Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
research papers
Efficient high-resolution refinement in cryo-EM with stochastic gradient descent
- Pages: 327-343
- First Published: 02 July 2025
In the context of cryo-EM reconstruction, we provide a theoretical analysis showing that the condition number of the optimization problem is particularly large at high resolution, leading to slow convergence of gradient-based methods such as stochastic gradient descent. We then propose a method to overcome this issue by computing a preconditioner using Hutchinson's estimator, which results in improved convergence speed, as evidenced by numerical experiments.
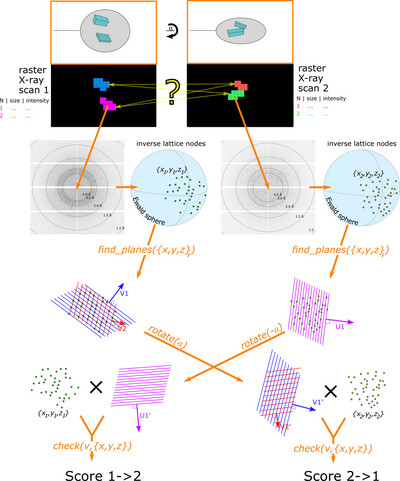
Enhanced capabilities for multi-crystal data collection based on double mesh scans
- Pages: 344-356
- First Published: 02 July 2025
Structural dynamics of IDR interactions in human SFPQ and implications for liquid–liquid phase separation
- Pages: 357-379
- First Published: 02 July 2025
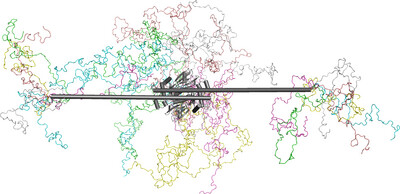
SFPQ and NONO are DBHS-family proteins that are essential for transcriptional regulation and the assembly of paraspeckles, which are subnuclear structures built on the long noncoding RNA NEAT1. Through SAXS, SANS and XL-MS analyses, we reveal that the disordered regions of SFPQ surrounding its DBHS domain enable flexible interactions and that the full-length proteins are capable of dimer partner exchange, highlighting how these dynamics may contribute to phase separation and impact disease processes.
Crystal structure of coagulation factor XII N-terminal domains 1–5
- Pages: 380-393
- First Published: 02 July 2025
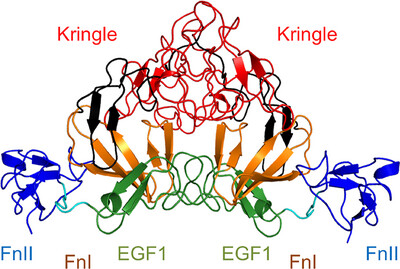
Factor XII (FXII) is a plasma serine protease which becomes activated by interactions with polyanions such as polyphosphates from bacteria, with Zn2+ as a critical cofactor. The crystal structure of FXII domains 1–5, coupled with a second crystal structure of the isolated FnII domain in complex with Zn2+ ions, advances our understanding of FXII structure and ligand recognition.