Synthesis, Structural Characterization, and Biological Activities of 1,3,4- Thiadiazole Derivatives Containing Sulfonylpiperazine Structures
You-hua Liu
National Key Laboratory of Green Pesticide, Key Laboratory of Green Pesticide and Agricultural Bioengineering, Ministry of Education, Center for R&D of Fine Chemicals of Guizhou University, Guiyang, 550025 China
These authors contributed equally to this work.
Search for more papers by this authorFa-li Wang
National Key Laboratory of Green Pesticide, Key Laboratory of Green Pesticide and Agricultural Bioengineering, Ministry of Education, Center for R&D of Fine Chemicals of Guizhou University, Guiyang, 550025 China
These authors contributed equally to this work.
Search for more papers by this authorXiao-li Ren
National Key Laboratory of Green Pesticide, Key Laboratory of Green Pesticide and Agricultural Bioengineering, Ministry of Education, Center for R&D of Fine Chemicals of Guizhou University, Guiyang, 550025 China
Search for more papers by this authorChang-kun Li
National Key Laboratory of Green Pesticide, Key Laboratory of Green Pesticide and Agricultural Bioengineering, Ministry of Education, Center for R&D of Fine Chemicals of Guizhou University, Guiyang, 550025 China
Search for more papers by this authorLin-hong Jin
National Key Laboratory of Green Pesticide, Key Laboratory of Green Pesticide and Agricultural Bioengineering, Ministry of Education, Center for R&D of Fine Chemicals of Guizhou University, Guiyang, 550025 China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Xia Zhou
- [email protected]
- +86-851-3620-521
National Key Laboratory of Green Pesticide, Key Laboratory of Green Pesticide and Agricultural Bioengineering, Ministry of Education, Center for R&D of Fine Chemicals of Guizhou University, Guiyang, 550025 China
Search for more papers by this authorYou-hua Liu
National Key Laboratory of Green Pesticide, Key Laboratory of Green Pesticide and Agricultural Bioengineering, Ministry of Education, Center for R&D of Fine Chemicals of Guizhou University, Guiyang, 550025 China
These authors contributed equally to this work.
Search for more papers by this authorFa-li Wang
National Key Laboratory of Green Pesticide, Key Laboratory of Green Pesticide and Agricultural Bioengineering, Ministry of Education, Center for R&D of Fine Chemicals of Guizhou University, Guiyang, 550025 China
These authors contributed equally to this work.
Search for more papers by this authorXiao-li Ren
National Key Laboratory of Green Pesticide, Key Laboratory of Green Pesticide and Agricultural Bioengineering, Ministry of Education, Center for R&D of Fine Chemicals of Guizhou University, Guiyang, 550025 China
Search for more papers by this authorChang-kun Li
National Key Laboratory of Green Pesticide, Key Laboratory of Green Pesticide and Agricultural Bioengineering, Ministry of Education, Center for R&D of Fine Chemicals of Guizhou University, Guiyang, 550025 China
Search for more papers by this authorLin-hong Jin
National Key Laboratory of Green Pesticide, Key Laboratory of Green Pesticide and Agricultural Bioengineering, Ministry of Education, Center for R&D of Fine Chemicals of Guizhou University, Guiyang, 550025 China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Xia Zhou
- [email protected]
- +86-851-3620-521
National Key Laboratory of Green Pesticide, Key Laboratory of Green Pesticide and Agricultural Bioengineering, Ministry of Education, Center for R&D of Fine Chemicals of Guizhou University, Guiyang, 550025 China
Search for more papers by this authorAbstract
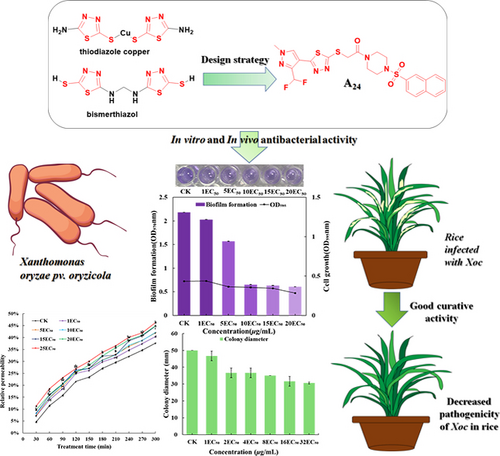
To develop novel bacterial biofilm inhibiting agents, a series of 1,3,4-thiadiazole derivatives containing sulfonylpiperazine structures were designed, synthesized, and characterized using 1H nuclear magnetic resonance (1H NMR), 13C nuclear magnetic resonance (13C NMR), and high-resolution mass spectrometry. Meanwhile, their biological activities were evaluated, and the ensuing structure–activity relationships were discussed. The bioassay results showed the substantial antimicrobial efficacy exhibited by most of the compounds. Among them, compound A24 demonstrated a strong efficacy with an EC50 value of 7.8 μg/mL in vitro against the Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzicola (Xoc) pathogen, surpassing commercial agents thiodiazole copper (31.8 μg/mL) and bismerthiazol (43.3 μg/mL). Mechanistic investigations into its anti-Xoc properties revealed that compound A24 operates by increasing the permeability of bacterial cell membranes, inhibiting biofilm formation and cell motility, and inducing morphological changes in bacterial cells. Importantly, in vivo tests showed its excellent protective and curative effects on rice bacterial leaf streak. Besides, molecular docking showed that the hydrophobic effect and hydrogen-bond interactions are key factors between the binding of A24 and AvrRxo1-ORF1. Therefore, these results suggest the utilization of 1,3,4-thiadiazole derivatives containing sulfonylpiperazine structures as a bacterial biofilm inhibiting agent, warranting further exploration in the realm of agrochemical development.
