Kinetic Resolution of 1,2-Diamines via Organocatalyzed Asymmetric Electrophilic Aminations of Anilines
Correction(s) for this article
-
Kinetic Resolution of 1,2-Diamines via Organocatalyzed Asymmetric Electrophilic Aminations of Anilines
- Volume 40Issue 24Chinese Journal of Chemistry
- pages: 3025-3025
- First Published online: November 15, 2022
Jinglei Xie
School of Physical Science and Technology, ShanghaiTech University, Shanghai, 201210 China
Key Laboratory of Petrochemical Catalytic Science and Technology, Liaoning Shihua University, Fushun, Liaoning, 113001 China
‡ These authors contributed equally.
Search for more papers by this authorZheng Guo
School of Physical Science and Technology, ShanghaiTech University, Shanghai, 201210 China
University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, 100049 China
‡ These authors contributed equally.
Search for more papers by this authorWei Liu
School of Physical Science and Technology, ShanghaiTech University, Shanghai, 201210 China
Search for more papers by this authorDekun Zhang
School of Physical Science and Technology, ShanghaiTech University, Shanghai, 201210 China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Yu-Peng He
Key Laboratory of Petrochemical Catalytic Science and Technology, Liaoning Shihua University, Fushun, Liaoning, 113001 China
State Key Laboratory of Fine Chemicals, Ningbo Institute of Dalian University of Technology, Ningbo, Zhejiang, 315016 China
E-mail: [email protected]; [email protected]Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Xiaoyu Yang
School of Physical Science and Technology, ShanghaiTech University, Shanghai, 201210 China
E-mail: [email protected]; [email protected]Search for more papers by this authorJinglei Xie
School of Physical Science and Technology, ShanghaiTech University, Shanghai, 201210 China
Key Laboratory of Petrochemical Catalytic Science and Technology, Liaoning Shihua University, Fushun, Liaoning, 113001 China
‡ These authors contributed equally.
Search for more papers by this authorZheng Guo
School of Physical Science and Technology, ShanghaiTech University, Shanghai, 201210 China
University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, 100049 China
‡ These authors contributed equally.
Search for more papers by this authorWei Liu
School of Physical Science and Technology, ShanghaiTech University, Shanghai, 201210 China
Search for more papers by this authorDekun Zhang
School of Physical Science and Technology, ShanghaiTech University, Shanghai, 201210 China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Yu-Peng He
Key Laboratory of Petrochemical Catalytic Science and Technology, Liaoning Shihua University, Fushun, Liaoning, 113001 China
State Key Laboratory of Fine Chemicals, Ningbo Institute of Dalian University of Technology, Ningbo, Zhejiang, 315016 China
E-mail: [email protected]; [email protected]Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Xiaoyu Yang
School of Physical Science and Technology, ShanghaiTech University, Shanghai, 201210 China
E-mail: [email protected]; [email protected]Search for more papers by this authorComprehensive Summary
An efficient kinetic resolution (KR) protocol for 1,2-diamines has been developed through asymmetric electrophilic aminations of anilines enabled by chiral phosphoric acid catalysis. A wide array of substituted 1,2-diamines were compatible with this method, generating both the recovered staring materials and the amination products with high enantioselectivities (with s-factor up to 218). Notably, this method is amenable to the kinetic resolution of 1,2-diamines bearing α-tertiary amine moieties, which represents the first KR of this type of 1,2-diamines. Facile removal of the introduced hydrazine group and oxidative cleavage of the N-aryl group to release the free primary amine demonstrate the value of this method.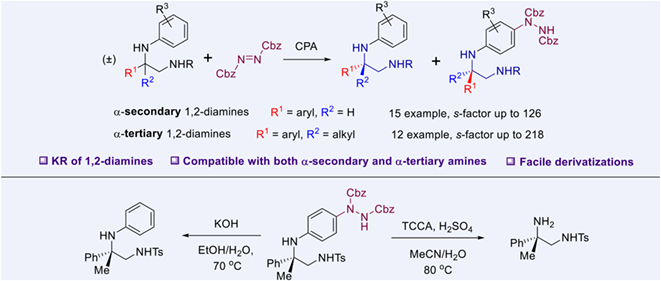
Supporting Information
| Filename | Description |
|---|---|
| cjoc202200125-sup-0001-Supinfo.pdfPDF document, 17.5 MB |
Appendix S1 Supporting Information |
Please note: The publisher is not responsible for the content or functionality of any supporting information supplied by the authors. Any queries (other than missing content) should be directed to the corresponding author for the article.
