Benz, S.; López-Andarias, J.; Mareda, J.; Sakai, N.; Matile, S. Catalysis with Chalcogen Bonds. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2017, 56, 812–815; (b) Benz, S.; Mareda, J.; Besnard, C.; Sakai, N.; Matile, S. Catalysis with chalcogen bonds: neutral benzodiselenazole scaffolds with high- precision selenium donors of variable strength. Chem. Sci. 2017, 8, 8164–8169; (c) Benz, S.; Poblador-Bahamonde, A. I.; Low-Ders, N.; Matile, S. Catalysis with Pnictogen, Chalcogen, and Halogen Bonds. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2018, 57, 5408–5412; (d) Benz, S.; Besnard, C.; Matile, S. Chalcogen-Bonding Catalysis: From Neutral to Cationic Benzodiselenazole Scaffolds. Helv. Chim. Acta 2018, 101, e1800075; (e) Strakova, K.; Assies, L.; Goujon, A.; Piazzolla, F.; Humeniuk, H. V.; Matile, S. Dithienothiophenes at Work: Access to Mechanosensitive Fluorescent Probes, Chalcogen-Bonding Catalysis, and Beyond. Chem. Rev. 2019, 119, 10977–11005; (f) Chen, X.-X.; Gomila, R. M.; García-Arcos, J. M.; Vonesch, M.; Gonzalez-Sanchis, N.; Roux, A.; Frontera, A.; Sakai, N.; Matile, S. Fluorogenic In Situ Thioacetalization: Expanding the Chemical Space of Fluorescent Probes, Including Unorthodox, Bifurcated, and Mechanosensitive Chalcogen Bonds. JACS Au 2023, 3, 2557–2565.
- 3(a) Wonner, P.; Vogel, L.; Düser, M.; Gomes, L.; Kniep, F.; Mallick, B.; Werz, D. B.; Huber, S. M. Carbon-Halogen Bond Activation by Selenium-Based Chalcogen Bonding. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2017, 56, 12009–12012; (b) Wonner, P.; Vogel, L.; Kniep, F.; Huber, S. M. Catalytic Carbon-Chlorine Bond Activation by Selenium-Based Chalcogen Bond Donors. Chem.–Eur. J. 2017, 23, 16972–16975; (c) Wonner, P.; Dreger, A.; Vogel, L.; Engelage, E.; Huber, S. M. Chalcogen Bonding Catalysis of a Nitro-Michael Reaction. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2019, 58, 16923–16927; (d) Wonner, P.; Steinke, T.; Vogel, L.; Huber, S. M. Carbonyl Activation by Selenium- and Tellurium-Based Chalcogen Bonding in a Michael Addition Reaction. Chem.–Eur. J. 2020, 26, 1258–1262; (e) Steinke, T.; Wonner, P.; Engelage, E.; Huber, S. M. Catalytic Activation of a Carbon-Chloride Bond by Dicationic Tellurium-Based Chalcogen Bond Donors. Synthesis 2021, 53, 2043–2050; (f) Tarannam, N.; Voelkel, M. H. H.; Huber, S. M.; Kozuch, S. Chalcogen vs Halogen Bonding Catalysis in a Water-Bridge-Cocatalyzed Nitro- Michael Reaction. J. Org. Chem. 2021, 87, 1661–1668; (g) Steinke, T.; Wonner, P.; Gauld, R. M.; Heinrich, S.; Huber, S. M. Catalytic Activation of Imines by Chalcogen Bond Donors in a Povarov [4+2] Cycloaddition Reaction. Chem.–Eur. J. 2022, 28, e202200917; (h) Pal, D.; Steinke, T.; Vogel, L.; Engelage, E.; Heinrich, S.; Kutzinski, D.; Huber, S. M. A Combined Halogen- and Chalcogen-Bonding Organocatalyst. Adv. Synth. Catal. 2023, 365, 2718–2723; (i) Steinke, T.; Engelage, E.; Huber, S. M. Chalcogen bonding in the solid-state structures of 1,3-bis(benzimidazoliumyl)benzene-based chalcogen-bonding donors. Acta Cryst. C 2023, 79, 26–35; (j) Akbaba, S.; Steinke, T.; Vogel, L.; Engelage, E.; Erdelyi, M.; Huber, S. M. Elucidating the Binding Mode of Sulfur- and Selenium-Based Cationic Chalcogen-Bond Donors. Chem.–Eur. J. 2024, e202400608.
