Towards High-Performance Aqueous Zn-Organic Batteries via Using I−-Based Active Electrolyte
Corresponding Author
Lei Yan
School of Materials Science and Chemical Engineering, Ningbo University, Ningbo, Zhejiang, 315211 China
E-mail: [email protected]; [email protected]
Search for more papers by this authorLei Liu
School of Materials Science and Chemical Engineering, Ningbo University, Ningbo, Zhejiang, 315211 China
Search for more papers by this authorChaoyi Qiu
School of Materials Science and Chemical Engineering, Ningbo University, Ningbo, Zhejiang, 315211 China
Search for more papers by this authorYutian Xiang
School of Materials Science and Chemical Engineering, Ningbo University, Ningbo, Zhejiang, 315211 China
Search for more papers by this authorHaoxiang Yu
School of Materials Science and Chemical Engineering, Ningbo University, Ningbo, Zhejiang, 315211 China
Search for more papers by this authorLiyuan Zhang
School of Materials Science and Chemical Engineering, Ningbo University, Ningbo, Zhejiang, 315211 China
Search for more papers by this authorTing-Feng Yi
Key Laboratory of Dielectric and Electrolyte Functional Material Hebei Province, School of Resources and Materials, Northeastern University at Qinhuangdao, Qinhuangdao, 066004 China
Search for more papers by this authorYonggang Wang
Department of Chemistry and Shanghai Key Laboratory of Molecular Catalysis and Innovative Materials, Institute of New Energy, iChEM (Collaborative Innovation Center of Chemistry for Energy Materials), Fudan University, Shanghai, 200433 China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Jie Shu
School of Materials Science and Chemical Engineering, Ningbo University, Ningbo, Zhejiang, 315211 China
E-mail: [email protected]; [email protected]
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Lei Yan
School of Materials Science and Chemical Engineering, Ningbo University, Ningbo, Zhejiang, 315211 China
E-mail: [email protected]; [email protected]
Search for more papers by this authorLei Liu
School of Materials Science and Chemical Engineering, Ningbo University, Ningbo, Zhejiang, 315211 China
Search for more papers by this authorChaoyi Qiu
School of Materials Science and Chemical Engineering, Ningbo University, Ningbo, Zhejiang, 315211 China
Search for more papers by this authorYutian Xiang
School of Materials Science and Chemical Engineering, Ningbo University, Ningbo, Zhejiang, 315211 China
Search for more papers by this authorHaoxiang Yu
School of Materials Science and Chemical Engineering, Ningbo University, Ningbo, Zhejiang, 315211 China
Search for more papers by this authorLiyuan Zhang
School of Materials Science and Chemical Engineering, Ningbo University, Ningbo, Zhejiang, 315211 China
Search for more papers by this authorTing-Feng Yi
Key Laboratory of Dielectric and Electrolyte Functional Material Hebei Province, School of Resources and Materials, Northeastern University at Qinhuangdao, Qinhuangdao, 066004 China
Search for more papers by this authorYonggang Wang
Department of Chemistry and Shanghai Key Laboratory of Molecular Catalysis and Innovative Materials, Institute of New Energy, iChEM (Collaborative Innovation Center of Chemistry for Energy Materials), Fudan University, Shanghai, 200433 China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Jie Shu
School of Materials Science and Chemical Engineering, Ningbo University, Ningbo, Zhejiang, 315211 China
E-mail: [email protected]; [email protected]
Search for more papers by this authorGraphical Abstract
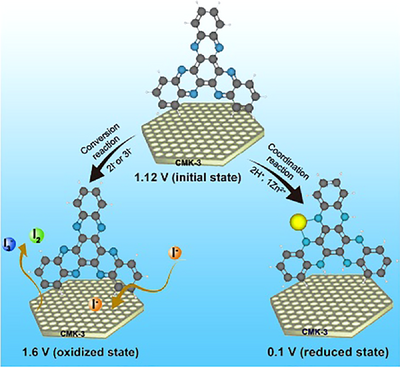
A high-performance Zn-organic battery (Zn//HATN@CMK-3 battery) is developed by using an I−-based active cathodic electrolyte. Benefiting from the high redox potential of the I−/I0 redox couple, the Zn//HATN@CMK-3 cell harvests a high average discharge voltage (0.75 V vs. Zn/Zn2+) and outstanding cycling stability at a high mass-loading (10 mg cm−2).
