Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
research papers
Diaboloidal mirrors: algebraic solution and surface shape approximations
- Pages: 1031-1040
- First Published: 02 June 2021
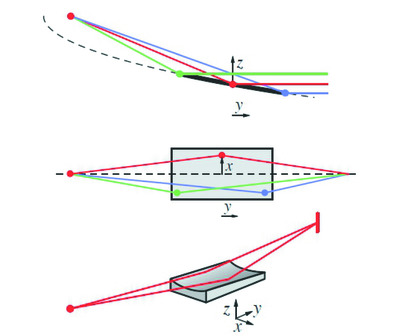
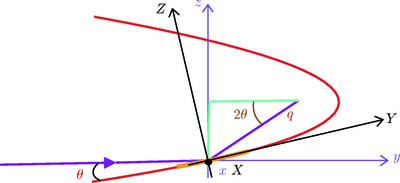
The diaboloidal mirror is a reflecting surface that converts a spherical wave to a cylindrical wave (or vice versa). Application of the mirror in a collimated two-crystal monochromator will be the main application area and will allow brightness preserving focusing, even with the very small source size of a multi-bend achromat ultra-high-brightness synchrotron source. An exact analytical solution for the surface shape of a diaboloidal mirror as a function of the conjugate parameters of the mirror placed in a beamline is presented.
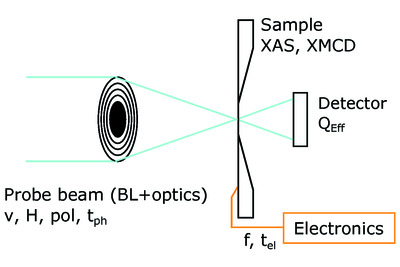
Simulations of applications using diaboloid mirrors
- Pages: 1041-1049
- First Published: 02 June 2021
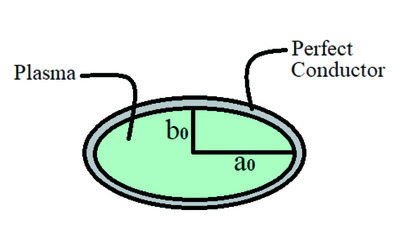
Elliptical plasma-filled waveguide as a new standard short-period undulator
- Pages: 1050-1058
- First Published: 02 June 2021
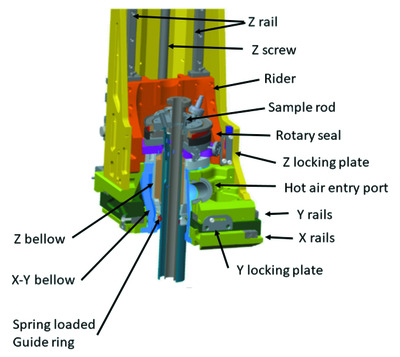
An ultra-high-stability four-axis ultra-high-vacuum sample manipulator
- Pages: 1059-1068
- First Published: 08 June 2021
Photon-counting MCP/Timepix detectors for soft X-ray imaging and spectroscopic applications
- Pages: 1069-1080
- First Published: 28 May 2021
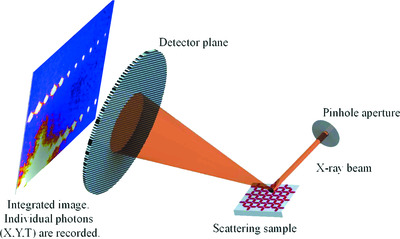
A photon-counting detector that employs microchannel plates combined with a quad Timepix readout is evaluated for soft X-ray imaging experiments conducted at synchrotron beamline facilities, where the time and position of each photon is registered by the detector. This work describes proof-of-principle experiments conducted with this technology where a spatial resolution of ∼6 µm is achieved with single-photon counting. Future developments of this technology for the possible extension of X-ray photon correlation spectroscopy analysis to sub-microsecond timescales are presented.
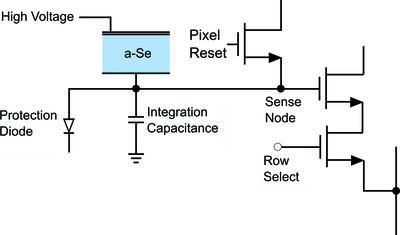
High-energy micrometre-scale pixel direct conversion X-ray detector
- Pages: 1081-1089
- First Published: 02 June 2021
Soft X-ray nanospectroscopy for quantification of X-ray linear dichroism on powders
- Pages: 1090-1099
- First Published: 19 May 2021
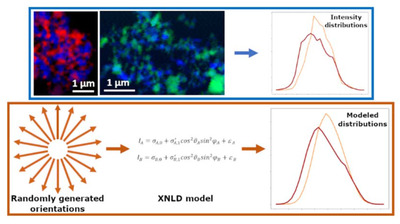
It is shown how soft X-ray nanospectroscopy maps of powders (particle size ∼200 nm) can be analyzed to quantitatively retrieve X-ray linear dichroism (XLD) parameters. A computational modeling procedure is described that can be used in conjunction with Monte Carlo simulations to prove statistical dissimilarity of XLD parameters between different samples.