References
- 1(a) Lucet, D.; Le Gall, T.; Mioskowski, C. The Chemistry of Vicinal Diamines. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 1998, 37, 2580–2627;
10.1002/(SICI)1521-3773(19981016)37:19<2580::AID-ANIE2580>3.0.CO;2-L CAS PubMed Web of Science® Google Scholar(b) Saibabu Kotti, S. R. S.; Timmons, C.; Li, G. Vicinal Diamino Functionalities as Privileged Structural Elements in Biologically Active Compounds and Exploitation of their Synthetic Chemistry. Chem. Biol. Drug. Des. 2006, 67, 101–114.
- 2 Kizirian, J.-C. Chiral Tertiary Diamines in Asymmetric Synthesis. Chem. Rev. 2008, 108, 140–205.
- 3(a) Du, H.; Yuan, W.; Zhao, B.; Shi, Y. Catalytic Asymmetric Diamination of Conjugated Dienes and Triene. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2007, 129, 11688–11689; (b) Ingalls, E. L.; Sibbald, P. A.; Kaminsky, W.; Michael, F. E. Enantioselective Palladium-Catalyzed Diamination of Alkenes Using N-Fluorobenzenesulfonimide. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 8854–8856; (c) Muñiz, K.; Barreiro, L.; Romero, R. M.; Martínez, C. Catalytic Asymmetric Diamination of Styrenes. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2017, 139, 4354–4357; (d) Vanable, E. P.; Kennemur, J. L.; Joyce, L. A.; Ruck, R. T.; Schultz, D. M.; Hull, K. L. Rhodium-Catalyzed Asymmetric Hydroamination of Allyl Amines. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2019, 141, 739–742.
- 4(a) Hernández-Toribio, J.; Arrayás, R. G.; Carretero, J. C. Direct Mannich Reaction of Glycinate Schiff Bases with N-(8-Quinolyl)sulfonyl Imines: A Catalytic Asymmetric Approach to anti-α,β-Diamino Esters. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2008, 130, 16150–16151; (b) Uraguchi, D.; Ueki, Y.; Ooi, T. Chiral Tetraaminophosphonium Carboxylate-Catalyzed Direct Mannich-Type Reaction. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2008, 130, 14088–14089; (c) Zhang, W.-Q.; Cheng, L.-F.; Yu, J.; Gong, L.-Z. A Chiral Bis(betaine) Catalyst for the Mannich Reaction of Azlactones and Aliphatic Imines. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2012, 51, 4085–4088; (d) Kano, T.; Kobayashi, R.; Maruoka, K. Versatile In Situ Generated N-Boc-Imines: Application to Phase-Transfer-Catalyzed Asymmetric Mannich-Type Reactions. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2015, 54, 8471–8474; (e) Lin, S.; Kawato, Y.; Kumagai, N.; Shibasaki, M. Catalytic Asymmetric Mannich-Type Reaction of N-Alkylidene-α-Aminoacetonitrile with Ketimines. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2015, 54, 5183–5186; (f) Ye, X.; Pan, Y.; Yang, X. Direct enantioselective Mannich reactions of α-azido cyclic ketones: asymmetric construction of chiral azides possessing an α-quaternary stereocenter. Chem. Commun. 2020, 56, 98–101.
- 5(a) Yamada, K.-i.; Harwood, S. J.; Gröger, H.; Shibasaki, M. The First Catalytic Asymmetric Nitro-Mannich-Type Reaction Promoted by a New Heterobimetallic Complex. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 1999, 38, 3504–3506;
10.1002/(SICI)1521-3773(19991203)38:23<3504::AID-ANIE3504>3.0.CO;2-E PubMed Web of Science® Google Scholar(b) Nishiwaki, N.; Rahbek Knudsen, K.; Gothelf, K. V.; Jørgensen, K. A. Catalytic Enantioselective Addition of Nitro Compounds to Imines—A Simple Approach for the Synthesis of Optically Active β-Nitro-α-Amino Esters. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2001, 40, 2992–2995;10.1002/1521-3773(20010817)40:16<2992::AID-ANIE2992>3.0.CO;2-3 CAS PubMed Web of Science® Google Scholar(c) Nugent, B. M.; Yoder, R. A.; Johnston, J. N. Chiral Proton Catalysis: A Catalytic Enantioselective Direct Aza-Henry Reaction. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2004, 126, 3418–3419; (d) Palomo, C.; Oiarbide, M.; Laso, A.; López, R. Catalytic Enantioselective Aza-Henry Reaction with Broad Substrate Scope. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2005, 127, 17622–17623.
