Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
research papers
Modelling covalent linkages in CCP4
- Pages: 712-726
- First Published: 24 May 2021
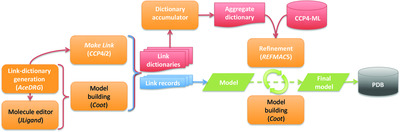
The mechanism for modelling covalent linkages in CCP4 is reviewed and the method of link-dictionary generation used by AceDRG is described. An overview of the various protocols available for the modelling and application of covalent linkages within the CCP4 suite is presented, providing instructive guidelines with a focus on practical application.
The missing link: covalent linkages in structural models
- Pages: 727-745
- First Published: 24 May 2021
UnityMol prototype for FAIR sharing of molecular-visualization experiences: from pictures in the cloud to collaborative virtual reality exploration in immersive 3D environments
- Pages: 746-754
- First Published: 28 May 2021
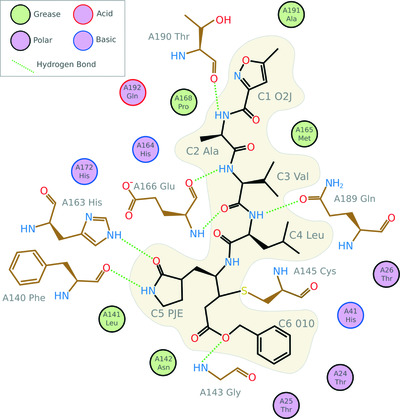
Crystallographic fragment screening-based study of a novel FAD-dependent oxidoreductase from Chaetomium thermophilum
- Pages: 755-775
- First Published: 24 May 2021
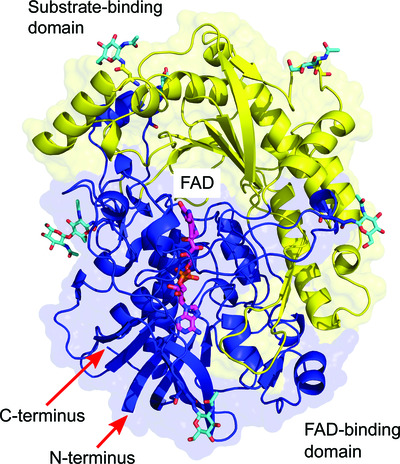
The high-resolution crystal structure of a novel FAD-dependent oxidoreductase from the GMC oxidoreductase superfamily reveals a novel His–Ser active-site pair located in an extensive active-site pocket. Crystallographic fragment screening led to the identification of subsites inside the active-site pocket, indicating a preference for polyaromatic substrates.
Salt bridges at the subdomain interfaces of the adenylation domain and active-site residues of Mycobacterium tuberculosis NAD+-dependent DNA ligase A (MtbLigA) are important for the initial steps of nick-sealing activity
- Pages: 776-789
- First Published: 24 May 2021
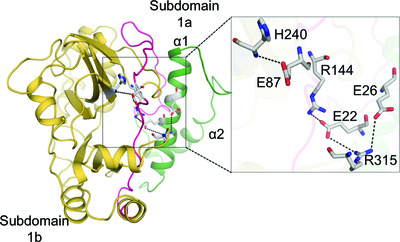
Structural and mutational studies of the active-site residues and also of those forming salt bridges between subdomains and active-site residues of the adenylation domain were carried out in M. tuberculosis NAD+-dependent DNA ligase A. The results suggest that specific salt bridges mediated by Glu22, Glu26 and Glu87 are important for the correct subdomain geometry and that their disruption critically impacts on the adenylation activity. At the same time, even conservative mutations of His236 and Lys123 in the active site lead to severe activity loss.
Are the St John's wort Hyp-1 superstructures different?
- Pages: 790-798
- First Published: 24 May 2021
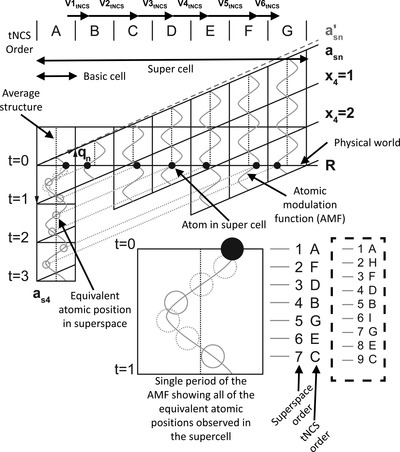
Two modulated structures of the Hyp-1–ANS complex with different unit-cell dimensions and contents were analyzed in (3+1)D superspace, revealing that they are very similar if not the same higher-dimensional structure with a slight shift in the q vector being responsible for the differences observed in 3D space.
