Chemistry, Biosynthesis, and Biological Activity of Halogenated Compounds Produced by Marine Microorganisms
Jiamin Wang
CAS Key Laboratory of Tropical Marine Bio-resources and Ecology/Guangdong Key Laboratory of Marine Materia Medica, South China Sea Institute of Oceanology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Guangzhou, Guangdong, 510301 China
University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, 19 Yuquan Road, Beijing, 100049 China
Search for more papers by this authorXiaoyan Pang
CAS Key Laboratory of Tropical Marine Bio-resources and Ecology/Guangdong Key Laboratory of Marine Materia Medica, South China Sea Institute of Oceanology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Guangzhou, Guangdong, 510301 China
Search for more papers by this authorChunmei Chen
CAS Key Laboratory of Tropical Marine Bio-resources and Ecology/Guangdong Key Laboratory of Marine Materia Medica, South China Sea Institute of Oceanology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Guangzhou, Guangdong, 510301 China
University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, 19 Yuquan Road, Beijing, 100049 China
Search for more papers by this authorChenghai Gao
Institute of Marine Drugs, Guangxi University of Chinese Medicine, Nanning, Guangxi, 530200 China
Search for more papers by this authorXuefeng Zhou
CAS Key Laboratory of Tropical Marine Bio-resources and Ecology/Guangdong Key Laboratory of Marine Materia Medica, South China Sea Institute of Oceanology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Guangzhou, Guangdong, 510301 China
Southern Marine Science and Engineering Guangdong Laboratory (Guangzhou), Guangzhou, Guangdong, 511458 China
University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, 19 Yuquan Road, Beijing, 100049 China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Yonghong Liu
CAS Key Laboratory of Tropical Marine Bio-resources and Ecology/Guangdong Key Laboratory of Marine Materia Medica, South China Sea Institute of Oceanology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Guangzhou, Guangdong, 510301 China
Institute of Marine Drugs, Guangxi University of Chinese Medicine, Nanning, Guangxi, 530200 China
Southern Marine Science and Engineering Guangdong Laboratory (Guangzhou), Guangzhou, Guangdong, 511458 China
University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, 19 Yuquan Road, Beijing, 100049 China
E-mail: [email protected], [email protected]Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Xiaowei Luo
Institute of Marine Drugs, Guangxi University of Chinese Medicine, Nanning, Guangxi, 530200 China
E-mail: [email protected], [email protected]Search for more papers by this authorJiamin Wang
CAS Key Laboratory of Tropical Marine Bio-resources and Ecology/Guangdong Key Laboratory of Marine Materia Medica, South China Sea Institute of Oceanology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Guangzhou, Guangdong, 510301 China
University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, 19 Yuquan Road, Beijing, 100049 China
Search for more papers by this authorXiaoyan Pang
CAS Key Laboratory of Tropical Marine Bio-resources and Ecology/Guangdong Key Laboratory of Marine Materia Medica, South China Sea Institute of Oceanology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Guangzhou, Guangdong, 510301 China
Search for more papers by this authorChunmei Chen
CAS Key Laboratory of Tropical Marine Bio-resources and Ecology/Guangdong Key Laboratory of Marine Materia Medica, South China Sea Institute of Oceanology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Guangzhou, Guangdong, 510301 China
University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, 19 Yuquan Road, Beijing, 100049 China
Search for more papers by this authorChenghai Gao
Institute of Marine Drugs, Guangxi University of Chinese Medicine, Nanning, Guangxi, 530200 China
Search for more papers by this authorXuefeng Zhou
CAS Key Laboratory of Tropical Marine Bio-resources and Ecology/Guangdong Key Laboratory of Marine Materia Medica, South China Sea Institute of Oceanology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Guangzhou, Guangdong, 510301 China
Southern Marine Science and Engineering Guangdong Laboratory (Guangzhou), Guangzhou, Guangdong, 511458 China
University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, 19 Yuquan Road, Beijing, 100049 China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Yonghong Liu
CAS Key Laboratory of Tropical Marine Bio-resources and Ecology/Guangdong Key Laboratory of Marine Materia Medica, South China Sea Institute of Oceanology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Guangzhou, Guangdong, 510301 China
Institute of Marine Drugs, Guangxi University of Chinese Medicine, Nanning, Guangxi, 530200 China
Southern Marine Science and Engineering Guangdong Laboratory (Guangzhou), Guangzhou, Guangdong, 511458 China
University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, 19 Yuquan Road, Beijing, 100049 China
E-mail: [email protected], [email protected]Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Xiaowei Luo
Institute of Marine Drugs, Guangxi University of Chinese Medicine, Nanning, Guangxi, 530200 China
E-mail: [email protected], [email protected]Search for more papers by this authorComprehensive Summary
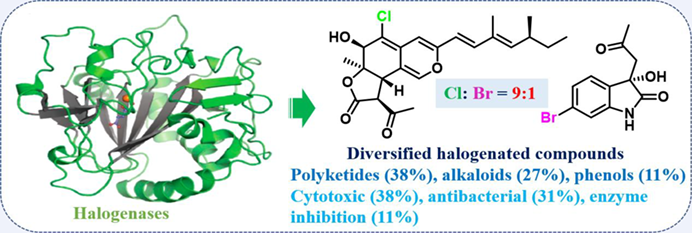
Natural products derived from marine microorganisms have been received great attention as a potential source of new compound entities for drug discovery. The unique marine environment brings us a large group of halogen-containing natural products with abundant biological functionality and good drugability. Meanwhile, biosynthetically halogenated reactions are known as a significant strategy used to increase the pharmacological activities and pharmacokinetic properties of compounds. Given that a tremendous increase in the number of new halogenated compounds from marine microorganisms in the last five years, it is necessary to summarize these compounds with their diverse structures and promising bioactivities. In this review, we have summarized the chemistry, biosynthesis (related halogenases), and biological activity of a total of 316 naturally halogenated compounds from marine microorganisms covering the period of 2015 to May 2021. Those reviewed chlorinated and brominated compounds with the ratio of 9 : 1 were predominantly originated from 36 genera of fungi (62%) and 9 bacterial strains (38%) with cytotoxic, antibacterial, and enzyme inhibitory activities, structural types of which are polyketides (38%), alkaloids (27%), phenols (11%), and others. This review would provide a plenty variety of promising lead halogenated compounds for drug discovery and inspire the development of new pharmaceutical agents.
References
- 1 Gribble, G. W. Naturally Occurring Organohalogen Compounds--A Comprehensive Survey. Fortschr. Chem. Org. Naturst. 1996, 68, 1–423.
- 2 Gribble, G. W. A Recent Survey of Naturally Occurring Organohalogen Compounds. Environ. Chem. 2015, 12, 396–405.
- 3 Gribble, G. W. Biological Activity of Recently Discovered Halogenated Marine Natural Products. Mar. Drugs 2015, 13, 4044–4136.
- 4 Duggar, B. M. Aureomycin: A Product of the Continuing Search for New Antibiotics. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2011, 1241, 163–169.
- 5 Dinos, G. P.; Athanassopoulos, C. M.; Missiri, D. A.; Giannopoulou, P. C.; Vlachogiannis, I. A.; Papadopoulos, G. E.; Papaioannou, D.; Kalpaxis, D. L. Chloramphenicol Derivatives as Antibacterial and Anticancer Agents: Historic Problems and Current Solutions. Antibiotics-Basel. 2016, 5, 20.
- 6 Kaplan, S. A.; Jack, M. L.; Weinfeld, R. E.; Glover, W.; Weissman, L.; Cotler, S. Biopharmaceutical and Clinical Pharmacokinetic Profile of Bromazepam. J. Pharmacokinet. Biopharm. 1976, 4, 1–16.
- 7 Bianco, A. C.; Salvatore, D.; Gereben, B.; Berry, M. J.; Larsen, P. R. Biochemistry, Cellular and Molecular Biology, and Physiological Roles of the Iodothyronine Selenodeiodinases. Endocr. Rev. 2002, 23, 38–89.
- 8 Harris, C. M.; Kannan, R.; Kopecka, H.; Harris, T. M. The Role of the Chlorine Substituents in the Antibiotic Vancomycin - Preparation and Characterization of Monodechlorovancomycin and Didechlorovancomycin. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1985, 107, 6652–6658.
- 9 Bunders, C. A.; Minvielle, M. J.; Worthington, R. J.; Ortiz, M.; Cavanagh, J.; Melander, C. Intercepting Bacterial Indole Signaling with Flustramine Derivatives. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2011, 133, 20160–20163.
