Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
editorial
Celebrating JSR's 30th anniversary: reminiscences of a Main Editor
- Page: 1414
- First Published: 01 October 2024
Foreword to the special virtual issue dedicated to the proceedings of the PhotonMEADOW2023 Joint Workshop
- Pages: 1415-1416
- First Published: 11 October 2024
Foreword to the special virtual issue on X-ray spectroscopy to understand functional materials: instrumentation, applications, data analysis
- Pages: 1417-1419
- First Published: 21 October 2024
research papers
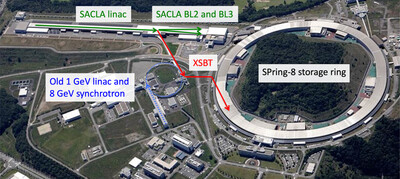
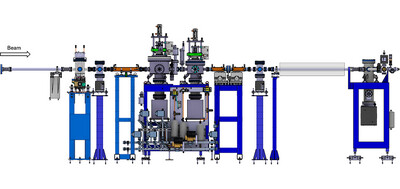
Green upgrading of SPring-8 to produce stable, ultrabrilliant hard X-ray beams
- Pages: 1420-1437
- First Published: 23 October 2024
Synchrotron CT dosimetry for wiggler operation at reduced magnetic field and spatial modulation with bow tie filters
- Pages: 1438-1445
- First Published: 22 October 2024

Operation at lower wiggler magnetic field strength reduces dose rates by an order of magnitude, and suppresses the influence of harmonic radiation, of significance near 30 keV. Beam shaping filters modulate the incident beam for near constant transmitted signal and offer protection by reducing the average dose to the scanned volume at 30–100 keV by about 10% for biological samples of 35–50 mm in diameter and by 20–30% for samples of up to 160 mm in diameter.
A general Bayesian algorithm for the autonomous alignment of beamlines
- Pages: 1446-1456
- First Published: 28 October 2024
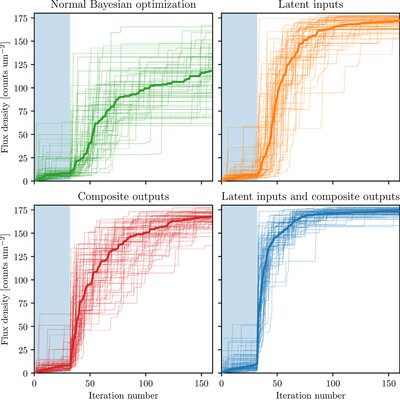
Automated alignment methods have the potential to accelerate greatly the efficiency of experiments done at synchrotron facilities and are an important step towards fully autonomous beamlines. Presented here is a general implementation of Bayesian optimization that performs well on many beamlines across different facilities.
A study of structural effects on the focusing and imaging performance of hard X-rays with 20–30 nm zone plates
- Pages: 1457-1463
- First Published: 28 October 2024
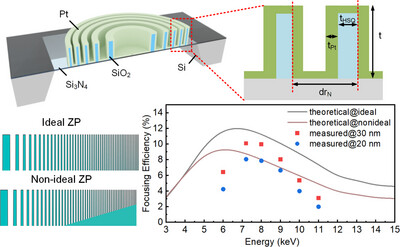
This work reports the structural effects on the focusing and imaging efficiency of 20–30 nm-resolution zone plates at Diamond Light Source and Shanghai Synchrotron Radiation Facility. The zone width and the duty cycle were optimized using a modified beam-propagation method for peak efficiency, and the effect of residual resist was also explored using simulation and experimental measurements.
