Direct Analysis of Whole Blood by a Disposable Monolithic Column Mass Spectrometry Analysis Kit†
Wenxin Wang
College of Chemistry and Molecular Science, Wuhan University, Wuhan, Hubei, 430072 China
Search for more papers by this authorJin Han
College of Chemistry and Molecular Science, Wuhan University, Wuhan, Hubei, 430072 China
Search for more papers by this authorYutong Zheng
College of Chemistry and Molecular Science, Wuhan University, Wuhan, Hubei, 430072 China
Search for more papers by this authorHaijie Wang
College of Chemistry and Molecular Science, Wuhan University, Wuhan, Hubei, 430072 China
Search for more papers by this authorChengbiao Zhu
College of Chemistry and Molecular Science, Wuhan University, Wuhan, Hubei, 430072 China
Search for more papers by this authorYongyi Li
College of Chemistry and Molecular Science, Wuhan University, Wuhan, Hubei, 430072 China
Search for more papers by this authorYuqi Feng
School of Bioengineering and Health, Wuhan Textile University, Wuhan, Hubei, 430200 China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Zhenwei Wei
College of Chemistry and Molecular Science, Wuhan University, Wuhan, Hubei, 430072 China
E-mail: [email protected]; [email protected]Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Xiangyu Wang
College of Chemistry and Molecular Science, Wuhan University, Wuhan, Hubei, 430072 China
School of Public Health, Wuhan University, Wuhan, Hubei, 430072 China
E-mail: [email protected]; [email protected]Search for more papers by this authorWenxin Wang
College of Chemistry and Molecular Science, Wuhan University, Wuhan, Hubei, 430072 China
Search for more papers by this authorJin Han
College of Chemistry and Molecular Science, Wuhan University, Wuhan, Hubei, 430072 China
Search for more papers by this authorYutong Zheng
College of Chemistry and Molecular Science, Wuhan University, Wuhan, Hubei, 430072 China
Search for more papers by this authorHaijie Wang
College of Chemistry and Molecular Science, Wuhan University, Wuhan, Hubei, 430072 China
Search for more papers by this authorChengbiao Zhu
College of Chemistry and Molecular Science, Wuhan University, Wuhan, Hubei, 430072 China
Search for more papers by this authorYongyi Li
College of Chemistry and Molecular Science, Wuhan University, Wuhan, Hubei, 430072 China
Search for more papers by this authorYuqi Feng
School of Bioengineering and Health, Wuhan Textile University, Wuhan, Hubei, 430200 China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Zhenwei Wei
College of Chemistry and Molecular Science, Wuhan University, Wuhan, Hubei, 430072 China
E-mail: [email protected]; [email protected]Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Xiangyu Wang
College of Chemistry and Molecular Science, Wuhan University, Wuhan, Hubei, 430072 China
School of Public Health, Wuhan University, Wuhan, Hubei, 430072 China
E-mail: [email protected]; [email protected]Search for more papers by this authorDedicated to the 130th Anniversary of Wuhan University.
Comprehensive Summary
A monolithic column-based mass spectrometry (MS) analysis kit was prepared for whole blood analysis with MS. The kit is disposable and can be used for purification, storage, transportation and direct analysis of whole blood. The kit mainly consists of a capillary for quantitative microsampling, a cation exchange monolithic column for purification and storage, and a syringe for loading sample. This kit is very friendly to various users that one can easily siphon the blood in the kit followed by rapid clean-up. We established a quantitative method using the kit with a limit detection as low as 0.33 nmol/L, and achieved more than five orders of magnitude enhancement in sensitivity compared to direct nanoelectrospray ionization MS analysis. The column can avoid analyte exposure to environment, which helps the storage of the sample for laboratory analysis. The relative standard deviation of immediate blood analysis and storage blood analysis within 10 d was less than 10%. This method has been successfully applied to the quantitative analysis of procainamide hydrochloride in 2 μL rat blood. These results indicate that this disposable kit does have the potential to achieve highly sensitive quantitative MS analysis in biological samples, which is expected to become a cost-effective and powerful tool for in vitro diagnostics.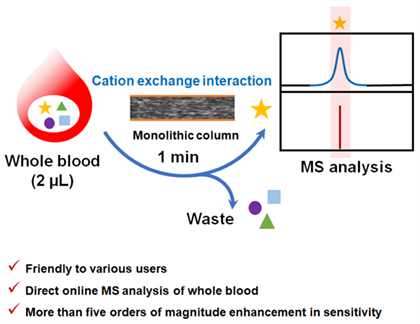
Supporting Information
| Filename | Description |
|---|---|
| cjoc202300646-sup-0001-supinfo.pdfPDF document, 1.2 MB |
Appendix S1: Supporting information |
Please note: The publisher is not responsible for the content or functionality of any supporting information supplied by the authors. Any queries (other than missing content) should be directed to the corresponding author for the article.