- 10Smith, B. M.; Smith, J. M.; Tsai, J. H.; Schultz, J. A.; Gilson, C. A.; Estrada, S. A.; Chen, R. R.; Park, D. M.; Prieto, E. B.; Gallardo, C. S.; Sengupta, D.; Dosa, P.; Covel, A.; Ren, A.; Webb, R. R.; Beeley, N. R. A.; Martin, M.; Morgan, M.; Espitia, S.; SaIdana, H. R.; Bjenning, C.; Whelan, K. T.; Grottick, A. J.; Menzaghi, F.; Thomsen, W. J. Discovery and Structure-Activity Relationship of (1R)-8-Chloro-2,3,4,5-Tetrahydro-1-Methyl-1H-3-Benzazepine (Lorcaserin), A Selective Serotonin 5-HT2C Receptor Agonist for the Treatment of Obesity. J. Med. Chem. 2008, 51, 305–313.
- 11 Carroll, A. R.; Copp, B. R.; Davis, R. A.; Keyzers, R. A.; Prinsep, M. R. Marine Natural Products. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2021, 38, 362–413.
- 12 Carroll, A. R.; Copp, B. R.; Davis, R. A.; Keyzers, R. A.; Prinsep, M. R. Marine Natural Products. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2020, 37, 175–223.
- 13 Wang, C.; Lu, H. Y.; Lan, J. Z.; Zaman, K. H. A.; Cao, S. G. A Review: Halogenated Compounds from Marine Fungi. Molecules 2021, 26, 458.
- 14 Latham, J.; Brandenburger, E.; Shepherd, S. A.; Menon, B. R. K.; Micklefield, J. Development of Halogenase Enzymes for Use in Synthesis. Chem. Rev. 2018, 118, 232–269.
- 15 Zeng, J.; Zhan, J. X. Chlorinated Natural Products and Related Halogenases. Isr. J. Chem. 2019, 59, 387–402.
- 16 Wang, L. S.; Zhou, X. F.; Fredimoses, M.; Liao, S. R.; Liu, Y. H. Naturally Occurring Organoiodines. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 57350–57376.
- 17 Hagmann, W. K. The Many Roles for Fluorine in Medicinal Chemistry. J. Med. Chem. 2008, 51, 4359–4369.
- 18 Nagai, H.; Watanabe, M.; Sato, S.; Kawaguchi, M.; Xiao, Y. Y.; Hayashi, K.; Watanabe, R.; Uchida, H.; Satake, M. New Aplysiatoxin Derivatives from the Okinawan Cyanobacterium Moorea producens. Tetrahedron 2019, 75, 2486–2494.
- 19 Nagai, H.; Sato, S.; Iida, K.; Hayashi, K.; Kawaguchi, M.; Uchida, H.; Satake, M. Oscillatoxin I: A New Aplysiatoxin Derivative, from a Marine Cyanobacterium. Toxins (Basel) 2019, 11, 366.
- 20 Kawaguchi, M.; Satake, M.; Zhang, B. T.; Xiao, Y. Y.; Fukuoka, M.; Uchida, H.; Nagai, H. Neo-Aplysiatoxin A Isolated from Okinawan Cyanobacterium Moorea producens. Molecules 2020, 25, 457.
- 21 Jiang, W.; Zhou, W.; Othman, R.; Uchida, H.; Watanabe, R.; Suzuki, T.; Sakamoto, B.; Nagai, H. A New Malyngamide from the Marine Cyanobacterium Moorea Producens. Nat. Prod. Res. 2018, 32, 97–104.
- 22 Sueyoshi, K.; Yamano, A.; Ozaki, K.; Sumimoto, S.; Iwasaki, A.; Suenaga, K.; Teruya, T. Three New Malyngamides from the Marine Cyanobacterium Moorea producens. Mar. Drugs 2017, 15, 367.
- 23 Boudreau, P. D.; Monroe, E. A.; Mehrotra, S.; Desfor, S.; Korobeynikov, A.; Sherman, D. H.; Murray, T. F.; Gerwick, L.; Dorrestein, P. C.; Gerwick, W. H. Expanding the Described Metabolome of the Marine Cyanobacterium Moorea producens JHB through Orthogonal Natural Products Workflows. PLoS One 2015, 10, e0133297.
- 24 Kleigrewe, K.; Almaliti, J.; Tian, I. Y.; Kinnel, R. B.; Korobeynikov, A.; Monroe, E. A.; Duggan, B. M.; Di Marzo, V.; Sherman, D. H.; Dorrestein, P. C.; Gerwick, L.; Gerwick, W. H. Combining Mass Spectrometric Metabolic Profiling with Genomic Analysis: A Powerful Approach for Discovering Natural Products from Cyanobacteria. J. Nat. Prod. 2015, 78, 1671–1682.
- 25 Lopez, J. A. V.; Petitbois, J. G.; Vairappan, C. S.; Umezawa, T.; Matsuda, F.; Okino, T., Columbamides D and E: Chlorinated Fatty Acid Amides from the Marine Cyanobacterium Moorea bouillonii Collected in Malaysia. Org. Lett. 2017, 19, 4231–4234.
- 26 Mehjabin, J. J.; Wei, L.; Petitbois, J. G.; Umezawa, T.; Matsuda, F.; Vairappan, C. S.; Morikawa, M.; Okino, T. Biosurfactants from Marine Cyanobacteria Collected in Sabah, Malaysia. J. Nat. Prod. 2020, 83, 1925–1930.
- 27 Gutierrez-Del-Rio, I.; Brugerolle de Fraissinette, N.; Castelo-Branco, R.; Oliveira, F.; Morais, J.; Redondo-Blanco, S.; Villar, C. J.; Iglesias, M. J.; Soengas, R.; Cepas, V.; Cubillos, Y. L.; Sampietro, G.; Rodolfi, L.; Lombo, F.; Gonzalez, S. M. S.; Lopez Ortiz, F.; Vasconcelos, V.; Reis, M. A. Chlorosphaerolactylates A–D: Natural Lactylates of Chlorinated Fatty Acids Isolated from the Cyanobacterium Sphaerospermopsis sp. LEGE 00249. J. Nat. Prod. 2020, 83, 1885–1890.
- 28 Sueyoshi, K.; Yamada, M.; Yamano, A.; Ozaki, K.; Sumimoto, S.; Iwasaki, A.; Suenaga, K.; Teruya, T. Ypaoamides B and C, Linear Lipopeptides from an Okeania sp. Marine Cyanobacterium. J. Nat. Prod. 2018, 81, 1103–1107.
- 29 Sueyoshi, K.; Kudo, T.; Yamano, A.; Sumimoto, S.; Iwasaki, A.; Suenaga, K.; Teruya, T. Odobromoamide, a Terminal Alkynyl Bromide-Containing Cyclodepsipeptide from the Marine Cyanobacterium Okeania sp. Bull. Chem. Soc. Jap. 2017, 90, 436–440.
- 30 Petitbois, J. G.; Casalme, L. O.; Lopez, J. A. V.; Alarif, W. M.; Abdel-Lateff, A.; Al-Lihaibi, S. S.; Yoshimura, E.; Nogata, Y.; Umezawa, T.; Matsuda, F.; Okino, T. Serinolamides and Lyngbyabellins from an Okeania sp. Cyanobacterium Collected from the Red Sea. J. Nat. Prod. 2017, 80, 2708–2715.
- 31 Via, C. W.; Glukhov, E.; Costa, S.; Zimba, P. V.; Moeller, P. D. R.; Gerwick, W. H.; Bertin, M. J. The Metabolome of a Cyanobacterial Bloom Visualized by MS/MS-Based Molecular Networking Reveals New Neurotoxic Smenamide Analogs (C, D, and E). Front. Chem. 2018, 6, 316.
- 32 Bertin, M. J.; Sauri, J.; Liu, Y.; Via, C. W.; Roduit, A. F.; Williamson, R. T. Trichophycins B–F, Chlorovinylidene-Containing Polyketides Isolated from a Cyanobacterial Bloom. J. Org. Chem. 2018, 83, 13256–13266.
- 33 Bhandari Neupane, J.; Neupane, R. P.; Luo, Y.; Yoshida, W. Y.; Sun, R.; Williams, P. G. Characterization of Leptazolines A–D, Polar Oxazolines from the Cyanobacterium Leptolyngbya sp., Reveals a Glitch with the "Willoughby-Hoye" Scripts for Calculating NMR Chemical Shifts. Org. Lett. 2019, 21, 8449–8453.
- 34 Leao, P. N.; Nakamura, H.; Costa, M.; Pereira, A. R.; Martins, R.; Vasconcelos, V.; Gerwick, W. H.; Balskus, E. P. Biosynthesis-Assisted Structural Elucidation of the Bartolosides, Chlorinated Aromatic Glycolipids from Cyanobacteria. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2015, 54, 11063–11067.
