Hydroxide Ion Conducting Antimony(V)-Doped Tin Pyrophosphate Electrolyte for Intermediate-Temperature Alkaline Fuel Cells†
Corresponding Author
Prof. Dr. Takashi Hibino
Graduate School of Environmental Studies, Nagoya University, Nagoya 464-8601 (Japan)
Graduate School of Environmental Studies, Nagoya University, Nagoya 464-8601 (Japan)Search for more papers by this authorDr. Yanbai Shen
Graduate School of Environmental Studies, Nagoya University, Nagoya 464-8601 (Japan)
Search for more papers by this authorMasakazu Nishida
Research Institute Instrumentation Frontier, National Institute of Advanced Industrial Science and Technology, Nagoya 463-8560 (Japan)
Search for more papers by this authorDr. Masahiro Nagao
Graduate School of Environmental Studies, Nagoya University, Nagoya 464-8601 (Japan)
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Prof. Dr. Takashi Hibino
Graduate School of Environmental Studies, Nagoya University, Nagoya 464-8601 (Japan)
Graduate School of Environmental Studies, Nagoya University, Nagoya 464-8601 (Japan)Search for more papers by this authorDr. Yanbai Shen
Graduate School of Environmental Studies, Nagoya University, Nagoya 464-8601 (Japan)
Search for more papers by this authorMasakazu Nishida
Research Institute Instrumentation Frontier, National Institute of Advanced Industrial Science and Technology, Nagoya 463-8560 (Japan)
Search for more papers by this authorDr. Masahiro Nagao
Graduate School of Environmental Studies, Nagoya University, Nagoya 464-8601 (Japan)
Search for more papers by this authorThis work was supported by KAKENHI (grant number 21350073).
Graphical Abstract
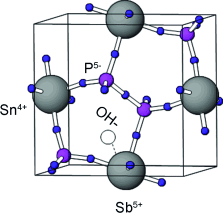
Ion conductor: A series of Sn1–xAxP2O7 (AV=V, Nb, Ta, and Sb) compounds was synthesized, among which Sn0.92Sb0.08P2O7 (see picture) showed the highest hydroxide ion conductivity in the temperature range of 50–200 °C (0.08 S cm−1 at 100 °C and 0.05 S cm−1 at 200 °C). This high conductivity was also confirmed under fuel-cell-operating conditions.
Supporting Information
Detailed facts of importance to specialist readers are published as ”Supporting Information”. Such documents are peer-reviewed, but not copy-edited or typeset. They are made available as submitted by the authors.
| Filename | Description |
|---|---|
| anie_201205022_sm_miscellaneous_information.pdf653.4 KB | miscellaneous_information |
Please note: The publisher is not responsible for the content or functionality of any supporting information supplied by the authors. Any queries (other than missing content) should be directed to the corresponding author for the article.
References
- 1
- 1aJ. R. Varcoe, R. C. T. Slade, Fuel Cells 2005, 5, 187–200;
- 1bG. Merle, M. Wessling, K. Nijmeijer, J. Membr. Sci. 2011, 377, 1–35.
- 2
- 2aJ. R. Varcoe, R. C. T. Slade, G. L. Wright, Y. L. Chen, J. Phys. Chem. B 2006, 110, 21041–21049;
- 2bX. Wu, K. Scott, J. Power Sources 2012, 206, 14–19.
- 3
- 3aK. Asazawa, K. Yamada, H. Tanaka, A. Oka, M. Taniguchi, T. Kobayashi, Angew. Chem. 2007, 119, 8170–8173;
10.1002/ange.200701334 Google ScholarAngew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2007, 46, 8024–8027;
- 3bE. E. Switzer, T. S. Olson, A. K. Datye, P. Atanassov, M. R. Hibbs, C. J. Cornelius, Electrochim. Acta 2009, 54, 989–995.
- 4
- 4aP. Hinksman, D. H. Isaac, P. Morrissey, Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2000, 68, 299–305;
- 4bS. Chempath, J. M. Boncella, L. R. Pratt, N. Henson, B. S. Pivovar, J. Phys. Chem. C 2010, 114, 11977–11983.
- 5
- 5aS. Gu, R. Cai, T. Luo, Z. Chen, M. Sun, Y. Liu, G. He, Y. Yan, Angew. Chem. 2009, 121, 6621–6624; Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2009, 48, 6499–6502;
- 5bH. Zarrin, J. Wu, M. Fowler, Z. W. Chen, J. Membr. Sci. 2012, 394–395, 193–201.
- 6J. H. Jiang, T. Aulich, J. Power Sources 2012, 209, 189–194.
- 7H. S. Kim, Y. Yamazaki, J. D. Kim, T. Kudo, I. Honma, Solid State Ionics 2010, 181, 883–888.
- 8P. K. B. Gover, N. D. Withers, S. Allen, R. L. Withers, J. S. O. Evans, J. Solid State Chem. 2002, 166, 42–48.
- 9
- 9aM. Nagao, A. Takeuchi, P. Heo, T. Hibino, M. Sano, A. Tomita, Electrochem. Solid-State Lett. 2006, 9, A 105–A109;
- 9bX. L. Chen, C. S. Wang, E. A. Payzant, C. R. Xia, D. Chu, J. Electrochem. Soc. 2008, 155, B 1264–B1269;
- 9cS. W. Tao, Solid State Ionics 2009, 180, 148–153;
- 9dS. R. Phadke, C. R. Bowers, E. D. Wachsman, J. C. Nino, Solid State Ionics 2011, 183, 26–31;
- 9eA. Tomita, N. Kajiyama, T. Kamiya, M. Nagao, T. Hibino, J. Electrochem. Soc. 2007, 154, B 1265–B1269;
- 9fK. Genzaki, P. Heo, M. Sano, T. Hibino, J. Electrochem. Soc. 2009, 156, B 806–B810;
- 9gX. Wu, A. Verma, K. Scott, Fuel Cells 2008, 8, 453–458;
- 9hR. Lan, S. W. Tao, J. Alloys Compd. 2009, 486, 380–385;
- 9iH. T. Wang, J. W. Liu, W. B. Wang, G. L. Ma, J. Power Sources 2010, 195, 5596–5600;
- 9jJ. Xiao, H. M. Zhang, Z. J. Yang, H. T. Wang, G. L. Ma, Z. F. Zhou, J. Alloys Compd. 2012, 521, 106–111.
- 10Y. C. Jin, Y. B. Shen, T. Hibino, J. Mater. Chem. 2010, 20, 6214–6217.
- 11R. D. Shannon, Acta. Crystallogr. 1976, 32, 751–767.
- 12B. L. Zhu, C. S. Xie, D. W. Zeng, W. L. Song, A. H. Wang, Mater. Chem. Phys. 2005, 89, 148–153.
- 13J. Sárkány, Appl. Catal. A 2002, 229, 291–312.
- 14K. N. Grew, W. K. S. Chiu, J. Electrochem. Soc. 2010, 157, B 327–B337.
- 15B. M. Lok, B. K. Marcus, C. L. Angell, Zeolites 1986, 6, 185–194.
- 16K. Tadanaga, Y. Furukawa, A. Hayashi, M. Tatsumisago, Adv. Mater. 2010, 22, 4401–4404.
- 17N. Bonanos, B. Ellis, K. S. Knight, M. N. Mahmood, Solid State Ionics 1989, 35, 179–188.