Abstract
Organic cathodes possess inherent structural diversity and fast redox kinetics, showing great application prospects in aqueous Zn batteries. Nevertheless, most of the reported organic cathodes display low average working voltage resulting in poor energy density. Herein, diquinoxalino [2,3-a:2′,3′-c] phenazine (HATN)@CMK-3 composite is utilized as cathode for aqueous zinc battery, which combines the Zn2+ and H+ co-storage and I−/I0 conversion by introducing I−-based active additive into 0.5 M Zn(OTf)2 electrolyte. The in situ/ex situ analyses and computational studies disclose that HATN@CMK-3 with C═N groups not only stores Zn2+ and H+ ions at low potential but also acts as a substrate to promote the conversion reaction of I−/I0 at high potential. Accordingly, the Zn//HATN@CMK-3 cell delivers a high average voltage of 0.75 V, prominent long-life (10 000 cycles) and, high energy density (198 Wh kg−1). Remarkably, under high mass loading (10 mg cm−2) or low-temperature conditions, the cell still achieves decent capacity and cycle stability.
Conflict of Interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Open Research
Data Availability Statement
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
Supporting Information
| Filename | Description |
|---|---|
| anie202506466-sup-0001-SuppMat.docx3.3 MB | Supporting Information |
Please note: The publisher is not responsible for the content or functionality of any supporting information supplied by the authors. Any queries (other than missing content) should be directed to the corresponding author for the article.
References
- 1J. F. Parker, C. N. Chervin, I. R. Pala, M. Machler, M. F. Burz, J. W. Long, D. R. Rolison, Science 2017, 356, 415–418.
- 2X. Y. Wu, Y. K. Xu, C. Zhang, D. P. Leonard, A. Markir, J. Lu, X. L. Ji, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2019, 141, 6338–6344.
- 3F. Wang, O. Borodin, T. Gao, X. L. Fan, W. Sun, F. D. Han, A. Faraone, J. A. Dura, K. Xu, C. S. Wang, Nat. Mater. 2018, 17, 543–549.
- 4Q. Li, A. Chen, D. Wang, Y. Zhao, X. Wang, X. Jin, B. Xiong, C. Zhi, Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 3699.
- 5H. Yu, Y. Zeng, N. W. Li, D. Luan, L. Yu, X. W. Lou, Sci. Adv. 2022, 8, eabm5766.
- 6D. Han, C. Cui, K. Zhang, Z. Wang, J. Gao, Y. Guo, Z. Zhang, S. Wu, L. Yin, Z. Weng, F. Kang, Q. H. Yang, Nat. Sustain. 2022, 5, 205–213.
- 7J. X. Zheng, D. C. Bock, T. Tang, Q. Zhao, J. F. Yin, K. R. Tallman, G. Wheeler, X. T. Liu, Y. Deng, S. Jin, A. C. Marschilok, E. S. Takeuchi, K. J. Takeuchi, L. A. Archer, Nat. Energy. 2021, 6, 398–406.
- 8Y. Liang, H. Dong, D. Aurbach, Y. Yao, Nat. Energy. 2020, 5, 646–656.
- 9D. J. Dong, T. R. Wang, Y. Sun, J. Fan, Y. C. Lu, Nat. Sustain. 2023, 6, 1474–1484.
- 10Y. Yuan, R. Sharpe, K. He, C. Li, M. T. Saray, T. Liu, W. Yao, M. Cheng, H. Jin, S. Wang, K. Amine, R. Shahbazian-Yassar, M. S. Islam, J. Lu, Nat. Sustain. 2022, 5, 890–898.