References
- 1 Chen, S. Y.; Wu, A. B. Y.; Lunde, R.; Lai, J. M. J. Osmotic Processor for Enabling Sensitive and Rapid Biomarker Detection via Lateral Flow Assays. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2022, 10, 12.
- 2 Herranz-Blanco, B.; Daoud, E.; Viganò, P.; García-Velasco, J. A.; Colli, E. Development and Validation of an Endometriosis Diagnostic Method Based on Serum Biomarkers and Clinical Variables. Biomolecules 2023, 13, 1052.
- 3 Kim, Y.; An, J. M.; Kim, J.; Chowdhury, T.; Yu, H. J.; Kim, K. M.; Kang, H.; Park, C. K.; Joung, J. F.; Park, S.; Kim, D. Pyridine-NBD: A homocysteine-selective fluorescent probe for glioblastoma (GBM) diagnosis based on a blood test. Anal. Chim. Acta 2022, 1202, 10.
- 4 Miller, B. S.; Bezinge, L.; Gliddon, H. D.; Huang, D.; Dold, G.; Gray, E. R.; Heaney, J.; Dobson, P. J.; Nastouli, E.; Morton, J. J. L.; McKendry, R. A. Spin-enhanced nanodiamond biosensing for ultrasensitive diagnostics. Nature 2020, 587, 588—593.
- 5 Seo, S. B.; Hwang, J. S.; Kim, E.; Kim, K.; Roh, S.; Lee, G.; Lim, J.; Kang, B.; Jang, S.; Son, S. U.; Kang, T.; Jung, J.; Kim, J. S.; Keun, H.; Han, T. S.; Lim, E. K. Isothermal amplification-mediated lateral flow biosensors for in vitro diagnosis of gastric cancer-related microRNAs. Talanta 2022, 246, 10.
- 6 Song, H. B.; Zhu, Y. Y. The in vitro diagnostics industry in China. View-China 2020, 1, 4.
- 7 Zhang, B.; Kumar, R. B.; Dai, H. J.; Feldman, B. J. A plasmonic chip for biomarker discovery and diagnosis of type 1 diabetes. Nat. Med. 2014, 20, 948–953.
- 8 Zhu, Z.; Guan, Z. C.; Jia, S. S.; Lei, Z. C.; Lin, S. C.; Zhang, H. M.; Ma, Y. L.; Tian, Z. Q.; Yang, C. J. Au@Pt Nanoparticle Encapsulated Target-Responsive Hydrogel with Volumetric Bar-Chart Chip Readout for Quantitative Point-of-Care Testing. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2014, 53, 12503–12507.
- 9 Baygildiev, T. M.; Vokuev, M. F.; Braun, A. V.; Yashkir, V. A.; Rybalchenko, I. V.; Rodin, I. A. Identification of 2-(diethylamino)ethylthiol dipeptide (Cys-Pro) adduct as biomarker of nerve agents VR and CVX in human plasma using liquid chromatography-high-resolution tandem mass spectrometry. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2021, 413, 1905–1916.
- 10 Carvalho, V. M. The coming of age of liquid chromatography coupled to tandem mass spectrometry in the endocrinology laboratory. J. Chromatogr. B 2012, 883, 50–58.
- 11 Kubinec, R.; Kotora, P.; Ferenczy, V.; Blasko, J.; Podolec, P.; Szabó, A. H.; Behulová, D.; Bierhanzl, V.; Cabala, R.; Stuchlík, S.; Filipiak, W.; Thang, N. M. Simultaneous analysis of carbohydrates, polyols and amines in urine samples using chemical ionization gas chromatography with tandem mass spectrometry. J. Sep. Sci. 2018, 41, 449–458.
- 12 Yoshioka, K.; Hirakawa, Y.; Kurano, M.; Ube, Y.; Ono, Y.; Kojima, K.; Iwama, T.; Kano, K.; Hasegawa, S.; Inoue, T.; Shimada, T.; Aoki, J.; Yatomi, Y.; Nangaku, M.; Inagi, R. Lysophosphatidylcholine mediates fast decline in kidney function in diabetic kidney disease commentary. Kidney Int. 2022, 101, 510–526.
- 13 Scherl, A. Clinical protein mass spectrometry. Methods 2015, 81, 3–14.
- 14 Fang, J.; Wu, Q.; Zhao, Y.; Zhao, H. Z.; Xu, S. Q.; Cai, Z. W. Comparison of different mass spectrometric approaches coupled to gas chromatography for the analysis of organochlorine pesticides in serum samples. J. Chromatogr. B 2017, 1040, 180–185.
