Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
ISSUE INFORMATION
SHORT COMMUNICATIONS
Ggtree: A serialized data object for visualization of a phylogenetic tree and annotation data
- First Published: 28 September 2022
IPGA: A handy integrated prokaryotes genome and pan-genome analysis web service
- First Published: 14 September 2022
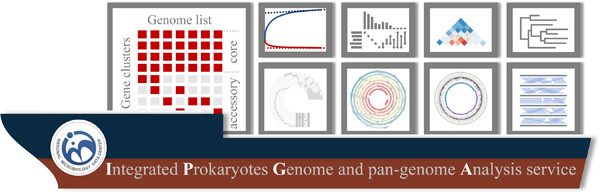
Integrated Prokaryotes Genome and pan-genome Analysis (IPGA) serves as a free and easy-to-use web-based system that could provide up-to-date pan-genome analysis service for non-bioinformaticians. IPGA offers users the most reliable pan-genome profile which enables users to perform additional comparative genomic analysis. IPGA provides a series of downstream analysis modules such as phylogenetic inference, synteny inference, and target genome annotation.
RESEARCH ARTICLES
TCM-Suite: A comprehensive and holistic platform for Traditional Chinese Medicine component identification and network pharmacology analysis
- First Published: 15 August 2022
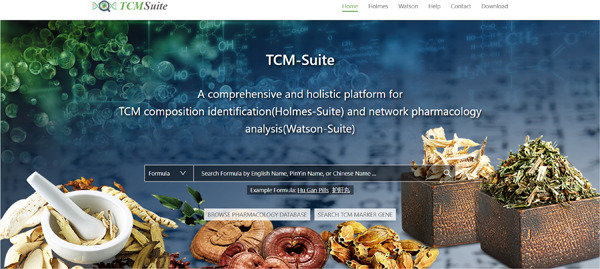
TCM-Suite platform is composed of two sub-databases, Holmes-Suite and Watson-Suite. Holmes-Suite database covers six marker genes, resulting in 235,470 kinds of biological ingredients. Watson-Suite retrieved massive data for mining the “herb-compound-protein-disease” interpretation. A holistic pipeline was designed to connect Holmes and Watson, showed by a user-friendly platform.
TCM2COVID: A resource of anti-COVID-19 traditional Chinese medicine with effects and mechanisms
- First Published: 05 August 2022
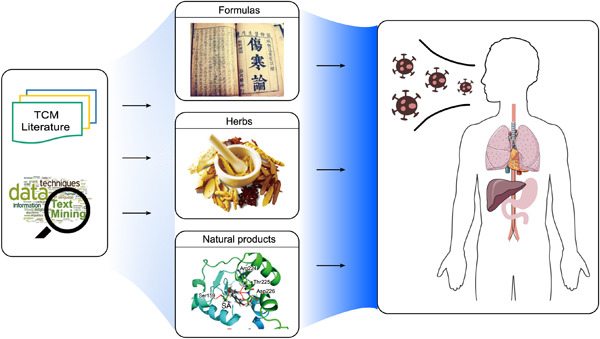
TCM2COVID documents over 280 traditional Chinese medicine formulas (including over 300 herbs) with detailed clinical evidence and therapeutic mechanism information; TCM2COVID records over 80 natural products with detailed potential therapeutic mechanisms; TCM2COVID launches a useful web server for querying, analyzing, and visualizing documented formulas similar to those supplied by the user (formula similarity analysis).
mibPOPdb: An online database for microbial biodegradation of persistent organic pollutants
- First Published: 17 August 2022
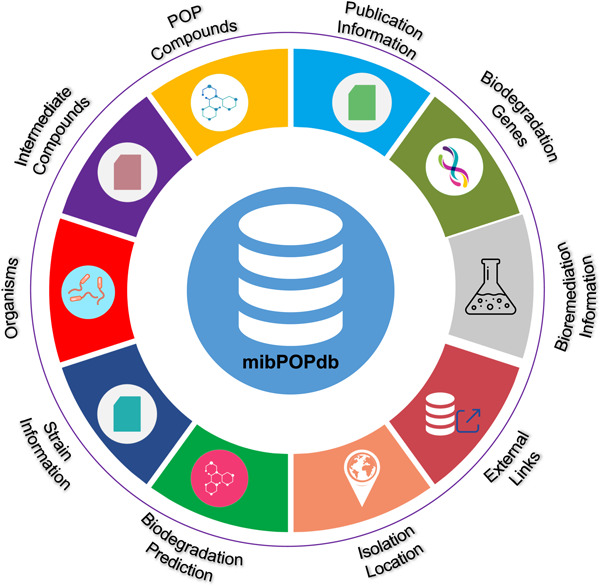
This study presents the Microbial Biodegradation of Persistent Organic Pollutants Database (mibPOPdb) database, a web-accessible literature-based microbial biodegradation of persistent organic pollutants (POPs) resource. We also developed a robust chemical biodegradability prediction model with Graph Neural Networks. By providing high-level curated information on POP-degrading microbial communities, mibPOPdb will be an essential platform for fostering studies on microbial biodegradation of POP compounds and how these microbes would help solve the problem of POP accumulation. In addition, the in silico model can be used to evaluate the persistence of organic chemicals, which is a critical task in ecological risk assessment studies.
