Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
FRONT COVER
MXene-Integrated Responsive Hydrogel Microneedles for Oral Ulcers Healing (2/2025)
- First Published: 04 April 2025
ISSUE INFORMATION
REVIEW
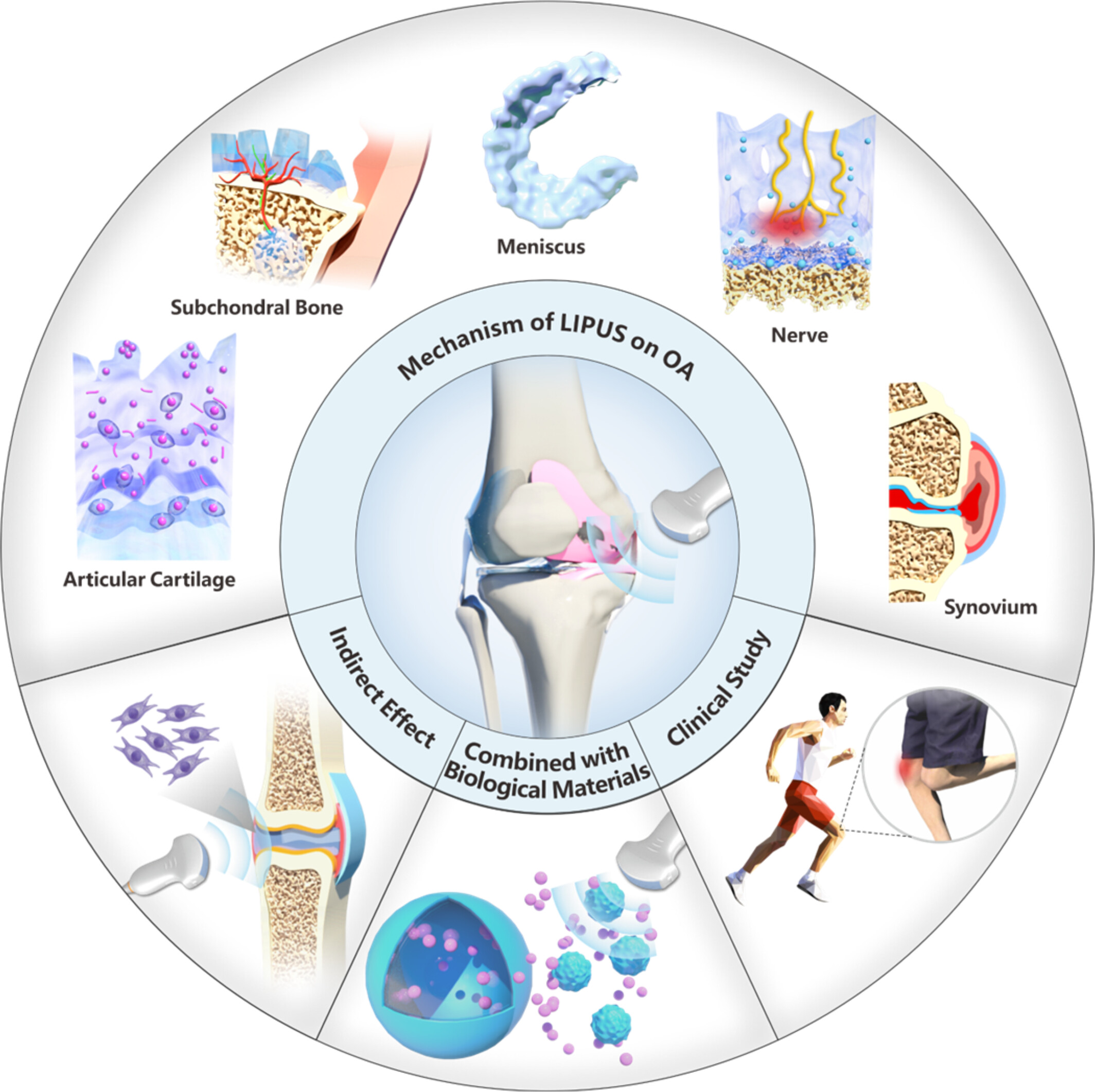
Research Progress of Osteoarthritis Treatment by Low Intensity Pulsed Ultrasound
