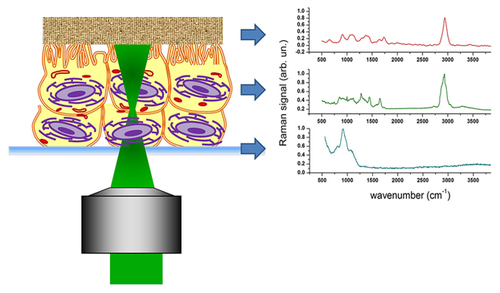
Assessment of conjunctival microvilli abnormality by micro-Raman analysis – by G. Rusciano et al
Corresponding Author
Giulia Rusciano
Department of Physics E. Pancini, University of Naples Federico II, via Cintia, 80126-I Naples, Italy
Corresponding author: e-mail: [email protected]
Search for more papers by this authorGianluigi Zito
Department of Physics E. Pancini, University of Naples Federico II, via Cintia, 80126-I Naples, Italy
Search for more papers by this authorGiuseppe Pesce
Department of Physics E. Pancini, University of Naples Federico II, via Cintia, 80126-I Naples, Italy
Search for more papers by this authorSalvatore Del Prete
Department of Neuroscience and Reproductive Sciences and Odontostomatology, University of Naples Federico II, via Pansini 5, 80131-I Naples, Italy
Search for more papers by this authorGilda Cennamo
Department of Neuroscience and Reproductive Sciences and Odontostomatology, University of Naples Federico II, via Pansini 5, 80131-I Naples, Italy
Search for more papers by this authorAntonio Sasso
Department of Physics E. Pancini, University of Naples Federico II, via Cintia, 80126-I Naples, Italy
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Giulia Rusciano
Department of Physics E. Pancini, University of Naples Federico II, via Cintia, 80126-I Naples, Italy
Corresponding author: e-mail: [email protected]
Search for more papers by this authorGianluigi Zito
Department of Physics E. Pancini, University of Naples Federico II, via Cintia, 80126-I Naples, Italy
Search for more papers by this authorGiuseppe Pesce
Department of Physics E. Pancini, University of Naples Federico II, via Cintia, 80126-I Naples, Italy
Search for more papers by this authorSalvatore Del Prete
Department of Neuroscience and Reproductive Sciences and Odontostomatology, University of Naples Federico II, via Pansini 5, 80131-I Naples, Italy
Search for more papers by this authorGilda Cennamo
Department of Neuroscience and Reproductive Sciences and Odontostomatology, University of Naples Federico II, via Pansini 5, 80131-I Naples, Italy
Search for more papers by this authorAntonio Sasso
Department of Physics E. Pancini, University of Naples Federico II, via Cintia, 80126-I Naples, Italy
Search for more papers by this authorAbstract
Conjunctival microvilli are microscopic cellular membrane protrusions on apical epithelial cells, which increase the surface area available for tear adherence. Pathological alterations of microvilli structure affect the tear film stability and, conversely, dysfunctions of tear film composition can lead to a suffering epithelium (dry-eye syndrome). In this work we propose the use of micro-Raman analysis to reveal conjunctival microvilli abnormalities. Samples were obtained by impression cytology from patients by different stage of dry-eye syndrome. Our experimental outcomes demonstrate that Raman analysis, combined with the use of Principal Component Analysis, is able to detect different stages of microvilli reduction. Globally, these results hold promise for the use of Raman analysis for an objective, effective, non-invasive and potentially also in-vivo analysis of the conjunctiva in all the cases of microvilli-related ocular pathologies.
References
- 1H. J. Davidson and J. K. Vanessa, Vet. Ophthalmol. 7, 71–77 (2004).
- 2M. Meloni, B. De Servi, D. Marasco, and S. Del Prete, Mol. Vis. 17, 113–126 (2011).
- 3H. D. Perry, Am. J. Manag. Care 14, S79–87 (2008).
- 4M. E. Johnson and P. J. Murphy, Prog. Retin. Eye Res. 23, 449–474 (2004).
- 5G. L. Cennamo, A. Del Prete, R. Forte, G. Cafiero, S. Del Prete, and D. Marasco, Eye 22, 138–143 (2008).
- 6D. Zoukhri, Exp. Eye Res. 82, 885–898 (2006).
- 7C. Baudouin, P. Aragona, E. M. Messmer, A. Tomlinson, M. Calonge, K. G. Boboridis, Y. A. Akova, G. Geerling, M. Labetoulle, and M. Rolando, Ocul. Surf. 11, 246–258 (2013).
- 8L. Tong, Z. Chen, C. S. De Paiva, R. Beuerman, D. Q. Li, and S. C. Pflugfelder, Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 47, 4295–4301 (2006).
- 9S. Chotikavanich, C. S. de Paiva, and D. Q. Lee, Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 50, 3203–3209 (2009).
- 10C. S. De Paiva, R. M. Corrales, and A. L. Villarreal, Exp. Eye Res. 83, 526–535 (2006).