MetaTrass: A high-quality metagenome assembler of the human gut microbiome by cobarcoding sequencing reads
- First Published: 15 August 2022
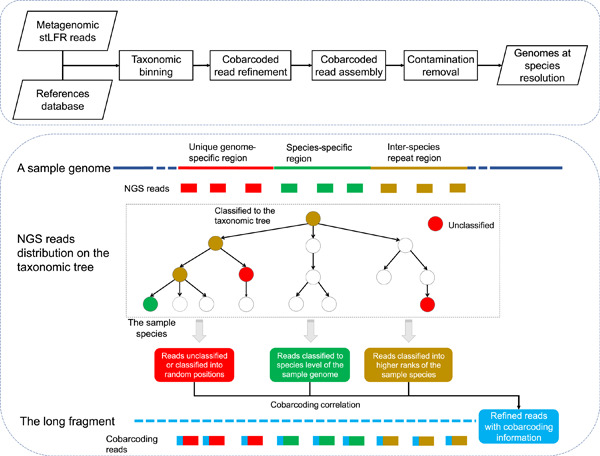
We developed a tool to get high-quality genomes with high taxonomic resolution by combining the cobarcoding information with public references. Compared with the conventional combination strategies, our pipeline generated a large number of high-quality genomes for the human microbial cobarcoding data sets.
Metabolite profiling of human-originated Lachnospiraceae at the strain level
- First Published: 13 October 2022
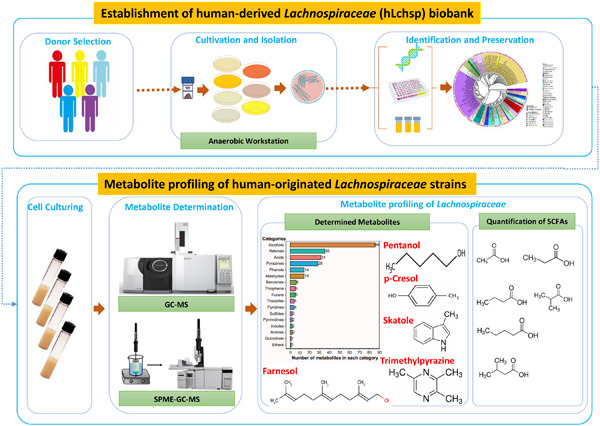
The human-originated Lachnospiraceae biobank included 77 species was constructed. In vitro metabolite profiling of 110 Lachnospiraceae strains yielded 242 metabolites of 17 categories. Many Lachnospiraceae strains produce short-chain fatty acids, and Agathobacter rectalis strain Lach-101 and Coprococcus comes strain NSJ-173 are the top two butyric acid producers in vitro.