- 4(a) Zhou, B.; Gabbaï, F. P. Redox-controlled chalcogen-bonding at tellurium: impact on Lewis acidity and chloride anion transport properties. Chem. Sci. 2020, 11, 7495–7500; (b) Zhou, B.; Gabbaï, F. P. Lewis Acidic Telluronium Cations: Enhanced Chalcogen-Bond Donor Properties and Application to Transfer Hydrogenation Catalysis. Organometallics 2021, 40, 2371–2374.
- 5(a) He, X.; Wang, X.; Tse, Y. L.; Ke, Z.; Yeung, Y. Y. Applications of Selenonium Cations as Lewis Acids in Organocatalytic Reactions. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2018, 57, 12869–12873; (b) He, X.; Wang, X.; Tse, Y.-L. S.; Ke, Z.; Yeung, Y.-Y. Bis-selenonium Cations as Bidentate Chalcogen Bond Donors in Catalysis. ACS Catal. 2021, 11, 12632–12642; (c) Zhang, Q.; Chan, Y. Y.; Zhang, M.; Yeung, Y. Y.; Ke, Z. Hypervalent Chalcogenonium···π Bonding Catalysis. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2022, 61, e202208009; (d) Yang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Wong, H.-C. F.; Huang, J.; Tse, Y.-L. S.; Yeung, Y.-Y. Design and Applications of Cyclopropenium Chalcogen Dihalides in Catalysis via C(sp3)–H···X Interactions. ACS Catal. 2024, 14, 3018–3027.
- 6(a) Wang, W.; Zhu, H.; Liu, S.; Zhao, Z.; Zhang, L.; Hao, J.; Wang, Y. Chalcogen–Chalcogen Bonding Catalysis Enables Assembly of Discrete Molecules. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2019, 141, 9175–9179; (b) Wang, W.; Zhu, H.; Feng, L.; Yu, Q.; Hao, J.; Zhu, R.; Wang, Y. Dual Chalcogen-Chalcogen Bonding Catalysis. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2020, 142, 3117–3124; (c) Kong, X.; Zhou, P. P.; Wang, Y. Chalcogen···π Bonding Catalysis. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2021, 60, 9395–9400; (d) Yuan, X.; Wang, Y. A Selenide Catalyst for the Activation of Alkenes through Se···π Bonding. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2022, 61, e202203671; (e) Zhu, H.; Zhou, P.-P.; Wang, Y. Cooperative chalcogen bonding interactions in confined sites activate aziridines. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 3563; (f) Zhao, Z.; Pang, Y.; Zhao, Z.; Zhou, P.-P.; Wang, Y. Supramolecular catalysis with ethers enabled by dual chalcogen bonding activation. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 6347; (g) Zhao, Z.; Wang, Y. Chalcogen Bonding Catalysis with Phosphonium Chalcogenide (PCH). Acc. Chem. Res. 2023, 56, 608–621.
- 7(a) Weiss, R.; Aubert, E.; Pale, P.; Mamane, V. Chalcogen-Bonding Catalysis with Telluronium Cations. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2021, 60, 19281–19286; (b) Pale, P.; Mamane, V. Chalcogen Bonds: How to Characterize Them in Solution? ChemPhysChem 2023, 24, e202200481; (c) Pale, P.; Mamane, V. Chalcogen Bonding Catalysis: Tellurium, the Last Frontier? Chem.–Eur. J. 2023, 29, e202302755; (d) Weiss, R.; Aubert, E.; Groslambert, L.; Pale, P.; Mamane, V. Evidence for and evaluation of fluorine–tellurium chalcogen bonding. Chem. Sci. 2023, 14, 7221–7229; (e) Groslambert, L.; Cornaton, Y.; Ditte, M.; Aubert, E.; Pale, P.; Tkatchenko, A.; Djukic, J. P.; Mamane, V. Affinity of Telluronium Chalcogen Bond Donors for Lewis Bases in Solution: A Critical Experimental-Theoretical Joint Study. Chem.–Eur. J. 2024, 30, e202302933.