- 35 Naman, C. B.; Almaliti, J.; Armstrong, L.; Caro-Diaz, E. J.; Pierce, M. L.; Glukhov, E.; Fenner, A.; Spadafora, C.; Debonsi, H. M.; Dorrestein, P. C.; Murray, T. F.; Gerwick, W. H. Discovery and Synthesis of Caracolamide A, an Ion Channel Modulating Dichlorovinylidene Containing Phenethylamide from a Panamanian Marine Cyanobacterium cf. Symploca Species. J. Nat. Prod. 2017, 80, 2328–2334.
- 36 Preisitsch, M.; Niedermeyer, T. H.; Heiden, S. E.; Neidhardt, I.; Kumpfmuller, J.; Wurster, M.; Harmrolfs, K.; Wiesner, C.; Enke, H.; Muller, R.; Mundt, S. Cylindrofridins A–C, Linear Cylindrocyclophane-Related Alkylresorcinols from the Cyanobacterium Cylindrospermum stagnale. J. Nat. Prod. 2016, 79, 106–115.
- 37 Cai, W. J.; Matthews, J. H.; Paul, V. J.; Luesch, H. Pitiamides A and B, Multifunctional Fatty Acid Amides from Marine Cyanobacteria. Planta. Med. 2016, 82, 897–902.
- 38 He, H.; Bertin, M. J.; Wu, S.; Wahome, P. G.; Beauchesne, K. R.; Youngs, R. O.; Zimba, P. V.; Moeller, P. D. R.; Sauri, J.; Carter, G. T. Cyanobufalins: Cardioactive Toxins from Cyanobacterial Blooms. J. Nat. Prod. 2018, 81, 2576–2581.
- 39 Choi, H.; Engene, N.; Byrum, T.; Hwang, S.; Oh, D. C.; Gerwick, W. H. Dragocins A–D, Structurally Intriguing Cytotoxic Metabolites from a Panamanian Marine Cyanobacterium. Org. Lett. 2019, 21, 266–270.
- 40 Zhu, M.; Zhang, X.; Feng, H.; Dai, J.; Li, J.; Che, Q.; Gu, Q.; Zhu, T.; Li, D. Penicisulfuranols A–F, Alkaloids from the Mangrove Endophytic Fungus Penicillium janthinellum HDN13-309. J. Nat. Prod. 2017, 80, 71–75.
- 41 Yang, Z.; Zhu, M. L.; Li, D. H.; Zeng, R.; Han, B. N., N-Me-Trichodermamide B Isolated from Penicillium janthinellum, with Antioxidant Properties Through Nrf2-Mediated Signaling Pathway. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2017, 25, 6614–6622.
- 42 Darsih, C.; Prachyawarakorn, V.; Wiyakrutta, S.; Mahidol, C.; Ruchirawat, S.; Kittakoop, P. Cytotoxic Metabolites from the Endophytic Fungus Penicillium chermesinum: Discovery of a Cysteine-Targeted Michael Acceptor as a Pharmacophore for Fragment-Based Drug Discovery, Bioconjugation and Click Reactions. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 70595–70603.
- 43 Chen, S.; Chen, D.; Cai, R.; Cui, H.; Long, Y.; Lu, Y.; Li, C.; She, Z. Cytotoxic and Antibacterial Preussomerins from the Mangrove Endophytic Fungus Lasiodiplodia theobromae ZJ-HQ1. J. Nat. Prod. 2016, 79, 2397–2402.
- 44 Gao, S. S.; Li, X. M.; Williams, K.; Proksch, P.; Ji, N. Y.; Wang, B. G. Rhizovarins A–F, Indole-Diterpenes from the Mangrove-Derived Endophytic Fungus Mucor irregularis QEN-189. J. Nat. Prod. 2016, 79, 2066–2074.
- 45 He, K. Y.; Zhang, C.; Duan, Y. R.; Huang, G. L.; Yang, C. Y.; Lu, X. R.; Zheng, C. J.; Chen, G. Y. New Chlorinated Xanthone and Anthraquinone Produced by a Mangrove-Derived Fungus Penicillium citrinum HL-5126. J. Antibiot (Tokyo) 2017, 70, 823–827.
- 46 Yu, H. L.; Jiang, S. H.; Bu, X. L.; Wang, J. H.; Weng, J. Y.; Yang, X. M.; He, K. Y.; Zhang, Z. G.; Ao, P.; Xu, J.; Xu, M. J. Structural Diversity of Anti-Pancreatic Cancer Capsimycins Identified in Mangrove-Derived Streptomyces xiamenensis 318 and Post-Modification via a Novel Cytochrome P450 Monooxygenase. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 40689.
- 47 Isaka, M.; Chinthanom, P.; Rachtawee, P.; Srichomthong, K.; Srikitikulchai, P.; Kongsaeree, P.; Prabpai, S. Cytotoxic Hydroanthraquinones from the Mangrove-Derived Fungus Paradictyoarthrinium diffractum BCC 8704. J. Antibiot (Tokyo) 2015, 68, 334–338.
- 48 Chen, Y.; Liu, Z.; Liu, H.; Pan, Y.; Li, J.; Liu, L.; She, Z. Dichloroisocoumarins with Potential Anti-Inflammatory Activity from the Mangrove Endophytic Fungus Ascomycota sp. CYSK-4. Mar. Drugs 2018, 16, 54.
- 49 Luo, X.; Lin, X.; Tao, H.; Wang, J.; Li, J.; Yang, B.; Zhou, X.; Liu, Y. Isochromophilones A–F, Cytotoxic Chloroazaphilones from the Marine Mangrove Endophytic Fungus Diaporthe sp. SCSIO 41011. J. Nat. Prod. 2018, 81, 934–941.
- 50 Shi, J.; Zeng, Y. J.; Zhang, B.; Shao, F. L.; Chen, Y. C.; Xu, X.; Sun, Y.; Xu, Q.; Tan, R. X.; Ge, H. M. Comparative Genome Mining and Heterologous Expression of an Orphan NRPS Gene Cluster Direct the Production of Ashimides. Chem. Sci. 2019, 10, 3042–3048.
- 51 Chen, M.; Zheng, Y. Y.; Chen, Z. Q.; Shen, N. X.; Shen, L.; Zhang, F. M.; Zhou, X. J.; Wang, C. Y. NaBr-Induced Production of Brominated Azaphilones and Related Tricyclic Polyketides by the Marine-Derived Fungus Penicillium janthinellum HK1-6. J. Nat. Prod. 2019, 82, 368–374.
- 52 Liu, S.; Zhao, Y.; Heering, C.; Janiak, C.; Muller, W. E. G.; Akone, S. H.; Liu, Z.; Proksch, P. Sesquiterpenoids from the Endophytic Fungus Rhinocladiella similis. J. Nat. Prod. 2019, 82, 1055–1062.
- 53 Mei, R. Q.; Nong, X. H.; Wang, B.; Sun, X. P.; Huang, G. L.; Luo, Y. P.; Zheng, C. J.; Chen, G. Y. A New Phenol Derivative Isolated from Mangrove-Derived Fungus Eupenicillium sp. HJ002. Nat. Prod. Res. 2020, 35, 4051–4057.
- 54 Zhang, P.; Li, X. M.; Li, X.; Wang, B. G. New Indole-Diterpenoids from the Algal-Associated Fungus Aspergillus nidulans. Phytochem. Lett. 2015, 12, 182–185.
- 55 Zhang, L. H.; Long, Y.; Lei, X. L.; Xu, J. Y.; Huang, Z. J.; She, Z. G.; Lin, Y. C.; Li, J.; Liu, L. Azaphilones Isolated from an Alga-Derived Fungus Penicillium sp. ZJ-27. Phytochem. Lett. 2016, 18, 180–186.
- 56 Mandelare, P. E.; Adpressa, D. A.; Kaweesa, E. N.; Zakharov, L. N.; Loesgen, S. Coculture of Two Developmental Stages of a Marine-Derived Aspergillus alliaceus Results in the Production of the Cytotoxic Bianthrone Allianthrone A. J. Nat. Prod. 2018, 81, 1014–1022.
- 57 Song, Y. P.; Miao, F. P.; Fang, S. T.; Yin, X. L.; Ji, N. Y. Halogenated and Nonhalogenated Metabolites from the Marine-Alga-Endophytic Fungus Trichoderma asperellum cf44-2. Mar. Drugs. 2018, 16, 266.