Millisecond timescale reactions observed via X-ray spectroscopy in a 3D microfabricated fused silica mixer
- Pages: 1100-1113
- First Published: 19 May 2021
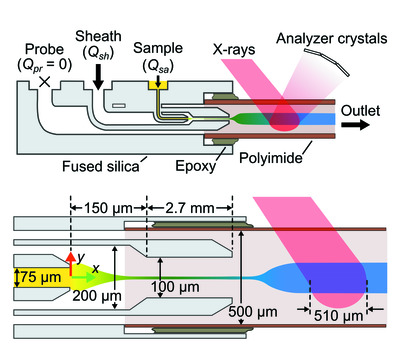
Presented is a 3D-microfabricated, 3D hydrodynamic focusing microfluidic mixer to study mixing-triggered reactions via X-ray spectroscopy. The 3D-microfabricated format of the device offers repeatable production. Meanwhile, the mixing scheme enables highly uniform sample residence times on the order of milliseconds.
Local atomic structure analysis around Mg atom doped in GaN by X-ray absorption spectroscopy and spectrum simulations
- Pages: 1114-1118
- First Published: 27 May 2021

The incorporated site of magnesium doped in gallium nitride has been identified by X-ray absorption spectroscopy using a superconducting tunnel junction array detector and spectrum simulations. In addition, the presence or absence of hydrogen around magnesium can be identified through distinctive characteristics expected from the spectrum simulations.
XANES reflects coordination change and underlying surface disorder of zinc adsorbed to silica
- Pages: 1119-1126
- First Published: 28 May 2021
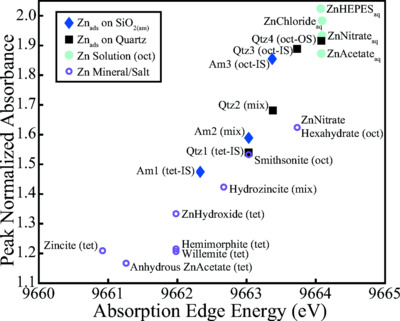
Zinc K-edge X-ray absorption near-edge structure (XANES) spectroscopy of Zn adsorbed (Znads) to quartz and amorphous silica [SiO2(am)] reflects coordination change and underlying surface disorder. XANES standards of Znads on silica are presented, including outer-sphere octahedral Znads on quartz, inner-sphere octahedral Znads on quartz, inner-sphere tetrahedral Znads on quartz, inner-sphere octahedral Znads on SiO2(am) and inner-sphere tetrahedral Znads on SiO2(am).
A cookbook for the investigation of coordination polymers by transition metal K-edge XMCD
- Pages: 1127-1136
- First Published: 02 June 2021

In order to set up the bases for extracting quantitative information from transition metal K-edge X-ray magnetic circular dichroism (XMCD) signals of coordination polymers, the effects of temperature and magnetic field on these signals are studied. A manual procedure for data treatment is also developed. Key points for transition metal K-edge XMCD measurements of coordination polymers on any XMCD-dedicated beamline are provided.
Using a modified double deep image prior for crosstalk mitigation in multislice ptychography
- Pages: 1137-1145
- First Published: 19 May 2021
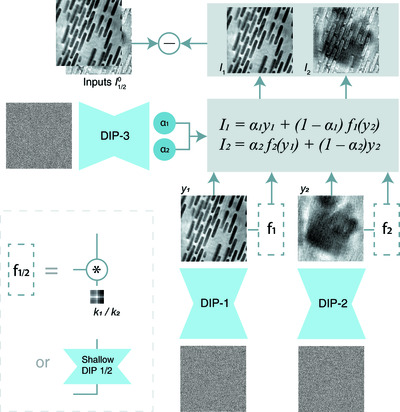
Using the `deep image prior' characteristic of generative neural networks, a post-processing method that mitigates the inter-slice crosstalk issue in multislice ptychography has been developed. Under certain scenarios, crosstalk can be suppressed effectively in slice images reconstructed using ptychographic diffraction data alone.