- 11J. Huang, Z. Wang, M. Hou, X. Dong, Y. Liu, Y. Wang, Y. Xia, Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 2906.
- 12H. F. Liang, Z. Cao, F. W. Ming, W. L. Zhang, D. H. Anjum, Y. Cui, L. Cavallo, H. N. Alshareef, Nano Lett. 2019, 19, 3199–3206.
- 13L. L. Wang, K.-W. Huang, J. T. Chen, J. R. Zheng, Sci. Adv. 2019, 5, eaax4279.
- 14H. Jiang, L. Tang, Y. Fu, S. Wang, S. K. Sandstrom, A. M. Scida, G. Li, D. Hoang, J. J. Hong, N.-C. Chiu, K. C. Stylianou, W. F. Stickle, D. Wang, J. Li, P. A. Greaney, C. Fang, X. Ji, Nat. Sustain. 2023, 6, 806–815.
- 15L. Y. Zhang, L. Chen, X. F. Zhou, Z. P. Liu, Adv. Energy Mater. 2015, 5, 1400930.
- 16T. H. Wang, J. T. Jin, X. D. Zhao, X. H. Qu, L. F. Jiao, Y. C. Liu, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2024, 63, 202412057.
- 17T. P. Nguyen, A. D. Easley, N. Kang, S. Khan, S.-M. Lim, Y. H. Rezenom, S. Wang, D. K. Tran, J. Fan, R. A. Letteri, X. He, L. Su, C.-H. Yu, J. L. Lutkenhaus, K. L. Wooley, Nature 2021, 593, 61–66.
- 18Y. Lu, J. Chen, Nat. Rev. Chem. 2020, 4, 127–142.
- 19J. Kim, Y. Kim, J. Yoo, G. Kwon, Y. Ko, K. Kang, Nat. Rev. Mater. 2022, 8, 54–70.
- 20D. J. Kim, D.-J. Yoo, M. T. Otley, A. Prokofjevs, C. Pezzato, M. Owczarek, S. J. Lee, J. W. Choi, J. F. Stoddart, Nat. Energy. 2019, 4, 51–59.
- 21Y. Chen, J. Li, Q. Zhu, K. Fan, Y. Cao, G. Zhang, C. Zhang, Y. Gao, J. Zou, T. Zhai, C. Wang, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2022, 61, e202116289.
- 22Z. Tie, L. Liu, S. Deng, D. Zhao, Z. Niu, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2020, 59, 4920–4924.
- 23Z. Ye, S. Xie, Z. Cao, L. Wang, D. Xu, H. Zhang, J. Matz, P. Dong, H. Fang, J. Shen, M. Ye, Energy Storage Mater. 2021, 37, 378–386.
- 24S. Li, J. Shang, M. Li, M. Xu, F. Zeng, H. Yin, Y. Tang, C. Han, H. M. Cheng, Adv. Mater. 2023, 35, 2207115.
- 25Z. Song, L. Miao, H. Duan, L. Ruhlmann, Y. Lv, D. Zhu, L. Li, L. Gan, M. Liu, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2022, 61, e202208821.
- 26X. Ma, X. Cao, M. Yao, L. Shan, X. Shi, G. Fang, A. Pan, B. Lu, J. Zhou, S. Liang, Adv. Mater. 2022, 34, 2105452.
- 27X. Wang, J. Tang, W. Tang, Adv. Funct. Mater. 2022, 32, 2200517.
- 28J. Yang, H. M. Hua, H. Y. Yang, P. B. Lai, M. H. Zhang, Z. H. Lv, Z. P. Wen, C. C. Li, J. B. Zhao, Y. Yang, Adv. Energy Mater. 2023, 13, 2204005.
- 29Z. W. Tie, Z. Q. Niu, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2020, 59, 21293–21303.
- 30Y.i Zhao, R. Zhou, Z. Song, X. D. Zhang, T. Zhang, A. B. Zhou, F. Wu, R. J. Chen, L. Li, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2022, e202212231.