- 8(a) Ma, W.; Kirchhoff, J.-L.; Strohmann, C.; Grabe, B.; Loh, C. C. J. Cooperative Bifurcated Chalcogen Bonding and Hydrogen Bonding as Stereocontrolling Elements for Selective Strain-Release Septanosylation. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2023, 145, 26611–26622; (b) Guo, H.; Kirchhoff, J.-L.; Strohmann, C.; Grabe, B.; Loh, C. C. J. Exploiting π and Chalcogen Interactions for the β-Selective Glycosylation of Indoles through Glycal Conformational Distortion. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2024, 63, e202316667; (c) Wang, C.; Krupp, A.; Strohmann, C.; Grabe, B.; Loh, C. C. J. Harnessing Multistep Chalcogen Bonding Activation in the α-Stereoselective Synthesis of Iminoglycosides. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2024, 146, 10608–10620; (d) Ma, W.; Schmidt, A.; Strohmann, C.; Loh, C. C. J. Stereoselective Entry into α,α’-C-Oxepane Scaffolds through a Chalcogen Bonding Catalyzed Strain-Release C-Septanosylation Strategy. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2024, 63, e20240570.
- 9(a) Bamberger, J.; Ostler, F.; Mancheño, O. G. Frontiers in Halogen and Chalcogen-Bond Donor Organocatalysis. ChemCatChem 2019, 11, 5198–5211; (b) Breugst, M.; Koenig, J. J. σ-Hole Interactions in Catalysis. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2020, 5473–5487; (c) Kolb, S.; Oliver, G. A.; Werz, D. B. Chemistry Evolves, Terms Evolve, but Phenomena Do Not Evolve: From Chalcogen–Chalcogen Interactions to Chalcogen Bonding. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2020, 59, 22306–22310; (d) Yan, W.; Zheng, M.; Xu, C.; Chen, F.-E. Harnessing noncovalent interaction of chalcogen bond in organocatalysis: From the catalyst point of view. Green Synth. Catal. 2021, 2, 329–336; (e) Hein, R.; Docker, A.; Davis, J. J.; Beer, P. D. Redox-Switchable Chalcogen Bonding for Anion Recognition and Sensing. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2022, 144, 8827–8836.
- 10 Lu, Y.; Liu, Q.; Wang, Z.-X.; Chen, X.-Y. Alkynyl Sulfonium Salts Can Be Employed as Chalcogen-Bonding Catalysts and Generate Alkynyl Radicals under Blue-Light Irradiation. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2022, 61, e202116071.
- 11(a) dos Santos, E. d. A.; Hamel, E.; Bai, R.; Burnett, J. C.; Tozatti, C. S. S.; Bogo, D.; Perdomo, R. T.; Antunes, A. M. M.; Marques, M. M.; Matos, M. d. F. C.; de Lima, D. P. Synthesis and evaluation of diaryl sulfides and diaryl selenide compounds for antitubulin and cytotoxic activity. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2013, 23, 4669–4673; (b) Scott, K. A.; Njardarson, J. T. Analysis of US FDA-Approved Drugs Containing Sulfur Atoms. Top. Curr. Chem. 2018, 376, 5; (c) Hou, W.; Xu, H. Incorporating Selenium into Heterocycles and Natural Products-From Chemical Properties to Pharmacological Activities. J. Med. Chem. 2022, 65, 4436–4456.
- 12(a) Beletskaya, I. P.; Ananikov, V. P. Transition-Metal-Catalyzed C−S, C−Se, and C−Te Bond Formation via Cross-Coupling and Atom-Economic Addition Reactions. Chem. Rev. 2011, 111, 1596–1636; (b) Chauhan, P.; Mahajan, S.; Enders, D. Organocatalytic Carbon–Sulfur Bond-Forming Reactions. Chem. Rev. 2014, 114, 8807–8864; (c) Shen, C.; Zhang, P.; Sun, Q.; Bai, S.; Hor, T. S. A.; Liu, X. Recent advances in C–S bond formation via C–H bond functionalization and decarboxylation. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2015, 44, 291–314; (d) Li, H.; Liu, Y.; Chiba, S. Leveraging of Sulfur Anions in Photoinduced Molecular Transformations. JACS Au 2021, 1, 2121–2129; (e) Beletskaya, I. P.; Ananikov, V. P. Transition-Metal-Catalyzed C–S, C–Se, and C–Te Bond Formations via Cross-Coupling and Atom-Economic Addition Reactions. Achievements and Challenges. Chem. Rev. 2022, 122, 16110–16293; (f) Behera, P. K.; Choudhury, P.; Behera, P.; Swain, A.; Pradhan, A. K.; Rout, L. Transition Metal Catalysed C-S Cross-Coupling Reactions at Room Temperature. ChemistrySelect 2022, 7, e202202919; (g) Feng, J.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, X.; Liu, J.; Benazzi, V.; Lu, K.; Zhao, X.; Protti, S. Recent Advances in Visible-Light-Driven C−S Bond Formation. Adv. Synth. Catal. 2023, 365, 3413–3431; (h) Wu, Z.; Pratt, D. A. Radical approaches to C–S bonds. Nat. Rev. Chem. 2023, 7, 573–589; (i) Bhanja, R.; Bera, S. K.; Mal, P. Photocatalyst-and Transition-Metal- Free Light-Induced Formation of Carbon-Chalcogen Bonds. Adv. Synth. Catal. 2024, 366, 168–182.
