Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
research papers
A fourfold interpenetrating three-dimensional cadmium(II) coordination polymer: synthesis, crystal structure and physical properties
- Pages: 257-261
- First Published: 06 May 2021
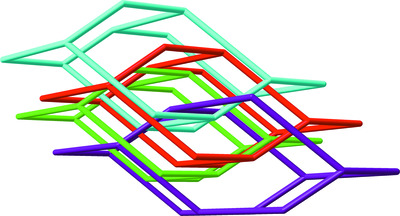
A cadmium(II) compound, prepared by reaction of Cd(NO3)2·4H2O with naphthalene-1,4-dicarboxylic acid and bis[4-(2-methylimidazol-1-yl)phenyl] ether in a mixture of H2O and dimethylformamide, possesses a fourfold interpenetrating diamond-like three-dimensional framework. The compound exhibits strong fluorescence emission in the solid state and excellent photocatalytic activity for the degradation of methylene blue (MB) at room temperature.
Varying degrees of homostructurality in a series of cocrystals of antimalarial drug 11-azaartemisinin with salicylic acids
- Pages: 262-270
- First Published: 06 May 2021
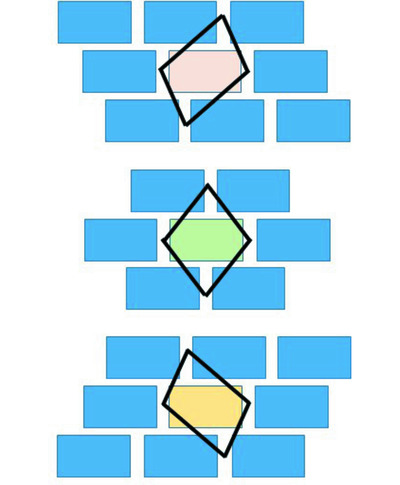
Cocrystals of the antimalarial drug 11-azaartemisinin (11-Aza) with salicylic acid (SalA) were reported recently and showed an enhanced dissolution rate. The use of bromo-substituted SalA compounds has now allowed the isolation of a larger family of these 1:1 cocrystals. All the structures involve molecular pairs with 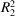 (8) heterosynthons between the 11-Aza lactam functionality and the benzoic acid group that are organized into highly preserved 21 stacks. These are organized into either isostructural (5-BrSalA) or modified arrangements (4-BrSalA and 3,5-Br2SalA), with varying degrees of homostructurality compared to the parent SalA cocrystal.
(8) heterosynthons between the 11-Aza lactam functionality and the benzoic acid group that are organized into highly preserved 21 stacks. These are organized into either isostructural (5-BrSalA) or modified arrangements (4-BrSalA and 3,5-Br2SalA), with varying degrees of homostructurality compared to the parent SalA cocrystal.
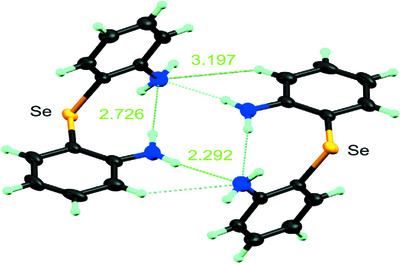
Bis(2-nitrophenyl) selenide, bis(2-aminophenyl) selenide and bis(2-aminophenyl) telluride: structural and theoretical analysis
- Pages: 271-280
- First Published: 17 May 2021
Crystal structure characterization and electronic structure of a rare-earth-containing Zintl phase in the Yb–Al–Sb family: Yb3AlSb3
- Pages: 281-285
- First Published: 26 May 2021
A rare-earth-containing compound, Yb3AlSb3 (Ca3AlAs3-type structure), has been successfully synthesized within the Yb–Al–Sb system through flux methods. The crystal structure features infinite corner-sharing AlSb4 tetrahedra, [AlSb2Sb2/2]6−, with Yb2+ cations residing between the tetrahedra to provide charge balance.
