Radiological manifestation of optic nerve infarction in a patient with invasive mucormycosis secondary to diabetic ketoacidosis in Pakistan
Abstract
A 35 years old male patient presented in the hospital with complaints of left-sided facial swelling, blindness in the left eye, and left eye proptosis. He had a concomitant history of diabetic ketoacidosis. Magnetic resonance imaging was advised, which revealed infected tissue of the left cheek, optic nerve infarction, intracranial extension, and leptomeningeal involvement by the disease process.
1 CLINICAL IMAGE AND DESCRIPTION
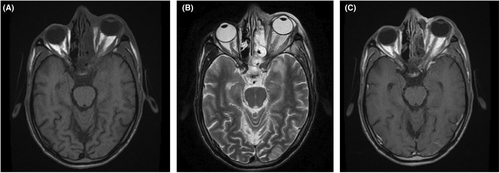
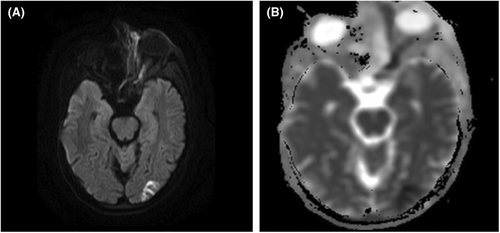
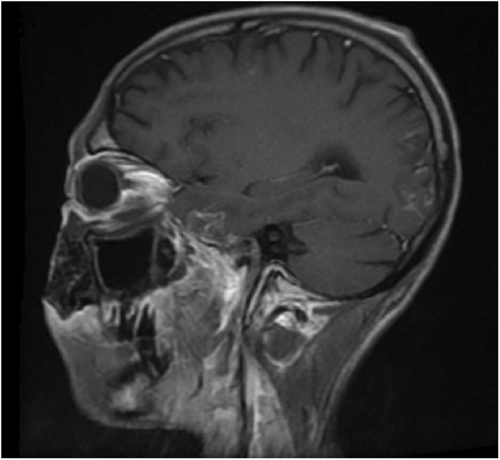
A 35 years old male patient presented in the hospital with complaints of left-sided facial swelling, blindness in the left eye, and left eye proptosis. He had a concomitant history of diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA). Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) was advised. MRI findings were suggestive of rhino occulo cerebral mucormycosis. Mucor, a fungus, can lead to deadly infection of the paranasal sinuses, eventually involving the orbit and brain.1 There were only limited cases of diffusion-weighted MRI demonstrating ischemic optic neuropathy when the literature was scoured.2 Figures 1-3 with description provide a comprehensive illustration.
AUTHOR CONTRIBUTIONS
Shehroze Tabassum: Conceptualization; writing – original draft; writing – review and editing. Aroma Naeem: Writing – original draft. Afshan Shakir: Writing – original draft; writing – review and editing. Faiza Afzal: Writing – original draft. Laya Ohadi: Writing – original draft.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT
None.
CONFLICT OF INTEREST
None.
CONSENT
Written informed consent was obtained from the patient for publication of this image report in accordance with journal's patient consent policy.
Open Research
DATA AVAILABILITY STATEMENT
The data and materials used in the current study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.