- 15 Sasamoto, K.; Ochiai, N.; Kanda, H. Dual low thermal mass gas chromatography-mass spectrometry for fast dual-column separation of pesticides in complex sample. Talanta 2007, 72, 1637–1643.
- 16 Wasinski, F. A. H.; Andersson, J. T. Qualitative analysis of phenols and alcohols in complex samples after derivatization to esters of ferrocene carboxylic acid by gas chromatography with mass spectrometric detection. J. Chromatogr. A 2007, 1157, 376–385.
- 17 Badea, S. L.; Geana, E. I.; Niculescu, V. C.; Ionete, R. E. Recent progresses in analytical GC and LC mass spectrometric based-methods for the detection of emerging chlorinated and brominated contaminants and their transformation products in aquatic environment. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 722, 13.
- 18 Jin, D. Q.; Shi, S. W.; Ma, Y.; Fang, Q. LC-Swan Probe: An Integrated In Situ Sampling Interface for Liquid Chromatography Separation and Mass Spectrometry Analysis. Anal. Chem. 2020, 92, 9214–9222.
- 19 Kulyk, D. S.; Sahraeian, T.; Lee, S.; Badu-Tawiah, A. K. Microsampling with a Solid-Phase Extraction Cartridge: Storage and Online Mass Spectrometry Analysis. Anal. Chem. 2021, 93, 13632–13640.
- 20 Ding, M. Y.; Wang, Z. H.; Zheng, R. Rapid Separation of Proteins by Capillary HPLC on a Short Polymethacrylate-based Strong Cation- exchange Monolithic Column. Chin. J. Chem. 2010, 28, 567–572.
- 21 Wang, X. Y.; Bai, P. R.; Li, Z. Y.; Zhu, Q. F.; Wei, Z. W.; Feng, Y. Q. Rapid and Economical Chemoselective Metabolomics Using Boronate Ester Formation on a Monolithic Substrate. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2022, 61, 5.
- 22 Wang, X. Y.; Xiong, C. F.; Ye, T. T.; Ding, J.; Feng, Y. Q. Online polymer monolith microextraction with in-situ derivatization for sensitive detection of endogenous brassinosteroids by LC-MS. Microchem. J. 2020, 158, 8.
- 23 Yang, J.; Yang, G. L.; Liu, H. Y.; Bai, L. G.; Zhang, Q. X. Novel Porous Monolithic Column Using Poly(high internal phase emulsion) Methacrylate as Materials for Immunoglobulin Separation Performance on HPLC. Chin. J. Chem. 2010, 28, 229–234.
- 24 Zhu, T.; Row, K. H. Simultaneous Determination of Caffeine and Theophylline in Human Plasma with a Weak Cation Monolithic SPE-column. Chin. J. Chem. 2010, 28, 1463–1468.
- 25 Wang, X. Y.; Wu, H. H.; Luo, R. Y.; Xia, D. H.; Jiang, Z. J.; Han, H. Separation and detection of free D- and L-amino acids in tea by off-line two-dimensional liquid chromatography. Anal. Methods 2017, 9, 6131–6138.
- 26 Wang, X. Y.; Xia, D. H.; Han, H.; Peng, K.; Zhu, P. J.; Crommen, J.; Wang, Q. Q.; Jiang, Z. J. Biomimetic small peptide functionalized affinity monoliths for monoclonal antibody purification. Anal. Chim. Acta 2018, 1017, 57–65.
- 27 Yang, G. L.; Bai, L. G.; Liu, H. Y.; Zhao, Y.; Li, F. X.; Cao, W. M. Novel Strong Cation-exchange Monolithic Column Using Poly(vinyl ester resin) as Stationary Phase Materials for Lysozyme Separation by HPLC. Chin. J. Chem. 2008, 26, 2063–2066.
- 28 Chiu, F. C. K.; Zhang, J. N.; Li, R. C.; Raymond, K. Efficient assay for the determination of atenolol in human plasma and urine by high-performance liquid chromatography with fluorescence detection. J. Chromatogr. B 1997, 691, 473–477.
- 29 Zaugg, S.; Thormann, W. Capillary electrophoretic separation, immunochemical recognition and analysis of the diastereomers quinine and quinidine and two quinidine metabolites in body fluids. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2001, 24, 785–799.
- 30 Fan, Y.; Feng, Y. Q.; Da, S. L.; Shi, Z. G. Poly (methacrylic acid-ethylene glycol dimethacrylate) monolithic capillary for in-tube solid phase microextraction coupled to high performance liquid chromatography and its application to determination of basic drugs in human serum. Anal. Chim. Acta 2004, 523, 251–258.




