Neurogenic pulmonary edema caused by right insular cortex infarction
Abstract
We report a case of neurogenic pulmonary edema (NPE) caused by middle cerebral artery infarction involving the right insular cortex. Hyperactivity of the insular cortex, which regulates sympathetic function, can cause NPE. The NPE should be considered in the differential diagnosis of dyspneic patients with insular cortex infarction.
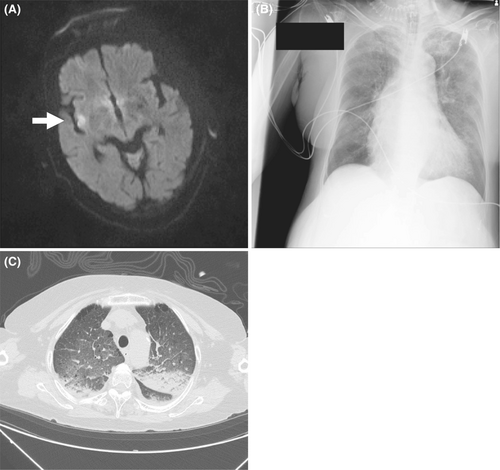
A 77-year-old woman presented in the emergency room with sudden left face and arm paralysis. A brain magnetic resonance imaging scan showed acute cerebral infarction in the right insular cortex (Figure 1A). During the scan, blood pressure was markedly elevated at 194/157 mmHg with atrial fibrillation at 181 beats/min. We observed acute dyspnea with hypoxemia, and urgently endotracheally intubated the patient. Chest X-ray and computed tomography showed bilateral pulmonary edema (Figure 1B,C). Additionally, echocardiography revealed no obvious heart failure signs. Based on the above findings, we made a diagnosis of neurogenic pulmonary edema (NPE). On the second day, chest X-ray showed marked pulmonary edema improvement, and the patient was extubated on the fourth day. NPE is a life-threatening complication that develops rapidly after a serious injury to the central nervous system.1 It is an acute respiratory disease in conjunction with severe neurological damage most often associated with subarachnoid hemorrhage. It has been proposed to stem from sympathetic hyperactivity leading to cardiopulmonary dysfunction.1 Sympathetic hyperactivity is thought to increase the release of catecholamines from peripheral sympathetic nerve endings, which can cause systemic vasoconstriction and the pooling of the blood from systemic circulation to the pulmonary circulation. This change is presumed to elicit an increase in the pulmonary capillary hydrostatic pressure and the leakage of intravascular fluid to the lung interstitial and alveolar space. Cerebral infarction that causes NPE is rare but includes brain stem infarction. The insular cortex plays a critical role in controlling the central autonomic nervous function that regulates cardiovascular system. The insular cortex damage is often associated with arrhythmia, myocardial dysfunction, and sympathetic activity dysregulation. Interestingly, a previous study in epileptic patients undergoing intraoperative insular stimulation prior temporal lobectomy for seizure control has shown that right insula stimulation, which is the infarcted lesion in this case, provokes sympathetic cardiovascular effects. On the contrary, left insula stimulation caused parasympathetic effects.2 Another study assessing sympathetic activity in ischemic insular versus non-insular cortex infarction has shown that plasma norepinephrine and epinephrine concentrations were significantly higher in the former than in latter with most prominent elevation in right insular cortex infarction.3 These findings indicated a hemispheric lateralization in sympathetic autonomic activity, which was mediated by the right-sided insular cortex. Hence, we could conclude that sympathetic hyperactivity due to right insular cortex injury caused NPE in this case. The NPE should be considered in the differential diagnosis of dyspneic patients with cerebral infarction involving the insular cortex.
AUTHOR CONTRIBUTIONS
AT and KA wrote the first draft. KT, YT, YW, TK, KY, and HN revised the manuscript. All the authors have contributed to the case management.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT
The authors declare no relevant acknowledgments.
FUNDING INFORMATION
No sources of funding were used.
CONFLICT OF INTEREST
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
CONSENT
Written consent from the patient was obtained for submission and publication of the case details and images from the patient.
Open Research
DATA AVAILABILITY STATEMENT
The data supporting the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon request; they are not publicly available due to privacy or ethical restrictions.