- 6(a) Uraguchi, D.; Kinoshita, N.; Kizu, T.; Ooi, T. Synergistic Catalysis of Ionic Brønsted Acid and Photosensitizer for a Redox Neutral Asymmetric α-Coupling of N-Arylaminomethanes with Aldimines. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2015, 137, 13768–13771; (b) Ma, W.; Zhang, J.; Xu, C.; Chen, F.; He, Y.-M.; Fan, Q.-H. Highly Enantioselective Direct Synthesis of Endocyclic Vicinal Diamines through Chiral Ru(diamine)-Catalyzed Hydrogenation of 2,2’-Bisquinoline Derivatives. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2016, 55, 12891–12894; (c) Chai, Z.; Yang, P.-J.; Zhang, H.; Wang, S.; Yang, G. Synthesis of Chiral Vicinal Diamines by Silver(I)- Catalyzed Enantioselective Aminolysis of N-Tosylaziridines. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2017, 56, 650–654; (d) Wang, Y.; Wang, Q.; Zhu, J. Organocatalytic Nucleophilic Addition of Hydrazones to Imines: Synthesis of Enantioenriched Vicinal Diamines. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2017, 56, 5612–5615; (e) Shao, X.; Li, K.; Malcolmson, S. J. Enantioselective Synthesis of anti-1,2-Diamines by Cu-Catalyzed Reductive Couplings of Azadienes with Aldimines and Ketimines. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2018, 140, 7083–7087.
- 7(a) Vedejs, E.; Jure, M. Efficiency in Nonenzymatic Kinetic Resolution. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2005, 44, 3974–4001; (b) Müller, C. E.; Schreiner, P. R. Organocatalytic Enantioselective Acyl Transfer onto Racemic as well as meso Alcohols, Amines, and Thiols. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2011, 50, 6012–6042; (c) Pellissier, H. Catalytic Non-Enzymatic Kinetic Resolution. Adv. Synth. Catal. 2011, 353, 1613–1666; (d) Petersen, K. S. Chiral Brønsted Acid Catalyzed Kinetic Resolutions. Asian J. Org. Chem. 2016, 5, 308–320; (e) Liu, W.; Yang, X. Recent Advances in (Dynamic) Kinetic Resolution and Desymmetrization Catalyzed by Chiral Phosphoric Acids. Asian J. Org. Chem. 2021, 10, 692–710; (f) Ding, B.; Xue, Q.; Jia, S.; Cheng, H.-G.; Zhou, Q. Recent Advances in Catalytic Nonenzymatic Kinetic Resolution of Tertiary Alcohols. Synthesis 2022, 54, 1721–1732; (g) Chen, Y.; Liu W.; Yang, X. Recent Advances in Kinetic Resolution of Tertiary Alcohols. Chin. J. Org. Chem. 2022, 42, 679–697.
- 8(a) Krasnov, V. P.; Gruzdev, D. A.; Levit, G. L. Nonenzymatic Acylative Kinetic Resolution of Racemic Amines and Related Compounds. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2012, 2012, 1471–1493;
(b) Kreituss, I.; Bode, J. W. Catalytic Kinetic Resolution of Saturated N-Heterocycles by Enantioselective Amidation with Chiral Hydroxamic Acids. Acc. Chem. Res. 2016, 49, 2807–2821;
(c) Liu, W.; Wang, D.; Zhang, D.; Yang, X. Catalytic Kinetic Resolution and Desymmetrization of Amines. Synlett 2022, DOI:https://doi.org/10.1055/a-1790-3230.
10.1055/a-1790-3230 Google Scholar
- 9(a) Arai, S.; Bellemin-Laponnaz, S.; Fu, G. C. Kinetic Resolution of Amines by a Nonenzymatic Acylation Catalyst. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2001, 40, 234–236;
10.1002/1521-3773(20010105)40:1<234::AID-ANIE234>3.0.CO;2-K CAS PubMed Web of Science® Google Scholar(b) Arp, F. O.; Fu, G. C. Kinetic Resolutions of Indolines by a Nonenzymatic Acylation Catalyst. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2006, 128, 14264–14265.
