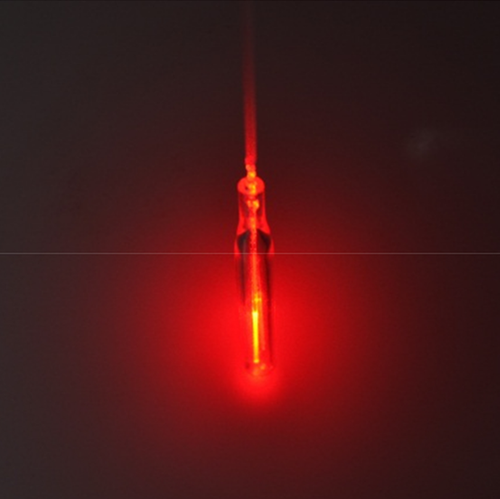
Endoluminal application of glass-capped diffuser for ex vivo endovenous photocoagulation
Corresponding author: e-mail: [email protected]
Abstract
Endovenous laser ablation (EVLA) has frequently been used to treat varicose veins for 20 years. In spite of 90˜95% occlusion rates, clinical complications such as burn and ecchymosis still occur due to excessive thermal injury to perivenous tissue. In the current study, a glass-capped diffusing applicator is designed to validate the feasibility of EVLA as an effective therapeutic device by applying circumferential light distribution. The proposed device is evaluated with a flat fiber as a reference in terms of temperature elevation, fiber degradation, and degree of coagulative necrosis after 532 nm-assisted EVLA at 100 J/cm. The diffusing fiber generates a 40% lower maximum temperature with a 90% lower transient temperature change in blood, compared to the flat fiber. Due to low irradiance (13.5 kW/cm2) and wide light distribution, the diffuser tip experiences no significant thermal degradation while severe carbonization occurs at the flat fiber tip. Ex vivo tissue tests verify that the diffusing fiber induces circumferential and consistent tissue denaturation to the vein wall (107.8 ± 7.8 µm) along with 19% vessel shrinkage. The proposed glass-capped diffusing applicator can be a feasible therapeutic device for EVLA with minimal complications by entailing low maximum temperatures and uniform tissue denaturation in the venous tissue.