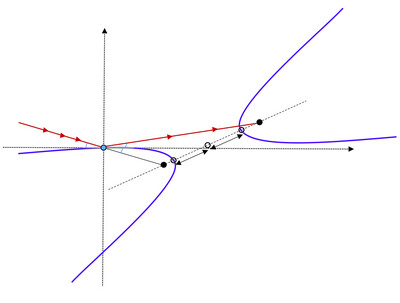
Mirror-centered representation of a focusing hyperbolic mirror for X-ray beamlines
- Pages: 1464-1468
- First Published: 29 October 2024
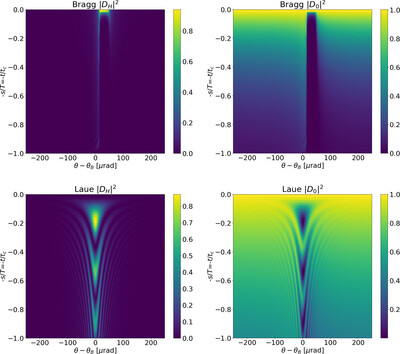
Formulation of perfect-crystal diffraction from Takagi–Taupin equations: numerical implementation in the crystalpy library
- Pages: 1469-1480
- First Published: 29 October 2024
High-transmission spectrometer for rapid resonant inelastic soft X-ray scattering (rRIXS) maps
- Pages: 1481-1488
- First Published: 30 September 2024
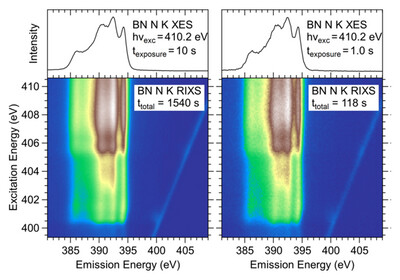
A high-transmission soft X-ray spectrometer has been developed and commissioned at the X-SPEC beamline of the KIT Light Source. With this spectrometer, single spectra can be measured with exposure times well below 1 s, allowing the rapid collection of full resonant inelastic soft X-ray scattering maps in less than one minute.
Coprecipitation of Ce(III) oxide with UO2
- Pages: 1489-1504
- First Published: 30 September 2024
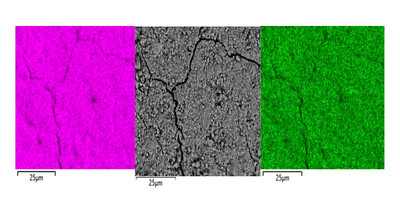
Neutralization of acidic solutions containing U (IV) and Ce (III) at room temperature in glove box atmosphere and in the presence of dithionite results in coprecipitation of these elements as amorphous solid solutions CexU1–xO2±y. The solids were investigated by a variety of methods to determine the nature of the solid solutions formed, their composition and the valence state of Ce and U.
Development of hard X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy in liquid cells using optimized microfabricated silicon nitride membranes
- Pages: 1505-1513
- First Published: 15 October 2024
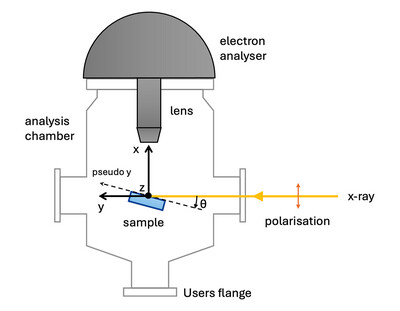
We have developed and successfully tested new environmental liquid cells for HAXPES studies using specially designed thin, low-stress silicon nitride membranes (15 to 25 nm thickness). The novel aspect is the fabrication of the membranes considering the geometry of the experimental setup, the dimensions of the beam and the use of platinum stripes to efficiently localize the membranes. The membranes are robust, able to withstand the 1 bar pressure difference between the liquid and vacuum, and the intense beam.
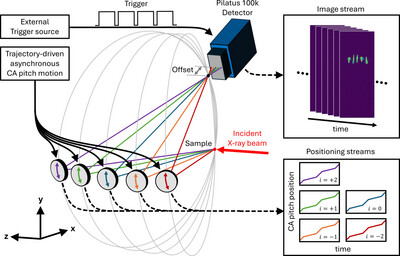
distect: automatic sample-position tracking for X-ray experiments using computer vision algorithms
- Pages: 1514-1524
- First Published: 31 October 2024
X-ray ghost imaging with a specially developed beam splitter
- Pages: 1525-1533
- First Published: 30 September 2024
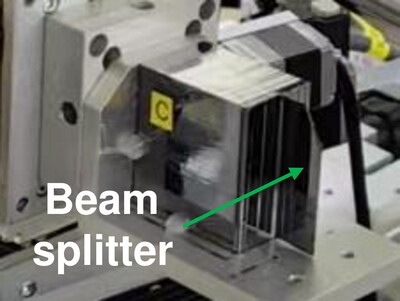
Compared with traditional imaging methods, the non-local characteristics of ghost imaging have the ability to greatly reduce the radiation dose of X-ray imaging in principle, and has important application prospects in radiation-sensitive fields such as biomedicine. Here a specially developed beam splitter applicable for the efficient implementation of X-ray ghost imaging is described.