Graphical Abstract
Conflict of interests
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Open Research
Data Availability Statement
The data that support the findings of this study are available in the supplementary material of this article.
Supporting Information
As a service to our authors and readers, this journal provides supporting information supplied by the authors. Such materials are peer reviewed and may be re-organized for online delivery, but are not copy-edited or typeset. Technical support issues arising from supporting information (other than missing files) should be addressed to the authors.
| Filename | Description |
|---|---|
| cbdv202400408-sup-0001-misc_information.pdf5.3 MB | Supporting Information |
Please note: The publisher is not responsible for the content or functionality of any supporting information supplied by the authors. Any queries (other than missing content) should be directed to the corresponding author for the article.
References
- 1D. O. Niño-Liu, P. C. Ronald, A. J. Bogdanove, Mol. Plant Pathol. 2006, 7(5), 303–24, https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1364-3703.2006.00344.x.
- 2N. Jiang, J. Yan, Y. Liang, Y. Shi, Z. He, Y. Wu, Q. Zeng, X. Liu, J. Peng, Rice 2020, 13(1), 3, https://doi.org/10.1186/s12284-019-0358-y.
- 3T. Liu, J. Shi, D. Liu, D. Zhang, B. Song, D. Hu, J. Agric. Food Chem. 2022, 70(1), 99–110, https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jafc.1c04715.
- 4P.-Y. Wang, M.-W. Wang, D. Zeng, M. Xiang, J.-R. Rao, Q.-Q. Liu, L.-W. Liu, Z.-B. Wu, Z. Li, B.-A. Song, S. Yang, J. Agric. Food Chem. 2019, 67(13), 3535–3545, https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jafc.8b06242.
- 5T. Fujikawa, H. Sawada, Sci. Rep. 2016, 6(1), 21399, https://doi.org/10.1038/srep21399.
- 6H. C. McCann, L. Li, Y. Liu, D. Li, H. Pan, C. Zhong, E. H. A. Rikkerink, M. D. Templeton, C. Straub, E. Colombi, P. B. Rainey, H. Huang, Genome Biol. Evol. 2017, 9(4), 932–944, https://doi.org/10.1093/gbe/evx055.
- 7X. Zou, M. Du, Y. Liu, L. Wu, L. Xu, Q. Long, A. Peng, Y. He, M. Andrade, S. Chen, The Plant Journal 2021, 106(4), 1039–1057, https://doi.org/10.1111/tpj.15217.
- 8E. Shahbaz, M. Ali, M. Shafiq, M. Atiq, M. Hussain, R. M. Balal, A. Sarkhosh, F. Alferez, S. Sadiq, M. A. Shahid, Plants (Basel) 2022, 1(1), https://doi.org/10.3390/plants12010123.
10.3390/plants12010123 Google Scholar
- 9C. Pereira, P. Costa, L. Pinheiro, V. M. Balcão, A. Almeida, Planta 2021, 253(2), 49, https://doi.org/10.1007/s00425-020-03549-1.
- 10F. Doni, M. N. Ishak, N. S. M. Suhaimi, Y. Syaputri, L. Han, Z. Mohamed, M. S. Mispan, Trop. Plant Pathol. 2023, 48(1), 1–10, https://doi.org/10.1007/s40858-022-00540-x.
- 11X. H. Li, J. H. Lee, J. Microbiol. 2017, 55(10), 753–766, https://doi.org/10.1007/s12275-017-7274-x.