- 58 Zhang, X.; Shu, C.; Li, Q.; Lian, X. Y.; Zhang, Z. Novel Cyclohexene and Benzamide Derivatives from Marine-Associated Streptomyces sp. ZZ502. Nat. Prod. Res. 2019, 33, 2151–2159.
- 59 Song, Y. P.; Shi, X. S.; Wang, B. G.; Ji, N. Y. Cadinane and Carotane Derivatives from the Marine Algicolous Fungus Trichoderma virens RR-dl-6-8. Fitoterapia 2020, 146, 104715.
- 60 Morehouse, N. J.; Flewelling, A. J.; Johnson, J. A.; Gray, C. A. Halogenated Bianthrones From Penicillium roseopurpureum: a Fungal Endophyte of the Marine Alga Petalonia fascia. Nat. Prod. Commun. 2020, 15, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1177/1934578X20901405.
- 61 Zhou, S. L.; Wang, M.; Zhao, H. G.; Huang, Y. H.; Lin, Y. Y.; Tan, G. H.; Chen, S. L. Penicilazaphilone C, a New Antineoplastic and Antibacterial Azaphilone from the Marine Fungus Penicillium sclerotiorum. Arch. Pharm. Res. 2016, 39, 1621–1627.
- 62 Ali, T.; Inagaki, M.; Chai, H. B.; Wieboldt, T.; Rapplye, C.; Rakotondraibe, L. H. Halogenated Compounds from Directed Fermentation of Penicillium concentricum, an Endophytic Fungus of the Liverwort Trichocolea tomentella. J. Nat. Prod. 2017, 80, 1397–1403.
- 63 Suzuki, T.; Yoshida, S.; Koseki, T.; Aboshi, T.; Murayama, T.; Supratman, U.; Shiono, Y. New Metabolites Produced by Cylindrocarpon sp. SY-39 from a Driftwood. Chem. Biodivers. 2018, 15, e1700493.
- 64 Bertin, M. J.; Wahome, P. G.; Zimba, P. V.; He, H.; Moeller, P. D. Trichophycin A, a Cytotoxic Linear Polyketide Isolated from a Trichodesmium thiebautii Bloom. Mar. Drugs 2017, 15, 10.
- 65 Belisle, R. S.; Via, C. W.; Schock, T. B.; Villareal, T. A.; Zimba, P. V.; Beauchesne, K. R.; Moeller, P. D. R.; Bertin, M. J. Trichothiazole A, a Dichlorinated Polyketide Containing an Embedded Thiazole Isolated from Trichodesmium Blooms. Tetrahedron Lett. 2017, 58, 4066–4068.
- 66 Zhou, Y. M.; Ju, G. L.; Xiao, L.; Zhang, X. F.; Du, F. Y. Cyclodepsipeptides and Sesquiterpenes from Marine-Derived Fungus Trichothecium roseum and Their Biological Functions. Mar. Drugs 2018, 16, 519.
- 67 Gu, B. B.; Wu, Y.; Tang, J.; Jiao, W. H.; Li, L.; Sun, F.; Wang, S. P.; Yang, F.; Lin, H. W. Azaphilone and Isocoumarin Derivatives from the Sponge-Derived Fungus Eupenicillium sp. 6A-9. Tetrahedron Lett. 2018, 59, 3345–3348.
- 68 Jia, Q.; Du, Y.; Wang, C.; Wang, Y.; Zhu, T.; Zhu, W. Azaphilones from the Marine Sponge-Derived Fungus Penicillium sclerotiorum OUCMDZ-3839. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 260.
- 69 Wang, C. Y.; Hao, J. D.; Ning, X. Y.; Wu, J. S.; Zhao, D. L.; Kong, C. J.; Shao, C. L.; Wang, C. Y. Penicilazaphilones D and E: Two New Azaphilones from a Sponge-Derived Strain of the Fungus Penicillium sclerotiorum. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 4348–4353.
- 70 Wu, Q.; Wu, C.; Long, H.; Chen, R.; Liu, D.; Proksch, P.; Guo, P.; Lin, W. Varioxiranols A–G and 19-O-Methyl-22-methoxypre-shamixanthone, PKS and Hybrid PKS-Derived Metabolites from a Sponge-Associated Emericella variecolor Fungus. J. Nat. Prod. 2015, 78, 2461–2470.
- 71 Scopel, M.; Mothes, B.; Lerner, C. B.; Henriques, A. T.; Macedo, A. J.; Abraham, W. R. Arvoredol—An Unusual Chlorinated and Biofilm Inhibiting Polyketide from a Marine Penicillium sp. of the Brazilian coast. Phytochem. Lett. 2017, 20, 73–76.
- 72 Saetang, P.; Rukachaisirikul, V.; Phongpaichit, S.; Preedanon, S.; Sakayaroj, J.; Hadsadee, S.; Jungsuttiwong, S. Antibacterial and Antifungal Polyketides from the Fungus Aspergillus unguis PSU-MF16. J. Nat. Prod. 2021, 84, 1498–1506.
- 73 Elsebai, M. F.; Ghabbour, H. A. Isocoumarin Derivatives from the Marine-Derived Fungus Phoma sp. 135. Tetrahedron Lett. 2016, 57, 354–356.
- 74 Zhao, Y.; Liu, D.; Proksch, P.; Yu, S.; Lin, W. Isocoumarin Derivatives from the Sponge-Associated Fungus Peyronellaea glomerata with Antioxidant Activities. Chem. Biodivers. 2016, 13, 1186–1193.
- 75 Meng, L. H.; Chen, H. Q.; Form, I.; Konuklugil, B.; Proksch, P.; Wang, B. G. New Chromone, Isocoumarin, and Indole Alkaloid Derivatives from Three Sponge-Derived Fungal Strains. Nat. Prod. Commun. 2016, 11, 1293–1296.
- 76 Frank, M.; Hartmann, R.; Plenker, M.; Mandi, A.; Kurtan, T.; Ozkaya, F. C.; Muller, W. E. G.; Kassack, M. U.; Hamacher, A.; Lin, W.; Liu, Z.; Proksch, P. Brominated Azaphilones from the Sponge-Associated Fungus Penicillium canescens Strain 4.14.6a. J. Nat. Prod. 2019, 82, 2159–2166.
- 77 Ngokpol, S.; Suwakulsiri, W.; Sureram, S.; Lirdprapamongkol, K.; Aree, T.; Wiyakrutta, S.; Mahidol, C.; Ruchirawat, S.; Kittakoop, P. Drimane Sesquiterpene-Conjugated Amino Acids from a Marine Isolate of the Fungus Talaromyces minioluteus (Penicillium Minioluteum). Mar. Drugs 2015, 13, 3567–3580.
- 78 Kong, F.; Zhao, C.; Hao, J.; Wang, C.; Wang, W.; Huang, X.; Zhu, W., New α-Glucosidase Inhibitors from a Marine Sponge-Derived Fungus, Aspergillus sp. OUCMDZ-1583. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 68852–68863.
- 79 Qin, C.; Lin, X.; Lu, X.; Wan, J.; Zhou, X.; Liao, S.; Tu, Z.; Xu, S.; Liu, Y. Sesquiterpenoids and Xanthones Derivatives Produced by Sponge- Derived Fungus Stachybotry sp. HH1 ZSDS1F1-2. J. Antibiot (Tokyo) 2015, 68, 121–125.
- 80 Zhao, Y.; Si, L.; Liu, D.; Proksch, P.; Zhou, D.; Lin, W. Truncateols A–N, New Isoprenylated Cyclohexanols from the Sponge-Associated Fungus Truncatella angustata with Anti-H1N1 Virus Activities. Tetrahedron. 2015, 71, 2708–2718.
- 81 Cheng, C.; Othman, E. M.; Reimer, A.; Grüne, M.; Kozjak-Pavlovic, V.; Stopper, H.; Hentschel, U.; Abdelmohsen, U. R. Ageloline A, New Antioxidant and Antichlamydial Quinolone from the Marine Sponge- Derived Bacterium Streptomyces sp. SBT345. Tetrahedron Lett. 2016, 57, 2786–2789.
- 82 Liu, D.; Li, Y.; Li, X.; Cheng, Z.; Huang, J.; Proksch, P.; Lin, W. Chartarolides A–C, Novel Meroterpenoids with Antitumor Activities. Tetrahedron Lett. 2017, 58, 1826–1829.
- 83 Cheng, C.; Balasubramanian, S.; Fekete, A.; Krischke, M.; Mueller, M. J.; Hentschel, U.; Oelschlaeger, T. A.; Abdelmohsen, U. R. Inhibitory Potential of Strepthonium A Against Shiga Toxin Production in Enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli (EHEC) Strain EDL933. Nat. Prod. Res. 2017, 31, 2818–2823.
