Green Oxidation Catalysts: Computational Design of High-Efficiency Models of Galactose Oxidase†
Leonardo Guidoni Dr.
Institut de chimie moléculaire et biologique Ecole polytechnique fédérale de Lausanne—BCH—LCBC, 1015 Lausanne, Switzerland, Fax: (+41) 21-693-0320
Search for more papers by this authorKatrin Spiegel
Institut de chimie moléculaire et biologique Ecole polytechnique fédérale de Lausanne—BCH—LCBC, 1015 Lausanne, Switzerland, Fax: (+41) 21-693-0320
Present address: Statistical and Biological Physics Sector, International School for Advanced Studies, Via Beirut, 4 34014, Trieste, Italy
Search for more papers by this authorMartin Zumstein
Institut de chimie moléculaire et biologique Ecole polytechnique fédérale de Lausanne—BCH—LCBC, 1015 Lausanne, Switzerland, Fax: (+41) 21-693-0320
Search for more papers by this authorUrsula Röthlisberger Prof. Dr.
Institut de chimie moléculaire et biologique Ecole polytechnique fédérale de Lausanne—BCH—LCBC, 1015 Lausanne, Switzerland, Fax: (+41) 21-693-0320
Search for more papers by this authorLeonardo Guidoni Dr.
Institut de chimie moléculaire et biologique Ecole polytechnique fédérale de Lausanne—BCH—LCBC, 1015 Lausanne, Switzerland, Fax: (+41) 21-693-0320
Search for more papers by this authorKatrin Spiegel
Institut de chimie moléculaire et biologique Ecole polytechnique fédérale de Lausanne—BCH—LCBC, 1015 Lausanne, Switzerland, Fax: (+41) 21-693-0320
Present address: Statistical and Biological Physics Sector, International School for Advanced Studies, Via Beirut, 4 34014, Trieste, Italy
Search for more papers by this authorMartin Zumstein
Institut de chimie moléculaire et biologique Ecole polytechnique fédérale de Lausanne—BCH—LCBC, 1015 Lausanne, Switzerland, Fax: (+41) 21-693-0320
Search for more papers by this authorUrsula Röthlisberger Prof. Dr.
Institut de chimie moléculaire et biologique Ecole polytechnique fédérale de Lausanne—BCH—LCBC, 1015 Lausanne, Switzerland, Fax: (+41) 21-693-0320
Search for more papers by this authorWe are grateful to the Swiss Center for Scientific Computing (Large User Project Grant 2002–2003) for providing computational resources. We thank Prof. H. Grützmacher for stimulating discussions and comments to the manuscript.
Graphical Abstract
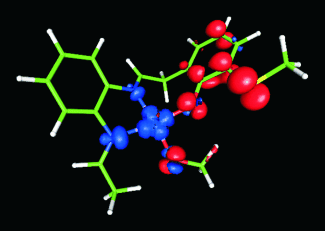
Ab initio calculations were used for the rational design of efficient alcohol oxidation catalysts that mimic the enzyme galactose oxidase. Different ligand substitutions were explored based on natural (copper, depicted) and alternative (rhodium) metal redox centers. The calculated turnover rate for the most efficient copper-based biomimetic compound is greater than that of the natural enzyme.
Supporting Information
Supporting information for this article is available on the WWW under http://www.wiley-vch.de/contents/jc_2002/2004/z54081_s.pdf or from the author.
Please note: The publisher is not responsible for the content or functionality of any supporting information supplied by the authors. Any queries (other than missing content) should be directed to the corresponding author for the article.
References
- 1R. A. Sheldon, I. W. C. E. Arends, G. J. Ten Brink, A. Dijksman, Acc. Chem. Res. 2002, 35, 774–781.
- 2M. A. Halcrow, L. M. L. Chia, X. M. Liu, E. J. L. McInnes, L. J. Yellowlees, F. E. Mabbs, I. J. Scowen, M. McPartlin, J. E. Davies, J. Chem. Soc. Dalton Trans. 1999, 1753–1762.
- 3Y. Shimazaki, S. Huth, A. Odani, O. Yamauchi, Angew. Chem. 2000, 112, 1732–1735;
10.1002/(SICI)1521-3757(20000502)112:9<1732::AID-ANGE1732>3.0.CO;2-X Google ScholarAngew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2000, 39, 1666–1669.10.1002/(SICI)1521-3773(20000502)39:9<1666::AID-ANIE1666>3.0.CO;2-O CAS PubMed Web of Science® Google Scholar
- 4Y. Wang, J. L. DuBois, B. Hedman, K. O. Hodgson, T. D. Stack, Science 1998, 279, 537–540.