- 10(a) Birman, V. B.; Jiang, H.; Li, X.; Guo, L.; Uffman, E. W. Kinetic Resolution of 2-Oxazolidinones via Catalytic, Enantioselective N-Acylation. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2006, 128, 6536–6537; (b) De, C. K.; Klauber, E. G.; Seidel, D. Merging Nucleophilic and Hydrogen Bonding Catalysis: An Anion Binding Approach to the Kinetic Resolution of Amines. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 17060–17061; (c) Fowler, B. S.; Mikochik, P. J.; Miller, S. J. Peptide-Catalyzed Kinetic Resolution of Formamides and Thioformamides as an Entry to Nonracemic Amines. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 132, 2870–2871; (d) Klauber, E. G.; De, C. K.; Shah, T. K.; Seidel, D. Merging Nucleophilic and Hydrogen Bonding Catalysis: An Anion Binding Approach to the Kinetic Resolution of Propargylic Amines. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 132, 13624–13626; (e) Binanzer, M.; Hsieh, S.-Y.; Bode, J. W. Catalytic Kinetic Resolution of Cyclic Secondary Amines. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2011, 133, 19698–19701; (f) Murray, J. I.; Flodén, N. J.; Bauer, A.; Fessner, N. D.; Dunklemann, D. L.; Bob-Egbe, O.; Rzepa, H. S.; Bürgi, T.; Richardson, J.; Spivey, A. C. Kinetic Resolution of 2-Substituted Indolines by N-Sulfonylation using an Atropisomeric 4-DMAP-N-oxide Organocatalyst. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2017, 56, 5760–5764.
- 11(a) Wang, Z.-C.; Xie, P.-P.; Xu, Y.; Hong, X.; Shi, S.-L. Low-Temperature Ni-Catalyzed C−N Cross-Coupling via Kinetic Resolution Enabled by a Bulky yet Flexible, Chiral N-Heterocyclic Carbene. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2021, 60, 16077–16084; (b) Saito, K.; Shibata, Y.; Yamanaka, M.; Akiyama, T. Chiral Phosphoric Acid-Catalyzed Oxidative Kinetic Resolution of Indolines Based on Transfer Hydrogenation to Imines. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 11740–11743; (c) Saito, K.; Akiyama, T. Chiral Phosphoric Acid Catalyzed Kinetic Resolution of Indolines Based on a Self-Redox Reaction. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2016, 55, 3148–3152; (d) Xiao, K.-J.; Chu, L.; Chen, G.; Yu, J.-Q. Kinetic Resolution of Benzylamines via Palladium(II)-Catalyzed C–H Cross-Coupling. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2016, 138, 7796–7800; (e) Das, S.; Majumdar, N.; De, C. K.; Kundu, D. S.; Döhring, A.; Garczynski, A.; List, B. Asymmetric Catalysis of the Carbonyl-Amine Condensation: Kinetic Resolution of Primary Amines. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2017, 139, 1357–1359; (f) Lu, R.; Cao, L.; Guan, H.; Liu, L. Iron-Catalyzed Aerobic Dehydrogenative Kinetic Resolution of Cyclic Secondary Amines. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2019, 141, 6318–6324; (g) González, J. M.; Cendón, B.; Mascareñas, J. L.; Gulías, M. Kinetic Resolution of Allyltriflamides through a Pd-Catalyzed C–H Functionalization with Allenes: Asymmetric Assembly of Tetrahydropyridines. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2021, 143, 3747–3752; (h) Wang, G.; Lu, R.; He, C.; Liu, L. Kinetic resolution of indolines by asymmetric hydroxylamine formation. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 2512; (i) Chu, L.; Xiao, K.-J.; Yu, J.-Q. Room-temperature enantioselective C-H iodination via kinetic resolution. Science 2014, 346, 451–455; (j) Cai, B.; Yang, Q.; Meng, L.; Wang, J. J. Kinetic Resolution of 2-Substituted 1,2-Dihydroquinolines by Rhodium-Catalyzed Asymmetric Hydroarylation. Chin. J. Chem. 2021, 39, 1606–1610.
- 12 Yang, W.; Long, Y.; Zhang, S.; Zeng, Y.; Cai, Q. Copper-Catalyzed Enantioselective Intramolecular N-Arylation, an Efficient Method for Kinetic Resolutions. Org. Lett. 2013, 15, 3598–3601; (b) Jiang, Q.; Qin, T.; Yang, X. Asymmetric Synthesis of Hydroquinazolines Bearing C4-Tetrasubstituted Stereocenters via Kinetic Resolution of α-Tertiary Amines. Org. Lett. 2022, 24, 625–630..
- 13(a) Kitagawa, O.; Yotsumoto, K.; Kohriyama, M.; Dobashi, Y.; Taguchi, T. Catalytic Asymmetric Synthesis of Vicinal Diamine Derivatives through Enantioselective N-Allylation Using Chiral π-Allyl Pd-Catalyst. Org. Lett. 2004, 6, 3605–3607; (b) Kitagawa, O.; Matsuo, S.; Yotsumoto, K.; Taguchi, T. Catalytic Asymmetric Desymmetrization of meso-Diamide Derivatives through Enantioselective N-Allylation with a Chiral π-Allyl Pd Catalyst: Improvement and Reversal of the Enantioselectivity. J. Org. Chem. 2006, 71, 2524–2527.