- 31Y. Wang, C. Wang, Z. Ni, Y. Gu, B. Wang, Z. Guo, Z. Wang, D. Bin, J. Ma, Y. Wang, Adv. Mater. 2020, 32, e2000338.
- 32Z. Guo, Y. Ma, X. Dong, J. Huang, Y. Wang, Y. Xia, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2018, 57, 11737–11741.
- 33H. Zhang, Y. Fang, F. Yang, X. Liu, X. Lu, Energy Environ. Sci. 2020, 13, 2515–2523.
- 34X. Yue, H. Liu, P. Liu, Chem. Commun. 2019, 55, 1647–1650.
- 35W. Wang, V. S. Kale, Z. Cao, Y. Lei, S. Kandambeth, G. Zou, Y. Zhu, E. Abouhamad, O. Shekhah, L. Cavallo, M. Eddaoudi, H. N. Alshareef, Adv. Mater. 2021, 33, 2103617.
- 36Q. Wang, X. Xu, G. Yang, Y. Liu, X. Yao, Chem. Commun. 2020, 56, 11859–11862.
- 37C. Mirle, V. Medabalmi, K. Ramanujam, ACS Appl. Energy Mater. 2021, 4, 1218–1227.
- 38H. Y. Shi, Y. J. Ye, K. Liu, Y. Song, X. Sun, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2018, 57, 16359–16363.
- 39K. W. Nam, H. Kim, Y. Beldjoudi, T. W. Kwon, D. J. Kim, J. F. Stoddart, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2020, 142, 2541–2548.
- 40Y. Zhang, Y. Liang, H. Dong, X. Wang, Y. Yao, J. Electrochem. Soc. 2020, 167, 070558.
- 41J. Xie, F. Yu, J. Zhao, W. Guo, H.-L. Zhang, G. Cui, Q. Zhang, Energy Storage Mater. 2020, 33, 283–289.
- 42W. Wang, V. S. Kale, Z. Cao, S. Kandambeth, W. Zhang, J. Ming, P. T. Parvatkar, E. Abou-Hamad, O. Shekhah, L. Cavallo, M. Eddaoudi, H. N. Alshareef, ACS Energy Lett. 2020, 5, 2256–2264.
- 43Q. Wang, Y. Liu, P. Chen, J. Power Sources. 2020, 468, 228401.
- 44Y. Gao, G. Li, F. Wang, J. Chu, P. Yu, B. Wang, H. Zhan, Z. Song, Energy Storage Mater. 2021, 40, 31.
- 45Z. Lin, H. Y. Shi, L. Lin, X. Yang, W. Wu, X. Sun, Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 4424.
- 46Q. Zhao, W. W. Huang, Z. Q. Luo, L. J. Liu, Y. Lu, Y. X. Li, L. Li, J. Y. Hu, H. Ma, J. Chen, Sci. Adv. 2018, 4, eaao1761.
- 47H. J. Zhu, L. Peng, F. Y. Kang, C. Y. Zhi, C. Yang, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2024, 146, 23786–23796.
- 48Q. Liu, Y. Wang, X. Yang, D. Zhou, X. Wang, P. Jaumaux, F. Kang, B. Li, X. Ji, G. Wang, Chem 2021, 7, 1993–2021.
- 49M. M. Wang, Y. H. Meng, M. Sajid, Z. H. Xie, P. Y. Tong, Z. T. Ma, K. Zhang, D. Y. Shen, R. H. Luo, L. Song, L. H. Wu, X. S. Zheng, X. Y. Li, W. Chen, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2024, 63, e202404784.
- 50Z. H. Chen, F. F. Wang, R. L. Ma, W. Y. Jiao, D. Y. Li, A. Du, Z. J. Yan, T. Y. Yin, X. J. Yin, Q. Li, X. Zhang, N. J. Yang, Z. Zhou, Q. H. Yang, C. P. Yang, ACS Energy Lett. 2024, 9, 2858–2866.
- 51L. Y. Hu, C. L. Dai, Y. D. Zhu, X. Hou, Z. M. Liu, X. Geng, H. L. Wang, J. Chen, N. Sun, Q. L. Rong, Y. H. Zhu, X. He, Y. J. Lin, Energy Environ. Sci. 2024, 17, 5552–5562.