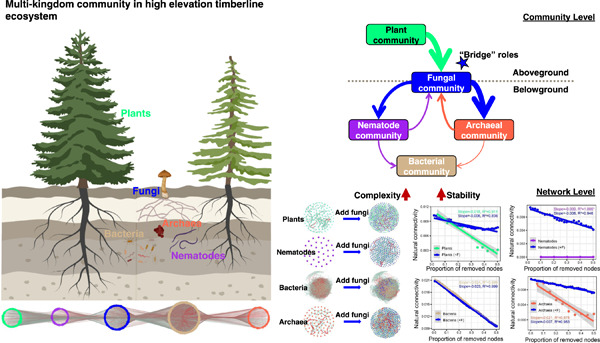
Fungi stabilize multi-kingdom community in a high elevation timberline ecosystem
- First Published: 15 August 2022
Gut microbiota composition in the sympatric and diet-sharing Drosophila simulans and Dicranocephalus wallichii bowringi shaped largely by community assembly processes rather than regional species pool
- First Published: 13 October 2022
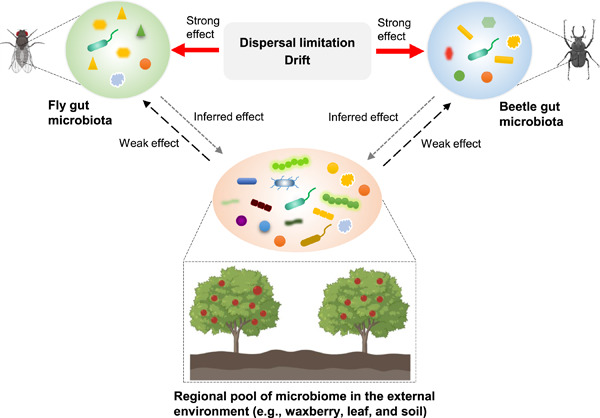
The diversity, composition, and network of gut microbiota differed between the sympatric and diet-sharing Drosophila simulans and Dicranocephalus wallichii bowringi. Host species shape the bacterial and fungal community in two insect hosts by altering the relative contribution of community assembly processes. A minority of gut microbiota within D. simulans and D. wallichii bowringi are drawn from a regional microbial pool from waxberries, leaves, or soil. The composition of insect gut microbiota is driven by community assembly processes in a host species-dependent manner more than regional microbial pools.
Targeting keystone species helps restore the dysbiosis of butyrate-producing bacteria in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease
- First Published: 16 November 2022
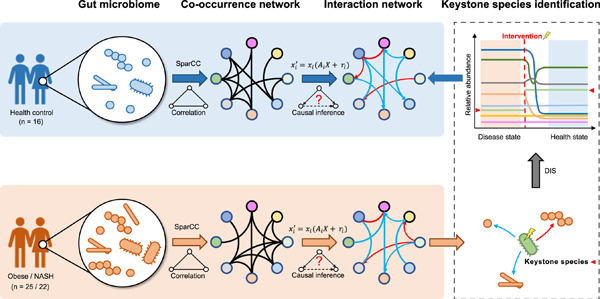
In this study, we applied an algorithm to the keystone species identification in the gut microbiome, based on current causal inference theories and the dynamic intervention simulation. We identified the nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) keystone species combination, represented by Porphyromonas loveana, Alistipes indistinctus, and Dialister pneumosintes, that showed the highest potential for the microbial intervention of NASH.
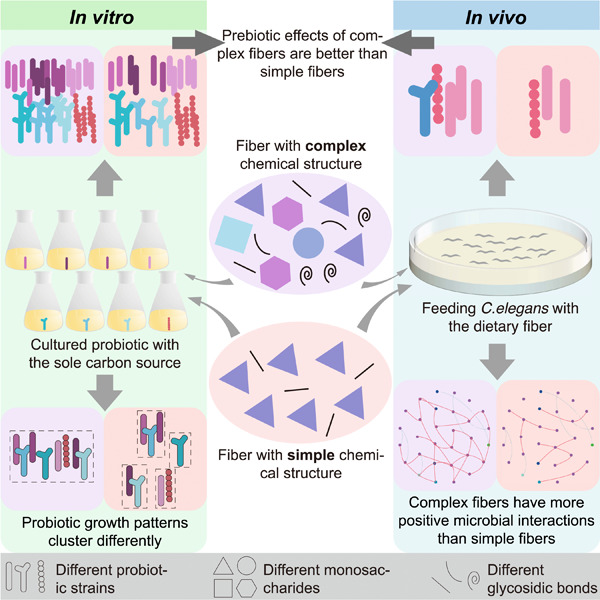
Dietary fiber chemical structure determined gut microbiota dynamics
- First Published: 28 November 2022
REVIEW ARTICLES
Charting the landscape of the environmental exposome
- First Published: 02 September 2022
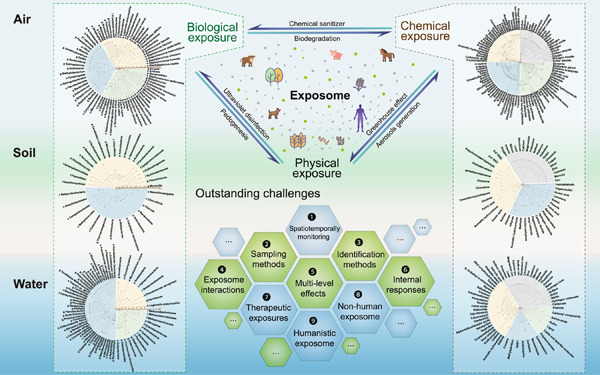
We describe the biological and chemical components of the environmental exposomes in three major environmental matrices that are highly relevant to human and social-economical health—air, soil, and water. We discuss how different exposome components can interact with each other. Finally, we propose a list of outstanding challenges to be tackled to push the field forward.