Development of crystal optics for X-ray multi-projection imaging for synchrotron and XFEL sources
- Pages: 1534-1550
- First Published: 21 October 2024

X-ray multi-projection imaging (XMPI) is an emerging technology that enables the acquisition of millions of 3D images per second, useful for observing rapid, stochastic phenomena previously inaccessible to conventional tomography. This study explores XMPI schemes and optics compatible with synchrotron and XFEL beams, and it experiments with MHz-rate XMPI at the European XFEL.
Mitigation of DMM-induced stripe patterns in synchrotron X-ray radiography through dynamic tilting
- Pages: 1551-1560
- First Published: 25 October 2024
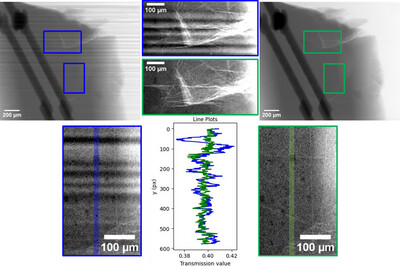
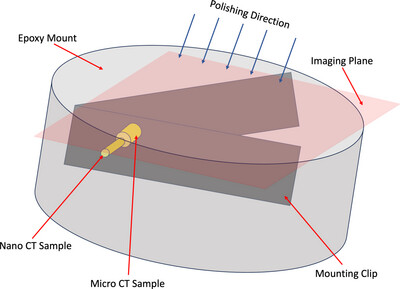
Correlative X-ray micro-nanotomography with scanning electron microscopy at the Advanced Light Source
- Pages: 1561-1570
- First Published: 29 October 2024
short communications
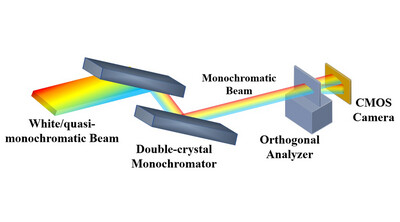
In situ/operando method for energy stability measurement of synchrotron radiation
- Pages: 1571-1575
- First Published: 15 October 2024
Thermal analysis of a reflection mirror by fluid and solid heat transfer method
- Pages: 1576-1581
- First Published: 15 October 2024
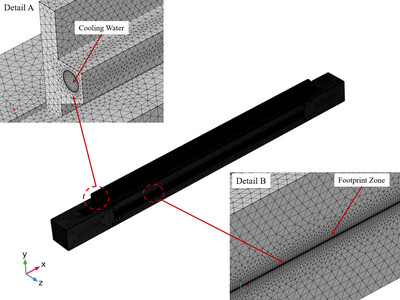
By thermal analysis of the reflection mirror in a free-electron laser under high repetition rates within the fluid and solid heat transfer method, the water temperature increase of the cooling tube was found to influence the wall temperature of the fluid–solid interface and results in an asymmetrical temperature distribution of the footprint centreline in the mirror. Here, a more accurate thermal analysis of the reflection mirror under a high heat load is presented that will improve the cooling scheme design of the mirror.
beamlines
Upgraded front ends for SLS 2.0 with next-generation high-power diaphragms and slits
- Pages: 1582-1592
- First Published: 22 October 2024
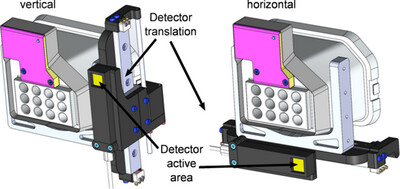
VMXm – A sub-micron focus macromolecular crystallography beamline at Diamond Light Source
- Pages: 1593-1608
- First Published: 31 October 2024
Five-analyzer Johann spectrometer for hard X-ray photon-in/photon-out spectroscopy at the Inner Shell Spectroscopy beamline at NSLS-II: design, alignment and data acquisition
- Pages: 1609-1621
- First Published: 31 October 2024
laboratory notes
A miniature X-ray diffraction setup on ID20 at the European Synchrotron Radiation Facility
- Pages: 1622-1626
- First Published: 25 October 2024