- 84 Wu, Z.; Li, Y.; Liu, D.; Ma, M.; Chen, J.; Lin, W. New Resorcinol Derivatives from a Sponge-Derived Fungus Hansfordia sinuosae. Chem. Biodivers. 2017, 14, e1700059.
- 85 Liu, J. T.; Wu, W.; Cao, M. J.; Yang, F.; Lin, H. W. Trienic Alpha-Pyrone and Ochratoxin Derivatives from a Sponge-Derived Fungus Aspergillus Ochraceopetaliformis. Nat. Prod. Res. 2018, 32, 1791–1797.
- 86 Qiu, P.; Ding, L.; Su, D.; He, S., A New Cyclopentenone Derivative from the Sponge-Associated Fungus Hypocrea koningii. Chem. Nat. Compd. 2018, 54, 631–633.
- 87 Elsebai, M. F.; Ghabbour, H. A.; Legrave, N.; Fontaine-Vive, F.; Mehiri, M. New Bioactive Chlorinated Cyclopentene Derivatives from the Marine-Derived Fungus Phoma sp. Med. Chem. Res. 2018, 27, 1885–1892.
- 88 El-Hawary, S. S.; Sayed, A. M.; Mohammed, R.; Khanfar, M. A.; Rateb, M. E.; Mohammed, T. A.; Hajjar, D.; Hassan, H. M.; Gulder, T. A. M.; Abdelmohsen, U. R. New Pim-1 Kinase Inhibitor From the Co-culture of Two Sponge-Associated Actinomycetes. Front. Chem. 2018, 6, 538.
- 89 Gu, B. B.; Jiao, F. R.; Wu, W.; Liu, L.; Jiao, W. H.; Sun, F.; Wang, S. P.; Yang, F.; Lin, H. W. Ochrasperfloroid, an Ochratoxin–Ergosteroid Heterodimer with Inhibition of IL-6 and NO Production from Aspergillus flocculosus 16D-1. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 7251–7256.
- 90 Guo, C.; Wang, P.; Lin, X.; Salendra, L.; Kong, F.; Liao, S.; Yang, B.; Zhou, X.; Wang, J.; Liu, Y. Phloroglucinol Heterodimers and Bis-Indolyl Alkaloids from the Sponge-Derived Fungus Aspergillus sp. SCSIO 41018. Org. Chem. Front. 2019, 6, 3053–3059.
- 91 Zhang, L.; Qiu, P.; Ding, L.; Li, Q.; Song, J.; Han, Z.; He, S. A New Antibacterial Chlorinated Amino Acid Derivative from the Sponge-Derived Fungus Aspergillus sp. LS53. Chem. Nat. Compd. 2020, 56, 109–111.
- 92 Shaala, L. A.; Youssef, D. T. A.; Alzughaibi, T. A.; Elhady, S. S., Antimicrobial Chlorinated 3-Phenylpropanoic Acid Derivatives from the Red Sea Marine Actinomycete Streptomyces coelicolor LY001. Mar. Drugs 2020, 18, 112.
- 93 Jiao, W. H.; Xu, Q. H.; Ge, G. B.; Shang, R. Y.; Zhu, H. R.; Liu, H. Y.; Cui, J.; Sun, F.; Lin, H. W. Flavipesides A–C, PKS-NRPS Hybrids as Pancreatic Lipase Inhibitors from a Marine Sponge Symbiotic Fungus Aspergillus flavipes 164013. Org. Lett. 2020, 22, 1825–1829.
- 94 Wei, M. Y.; Xu, R. F.; Du, S. Y.; Wang, C. Y.; Xu, T. Y.; Shao, C. L. A New Griseofulvin Derivative from the Marine-Derived Arthrinium sp. Fungus and Its Biological Activity. Chem. Nat. Compd. 2016, 52, 1011–1014.
- 95 Ma, J.; Zhang, X. L.; Wang, Y.; Zheng, J. Y.; Wang, C. Y.; Shao, C. L. Aspergivones A and B, Two New Flavones Isolated from a Gorgonian- Derived Aspergillus candidus Fungus. Nat. Prod. Res. 2017, 31, 32–36.
- 96 Xing, Q.; Gan, L. S.; Mou, X. F.; Wang, W.; Wang, C. Y.; Wei, M. Y.; Shao, C. L. Isolation, Resolution and Biological Evaluation of Pestalachlorides E and F Containing Both Point and Axial Chirality. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 22653–22658.
- 97 Liu, Z.; Qiu, P.; Liu, H.; Li, J.; Shao, C.; Yan, T.; Cao, W.; She, Z. Identification of Anti-Inflammatory Polyketides from the Coral-Derived Fungus Penicillium sclerotiorin: In Vitro Approaches and Molecular-Modeling. Bioorg. Chem. 2019, 88, 102973.
- 98 Liu, D. H.; Sun, Y. Z.; Kurtan, T.; Mandi, A.; Tang, H.; Li, J.; Su, L.; Zhuang, C. L.; Liu, Z. Y.; Zhang, W. Osteoclastogenesis Regulation Metabolites from the Coral-Associated Fungus Pseudallescheria boydii TW-1024-3. J. Nat. Prod. 2019, 82, 1274–1282.
- 99 Kong, F. D.; Ma, Q. Y.; Huang, S. Z.; Wang, P.; Wang, J. F.; Zhou, L. M.; Yuan, J. Z.; Dai, H. F.; Zhao, Y. X. Chrodrimanins K-N and Related Meroterpenoids from the Fungus Penicillium sp. SCS-KFD09 Isolated from a Marine Worm, Sipunculus nudus. J. Nat. Prod. 2017, 80, 1039–1047.
- 100 Kong, F. D.; Zhang, R. S.; Ma, Q. Y.; Xie, Q. Y.; Wang, P.; Chen, P. W.; Zhou, L. M.; Dai, H. F.; Luo, D. Q.; Zhao, Y. X. Chrodrimanins O-S from the Fungus Penicillium sp. SCS-KFD09 Isolated from a Marine Worm, Sipunculusnudus. Fitoterapia 2017, 122, 1–6.
- 101 Ivanets, E. V.; Yurchenko, A. N.; Smetanina, O. F.; Rasin, A. B.; Zhuravleva, O. I.; Pivkin, M. V.; Popov, R. S.; von Amsberg, G.; Afiyatullov, S. S.; Dyshlovoy, S. A. Asperindoles A–D and a p-Terphenyl Derivative from the Ascidian-Derived Fungus Aspergillus sp. KMM 4676. Mar. Drugs 2018, 16, 232.
- 102 Zhang, F.; Braun, D. R.; Chanana, S.; Rajski, S. R.; Bugni, T. S. Phallusialides A–E, Pyrrole-Derived Alkaloids Discovered from a Marine-Derived Micromonospora sp. Bacterium Using MS-Based Metabolomics Approaches. J. Nat. Prod. 2019, 82, 34323439.
- 103 Ferreira, E. L.; Williams, D. E.; Ioca, L. P.; Morais-Urano, R. P.; Santos, M. F.; Patrick, B. O.; Elias, L. M.; Lira, S. P.; Ferreira, A. G.; Passarini, M. R.; Sette, L. D.; Andersen, R. J.; Berlinck, R. G. Structure and Biogenesis of Roussoellatide, a Dichlorinated Polyketide from the Marine-Derived Fungus Roussoella sp. DLM33. Org. Lett. 2015, 17, 5152–5155.
- 104 Yan, D. F.; Lan, W. J.; Wang, K. T.; Huang, L.; Jiang, C. W.; Li, H. J. Two Chlorinated Benzofuran Derivatives from the Marine Fungus Pseudallescheria boydii. Nat. Prod. Commun. 2015, 10, 621–622.
- 105 He, X.; Zhang, Z.; Chen, Y.; Che, Q.; Zhu, T.; Gu, Q.; Li, D. Varitatin A, a Highly Modified Fatty Acid Amide from Penicillium variabile Cultured with a DNA Methyltransferase Inhibitor. J. Nat. Prod. 2015, 78, 2841–2845.
- 106 Lacret, R.; Perez-Victoria, I.; Oves-Costales, D.; de la Cruz, M.; Domingo, E.; Martin, J.; Diaz, C.; Vicente, F.; Genilloud, O.; Reyes, F. MDN-0170, a New Napyradiomycin from Streptomyces sp. Strain CA-271078. Mar. Drugs 2016, 14, 188.