Gut microbiota-stem cell niche crosstalk: A new territory for maintaining intestinal homeostasis
- First Published: 27 September 2022
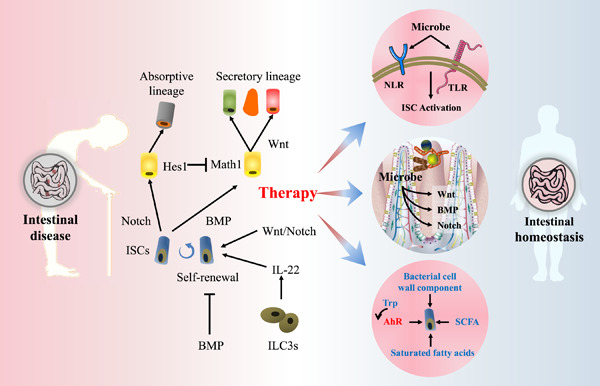
Intestinal stem cells (ISCs) are protected by their niche and are regulated by Wnt, bone morphogenetic protein, and Notch. ISCs and their relationship with intestinal microbiota provide a feasible pathway to alleviate intestinal diseases. Diverse bacteria-related postbiotics regulate ISCs and maintain their homeostasis.
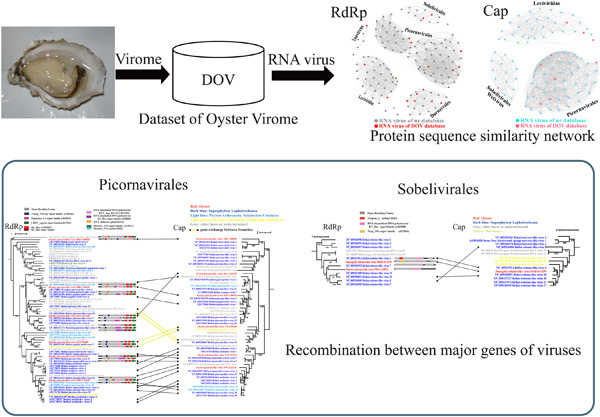
Over two decades of research on the marine RNA virosphere
- First Published: 17 October 2022
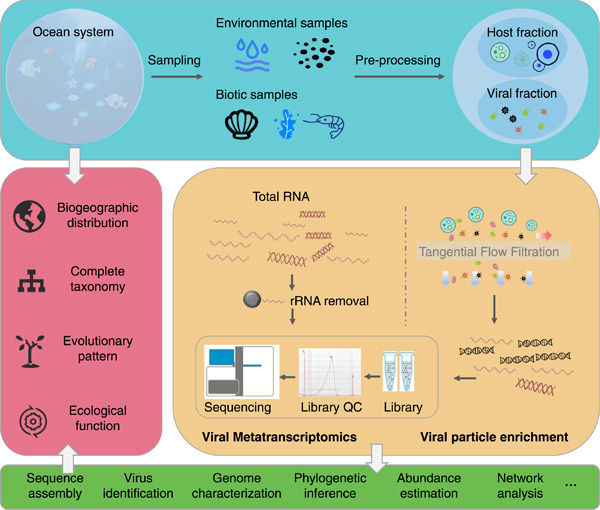
Advances in meta-omics provide a surge of marine RNA virus information. Deep marine virus discovery contributes greatly to the megataxonomy of RNA viruses. Understanding diversity and biogeography helps reveal the significance of marine RNA viruses, including evolutionary trajectories, hierarchical taxonomy, and ecological importance.
