One Pot Synthesis and Biological Activity Studies of New Spirooxindoles
Abstract
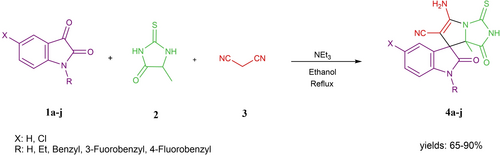
This article reports one-pot synthesis of ten novel spirooxindoles using 5-methyl-2-thiohydantoin, isatin derivatives, and malononitrile in good to high yields (65-90 %). The structures of the synthesized compounds were deduced by 1H-NMR, 13C NMR, FT-IR, and Mass spectral data. The antibacterial activity of the compounds was evaluated against two Gram-positive bacteria (Staphylococcus aureus and Bacillus subtilis) and two Gram-negative bacteria (Escherichia coli and Pseudomonas aeruginosa) based on the Kirby-Bauer method. According to the obtained data, the synthesized compounds show more activity against Gram-positive bacteria than Gram-negative bacteria. Also, the antioxidant activity of these compounds was measured using the DPPH radical scavenging test method, which showed good to excellent activity (59.65–94.03 %). Among them, the chlorinated derivatives (4 f–j) exhibited more antioxidant activity (84.85–94.03 %) than the other compounds (4 a–e) (56.65–74.4 %) and even ascorbic acid as a standard antioxidant compound (82.3 %).
Graphical Abstract
Conflict of interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Open Research
Data Availability Statement
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.