- 107 Ma, M.; Yi, W.; Qin, L.; Lian, X. Y.; Zhang, Z. Talaromydien a and Talaroisocoumarin A, New Metabolites from the Marine-Sourced Fungus Talaromyces sp. ZZ1616. Nat. Prod. Res. 2020, 36, 460–465.
- 108 Meng, L. H.; Li, X. M.; Zhang, F. Z.; Wang, Y. N.; Wang, B. G. Talascortenes A–G, Highly Oxygenated Diterpenoid Acids from the Sea-Anemone-Derived Endozoic Fungus Talaromyces scorteus AS-242. J. Nat. Prod. 2020, 83, 2528–2536.
- 109 Wang, W.; Yang, J.; Liao, Y. Y.; Cheng, G.; Chen, J.; Cheng, X. D.; Qin, J. J.; Shao, Z. Cytotoxic Nitrogenated Azaphilones from the Deep-Sea- Derived Fungus Chaetomium globosum MP4-S01-7. J. Nat. Prod. 2020, 83, 1157–1166.
- 110 Chen, S.; Liu, Z.; Chen, Y.; Tan, H.; Liu, H.; Zhang, W. Tersaphilones A–E, Cytotoxic Chlorinated Azaphilones from the Deep-Sea-Derived Fungus Phomopsis tersa FS441. Tetrahedron 2021, 78, 131806.
- 111 Sun, C.; Ge, X.; Mudassir, S.; Zhou, L.; Yu, G.; Che, Q.; Zhang, G.; Peng, J.; Gu, Q.; Zhu, T.; Li, D. New Glutamine-Containing Azaphilone Alkaloids from Deep-Sea-Derived Fungus Chaetomium globosum HDN151398. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 253.
- 112 Song, Y.; Yang, J.; Yu, J.; Li, J.; Yuan, J.; Wong, N. K.; Ju, J. Chlorinated Bis-Indole Alkaloids from Deep-Sea Derived Streptomyces sp. SCSIO 11791 with Antibacterial and Cytotoxic Activities. J. Antibiot (Tokyo) 2020, 73, 542–547.
- 113 Niu, S.; Liu, D.; Proksch, P.; Shao, Z.; Lin, W. New Polyphenols from a Deep Sea Spiromastix sp. Fungus, and Their Antibacterial Activities. Mar. Drugs 2015, 13, 2526–2540.
- 114 Niu, S.; Si, L.; Liu, D.; Zhou, A.; Zhang, Z.; Shao, Z.; Wang, S.; Zhang, L.; Zhou, D.; Lin, W. Spiromastilactones: A New Class of Influenza Virus Inhibitors from Deep-Sea Fungus. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2016, 108, 229–244.
- 115 Wang, W.; Li, S.; Chen, Z.; Li, Z.; Liao, Y.; Chen, J. Secondary Metabolites Produced by the Deep-Sea-Derived Fungus Engyodontium album. Chem. Nat. Compd. 2017, 53, 224–226.
- 116 Wang, W.; Liao, Y.; Chen, R.; Hou, Y.; Ke, W.; Zhang, B.; Gao, M.; Shao, Z.; Chen, J.; Li, F. Chlorinated Azaphilone Pigments with Antimicrobial and Cytotoxic Activities Isolated from the Deep Sea Derived Fungus Chaetomium sp. NA-S01-R1. Mar. Drugs 2018, 16, 61.
- 117 Wang, J. F.; Zhou, L. M.; Chen, S. T.; Yang, B.; Liao, S. R.; Kong, F. D.; Lin, X. P.; Wang, F. Z.; Zhou, X. F.; Liu, Y. H. New Chlorinated Diphenyl Ethers and Xanthones from a Deep-Sea-Derived Fungus Penicillium chrysogenum SCSIO 41001. Fitoterapia 2018, 125, 49–54.
- 118 Niu, S.; Liu, Q.; Xia, J. M.; Xie, C. L.; Luo, Z. H.; Shao, Z.; Liu, G.; Yang, X. W. Polyketides from the Deep-Sea-Derived Fungus Graphostroma sp. MCCC 3A00421 Showed Potent Antifood Allergic Activities. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2018, 66, 1369–1376.
- 119 Tang, X. X.; Liu, S. Z.; Yan, X.; Tang, B. W.; Fang, M. J.; Wang, X. M.; Wu, Z.; Qiu, Y. K. Two New Cytotoxic Compounds from a Deep-Sea Penicillum citreonigrum XT20-134. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 509.
- 120 Kim, S. M.; Son, S.; Kim, J. W.; Jeon, E. S.; Ko, S. K.; Ryoo, I. J.; Shin, K. S.; Hirota, H.; Takahashi, S.; Osada, H.; Jang, J. H.; Ahn, J. S. Penidioxolanes A and B, 1,3-Dioxolane Containing Azaphilone Derivatives from Marine-Derived Penicillium sp. KCB12C078. Nat. Prod. Sci. 2015, 21, 231–236.
- 121 Cardoso-Martinez, F.; de la Rosa, J. M.; Diaz-Marrero, A. R.; Darias, J.; Cerella, C.; Diederich, M.; Cueto, M. Tanzawaic Acids Isolated from a Marine-Derived Fungus of the Genus Penicillium with Cytotoxic Activities. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2015, 13, 7248–7256.
- 122 Saha, S.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, G.; Zhu, Y.; Chen, Y.; Liu, W.; Yuan, C.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, C. Activation and Characterization of a Cryptic Gene Cluster Reveals a Cyclization Cascade for Polycyclic Tetramate Macrolactams. Chem. Sci. 2017, 8, 1607–1612.
- 123 Zhang, Z.; He, X.; Liu, C.; Che, Q.; Zhu, T.; Gu, Q.; Li, D. Clindanones A and B and Cladosporols F and G, Polyketides from the Deep-Sea Derived Fungus Cladosporium cladosporioides HDN14-342. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 76498–76504.
- 124 Luo, M.; Cui, Z.; Huang, H.; Song, X.; Sun, A.; Dang, Y.; Lu, L.; Ju, J. Amino Acid Conjugated Anthraquinones from the Marine-Derived Fungus Penicillium sp. SCSIO sof101. J. Nat. Prod. 2017, 80, 1668–1673.
- 125 Ding, H.; Zhang, D.; Zhou, B.; Ma, Z. Inhibitors of BRD4 Protein from a Marine-Derived Fungus Alternaria sp. NH-F6. Mar. Drugs 2017, 15, 76.
- 126 Le, T. C.; Yim, C. Y.; Park, S.; Katila, N.; Yang, I.; Song, M. C.; Yoon, Y. J.; Choi, D. Y.; Choi, H.; Nam, S. J.; Fenical, W. Lodopyridones B and C from a Marine Sediment-Derived Bacterium Saccharomonospora sp. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2017, 27, 3123–3126.
- 127 Asolkar, R. N.; Singh, A.; Jensen, P. R.; Aalbersberg, W.; Carte, B. K.; Feussner, K. D.; Subramani, R.; DiPasquale, A.; Rheingold, A. L.; Fenical, W. Marinocyanins, Cytotoxic Bromo-Phenazinone Meroterpenoids from a Marine Bacterium from the Streptomycete clade MAR4. Tetrahedron 2017, 73, 2234–2241.
- 128 Paulus, C.; Rebets, Y.; Tokovenko, B.; Nadmid, S.; Terekhova, L. P.; Myronovskyi, M.; Zotchev, S. B.; Ruckert, C.; Braig, S.; Zahler, S.; Kalinowski, J.; Luzhetskyy, A. New Natural Products Identified by Combined Genomics-Metabolomics Profiling of Marine Streptomyces sp. MP131-18. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 42382.
- 129 Smetanina, O. F.; Yurchenko, A. N.; Ivanets, E. V.; Kalinovsky, A. I.; Khudyakova, Y. V.; Dyshlovoy, S. A.; von Amsberg, G.; Yurchenko, E. A.; Afiyatullov, S. S. Unique Prostate Cancer-Toxic Polyketides from Marine Sediment-Derived Fungus Isaria felina. J. Antibiot (Tokyo) 2017, 70, 856–858.
- 130 Zhang, C.; Yang, Z.; Qin, X.; Ma, J.; Sun, C.; Huang, H.; Li, Q.; Ju, J. Genome Mining for Mycemycin: Discovery and Elucidation of Related Methylation and Chlorination Biosynthetic Chemistries. Org. Lett. 2018, 20, 7633–7636.
- 131 Perez-Bonilla, M.; Oves-Costales, D.; de la Cruz, M.; Kokkini, M.; Martin, J.; Vicente, F.; Genilloud, O.; Reyes, F. Phocoenamicins B and C, New Antibacterial Spirotetronates Isolated from a Marine Micromonospora sp. Mar. Drugs 2018, 16, 95.
