Generative Pre-Trained Transformer 4 in healthcare: Challenges, opportunities, and recommendations
Graphical Abstract
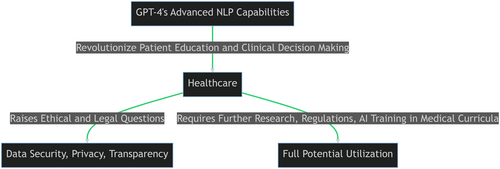
GPT-4's advanced natural language processing capabilities can revolutionize patient education and clinical decision-making in healthcare, providing personalized and easily accessible content. Despite its potential, GPT-4's integration into healthcare raises important ethical and legal questions, particularly around data security, privacy, and transparency. To fully utilize GPT-4 in healthcare, further research, comprehensive regulations, and AI training in medical curricula are recommended.
Abbreviations
-
- AI
-
- Artificial Intelligence
-
- AI-based
-
- Artificial Intelligence-based
-
- COVID-19
-
- Coronavirus disease 2019
-
- EHRs
-
- Electronic Health Records
-
- GPT
-
- Generative Pre-Trained Transformer
-
- NLP
-
- Natural Language Processing
1 INTRODUCTION
Integrating advanced artificial intelligence (AI) systems, such as OpenAI's Generative Pre-Trained Transformer 4 (GPT-4), into the healthcare sector can revolutionize various aspects of medical practice, from patient education to clinical decision-making overall patient care [1]. GPT-4's superior natural language processing (NLP) capabilities can empower healthcare professionals to make well-informed clinical decisions, enhance patient comprehension and bridge the gap in access and understanding for diverse patient populations, particularly outpatient settings. The transformative potential of GPT-4 in healthcare has its challenges and as the industry moves toward incorporating AI into its practices, addressing concerns related to data security and privacy becomes crucial.
Furthermore, the rapid evolution of AI in medicine highlights the need for a paradigm shift in medical education by incorporating AI training and fostering a comprehensive understanding of its applications and limitations. This article explores the transformative potential of GPT-4's advanced NLP capabilities, highlighting how it can empower healthcare providers to make well-informed clinical decisions, enhance patient comprehension, and bridge access and understanding gaps for diverse patient populations.
2 ENHANCING PATIENT EDUCATION AND CLINICAL DECISION-MAKING
A primary application of GPT-4 lies in patient education. Traditional patient education techniques frequently rely on written materials and verbal instructions, which may make it difficult for patients to comprehend and remember the information. Health communication and information provision account for over 50% of the barriers to providing prevalent chronic illness patients with the best outpatient specialist services [2]. GPT-4 can produce specialized, precise, and easily accessible content, making patient education more exciting and interactive. As a result, the materials produced by GPT-4 can be customized to meet the requirements and comprehension levels of patients with inadequate health literacy. It can serve as a supplemental informational tool for patients and doctors, enhancing outcomes [3].
Medical knowledge of illness and treatment for patients in an outpatient context is a complicated and dynamic process involving numerous players. Patients with complicated care requirements are more at risk of receiving substandard treatment because caregivers may struggle to follow conventional instructions, especially when moving from inpatient to outpatient settings [4]. Additionally, GPT-4 can provide real-time assessments of patient competency and understanding, allowing medical personnel to modify their strategy to meet the needs of each patient. This may lead to better patient outcomes and better general healthcare quality. Healthcare professionals can ensure that patients can better control their health by including GPT-4 in patient education, improving overall health outcomes [5].
Physicians can also supplement their understanding of chronic diseases by utilizing NLP methods, as employed by GPT-4, to analyze electronic health records. GPT-4 can help physicians discover potential health risks and provide more focused, individualized care by evaluating patient data and making real-time suggestions. The potential of GPT-4 in extracting valuable insights from unstructured clinical data can aid in clinical decision-making and possibly prevent or delay the onset of chronic diseases. This can contribute to improved patient outcomes, diminished healthcare expenses, and heightened efficiency within the healthcare system [6].
3 OVERCOMING LANGUAGE AND CULTURAL BARRIERS IN HEALTHCARE
Integrating GPT-4 into telehealth services can significantly improve healthcare accessibility and quality by providing personalized medical support and overcoming language and cultural barriers. GPT-4, the successor to the highly successful GPT-3 language model, has been trained on a vast amount of multicultural data. As a result, it can generate information in multiple languages and consider cultural subtleties, which can help close gaps in healthcare access and comprehension for diverse patient populations.
In areas with poor healthcare access or linguistic challenges, GPT-4-generated content can provide high-quality, easily accessible, and culturally appropriate treatment to patients, regardless of their background or language. Moreover, the recent introduction of GPT-4 integration with plugins such as “Speak” can help overcome linguistic challenges in rural areas with limited resources.
