The Role of Water and Sodium Ions in the Activation of the μ-Opioid Receptor†
We acknowledge financial support from the European Community’s Seventh Framework Program (FP7/2007–2013; grant 211800) and the National Center of Science, Poland (DEC-2011/03/B/NZ1/03204). S.Y. was supported in part by the Swiss Sciex program (grant 11.150). Calculations were done in part at the Interdisciplinary Centre for Mathematical and Computational Modelling in Warsaw (grant G07-13).
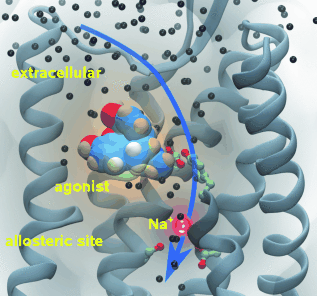
Graphical Abstract
Dual effect of sodium ions: The activation of G-protein-coupled receptors depends on the presence of water molecules inside the receptor and also on allosteric interactions. The binding of sodium ions to the allosteric site of the μ opioid receptor was studied by microsecond molecular dynamics simulations and their seemingly contradictory roles in preventing ligand binding and facilitating receptor activation were explained.