FragMAXapp: crystallographic fragment-screening data-analysis and project-management system
- Pages: 799-808
- First Published: 24 May 2021
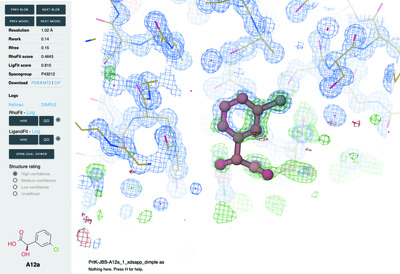
The amount of data generated during crystallographic fragment-screening projects requires sophisticated automated methods to analyse the data and to identify binders. FragMAXapp is the MAX IV Laboratory approach to managing fragment-screening campaigns: a web application that provides scientists with access to the MAX IV computing cluster and visualization tools.
Structure of human factor VIIa–soluble tissue factor with calcium, magnesium and rubidium
- Pages: 809-819
- First Published: 24 May 2021

Blood coagulation factor VIIa contains sodium, magnesium and calcium sites. In the present study, sodium increased the amidolytic activity of factor VIIa by ∼20-fold and stabilized the sodium loops and the tissue factor-binding region; however, rubidium occupied two calcium sites in factor VIIa but not the sodium site.
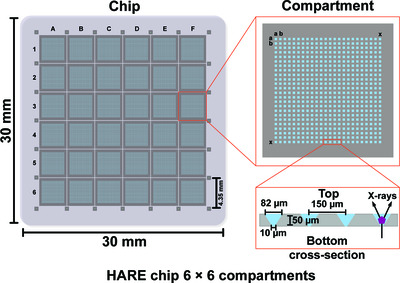
A simple vapor-diffusion method enables protein crystallization inside the HARE serial crystallography chip
- Pages: 820-834
- First Published: 24 May 2021
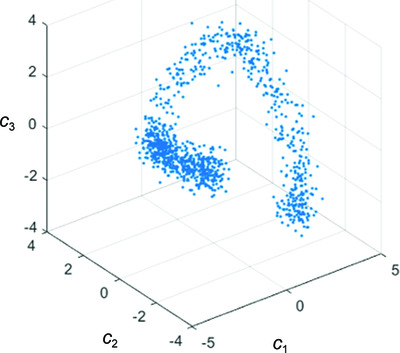
Principal component analysis is limited to low-resolution analysis in cryoEM
- Pages: 835-839
- First Published: 24 May 2021
Expression and analysis of the SAM-dependent RNA methyltransferase Rsm22 from Saccharomyces cerevisiae
- Pages: 840-853
- First Published: 24 May 2021
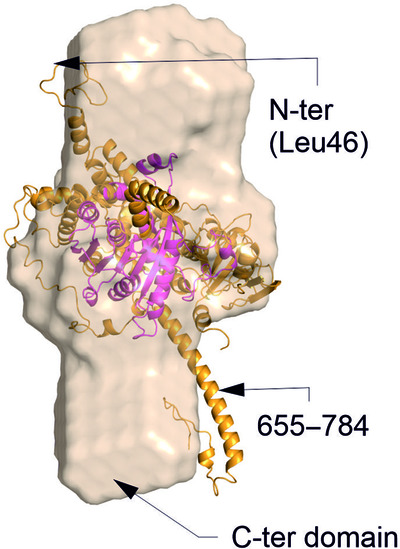
Rsm22-family proteins are conserved putative SAM-dependent methyltransferases with important functions in mitochondrial translation. Here, the results of a comparative bioinformatics analysis of Rsm22-type proteins are presented, the expression, biophysical characterization and crystallization of Saccharomyces cerevisiae Rsm22 are reported, a low-resolution SAXS structure of the protein is revealed, and SAM-dependent RNA methyl transferase activity of the protein is demonstrated.
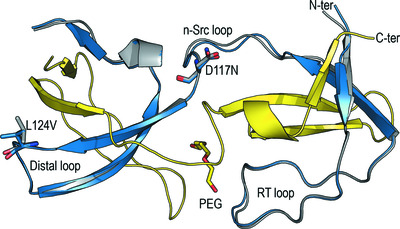
The impact of oncogenic mutations of the viral Src kinase on the structure and stability of the SH3 domain
- Pages: 854-866
- First Published: 24 May 2021