COMMENTARY
Genetic diversity and community composition of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi associated with root and rhizosphere soil of the pioneer plant Pueraria phaseoloides
- First Published: 30 September 2022
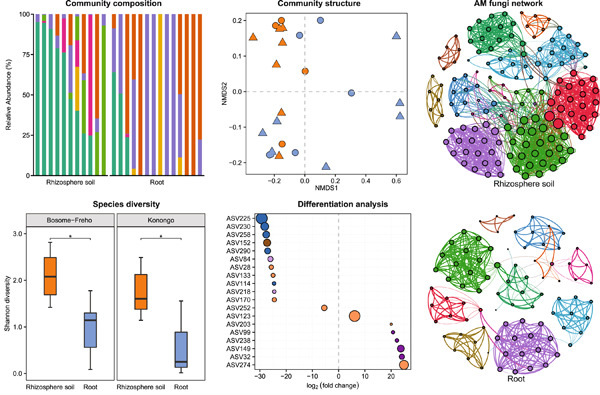
The pioneering plant Pueraria phaseoloides had a strong modulation effect on arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi (AMF) communities. Irrespective of geographical location, community composition of AMF in rhizosphere soil differed from that of the root. Co-occurrence network analysis revealed two AMF keystone species in rhizosphere soil (Acaulospora) and roots (Rhizophagus) of P. phaseoloides.
CORRESPONDENCE
Donors' experiences and attitudes of fecal microbiota transplantation: An empirical bioethics study from China
- First Published: 21 November 2022
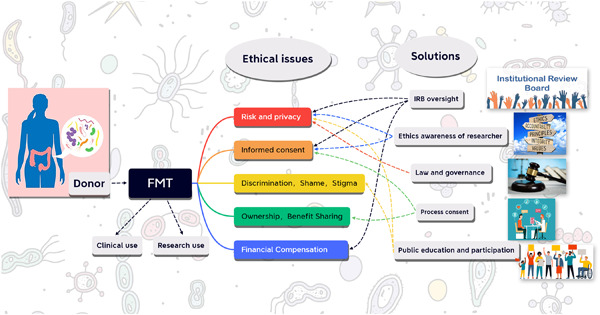
Donor participation is a critical part of ensuring the development of human microbiome research and the clinical application of fecal microbiota transplantation (FMT). Most FMT donors are still not sufficiently aware of the risks associated with the act of donating gut microbiota, especially the risk of data privacy disclosure. Enhanced awareness of the moral responsibility of the researchers and ethical oversight by ethics committees are needed.
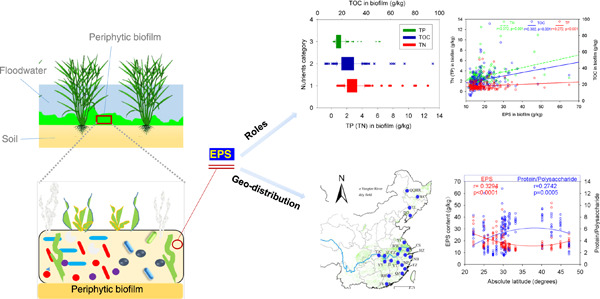
Geographic imprint and ecological functions of the abiotic component of periphytic biofilms
- First Published: 25 October 2022
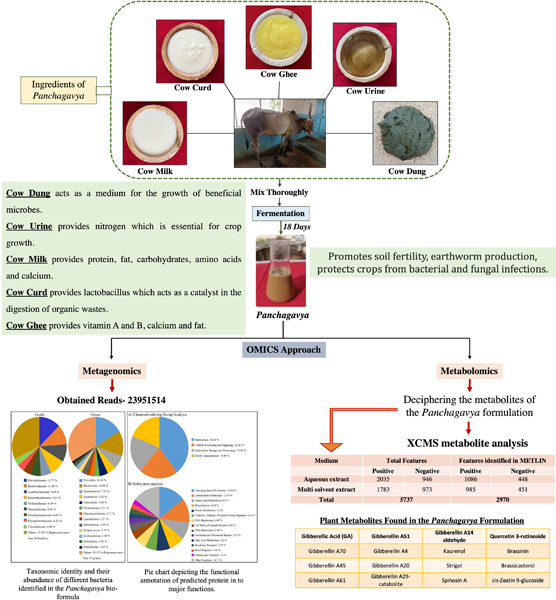
Decoding the microbiome and metabolome of the Panchagavya—An indigenous fermented bio-formulation
- First Published: 15 November 2022









3066-988X.cover.jpg)