- 13For selected examples, see: (a) Mann, G.; Baranano, D.; Hartwig, J. F.; Rheingold, A. L.; Guzei, I. A. Carbon−Sulfur Bond-Forming Reductive Elimination Involving sp-, sp2-, and sp3-Hybridized Carbon. Mechanism, Steric Effects, and Electronic Effects on Sulfide Formation. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1998, 120, 9205–9219; (b) Alvaro, E.; Hartwig, J. F. Resting State and Elementary Steps of the Coupling of Aryl Halides with Thiols Catalyzed by Alkylbisphosphine Complexes of Palladium. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 7858–7868; (c) Buchwald, S. L.; Bolm, C. On the Role of Metal Contaminants in Catalyses with FeCl3. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2009, 48, 5586–5587; (d) Uyeda, C.; Tan, Y.; Fu, G. C.; Peters, J. C. A New Family of Nucleophiles for Photoinduced, Copper-Catalyzed Cross-Couplings via Single-Electron Transfer: Reactions of Thiols with Aryl Halides Under Mild Conditions (0 °C). J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 9548–9552; (e) Oderinde, M. S.; Frenette, M.; Robbins, D. W.; Aquila, B.; Johannes, J. W. Photoredox Mediated Nickel Catalyzed Cross-Coupling of Thiols with Aryl and Heteroaryl Iodides via Thiyl Radicals. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2016, 138, 1760−1763; (f) Liu, B.; Lim, C.-H.; Miyake, G. M. Visible-light-promoted C−S cross-coupling via intermolecular charge transfer. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2017, 139, 13616–13619; (g) Jiang, M.; Li, H.; Yang, H.; Fu, H. Room-Temperature Arylation of Thiols: Breakthrough with Aryl Chlorides. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2017, 56, 874–879; (h) Vara, B. A.; Li, X.; Berritt, S.; Walters, C. R.; Petersson, E. J.; Molander, G. A. Scalable thioarylation of unprotected peptides and biomolecules under Ni/photoredox catalysis. Chem. Sci. 2018, 9, 336–344; (i) Zhu, Y.-Y.; Lan, G.; Fan, Y.; Veroneau, S. S.; Song, Y.; Micheroni, D.; Lin, W. Merging Photoredox and Organometallic Catalysts in a Metal−Organic Framework Significantly Boosts Photocatalytic Activities. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2018, 57, 14090–14094; (j) Liu, D.; Ma, H.-X.; Fang, P.; Mei, T.-S. Nickel-Catalyzed Thiolation of Aryl Halides and Heteroaryl Halides through Electrochemistry. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2019, 58, 5033–5037; (k) Wang, Y.; Deng, L.; Wang, X.; Wu, Z.; Wang, Y.; Pan, Y. Electrochemically Promoted Nickel-Catalyzed Carbon−Sulfur Bond Formation. ACS Catal. 2019, 9, 1630–1634; (l) Oechsner, R. M.; Wagner, J. P.; Fleischer, I. Acetate Facilitated Nickel Catalyzed Coupling of Aryl Chlorides and Alkyl Thiols. ACS Catal. 2022, 12, 2233–2243.