- 14 De, C. K.; Seidel, D. Catalytic Enantioselective Desymmetrization of meso-Diamines: A Dual Small-Molecule Catalysis Approach. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2011, 133, 14538–14541.
- 15 Min, C.; Mittal, N.; De, C. K.; Seidel, D. A dual-catalysis approach to the kinetic resolution of 1,2-diaryl-1,2-diaminoethanes. Chem. Commun. 2012, 48, 10853–10855.
- 16(a) Liu, W.; Jiang, Q.; Yang, X. A Versatile Method for Kinetic Resolution of Protecting-Group-Free BINAMs and NOBINs through Chiral Phosphoric Acid Catalyzed Triazane Formation. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2020, 59, 23598–23602; (b) Chen, Y.; Zhu, C.; Guo, Z.; Liu, W.; Yang, X. Asymmetric Synthesis of Hydroquinolines with α,α-Disubstitution through Organocatalyzed Kinetic Resolution. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2021, 60, 5268–5272; (c) Zhang, D.; Chen, Y.; Lai, Y.; Yang, X. Enantioselective desymmetrization of 2-substituted and 2,2-disubstituted 1,3-propanediamines via asymmetric para-aminations of anilines. Cell Rep. Phy. Sci. 2021, 2, 100413; (d) Pan, Y.; Wang, D.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, D.; Liu, W.; Yang, X. Kinetic Resolution of α-Tertiary Propargylic Amines through Asymmetric Remote Aminations of Anilines. ACS Catal. 2021, 8443–8448; (e) Guo, Z.; Xie, J.; Hu, T.; Chen, Y.; Tao, H.; Yang, X. Kinetic resolution of N-aryl β-amino alcohols via asymmetric aminations of anilines. Chem. Commun. 2021, 57, 9394–9397; (f) Wang, D.; Shao, Y.-B.; Chen, Y.; Xue, X.-S.; Yang, X. Enantioselective Synthesis of Planar-Chiral Macrocycles through Asymmetric Electrophilic Aromatic Amination. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2022, e202201064; (g) He, F.; Shen, G.; Yang, X. Asymmetric Aminations and Kinetic Resolution of Acyclic α-Branched Ynones. Chin. J. Chem. 2022, 40, 15–20.
- 17(a) Akiyama, T.; Itoh, J.; Yokota, K.; Fuchibe, K. Enantioselective Mannich-Type Reaction Catalyzed by a Chiral Brønsted Acid. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2004, 43, 1566–1568; (b) Uraguchi, D.; Terada, M. Chiral Brønsted Acid-Catalyzed Direct Mannich Reactions via Electrophilic Activation. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2004, 126, 5356–5357; (c) Akiyama, T. Stronger Brønsted Acids. Chem. Rev. 2007, 107, 5744–5758; (d) Terada, M. Chiral Phosphoric Acids as Versatile Catalysts for Enantioselective Carbon-Carbon Bond Forming Reactions. Synthesis 2010, 2010, 1929–1982; (e) Parmar, D.; Sugiono, E.; Raja, S.; Rueping, M. Complete Field Guide to Asymmetric BINOL-Phosphate Derived Brønsted Acid and Metal Catalysis: History and Classification by Mode of Activation; Brønsted Acidity, Hydrogen Bonding, Ion Pairing, and Metal Phosphates. Chem. Rev. 2014, 114, 9047–9153; (f) Rahman, A.; Lin, X., Development and application of chiral spirocyclic phosphoric acids in asymmetric catalysis. Org. Biomol. Chem.2018, 16, 4753-4777; (g) Li, X.; Song, Q. Recent advances in asymmetric reactions catalyzed by chiral phosphoric acids. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2018, 29, 1181–1192; (h) Lin, X.; Wang, L.; Han, Z.; Chen, Z. Chiral Spirocyclic Phosphoric Acids and Their Growing Applications. Chin. J. Chem. 2021, 39, 802–824.
- 18 Kagna, H. B.; Fiaud, J. C. Topics in Stereochemistry. In Kinetic Resolution, Eds.: Eliel, E. L.; Wilen, S. H., Wiley, New York, 1988, Vol. 18, pp. 249–330.
- 19See Supporting Information for details.
- 20 Cao, K.; Tan, S. M.; Lee, R.; Yang, S.; Jia, H.; Zhao, X.; Qiao, B.; Jiang, Z. Catalytic Enantioselective Addition of Prochiral Radicals to Vinylpyridines. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2019, 141, 5437–5443.