Why is my image noisy? A look into the terms contributing to a time-resolved X-ray microscopy image
- Pages: 1146-1158
- First Published: 27 May 2021
The influence of strain on image reconstruction in Bragg coherent X-ray diffraction imaging and ptychography
- Pages: 1159-1165
- First Published: 02 June 2021
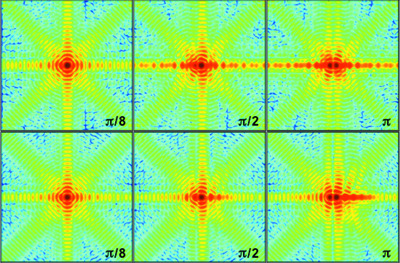
A quantitative analysis of the effect of strain on image reconstruction in Bragg coherent X-ray diffraction imaging and ptychography reveals reconstruction artifacts caused by the limited spatial resolution. With the modulus homogenization constraint applied, the reconstruction artifacts are efficiently removed and an Fe–Al alloy sample with strong strain that features π phase steps due to anti-phase domain boundaries is successfully reconstructed.
Quantitative phase measurements of human cell nuclei using X-ray ptychography
- Pages: 1166-1173
- First Published: 23 June 2021
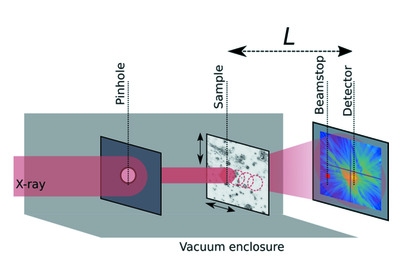
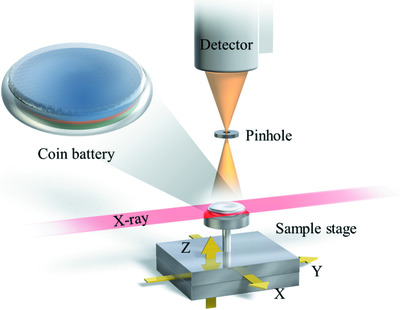
Direct cross-sectional imaging using X-ray Compton scattering: application to commercial batteries
- Pages: 1174-1177
- First Published: 25 June 2021
short communications
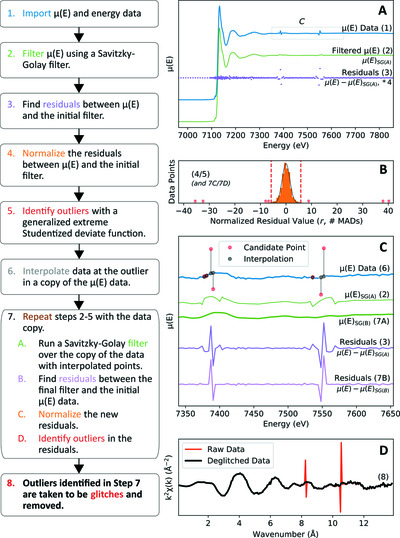
An algorithm for the automatic deglitching of X-ray absorption spectroscopy data
- Pages: 1178-1183
- First Published: 19 May 2021
beamlines
IRIXS Spectrograph: an ultra high-resolution spectrometer for tender RIXS
- Pages: 1184-1192
- First Published: 27 May 2021
BL-02: a versatile X-ray scattering and diffraction beamline for engineering applications at Indus-2 synchrotron source
- Pages: 1193-1201
- First Published: 27 May 2021
Reducing the thermal deformation of InSb crystal by using double-bounce HHRMs in the TPS tender X-ray absorption spectroscopy beamline
- Pages: 1202-1209
- First Published: 28 May 2021
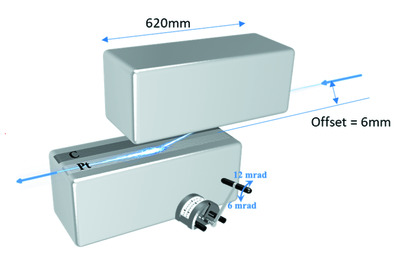
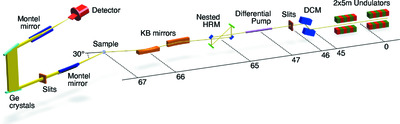
The double-bounce high harmonics rejection mirrors (HHRMs) system has a key role in the design of the Taiwan Photon Source tender X-ray absorption spectroscopy beamline and will reduce the thermal load of downstream optics and benefit in cutting off the high-order harmonics. Double-bounce HHRMs in front of the collimating mirror and double-crystal monochromator could provide an optical design concept for a wide range of spectroscopic measurement requirements, particularly at synchrotron facilities with a high-current storage ring.