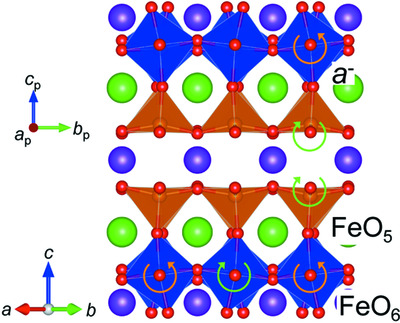
Unique octahedral rotation pattern in the oxygen-deficient Ruddlesden–Popper compound Gd3Ba2Fe4O12
- Pages: 286-290
- First Published: 26 May 2021
Novel Ba2+ and Pb2+ metal–organic frameworks based on a semi-rigid tetracarboxylic acid: syntheses, structures, topologies and luminescence properties
- Pages: 291-298
- First Published: 26 May 2021
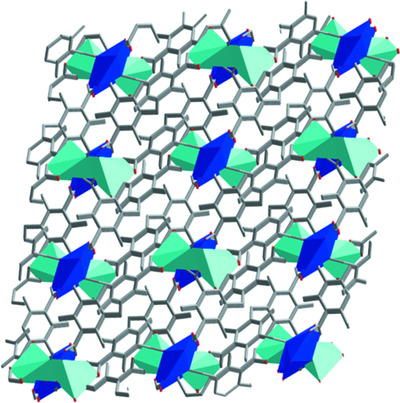
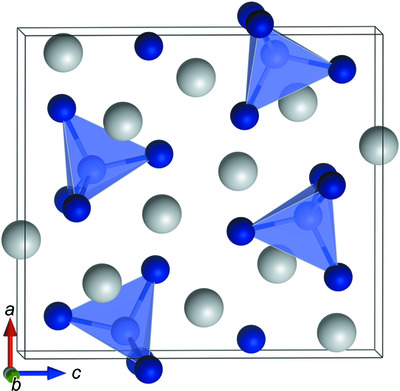
Two new main-group metal–organic frameworks (MOFs) based on the semi-rigid tetracarboxylic acid 5,5′-methylenebis(2,4,6-trimethylisophthalic acid) were prepared under hydrothermal conditions and characterized. The Ba complex reveals a three-dimensional flu network formed via bridging tetranuclear SBUs, while the Pb complex displays a three-dimensional framework with an sqp topology based on one-dimensional metal chains. The luminescence properties of both complexes have been investigated in the solid state.
Synthesis, spectroscopic investigation, crystal structure analysis, quantum chemical study, biological activity and molecular docking of three isatin derivatives
- Pages: 299-311
- First Published: 26 May 2021
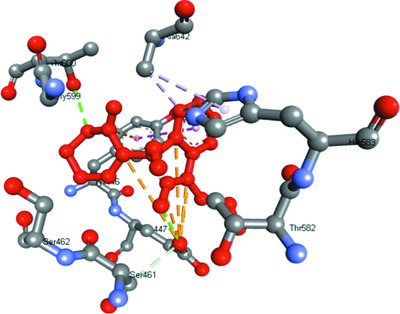
Three isatin derivatives were synthesized, crystallized by the slow-evaporation technique, characterized by 1H and 13C NMR spectroscopy, and analysed by the single-crystal X-ray diffraction (XRD) method. Quantum chemical parameters were calculated and the druglikeness and bioactivity scores of the compounds were predicted. The activities of these isatin derivatives against bacterial and fungal strains were determined using the well-diffusion assay method. Molecular docking studies were carried out to predict the binding mode of the isatin compounds with the penicillin binding protein enzyme.
Contributions of secondary alcohol–ketone O—H…O=C and furan–acetate Csp2—H…OOC synthons to the supramolecular packings of two bioactive molecules
- Pages: 312-320
- First Published: 27 May 2021
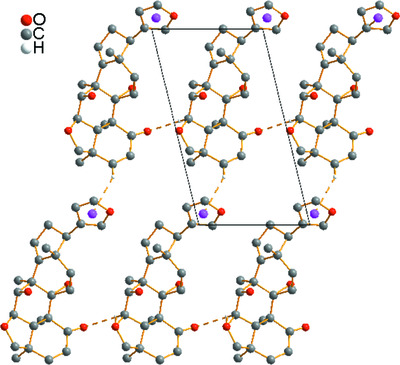
The crystal structures of rubescin D and monadelphin A, bioactive molecules of the vilasinin and gedunin classes of limonoids, respectively, are reported. The synthons involved in the packing modes are analyzed on the basis of their occurrences in compounds from the Cambridge Structural Database displaying the same moieties. The effects of these synthons are determined by comparing the supramolecular arrangements of both compounds with those of structures having the same skeleton but different substituents.