The literature has demonstrated an increased utilization of telemedicine, including language models, due to the COVID-19 pandemic [7, 8]. Given the magnitude of the pandemic, which has been deemed the most catastrophic public health crisis in at least a century, it has highlighted the prospective utility of NLP in alleviating the continuous and long-standing effects of pandemics by effectively harnessing extensive amounts of text-based data that are generated from various sources. However, the practical deployment of NLP systems is accompanied by several challenges that warrant further attention to provide direction for future research initiatives and improve health and social response infrastructures.
4 THE ART OF ASKING QUESTIONS: A CRUCIAL CONSIDERATION FOR GPT-4
A critical aspect of effectively leveraging GPT-4's capabilities involves careful crafting of the questions posed to it. GPT-4's responses can significantly vary based on the phrasing of inquiries, pointing to inherent sensitivity to language nuances. This characteristic necessitates a keen understanding of the art of asking questions. For instance, consider a healthcare provider querying GPT-4 about a medical condition like diabetes. A general, non-specific question such as “What is diabetes?” would yield a broad, general response, possibly defining diabetes and discussing its common symptoms or types. However, if the question is rephrased to “What are the long-term complications of type 2 diabetes?” the response would likely be more detailed and focused on the specific complications of this form of diabetes. Similarly, asking GPT-4 ″What are the treatment options for hypertension?” might elicit a wide range of responses, from lifestyle changes to various medications. But, if the question is refined to “What are the first-line medications for treating hypertension according to the latest guidelines?” The AI model is more likely to generate a narrower and more precise answer listing the recommended first-line medications. These examples underscore the significance of question phrasing when interacting with GPT-4. Diverse phrasing and sentence constructions can lead to varied outputs, highlighting the need for caution and insight when interpreting and applying the model's responses. This is especially important in healthcare, where precision and accuracy are essential.
5 ETHICAL CONSIDERATIONS, HEALTHCARE PROFESSIONAL TRAINING, AND POLICY IMPLICATIONS
However, incorporating GPT-4 into healthcare creates severe ethical and legal questions. For instance, data security and privacy are crucial when working with patient data. Establishing the reliability and accuracy of the information generated by GPT-4 also requires resolving potential biases in the algorithm and maintaining transparency in the decision-making process. Policymakers must address these challenges by developing comprehensive regulations that ensure data protection, algorithmic fairness, and transparency in AI-based healthcare applications [9].
For GPT-4 to be successfully incorporated into healthcare, its personnel must have the proper training and knowledge. The medical curriculum should include AI training focusing on NLP and understanding patient interactions with AI. This can improve patient outcomes while decreasing data security and privacy concerns [10].
Despite its potential benefits, it is vital to note the limitations of GPT-4, particularly in critical fields like healthcare. Known for occasionally generating ‘hallucinations’—plausible but factually incorrect statements—GPT-4 should be used with caution. These inaccuracies underline the need for healthcare professionals to cross-verify any information provided by the AI model and preclude its solitary use for critical medical decision-making without appropriate clinical validation. While GPT-4 demonstrates notable advancements in NLP, its availability to the public is somewhat limited. As of the writing of this commentary, GPT-4 is accessible to ChatGPT Plus subscribers, a $20 monthly subscription service. However, it is essential to highlight that OpenAI continues to support free access to GPT-3.5, albeit with some usage restrictions compared to the subscription version. In the future, this may be subject to change.
6 RECOMMENDATIONS
-
Encouraging further research on the applications, benefits, and limitations of GPT-4 in healthcare.
-
Developing comprehensive regulations to address data security, privacy, and transparency concerns in AI-based healthcare applications.
-
Integrating AI training, with a focus on GPT-4, into medical curricula to prepare healthcare professionals for the future of medicine.

Benefits and challenges of Generative Pre-Trained Transformer 4 (GPT-4) in transforming healthcare.
7 CONCLUSION
To use GPT-4 responsibly in healthcare, professionals, and patients must understand its role. For medical experts, GPT-4 should supplement, not replace, clinical judgment. Its output must be cross-verified with trusted medical resources. On the other hand, patients should view GPT-4 as a source of general health information rather than personalized advice. Responsible GPT-4 usage requires seeing it as an informational tool, not a substitute for professional medical counsel. Always consult a healthcare professional for medical concerns. GPT-4 provides many opportunities to improve patient education and outpatient treatment. However, difficulties with ethics, law, and education must be resolved to integrate successfully. Patient education can advance by incorporating GPT-4 and generative AI to better prepare patients and medical professionals for the continuously changing world of medicine. GPT-4 can change the healthcare industry and improve patient outcomes worldwide with the proper instruction, training, and implementation. By addressing policy and societal implications, GPT-4 has the potential to reshape healthcare and contribute to a more equitable and accessible system for all.
AUTHOR CONTRIBUTION
Hassam Ali: Conceptualization (Equal); Formal analysis (Equal); Funding acquisition (Equal); Methodology (Equal); Project administration (Equal).
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
None.
CONFLICT OF INTEREST STATEMENT
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
ETHICS STATEMENT
Not applicable.
INFORMED CONSENT
Not applicable.
Open Research
DATA AVAILABILITY STATEMENT
Data sharing is not applicable to this article as no data sets were generated or analyzed during the current study.