- 5R. Pratt, T. D. P. Stack, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2003, 125, 8716–8717.
- 6P. Chaudhuri, M. Hess, U. Flörke, K. Wieghardt, Angew. Chem. 1998, 110, 2340–2343;
10.1002/(SICI)1521-3757(19980817)110:16<2340::AID-ANGE2340>3.0.CO;2-C Google ScholarAngew. Chem. Int. Ed. 1998, 37, 2217–2220.10.1002/(SICI)1521-3773(19980904)37:16<2217::AID-ANIE2217>3.0.CO;2-D CAS PubMed Web of Science® Google Scholar
- 7S. Itoh, M. Taki, S. Takayama, S. Nagatomo, T. Kitagawa, N. Sakurada, R. Arakawa, S. Fukuzumi, Angew. Chem. 1999, 111, 2944–2946;
10.1002/(SICI)1521-3757(19990917)111:18<2944::AID-ANGE2944>3.0.CO;2-F Web of Science® Google ScholarAngew. Chem. Int. Ed. 1999, 38, 2774–2776.10.1002/(SICI)1521-3773(19990917)38:18<2774::AID-ANIE2774>3.0.CO;2-E CAS PubMed Web of Science® Google Scholar
- 8P. Chaudhuri, M. Hess, J. Muller, K. Hildenbrand, E. Bill, T. Weyhermuller, K. Wieghardt, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1999, 121, 9599–9610.
- 9F. Thomas, G. Gellon, I. G. Luneau, E. Saint-Aman, J. L. Pierre, Angew. Chem. 2002, 114, 3173–3176;
Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2002, 41, 3047–3050.
10.1002/1521-3773(20020816)41:16<3047::AID-ANIE3047>3.0.CO;2-W CAS PubMed Web of Science® Google Scholar
- 10P. Chaudhuri, M. Hess, T. Weyhermüller, K. Wieghardt, Angew. Chem. 1999, 111, 1165–1168;
10.1002/(SICI)1521-3757(19990419)111:8<1165::AID-ANGE1165>3.0.CO;2-X Google ScholarAngew. Chem. Int. Ed. 1999, 38, 1095–1098.10.1002/(SICI)1521-3773(19990419)38:8<1095::AID-ANIE1095>3.0.CO;2-I CAS PubMed Web of Science® Google Scholar
- 11R. M. Wachter, B. P. Branchaud, Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1998, 1384, 43–54.
- 12A. J. Baron, C. Stevens, C. Wilmot, K. D. Seneviratne, V. Blakeley, D. M. Dooley, S. E. V. Phillips, P. Knowles, M. J. Mc. Pherson, J. Biol. Chem. 1994, 269, 25 095–25 105.
- 13M. M. Whittaker, D. P. Ballou, J. W. Whittaker, Biochemistry 1998, 37, 8426–8436.
- 14J. W. Whittaker, Chem. Rev. 2003, 103, 2347–2363.
- 15J. Müller, T. Weyhermüller, E. Bill, P. Hildebrandt, L. Ould-Moussa, T. Glaser, K. Wieghardt, Angew. Chem. 1998, 110, 637–640;
Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 1998, 37, 616–619.
10.1002/(SICI)1521-3773(19980316)37:5<616::AID-ANIE616>3.0.CO;2-4 CAS Web of Science® Google Scholar
- 16F. Himo, L. A. Eriksson, F. Maseras, P. E. M. Siegbahn, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2000, 122, 8031–8036.
- 17U. Rothlisberger, P. Carloni, Int. J. Quantum Chem. 1999, 73, 209–218.
- 18U. Rothlisberger, P. Carloni, K. Doclo, M. Parrinello, J. Biol. Inorg. Chem. 2000, 5, 236–250.
- 19L. Guidoni, P. Maurer, S. Piana, U. Rothlisberger, Quant. Struct. Act. Relat. 2002, 21, 173–181.
- 20CPMD V3.7 Copyright IBM Corp 1990–2003, Copyright MPI fuer Festkoerperforschung Stuttgart, 1997.
- 21G. T. Velde, F. M. Bickelhaupt, E. J. Baerends, C. F. Guerra, S. J. A. Van Gisbergen, J. G. Snijders, T. Ziegler, J. Comput. Chem. 2001, 22, 931–967.
- 22A. D. Becke, Phys. Rev. A 1988, 38, 3098–3100.
- 23C. L. Lee, W. Yang, R. G. Parr, Phys. Rev. B 1988, 37, 785–789.
- 24B. Ensing, E. J. Meijer, P. E. Blochl, E. J. Baerends, J. Phys. Chem. A 2001, 105, 3300–3310.