Performance evaluation of automated segmentation software on optical coherence tomography volume data
Jing Tian
Bascom Palmer Eye Institute, University of Miami, 900 NW 17th Street, Miami, FL 33136 United States
Authors contributed equallySearch for more papers by this authorBoglarka Varga
Semmelweis University, 39 Maria Street, 1085 Budapest, Hungary
Search for more papers by this authorErika Tatrai
Semmelweis University, 39 Maria Street, 1085 Budapest, Hungary
Search for more papers by this authorPalya Fanni
Semmelweis University, 39 Maria Street, 1085 Budapest, Hungary
Search for more papers by this authorGabor Mark Somfai
Semmelweis University, 39 Maria Street, 1085 Budapest, Hungary
Search for more papers by this authorWilliam E. Smiddy
Bascom Palmer Eye Institute, University of Miami, 900 NW 17th Street, Miami, FL 33136 United States
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Delia Cabrera Debuc
Bascom Palmer Eye Institute, University of Miami, 900 NW 17th Street, Miami, FL 33136 United States
Authors contributed equallyCorresponding author: e-mail: [email protected]
Search for more papers by this authorJing Tian
Bascom Palmer Eye Institute, University of Miami, 900 NW 17th Street, Miami, FL 33136 United States
Authors contributed equallySearch for more papers by this authorBoglarka Varga
Semmelweis University, 39 Maria Street, 1085 Budapest, Hungary
Search for more papers by this authorErika Tatrai
Semmelweis University, 39 Maria Street, 1085 Budapest, Hungary
Search for more papers by this authorPalya Fanni
Semmelweis University, 39 Maria Street, 1085 Budapest, Hungary
Search for more papers by this authorGabor Mark Somfai
Semmelweis University, 39 Maria Street, 1085 Budapest, Hungary
Search for more papers by this authorWilliam E. Smiddy
Bascom Palmer Eye Institute, University of Miami, 900 NW 17th Street, Miami, FL 33136 United States
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Delia Cabrera Debuc
Bascom Palmer Eye Institute, University of Miami, 900 NW 17th Street, Miami, FL 33136 United States
Authors contributed equallyCorresponding author: e-mail: [email protected]
Search for more papers by this authorAbstract
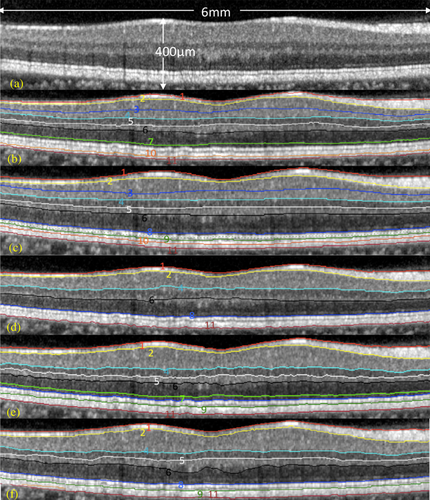
Over the past two decades a significant number of OCT segmentation approaches have been proposed in the literature. Each methodology has been conceived for and/or evaluated using specific datasets that do not reflect the complexities of the majority of widely available retinal features observed in clinical settings. In addition, there does not exist an appropriate OCT dataset with ground truth that reflects the realities of everyday retinal features observed in clinical settings. While the need for unbiased performance evaluation of automated segmentation algorithms is obvious, the validation process of segmentation algorithms have been usually performed by comparing with manual labelings from each study and there has been a lack of common ground truth. Therefore, a performance comparison of different algorithms using the same ground truth has never been performed. This paper reviews research-oriented tools for automated segmentation of the retinal tissue on OCT images. It also evaluates and compares the performance of these software tools with a common ground truth.