- 132 da Silva, A. B.; Pinto, F. C. L.; Silveira, E. R.; Costa-Lotufo, L. V.; Costa, W. S.; Ayala, A. P.; Canuto, K. M.; Barros, A. B.; Araujo, A. J.; Marinho Filho, J. D. B.; Pessoa, O. D. L. 4-Hydroxy-pyran-2-one and 3-Hydroxy- N-methyl-2-oxindole Derivatives of Salinispora arenicola from Brazilian Marine Sediments. Fitoterapia 2019, 138, 104357.
- 133 Ge, X.; Sun, C.; Feng, Y.; Wang, L.; Peng, J.; Che, Q.; Gu, Q.; Zhu, T.; Li, D.; Zhang, G. Anthraquinone Derivatives from a Marine-Derived Fungus Sporendonema casei HDN16-802. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 334.
- 134 Ji, Y. B.; Chen, W. J.; Shan, T. Z.; Sun, B. Y.; Yan, P. C.; Jiang, W. Antibacterial Diphenyl Ether, Benzophenone and Xanthone Derivatives from Aspergillus flavipes. Chem. Biodivers. 2020, 17, e1900640.
- 135 Wang, W.; Park, C.; Oh, E.; Sung, Y.; Lee, J.; Park, K. H.; Kang, H. Benzophenone Compounds, from a Marine-Derived Strain of the Fungus Pestalotiopsis neglecta, Inhibit Proliferation of Pancreatic Cancer Cells by Targeting the MEK/ERK Pathway. J. Nat. Prod. 2019, 82, 3357–3365.
- 136 Ryu, M. J.; Hwang, S.; Kim, S.; Yang, I.; Oh, D. C.; Nam, S. J.; Fenical, W. Meroindenon and Merochlorins E and F, Antibacterial Meroterpenoids from a Marine-Derived Sediment Bacterium of the Genus Streptomyces. Org. Lett. 2019, 21, 5779–5783.
- 137 Cao, D. T.; Nguyen, T. L.; Tran, V. H.; Huong, D. T. M.; Quyen, V. T.; Nguyen, M. A.; Le-Thi, M.; Chau, V. M.; Pham, V. C. Synthesis, Structure and Antimicrobial Activity of Novel Metabolites from a Marine Actinomycete in Vietnam's east sea. Nat. Prod. Commun. 2019, 14, 121–124.
- 138 Harizani, M.; Katsini, E.; Georgantea, P.; Roussis, V.; Ioannou, E. New Chlorinated 2,5-Diketopiperazines from Marine-Derived Bacteria Isolated from Sediments of the Eastern Mediterranean Sea. Molecules 2020, 25, 1509.
- 139 Han, Y.; Sun, C.; Li, C.; Zhang, G.; Zhu, T.; Li, D.; Che, Q. Antibacterial Phenalenone Derivatives from Marine-Derived Fungus Pleosporales sp. HDN1811400. Tetrahedron Lett. 2021, 68, 152938.
- 140 Liu, D.; Yan, L.; Ma, L.; Huang, Y.; Pan, X.; Liu, W.; Lv, Z. Diphenyl Derivatives from Coastal Saline Soil Fungus Aspergillus iizukae. Arch. Pharm. Res. 2015, 38, 1038–1043.
- 141 Bae, M.; Chung, B.; Oh, K. B.; Shin, J.; Oh, D. C. Hormaomycins B and C: New Antibiotic Cyclic Depsipeptides from a Marine Mudflat-Derived Streptomyces sp. Mar. Drugs 2015, 13, 5187–5200.
- 142 Yamazaki, H.; Takahashi, O.; Murakami, K.; Namikoshi, M. Induced Production of a New Unprecedented Epitrithiodiketopiperazine, Chlorotrithiobrevamide, by a Culture of the Marine-Derived Trichoderma cf. brevicompactum with Dimethyl Sulfoxide. Tetrahedron Lett. 2015, 56, 6262–6265.
- 143 Kim, S. H.; Shin, Y.; Lee, S. H.; Oh, K. B.; Lee, S. K.; Shin, J.; Oh, D. C. Salternamides A-D from a Halophilic Streptomyces sp. Actinobacterium. J. Nat. Prod. 2015, 78, 836–843.
- 144 Uchida, R.; Nakajyo, K.; Kobayashi, K.; Ohshiro, T.; Terahara, T.; Imada, C.; Tomoda, H. 7-Chlorofolipastatin, an Inhibitor of Sterol O-Acyltransferase, Produced by Marine-Derived Aspergillus ungui NKH-007. J. Antibiot (Tokyo) 2016, 69, 647–651.
- 145 Yun, K.; Khong, T. T.; Leutou, A. S.; Kim, G. D.; Hong, J.; Lee, C. H.; Son, B. W. Cristazine, a New Cytotoxic Dioxopiperazine Alkaloid from the Mudflat-Sediment-Derived Fungus Chaetomium cristatum. Chem. Pharm. Bull. (Tokyo) 2016, 64, 59–62.
- 146 Leutou, A. S.; Yun, K.; Son, B. W. Induced Production of 6,9-Dibromoflavasperone, a New Radical Scavenging Naphthopyranone in the Marine-Mudflat-Derived Fungus Aspergillus niger. Arch. Pharm. Res. 2016, 39, 806–810.
- 147 Igarashi, Y.; Matsuoka, N.; In, Y.; Kataura, T.; Tashiro, E.; Saiki, I.; Sudoh, Y.; Duangmal, K.; Thamchaipenet, A. Nonthmicin, a Polyether Polyketide Bearing a Halogen-Modified Tetronate with Neuroprotective and Antiinvasive Activity from Actinomadura sp. Org. Lett. 2017, 19, 1406–1409.
- 148 Chen, M.; Shen, N. X.; Chen, Z. Q.; Zhang, F. M.; Chen, Y. Penicilones A–D, Anti-MRSA Azaphilones from the Marine-Derived Fungus Penicillium janthinellum HK1-6. J. Nat. Prod. 2017, 80, 1081–1086.
- 149 Son, S.; Ko, S. K.; Jang, M.; Lee, J. K.; Kwon, M. C.; Kang, D. H.; Ryoo, I. J.; Lee, J. S.; Hong, Y. S.; Kim, B. Y.; Jang, J. H.; Ahn, J. S. Polyketides and Anthranilic Acid Possessing 6-Deoxy-alpha-l-talopyranose from a Streptomyces Species. J. Nat. Prod. 2017, 80, 1378–1386.
- 150 Yuan, J.; Wang, L.; Ren, J.; Huang, J. P.; Yu, M.; Tang, J.; Yan, Y.; Yang, J.; Huang, S. X. Antibacterial Pentacyclic Polyketides from a Soil-Derived Streptomyces. J. Nat. Prod. 2020, 83, 1919–1924.
- 151 Zhao, P.; Yang, M.; Zhu, G.; Zhao, B.; Wang, H.; Liu, H.; Wang, X.; Qi, J.; Yin, X.; Yu, L.; Meng, Y.; Li, Z.; Zhang, L.; Xia, X. Mollicellins S–U, Three New Depsidones from Chaetomium brasiliense SD-596 with Anti-MRSA Activities. J. Antibiot (Tokyo) 2021, 74, 317–323.
- 152 Ding, L.; He, S.; Wu, W.; Jin, H.; Zhu, P.; Zhang, J.; Wang, T.; Yuan, Y.; Yan, X. Discovery and Structure-Based Optimization of 6-Bromotryptamine Derivatives as Potential 5-HT2A Receptor Antagonists. Molecules 2015, 20, 17675–17683.
- 153 Bu, Y. Y.; Yamazaki, H.; Ukai, K.; Namikoshi, M. Penicillimide, an Open-Chain Hemisuccinimide from Okinawan Marine-Derived Penicillium copticola. J. Antibiot (Tokyo) 2015, 68, 537–539.
- 154 Roullier, C.; Guitton, Y.; Valery, M.; Amand, S.; Prado, S.; Robiou du Pont, T.; Grovel, O.; Pouchus, Y. F. Automated Detection of Natural Halogenated Compounds from LC-MS Profiles-Application to the Isolation of Bioactive Chlorinated Compounds from Marine-Derived Fungi. Anal. Chem. 2016, 88, 9143–9150.
- 155 Umetsu, S.; Kanda, M.; Imai, I.; Sakai, R.; Fujita, M. J. Questiomycins, Algicidal Compounds Produced by the Marine Bacterium Alteromonas sp. D and Their Production Cue. Molecules 2019, 24, 4522.