- 12R. Mishra, A. K. Panda, S. De Mandal, M. Shakeel, S. S. Bisht, J. Khan, Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 566325, https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2020.566325.
- 13M. Sena-Vélez, C. Redondo, I. Gell, E. Ferragud, E. Johnson, J. H. Graham, J. Cubero, Plant Pathol. 2015, 64(4), 767–775, https://doi.org/10.1111/ppa.12311.
- 14S. Q. An, N. Potnis, M. Dow, F. J. Vorhölter, Y. Q. He, A. Becker, D. Teper, Y. Li, N. Wang, L. Bleris, J. L. Tang, FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2020, 44(1), 1–32, https://doi.org/10.1093/femsre/fuz024.
- 15K. Sauer, P. Stoodley, D. M. Goeres, L. Hall-Stoodley, M. Burmølle, P. S. Stewart, T. Bjarnsholt, Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2022, 20(10), 608–620, https://doi.org/10.1038/s41579-022-00767-0.
- 16X. Li, N. Gu, T. Y. Huang, F. Zhong, G. Peng, Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 1114199, https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2022.1114199.
- 17F. F. Tuon, L. R. Dantas, P. H. Suss, V. S. Tasca Ribeiro, Pathogens (Basel, Switzerland) 2022, 11(3), https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens11030300.
- 18M. T. T. Thi, D. Wibowo, B. H. A. Rehm, Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21(22), https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21228671.
- 19D. Stanley, R. Batacan Jr., Y. S. Bajagai, Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2022, 106(21), 6953–6962, https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-022-12193-6.
- 20A. Mann, K. Nehra, J. S. Rana, T. Dahiya, Current research in microbial sciences 2021, 2, 100030, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.crmicr.2021.100030.
- 21C. Manyi-Loh, S. Mamphweli, E. Meyer, A. Okoh, Molecules 2018, 23(4), https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23040795.
- 22K. Grossmann, T. Ehrhardt, Pest Manage. Sci. 2007, 63(5), 429–39, https://doi.org/10.1002/ps.1341.
- 23P. Devendar, G.-F. Yang, Top. Curr. Chem. 2017, 375(6), 82, https://doi.org/10.1007/s41061-017-0169-9.
10.1007/s41061-017-0169-9 Google Scholar
- 24Y. Zhu, W. Dong, W. Tang, Advanced Agrochem 2022, 1(2), 125–138, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aac.2022.11.004.
10.1016/j.aac.2022.11.004 Google Scholar
- 25J. Yu, X. Jiang, Advanced Agrochem 2023, 2(1), 3–14, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aac.2022.12.003.
10.1016/j.aac.2022.12.003 Google Scholar
- 26K. A. Scott, J. T. Njardarson, Top. Curr. Chem. 2018, 376(1), 5, https://doi.org/10.1007/s41061-018-0184-5.
10.1007/s41061-018-0184-5 Google Scholar
- 27J. He, X.-M. Tang, T.-T. Liu, F. Peng, Q. Zhou, L.-W. Liu, M. He, W. Xue, Chem. Pap. 2021, 75(3), 1021–1027, https://doi.org/10.1007/s11696-020-01363-3.
- 28D. Jiang, J. Zhang, H. He, J. Li, D. Hu, B. Song, Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2021, 53, 128431, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bmcl.2021.128431.
- 29Q. Zhou, X. Tang, S. Chen, W. Zhan, D. Hu, R. Zhou, N. Sun, Y. Wu, W. Xue, J. Agric. Food Chem. 2022, 70(4), 1029–1036, https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jafc.1c05933.
- 30S. Pathania, R. K. Narang, R. K. Rawal, Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2019, 180, 486–508, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejmech.2019.07.043.
- 31A. A. Othman, M. Kihel, S. Amara, Arab. J. Chem. 2019, 12(7), 1660–1675, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arabjc.2014.09.003.
- 32Z. Wu, J. Shi, J. Chen, D. Hu, B. Song, J. Agric. Food Chem. 2021, 69(31), 8660–8670, https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jafc.1c01626.
- 33Q. Wu, H. Cai, T. Yuan, S. Li, X. Gan, B. Song, Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2020, 30(10), 127113, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bmcl.2020.127113.
- 34M. Zhang, W. Xu, K. Wei, H. Liu, Q. Yang, Q. Liu, L. Yang, Y. Luo, W. Xue, J. Heterocycl. Chem. 2019, 56(7), 1966–1977, https://doi.org/10.1002/jhet.3576.