Supporting Information
| Filename | Description |
|---|---|
| jbio201500239-sup-0001-author-biographies.pdfPDF document, 183.6 KB | Author Biographies |
| jbio201500239-sup-0002-Video-S1.movQuickTime video, 6.3 MB | Video S1: The example of exported video from Spectralis. The annotated color lines were extracted to form the retinal surfaces. |
| jbio201500239-sup-0003-Data-S2.zipZip archive, 16.5 MB | Data S2: The OCT dataset, segmentation results from five software tools and the manual labeling from two observers. |
Please note: The publisher is not responsible for the content or functionality of any supporting information supplied by the authors. Any queries (other than missing content) should be directed to the corresponding author for the article.
References
- 1D. Huang, E. A. Swanson, C. P. Lin, J. S. Schuman, W. G. Stinson, W. Chang, M. R. Hee, T. Flotte, K. Gregory, C. A. Puliafito, and J. G. Fujimoto, Science 80, 1178–1181 (1991).
- 2A. M. Zysk, F. T. Nguyen, A. L. Oldenburg, D. L. Marks, and S. A. Boppart, J. Biomed. Opt. 12, 051403 (2007).
- 3R. Hamdan, R. G. Gonzalez, S. Ghostine, and C. Caussin, Archives of Cardiovascular Diseases 105, 529–534 (2012).
- 4C. A. Puliafito, Ophthalmic Surg. Lasers Imaging 41, S5 (2010).
- 5J. S. Schuman, C. A. Puliafito, J. G. Fujimoto, and S. D. Jay, Optical Coherence Tomography of Ocular Diseases, 3rd ed. Thorofare: Slack, Inc, 2004.
- 6W. Drexler, Journal of Biomedical Optics 9, 47 (2004).
- 7A. F. Fercher, Z. Med. Phys. 20, 251–76 (2010).
- 8 Biopigen Inc, Envisu C-Class SDOCT System | Bioptigen, Inc. [Online]. Available: http://www.bioptigen.com/products/c-class/ [Accessed: 06-Sep-2015].
- 9 Canon, Canon OCT-HS100 – Eye Care – Canon Europe, 02-Jan-2012. [Online]. Available: http://www.canon-europe.com/medical/eye_care/oct-hs100/ [Accessed: 06-Sep-2015].
- 10 Optovue Inc, iVUE SD-OCT. [Online]. Available: http://optovue.com/wp-content/uploads/2013/08/iVue-Brochure.pdf [Accessed: 06-Sep-2015].
- 11 Heidelberg Engineering GmbH, Spectralis HRA+OCT User Manual Software Version 6.0, 2014.
- 12D. Koozekanani, K. Boyer, and C. Roberts, IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 20, 900–916 (2001).
- 13D. Cabrera Fernández, H. M. Salinas, and C. A. Puliafito, Opt. Express 13, 10200–10216 (2005).
- 14T. Fabritius, S. Makita, M. Miura, R. Myllylä, and Y. Yasuno, Opt. Express 17, 15659–15669 (2009).
- 15M. Shahidi, Z. Wang, and R. Zelkha, Am. J. Ophthalmol. 139, 1056–61 (2005).
- 16H. Ishikawa, D. M. Stein, G. Wollstein, S. Beaton, J. G. Fujimoto, and J. S. Schuman, Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 46, 2012–7 (2005).
- 17G. Gregori and R. W. Knighton, Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 45, 3007 (2004).
- 18M. D. Abràmoff, M. K. Garvin, and M. Sonka, IEEE Rev. Biomed. Eng. 3, 169–208 (2010).
- 19S. J. Chiu, X. T. Li, P. Nicholas, C. A. Toth, J. A. Izatt, and S. Farsiu, Opt. Express 18, 19413–19428 (2010).
- 20M. K. Garvin, M. D. Abràmoff, X. Wu, S. R. Russell, T. L. Burns, and M. Sonka, IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 28, 1436–144 (2009).
- 21A. Lang, A. Carass, M. Hauser, E. S. Sotirchos, P. A. Calabresi, H. S. Ying, and J. L. Prince, Biomed. Opt. Express 4, 1133–52 (2013).
- 22P. A. Dufour, L. Ceklic, H. Abdillahi, S. Schroder, S. De Dzanet, U. Wolf-Schnurrbusch, and J. Kowal, IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 32, 531–543 (2013).