- 156 Kwon, J.; Lee, H.; Ko, W.; Kim, D. C.; Kim, K. W.; Kwon, H. C.; Guo, Y.; Sohn, J. H.; Yim, J. H.; Kim, Y. C.; Oh, H.; Lee, D. Chemical Constituents Isolated from Antarctic Marine-Derived Aspergillus sp. SF-5976 and Their Anti-Inflammatory Effects in LPS-Stimulated RAW 264.7 and BV2 Cells. Tetrahedron 2017, 73, 3905–3912.
- 157 Hussain, H.; Root, N.; Jabeen, F.; Al-Harrasi, A.; Ahmad, M.; Mabood, F.; Hassan, Z.; Shah, A.; Green, I. R.; Schulz, B.; Krohn, K. Microsphaerol and Seimatorone: Two New Compounds Isolated from the Endophytic Fungi, Microsphaeropsis sp and Seimatosporium sp. Chem. Biodivers. 2015, 12, 289–294.
- 158 Fukuda, T.; Takahashi, M.; Kasai, H.; Nagai, K.; Tomoda, H. Chlokamycin, a New Chloride from the Marine-Derived Streptomyces sp MA2-12. Nat. Prod. Commun. 2017, 12, 1223–1226.
- 159 Reynolds, K. A.; Luhavaya, H.; Li, J.; Dahesh, S.; Nizet, V.; Yamanaka, K.; Moore, B. S. Isolation and Structure Elucidation of Lipopeptide Antibiotic Taromycin B from the Activated Taromycin Biosynthetic Gene Cluster. J. Antibiot (Tokyo) 2018, 71, 333–338.
- 160 Le, T. C.; Katila, N.; Park, S.; Lee, J.; Yang, I.; Choi, H.; Choi, D. Y.; Nam, S. J. Two New Secondary Metabolites, Saccharochlorines A and B, from a Marine Bacterium Saccharomonospora sp. KCTC-19160. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2020, 30, 127145.
- 161 Subko, K.; Kildgaard, S.; Vicente, F.; Reyes, F.; Genilloud, O.; Larsen, T. O. Bioactive Ascochlorin Analogues from the Marine-Derived Fungus Stilbella fimetaria. Mar. Drugs 2021, 19, 46.
- 162 van Pee, K. H.; Dong, C. J.; Flecks, S.; Naismith, J.; Patallo, E. P.; Wage, T. Biological halogenation has moved far beyond haloperoxidases. Adv. Appl. Microbiol. 2006, 59, 127–157.
- 163 Prakash, G. K. S.; Mathew, T.; Hoole, D.; Esteves, P. M.; Wang, Q.; Rasul, G.; Olah, G. A. N-Halosuccinimide/BF3-H2O, Efficient Electrophilic Halogenating Systems for Aromatics. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2004, 126, 15770–15776.
- 164 Agarwal, V.; Miles, Z. D.; Winter, J. M.; Eustaquio, A. S.; El Gamal, A. A.; Moore, B. S. Enzymatic Halogenation and Dehalogenation Reactions: Pervasive and Mechanistically Diverse. Chem. Rev. 2017, 117, 5619–5674.
- 165 Hager, L. P.; Morris, D. R.; Brown, F. S.; Eberwein, H. Chloroperoxidase. II. Ultilization of Halogen Anions. J. Biol. Chem. 1966, 241, 1769–1777.
- 166 Morris, D. R.; Hager, L. P. Chloroperoxidase I. Isolation and Properties of the Crystalline Glycoprotein. J. Biol. Chem. 1966, 241, 1763–1768.
- 167 Winter, J. M.; Moore, B. S. Exploring the Chemistry and Biology of Vanadium-dependent Haloperoxidases. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 18577–18581.
- 168 McKinnie, S. M. K.; Miles, Z. D.; Moore, B. S. Characterization and Biochemical Assays of Streptomyces Vanadium-Dependent Chloroperoxidases (Chapter 13). In Methods in Enzymology, Elsevier Press, Amsterdam, 2018, pp. 405–424.
- 169 Zhao, C. H.; Yan, S.; Li, Q.; Zhu, H. C.; Zhong, Z. Y.; Ye, Y.; Deng, Z. X.; Zhang, Y. H. An Fe2+- and alpha-Ketoglutarate-Dependent Halogenase Acts on Nucleotide Substrates. Angew. Chem. Inte. Ed. 2020, 59, 9478–9484.
- 170 Blasiak, L. C.; Vaillancourt, F. H.; Walsh, C. T.; Drennan, C. L. Crystal Structure of the Non-Haem Iron Halogenase SyrB2 in Syringomycin Biosynthesis. Nature 2006, 440, 368–371.
- 171 Galonic, D. P.; Vaillancourt, F. H.; Walsh, C. T. Halogenation of Unactivated Carbon Centers in Natural Product Biosynthesis: Trichlorination of Leucine During Barbamide Biosynthesis. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2006, 128, 3900–3901.
- 172 Smith, D. R. M.; Uria, A. R.; Helfrich, E. J. N.; Milbredt, D.; van Pee, K. H.; Piel, J.; Goss, R. J. M. An Unusual Flavin-Dependent Halogenase from the Metagenome of the Marine Sponge Theonella swinhoei WA. ACS Chem. Biol. 2017, 12, 1281–1287.
- 173 Andorfer, M. C.; Belsare, K. D.; Girlich, A. M.; Lewis, J. C. Aromatic Halogenation by Using Bifunctional Flavin Reductase-Halogenase Fusion Enzymes. ChemBioChem 2017, 18, 2099–2103.
- 174 Andorfer, M. C.; Lewis, J. C. Understanding and Improving the Activity of Flavin-Dependent Halogenases Via Random and Targeted Mutagenesis. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2018, 87, 159–185.
- 175 Chen, X. P.; Huang, M. F.; Wang, B. F. Flavin-dependent Tryptophan Halogenases and Their Use in Formation of Novel Tryptophan Derived Compounds. Chin. J. Chem. 2008, 26, 1468–1492.
- 176 Eustaquio, A. S.; Pojer, F.; Noel, J. P.; Moore, B. S. Discovery and Characterization of a Marine Bacterial SAM-Dependent Chlorinase. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2008, 4, 69–74.
- 177 Dong, C. J.; Huang, F. L.; Deng, H.; Schaffrath, C.; Spencer, J. B.; O'Hagan, D.; Naismith, J. H. Crystal Structure and Mechanism of a Bacterial Fluorinating Enzyme. Nature 2004, 427, 561–565.
- 178 O'Hagan, D.; Schaffrath, C.; Cobb, S. L.; Hamilton, J. T. G.; Murphy, C. D. Biosynthesis of an Organofluorine Molecule-A Fluorinase Enzyme has been Discovered That Catalyses Carbon-Fluorine Bond Formation. Nature 2002, 416, 279–279.
- 179 Gozari, M.; Alborz, M.; El-Seedi, H. R.; Jassbi, A. R. Chemistry, Biosynthesis and Biological Activity of Terpenoids and Meroterpenoids in Bacteria and Fungi Isolated from Different Marine Habitats. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2021, 210, 112957.
- 180 Zeng, J.; Zhan, J. X. Characterization of a Tryptophan 6-Halogenase from Streptomyces toxytricini. Biotechnol. Lett. 2011, 33, 1607–1613.
- 181 Kirk, K. L. Fluorination in Medicinal Chemistry: Methods, Strategies, and Recent Developments. Org. Process Res. Dev. 2008, 12, 305–321.
- 182 Carvalho, M. F.; Oliveira, R. S. Natural Production of Fluorinated Compounds and Biotechnological Prospects of the Fluorinase Enzyme. Cri. Rev. Biotechnol. 2017, 37, 880–897.
- 183 Dembitsky, V. M. Biogenic Iodine and Iodine-Containing Metabolites. Nat. Prod. Commun. 2006, 1, 139–175.
- 184 Gribble, G. W. Naturally Occurring Organohalogen Compounds: Recent Developments. Abstr. Pap. Am. Chem. Soc. 2001, 222, U435–U436.
- 185 Gribble, G. J. The Natural Production of Organobromine Compounds. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2000, 7, 37–49.
- 186 O'Hagan, D.; Harper, D. B. Fluorine-Containing Natural Products. J. Fluor. Chem. 1999, 100, 127–133.
- 187vanPee, K. H. Biosynthesis of Halogenated Metabolites by Bacteria. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 1996, 50, 375–399.
- 188 Littlechild, J. Haloperoxidases and Their Role in Biotransformation Reactions. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 1999, 3, 28–34.