- 14(a) Fang, Y.; Rogge, T.; Ackermann, L.; Wang, S.-Y.; Ji, S.-J. Nickel-catalyzed reductive thiolation and selenylation of unactivated alkyl bromides. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 2240; (b) Liu, Y.; Xing, S.; Zhang, J.; Liu, W.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, K.; Yang, L.; Jiang, K.; Shao, X. Construction of diverse C–S/C–Se bonds via nickel catalyzed reductive coupling employing thiosulfonates and a selenosulfonate under mild conditions. Org. Chem. Front. 2022, 9, 1375–1382.
- 15 Bunnett, J. F.; Creary, X. Arylation of arenethiolate ions by the SRN1 mechanism. Convenient synthesis of diaryl sulfides. J. Org. Chem. 1974, 39, 3173–3174.
- 16(a) Diccianni, J. B.; Diao, T. Mechanisms of Nickel-Catalyzed Cross- Coupling Reactions. Trends Chem. 2019, 1, 830–844; (b) Diccianni, J.; Lin, Q.; Diao, T. Mechanisms of Nickel-Catalyzed Coupling Reactions and Applications in Alkene Functionalization. Acc. Chem. Res. 2020, 53, 906–919; (c) Liu, J.; Ye, Y.; Sessler, J. L.; Gong, H. Cross-Electrophile Couplings of Activated and Sterically Hindered Halides and Alcohol Derivatives. Acc. Chem. Res. 2020, 53, 1833–1845; (d) Poremba, K. E.; Dibrell, S. E.; Reisman, S. E. Nickel-Catalyzed Enantioselective Reductive Cross-Coupling Reactions. ACS Catal. 2020, 10, 8237–8246; (e) Zhu, S.; Zhao, X.; Li, H.; Chu, L. Catalytic three-component dicarbofunctionalization reactions involving radical capture by nickel. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2021, 50, 10836–10856; (f) Pang, X.; Su, P.-F.; Shu, X.-Z. Reductive Cross-Coupling of Unreactive Electrophiles. Acc. Chem. Res. 2022, 55, 2491–2509; (g) Yi, L.; Ji, T.; Chen, K.-Q.; Chen, X.-Y.; Rueping, M. Nickel-Catalyzed Reductive Cross-Couplings: New Opportunities for Carbon–Carbon Bond Formations through Photochemistry and Electrochemistry. CCS Chem. 2022, 4, 9–30; (h) Gong, Y.; Hu, J.; Qiu, C.; Gong, H. Insights into Recent Nickel-Catalyzed Reductive and Redox C–C Coupling of Electrophiles, C(sp3)–H Bonds and Alkenes. Acc. Chem. Res. 2024, 57, 1149–1162.
- 17(a) Tu, Y.-L.; Zhang, B.-B.; Qiu, B.-S.; Wang, Z.-X.; Chen, X.-Y. Cross- Electrophile C−PIII Coupling of Chlorophosphines with Organic Halides: Photoinduced PIII and Aminoalkyl Radical Generation Enabled by Pnictogen Bonding. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2023, 62, e202310764; (b) Meng, C.-F.; Zhang, B.-B.; Liu, Q.; Chen, K.-Q.; Wang, Z.-X.; Chen, X.-Y. Achieving Nickel-Catalyzed Reductive C(sp2)–B Coupling of Bromoboranes via Reversing the Activation Sequence. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2024, 146, 7210–7215.
- 18 Juliá, F.; Constantin, T.; Leonori, D. Applications of Halogen-Atom Transfer (XAT) for the Generation of Carbon Radicals in Synthetic Photochemistry and Photocatalysis. Chem. Rev. 2022, 122, 2292–2352.
- 19 Cismesia, M. A.; Yoon, T. P. Characterizing chain processes in visible light photoredox catalysis. Chem. Sci. 2015, 6, 5426–5434.
- 20 Constantin, T.; Zanini, M.; Regni, A.; Sheikh, N. S.; Juliá, F.; Leonori, D. Aminoalkyl radicals as halogen-atom transfer agents for activation of alkyl and aryl halides. Science 2020, 367, 1021–1026.
- 21 Dong, Y.; Ji, P.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, C.; Meng, X.; Wang, W. Organophotoredox-Catalyzed Formation of Alkyl-Aryl and -Akyl C-S/Se Bonds from Coupling of Redox-Active Esters with Thio/Selenosulfonates. Org. Lett. 2020, 22, 9562−9567.