- 23A. Yazdanpanah, G. Hamarneh, B. R. Smith, and M. V. Sarunic, IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 30, 484–96 (2011).
- 24V. Kajić, B. Povazay, B. Hermann, B. Hofer, D. Marshall, P. L. Rosin, and W. Drexler, Opt. Express 18, 14730–44 (2010).
- 25Q. Chen, T. Leng, L. Zheng, L. Kutzscher, J. Ma, L. de Sisternes, and D. L. Rubin, Med. Image Anal. 17, 1058–72 (2013).
- 26M. A. Mayer, J. Hornegger, C. Y. Mardin, and R. P. Tornow, Biomed. Opt. Express 1, 1358–1383 (2010).
- 27D. C. DeBuc, A review of algorithms for segmentation of retinal image data using optical coherence tomography (2011).
- 28J. D. Oakley, I. Gabilondo, C. Songster, D. Russakoff, A. Green, and P. Villoslada, Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 55, 4790 (2014).
- 29J. Tian, B. Varga, G. M. Somfai, W.-H. Lee, W. E. Smiddy, and Delia Cabrera DeBuc, PlosOne 8, 0133908 (2015).
- 30K. Lee, M. D. Abramoff, M. Garvin, and M. Sonka, The Iowa Reference Algorithms (Retinal Image Analysis Lab, Iowa Institute for Biomedical Imaging, Iowa City, IA). [Online]. Available: https://www.iibi.uiowa.edu/content/iowa-reference-algorithms-human-and-murine-oct-retinal-layer-analysis-and-display.
- 31A. Lang, NITRC: AURA tools : AUtomated Retinal Analysis tools: Tool/Resource Info, 2015. [Online]. Available: http://www.nitrc.org/projects/aura_tools/ [Accessed: 22-Jun-2015].
- 32P. A. Dufour, OCT Segmentation Application. [Online]. Available: http://pascaldufour.net/Research/software_data.html [Accessed: 22-Jun-2015].
- 33G. Staurenghi, S. Sadda, U. Chakravarthy, and R. F. Spaide, Ophthalmology 121, 1572–1578 (2014).
- 34E. W. Dijkstra,
Numer. Math.
1,
269–271
(1959).
10.1007/BF01386390 Google Scholar
- 35K. Li, X. Wu, D. Z. Chen, and M. Sonka, IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 28, 119–134 (2006).
- 36M. Mayer, Read heidelberg engineering (he) oct raw files., 2011. [Online]. Available: http://www5.informatik.unierlangen.de/fileadmin/Persons/MayerMarkus/openVol.m URL.
- 37 MathWorks, MATLAB Runtime – MATLAB Compiler. [Online]. Available: http://www.mathworks.com/products/compiler/mcr/?refresh=true [Accessed: 22-Jun-2015].
- 38D. DeBuc,
E. Tatrai,
L. Laurik,
B. E. Varga,
V. Olvedy,
A. Somogyi,
W. E. Smiddy, and
G. M. Somfai,
J. Clin. Exp. Ophthalmol.
04, no.
04,
(2013).
10.4172/2155-9570.1000289 Google Scholar
- 39Z. Hu, M. Nittala, and S. Sadda, Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 54, 5492 (2013).
- 40H. Chen, X. Chen, Z. Qiu, D. Xiang, W. Chen, F. Shi, J. Zheng, W. Zhu, and M. Sonka, Sci. Rep. 5, 9269 (2015).
- 41K. A. Vermeer, J. van der Schoot, H. G. Lemij, and J. F. de Boer, Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 53, 6102–6108 (2012).
- 42T. E. de Carlo, A. Romano, N. K. Waheed, and J. S. Duker, Int. J. Retin. Vitr. 1, 5 (2015).
- 43M. Tiemann, History of the OSI | Open Source Initiative, Sciencecommons.org., 2010. [Online]. Available: http://opensource.org/history [Accessed: 07-Sep-2015].