- 11G. L. Cennamo, A. Del Prete, R. Forte, G. Cafiero, S. Del Prete, and D. Marasco, Eye 22, 138–143 (2008).
- 12H. Lin and S. C. Yiu, Saudi Journal of Ophthalmology 28, 173–181 (2014).
- 13M. J. Doughty, Curr. Eye Res. 24, 341–353 (2002).
- 14R. De Nicola, A. Labbé, N. Amar, B. Dupas, and C. Baudouin, J. Fr. Ophtalmol. 98, 691–698 (2005).
- 15G. Cennamo, R. Forte, S. Del Prete, and D. Cardone, Cornea 32, 1227–1231 (2013).
- 16G. J. Thomas, Annu Rev Biophys Biomol Struct 28, 1–27 (1999).
- 17J. W. Chan, D. S. Taylor, T. Zwerdling, S. M. Lane, K. Ihara, and T. Huser, Biophys. J. 90, 648–656 (2006).
- 18A. C. De Luca, G. Rusciano, R. Ciancia, V. Martinelli, G. Pesce, B. Rotoli, L. Selvaggi, and A. Sasso, Opt. Express 16, 7943–7957 (2008).
- 19G. Rusciano, A. C. De Luca, G. Pesce, and A. Sasso, Sensors 8, 7818–7832 (2008).
- 20G. Rusciano, G. Pesce, M. Salemme, L. Selvaggi, C. Vaccaro, A. Sasso, and R. Carotenuto, Methods 51, 27–36 (2010).
- 21R. Isticato, T. Sirec, R. Giglio, L. Baccigalupi, G. Rusciano, G. Pesce, G. Zito, A. Sasso, M. De Felice, and E. Ricca, Plos One 8, e74949 (2013).
- 22R. Salzer, G. Steiner, H. H. Mantsch, J. Mansfield, and E. N. Lewis, Anal. Chem. 366, 712–726 (2000).
- 23L. P. Choo-Smoth, H. G. Edwards, H. P. Endtz, J. M. Kros, F. Heule, H. Barr, J. S. Jr Robinson, H. A. Bruining, and G. J. Puppels, Biopolymers 67, 1–9 (2002).
- 24E. B. Hanlon, R. Manoharan, T. W. Koo, K. E. Shafer, J. T. Motz, M. Fitzmaurice, J. R. Kramer, I. Itzkan, R. R. Dasari, and M. S. Feld, Phys. Med. Biol. 45, R1–59 (2000).
- 25R. Malini, K. Venkatakrishna, J. Kurien, K. M. Pai, L. Rao, V. B. Kartha, and C. M. Krishna, Biopolimers 81, 179–193 (2006).
- 26I. A. Boere, T. C. B. Schut, J. van den Boogert, R. W. F. de Bruin, and G. J. Puppels, Vib. Spectrosc. 32, 47–55 (2003).
- 27A. Molckovsky, L. M. Song, M. G. Shim, N. E. Marcon, and B. C. Wilson, Gastrointest. Endosc. 57, 396–402 (2003).
- 28J. W. Chan, D. S. Taylor, S. M. Lane, T. Zwerdling, J. Tuscano, and T. Huser, Anal. Chem. 80, 2180–2187 (2008).
- 29H. Yao, Z. Tao, M. Ai, L. Peng, G. Wang, B. He, and Y. Li, Vib. Spectrosc. 50, 193–197 (2009).
- 30Y. H. Ong, M. Lim, and Q. Liu, Opt. Express 20, 22158–22171 (2012).
- 31A. C. S. Talari, C. A. Evans, I. Holen, R. E. Coleman, and I. U. Rehman, J. Raman Spectrosc. 46, 421–427 (2015).
- 32R. J. Erckens, F. H. M. Jongsma, J. P. Wicksted, F. Hendrikse, W. F. March, M. Motamedi, Lasers Med. Sci. 16, 236–252 (2001).
- 33G. Rusciano, P. Capriglione, G. Pesce, S. Del Prete, G. Cennamo, D. Di Cave, L. Cerulli, and A. Sasso, Plos One 8, e72127-1–8 (2013).
- 34G. Rusciano, Phys. Med. 26, 233–239 (2010).
- 35G. Rusciano, G. Zito, R. Isticato, T. Sirec, E. Ricca, E. Bailo, and A. Sasso, ACS Nano 8, 12300–12309 (2014).
- 36C. Fraley and A. E. Raftery, Journal of the American Statistical Association 97, 611–631 (2002).
- 37A. F. Palonpon, J. Ando, H. Yamakoshi, K. Dodo, M. Sodeoka, S. Kawata, and K. Fujita, Nature Protocols 8, 677–692 (2013).
- 38K. Zhang, A. Feldner, S. Fischer, Cellulose 18, 995–1003 (2011).
- 39 MATLAB and Statistics Toolbox Release 2012b, The MathWorks, Inc., Natick, Massachusetts, United States.