BL-11C Micro-MX: a high-flux microfocus macromolecular-crystallography beamline for micrometre-sized protein crystals at Pohang Light Source II
- Pages: 1210-1215
- First Published: 02 June 2021
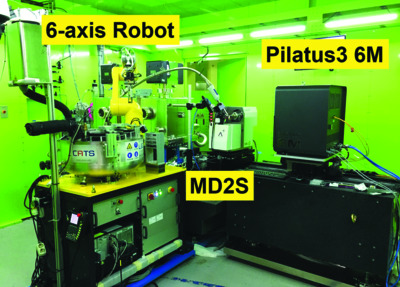
A new protein crystallography beamline (BL-11C) has been constructed at Pohang Light Source II. The BL-11C beamline allows routine protein-structure determinations under a robot sample-mounting system and room-temperature structure determinations through synchrotron serial crystallography experiments.
The fast multi-frame X-ray diffraction detector at the Dynamic Compression Sector
- Pages: 1216-1228
- First Published: 02 June 2021
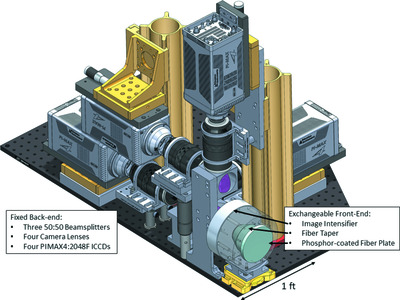
A multi-frame, X-ray diffraction (XRD) detector system has been developed for use in time-resolved XRD measurements during single-event experiments at the Dynamic Compression Sector at the Advanced Photon Source. The detector is capable of collecting four XRD patterns during an experiment, each from a single X-ray bunch. The temporal resolution and data post-processing procedures are discussed in detail.
The photon beamline vacuum system of the European XFEL
- Pages: 1229-1236
- First Published: 08 June 2021
Tools for supporting solution scattering during the COVID-19 pandemic
- Pages: 1237-1244
- First Published: 25 June 2021
computer programs
MAP2XANES: a Jupyter interactive notebook for elemental mapping and XANES speciation
- Pages: 1245-1252
- First Published: 19 May 2021
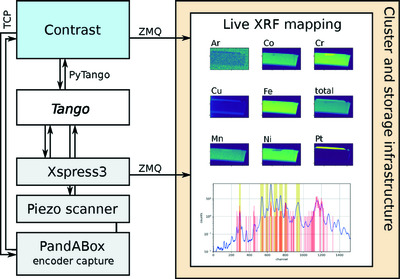
Contrast – a lightweight Python framework for beamline orchestration and data acquisition
- Pages: 1253-1260
- First Published: 08 June 2021
PyPhase – a Python package for X-ray phase imaging
- Pages: 1261-1266
- First Published: 25 June 2021
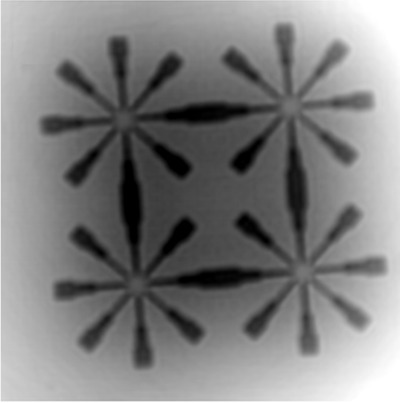
PyPhase is a free and open-source Python package for propagation-based near-field phase reconstructions, which implements some of the most popular phase-retrieval algorithms in a highly modular framework supporting the deployment on large-scale computing facilities. This makes integration, development of new phase-retrieval algorithms, and the deployment on different computing infrastructures straightforward.
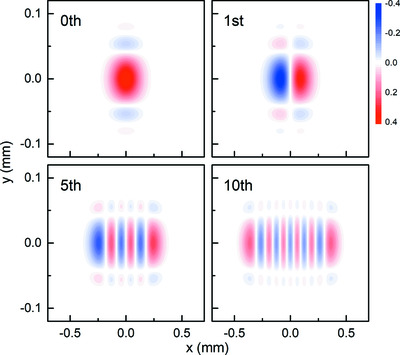
Major upgrade of the synchrotron radiation calculation code SPECTRA
- Pages: 1267-1272
- First Published: 11 June 2021