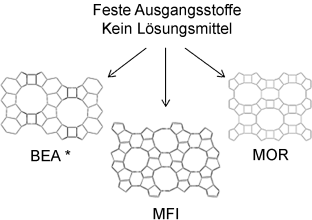
Graphical Abstract
Kein Lösungsmittel bedeutet kein Lösungsmittelabfall und keine Wiederaufbereitungskosten, weshalb derzeit ein großes Interesse an der Entwicklung von lösungsmittelfreien Methoden besteht. In einer neueren Studie wurden verschiedene Zeolithe durch das Vermahlen der trockenen Ausgangsstoffe und Erhitzen auf 180 °C synthetisiert. Die Methode könnte zu erheblichen Einsparungen in der Zeolithsynthese führen.