Strophasterols A to D with an Unprecedented Steroid Skeleton: From the Mushroom Stropharia rugosoannulata†
This work was partially supported by the Japan Society for the Promotion of Science, and by a Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research on lnnovative Areas “Chemical Biology of Natural Products” from The Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology (Japan). We also thank T. Nishikawa (Nagoya University) and V. K. Deo (Shizuoka University) for valuable discussions. J.W. is a Research Fellow of the Japan Society for the Promotion of Science (Japan).
Graphical Abstract
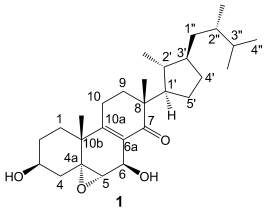
Skeletons in the closet: Four new compounds have been isolated from the title mushroom. The compounds display a new steroid skeleton (e.g., 1) not previously reported for steroids. Preliminary bioactivity tests show that compound 1 can protect neuronal cells by attenuating the endoplasmic reticulum stress, and has weak anti-methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus activity.