- 35P. Li, L. Shi, M.-N. Gao, X. Yang, W. Xue, L.-H. Jin, D.-Y. Hu, B.-A. Song, Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2015, 25(3), 481–484, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bmcl.2014.12.038.
- 36Y.-T. Li, W.-Q. Yao, S. Zhou, J.-X. Xu, H. Lu, J. Lin, X.-Y. Hu, S.-K. Zhang, Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2021, 34, 127762, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bmcl.2020.127762.
- 37M. Lv, G. Liu, M. Jia, H. Xu, Bioorg. Chem. 2018, 81, 88–92, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bioorg.2018.07.034.
- 38H. Dai, G. Li, J. Chen, Y. Shi, S. Ge, C. Fan, H. He, Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2016, 26(15), 3818–3821, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bmcl.2016.04.094.
- 39X. Gan, D. Hu, Z. Chen, Y. Wang, B. Song, Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2017, 27(18), 4298–4301, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bmcl.2017.08.038.
- 40M. F. Khan, M. M. Alam, G. Verma, W. Akhtar, M. Akhter, M. Shaquiquzzaman, Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2016, 120, 170–201, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejmech.2016.04.077.
- 41J. V. Faria, P. F. Vegi, A. G. C. Miguita, M. S. dos Santos, N. Boechat, A. M. R. Bernardino, Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2017, 25(21), 5891–5903, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bmc.2017.09.035.
- 42B.-L. Wang, H.-W. Zhu, Y. Ma, L.-X. Xiong, Y.-Q. Li, Y. Zhao, J.-F. Zhang, Y.-W. Chen, S. Zhou, Z.-M. Li, J. Agric. Food Chem. 2013, 61(23), 5483–5493, https://doi.org/10.1021/jf4012467.
- 43H. Song, Y. Liu, L. Xiong, Y. Li, N. Yang, Q. Wang, J. Agric. Food Chem. 2013, 61(37), 8730–8736, https://doi.org/10.1021/jf402719z.
- 44H. Dai, J. Chen, G. Li, S. Ge, Y. Shi, Y. Fang, Y. Ling, Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2017, 27(4), 950–953, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bmcl.2016.12.083.
- 45B. Yu, S. Zhou, L. Cao, Z. Hao, D. Yang, X. Guo, N. Zhang, V. A. Bakulev, Z. Fan, J. Agric. Food Chem. 2020, 68(27), 7093–7102, https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jafc.0c00062.
- 46Y. Zhao, A. Zhang, X. Wang, K. Tao, H. Jin, T. Hou, J. Agric. Food Chem. 2022, 70(42), 13464–13472, https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jafc.2c00748.
- 47Y. An, G. Xu, M. Cai, S. Wang, X. z. Wang, Y. Chen, L. Dai, Tetrahedron 2021, 79, 131829, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tet.2020.131829.
- 48Y. Yin, S. Sha, X. Wu, S.-F. Wang, F. Qiao, Z.-C. Song, H.-L. Zhu, Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2019, 182, 111630, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejmech.2019.111630.
- 49X.-D. Yin, K.-Y. Ma, Y.-L. Wang, Y. Sun, X.-F. Shang, Z.-M. Zhao, R.-X. Wang, Y.-J. Chen, J.-K. Zhu, Y.-Q. Liu, J. Agric. Food Chem. 2020, 68(40), 11096–11104, https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jafc.0c01322.
- 50M. Ding, S. Wan, N. Wu, Y. Yan, J. Li, X. Bao, J. Agric. Food Chem. 2021, 69(50), 15084–15096, https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jafc.1c02144.
- 51J. Zhou, Q.-Q. Tao, P.-Y. Wang, W.-B. Shao, Z.-B. Wu, Z. Li, S. Yang, Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2018, 28(10), 1742–1746, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bmcl.2018.04.034.
- 52S. Wang, J. Chen, J. Shi, Z. Wang, D. Hu, B. Song, J. Agric. Food Chem. 2021, 69(40), 11804–11815, https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jafc.1c03087.
- 53Q. Han, C. Zhou, S. Wu, Y. Liu, L. Triplett, J. Miao, J. Tokuhisa, L. Deblais, H. Robinson, Jan E. Leach, J. Li, B. Zhao, Structure 2015, 23(10), 1900–1909, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.str.2015.06.030.
- 54L. Zou, C. Zhang, Y. Li, X. Yang, Y. Wang, Y. Yan, R. Yang, M. Huang, F. Haq, C. H. Yang, G. Chen, Mol. Plant Pathol. 2021, 22(4), 480–492, https://doi.org/10.1111/mpp.13033.