Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
research papers
MrParse: finding homologues in the PDB and the EBI AlphaFold database for molecular replacement and more
- Pages: 553-559
- First Published: 26 April 2022

MrParse is a software package designed to aid decision making in molecular replacement (MR). It performs a sequence search to find search models, not only in the PDB, as would conventionally be performed, but also in the EBI AlphaFold database, and provides a series of analyses relevant to MR such as crystal pathology detection and sequence analysis.
The BAM7 gene in Zea mays encodes a protein with similar structural and catalytic properties to Arabidopsis BAM2
- Pages: 560-570
- First Published: 08 April 2022
Crystal structure of the middle and C-terminal domains of Hsp90α labeled with a coumarin derivative reveals a potential allosteric binding site as a drug target
- Pages: 571-585
- First Published: 08 April 2022

Allosteric inhibitors that bind to the middle domain (MD) or C-terminal domain (CTD) of Hsp90 have become promising drug leads for the development of effective and nontoxic chemicals in anticancer drug discovery. The structure of MDCC-labeled Hsp90α MD and CTD reported here provides the first direct visual insight into allosteric binding inhibitors of Hsp90 MD or CTD and provides a basis for the design of novel drugs for the treatment of cancer and neurodegenerative diseases.
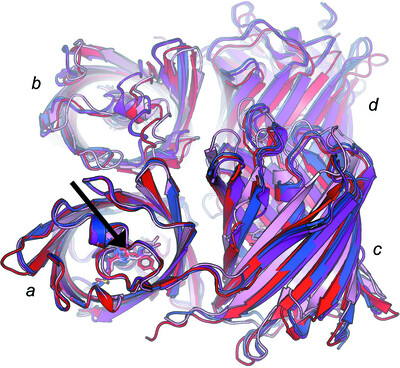
Structural studies of a novel auxiliary-domain-containing phenylalanine hydroxylase from Bacillus cereus ATCC 14579
- Pages: 586-598
- First Published: 08 April 2022
Over the rainbow: structural characterization of the chromoproteins gfasPurple, amilCP, spisPink and eforRed
- Pages: 599-612
- First Published: 08 April 2022
Crystal structure of the domain-swapped dimeric maltodextrin-binding protein MalE from Salmonella enterica
- Pages: 613-622
- First Published: 08 April 2022
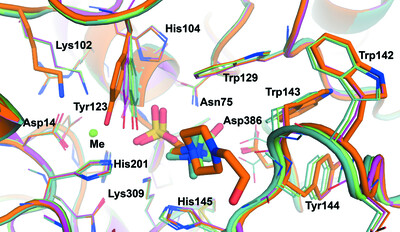
Monoclonal antibody 7H2.2 binds the C-terminus of the cancer-oocyte antigen SAS1B through the hydrophilic face of a conserved amphipathic helix corresponding to one of only two regions predicted to be ordered
- Pages: 623-632
- First Published: 20 April 2022
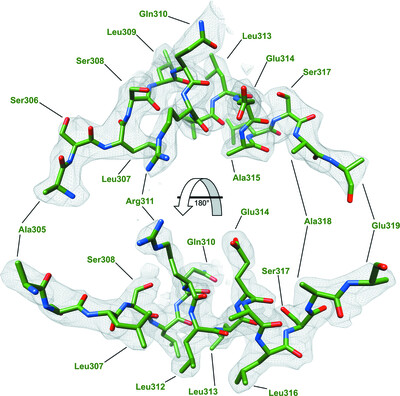
The structure of the antigen-binding fragment of mouse monoclonal antibody 7H2.2 in complex with a 15-residue fragment from the metalloproteinase sperm acrosomal SLLP1 binding protein (SAS1B) has been determined at 2.75 Å resolution. The antigen is an amphipathic α-helix that corresponds to one of only two elements of secondary structure that are predicted to be ordered within the C-terminal region of SAS1B, which provides a basis for the targeted use of SAS1B.
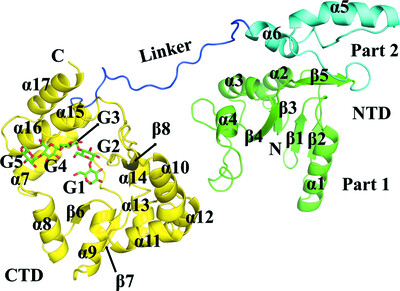
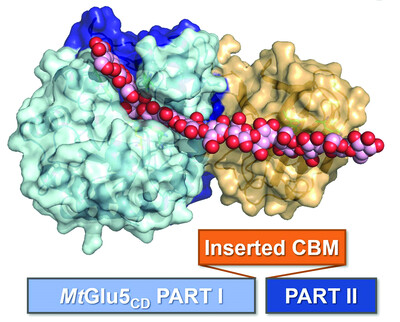
Synergic action of an inserted carbohydrate-binding module in a glycoside hydrolase family 5 endoglucanase
- Pages: 633-646
- First Published: 20 April 2022
The structure of Phocaeicola vulgatus sialic acid acetylesterase
- Pages: 647-657
- First Published: 26 April 2022
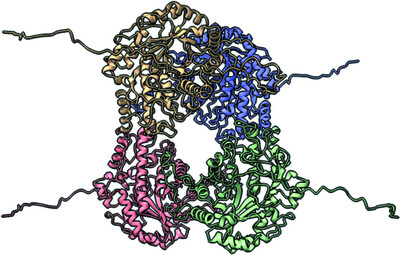
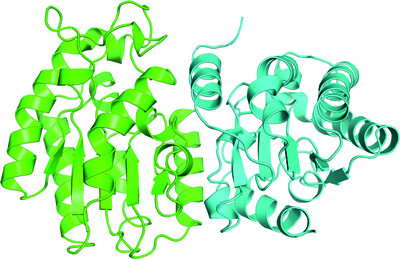
A GH115 α-glucuronidase structure reveals dimerization-mediated substrate binding and a proton wire potentially important for catalysis
- Pages: 658-668
- First Published: 20 April 2022
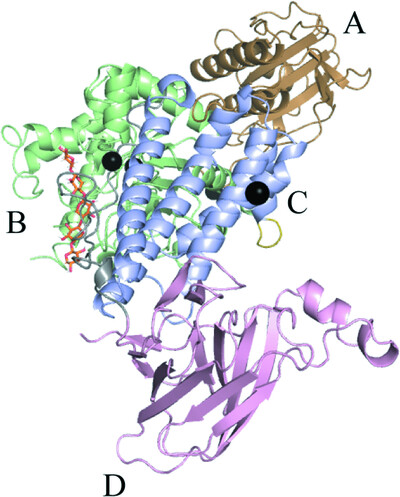
The crystal structure of a GH115 α-glucuronidase obtained in complex with xylohexaose and Ca2+ reveals that the two molecules constituting the homodimer cooperatively bind the substrate and that a divalent ion is involved in formation of the Michaelis–Menten complex and is likely to contribute to the formation of a protein wire that is essential for catalysis.
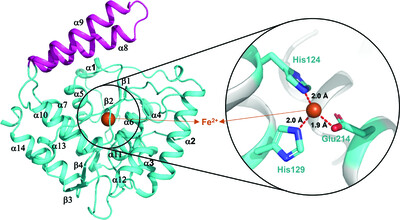
Structural insights into choline-O-sulfatase reveal the molecular determinants for ligand binding
- Pages: 669-682
- First Published: 26 April 2022