- 52L. J. Gao, Z. X. Li, Y. P. Zou, S. F. Yin, P. Peng, Y. Y. Shao, X. Liang, iScience. 2020, 23, 101348.
- 53X. L. Li, S. X. Wang, D. C. Zhang, P. Li, Z. Chen, A. Chen, Z. D. Huang, G. J. Liang, A. L. Rogach, C. Y. Zhi, Adv. Mater. 2024, 36, 2304557.
- 54F. L. Zhu, Z. Q. Li, Z. J. Wang, Y. Z. Fu, W. Guo, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2024, 146, 11193.
- 55K. Li, Z. Y. Hu, J. Z. Ma, S. Chen, D. X. Mu, J. T. Zhang, Adv. Mater. 2019, 31, 1902399.
- 56Z. S. Zhang, Y. L. Zhu, M. Yu, Y. Jiao, Y. Huang, Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 6489.
- 57H. Chen, X. Li, K. Q. Fang, H. Y. Wang, J. Q. Ning, Y. Hu, Adv. Energy Mater. 2023, 13, 2302187.
- 58W. Z. Gao, S. T. Cheng, Y. X. Zhang, E. Q. Xie, J. C. Fu, Adv. Funct. Mater. 2023, 33, 2211979.
- 59F. F. Wang, W. B. Liang, X. Y. Liu, T. Y. Yin, Z. H. Chen, Z. J. Yan, F. B. Li, W. Liu, J. Lu, C. P. Yang, Q.-H. Yang, Adv. Energy Mater. 2024, 14, 2400110.
- 60N. Wang, Z. W. Guo, Z. G. Ni, J. Xu, X. Qiu, J. Ma, P. Wei, Y. G. Wang, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2021, 60, 20826–20832.
- 61M. H. Yu, N. Chandrasekhar, R. K. M. Raghupathy, K. H. Ly, H. Z. Zhang, E. Dmitrieva, C. L. Liang, X. H. Lu, T. D. Kühne, H. Mirhosseini, I. M. Weidinger, X. L. Feng, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2020, 142, 19570–19578.
- 62S. B. Zheng, D. J. Shi, D. Yan, Q. R. Wang, T. J. Sun, T. Ma, L. Li, D. He, Z. L. Tao, J. Chen, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2022, 61, e202117511.
- 63F. Wan, L. L. Zhang, X. Y. Wang, S. S. Bi, Z. Q. Niu, J. Chen, Adv. Funct. Mater. 2018, 28, 1804975.
- 64H. Glatz, E. Lizundia, F. Pacifico, D. Kundu, ACS Appl. Energy Mater. 2019, 2, 1288.
- 65J. Xie, F. Yu, J. W. Zhao, W. Guo, H.-L. Zhang, G. L. Cui, Q. C. Zhang, Energy Storage Mater. 2020, 33, 283–289.
- 66D. Kundu, P. Oberholzer, C. Glaros, A. Bouzid, E. Tervoort, A. Pasquarello, M. Niederberger, Chem. Mater. 2018, 30, 3874–3881.
- 67C. C. Li, L. Hu, X. Y. Ren, L. Lin, C. Z. Zhan, Q. S. Weng, X. Q. Sun, X. L. Yu, Adv. Funct. Mater. 2024, 34, 2313241.
- 68D. Kundu, B. D. Adams, V. Duffort, S. H. Vajargah, L. F. Nazar, Nat. Energy. 2016, 1, 16119.
- 69J. H. Peng, H. H. Sun, M. Y. Wen, Y. M. Chen, Z. X. Luo, Y. Huyan, Y. M. Xue, J.-G. Wang, Nano Lett. 2024, 24, 14941–14949.
- 70Y. Huyan, Z. X. Luo, Z. D. Hou, M. W. Jiang, C. G. Wei, J.-G. Wang, Energy Storage Mater. 2024, 72, 103702.