- First Published: 16 May 2025
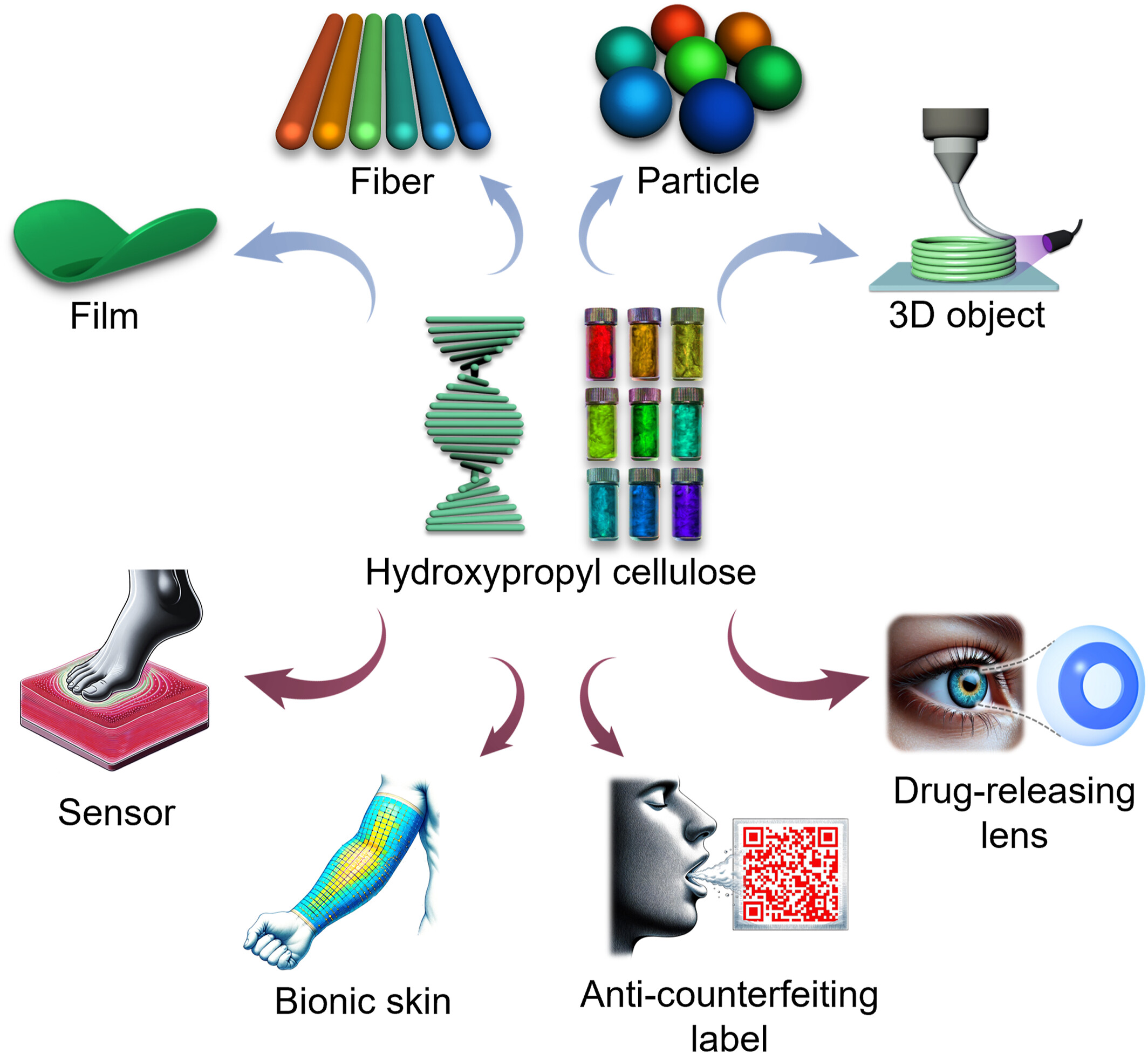
Self-Assembled Hydroxypropyl Celluloses With Structural Colors for Biomedical Applications
- First Published: 20 April 2025
The Application of Microfluidic Chips in Primary Urological Cancer: Recent Advances and Future Perspectives
- First Published: 19 May 2025
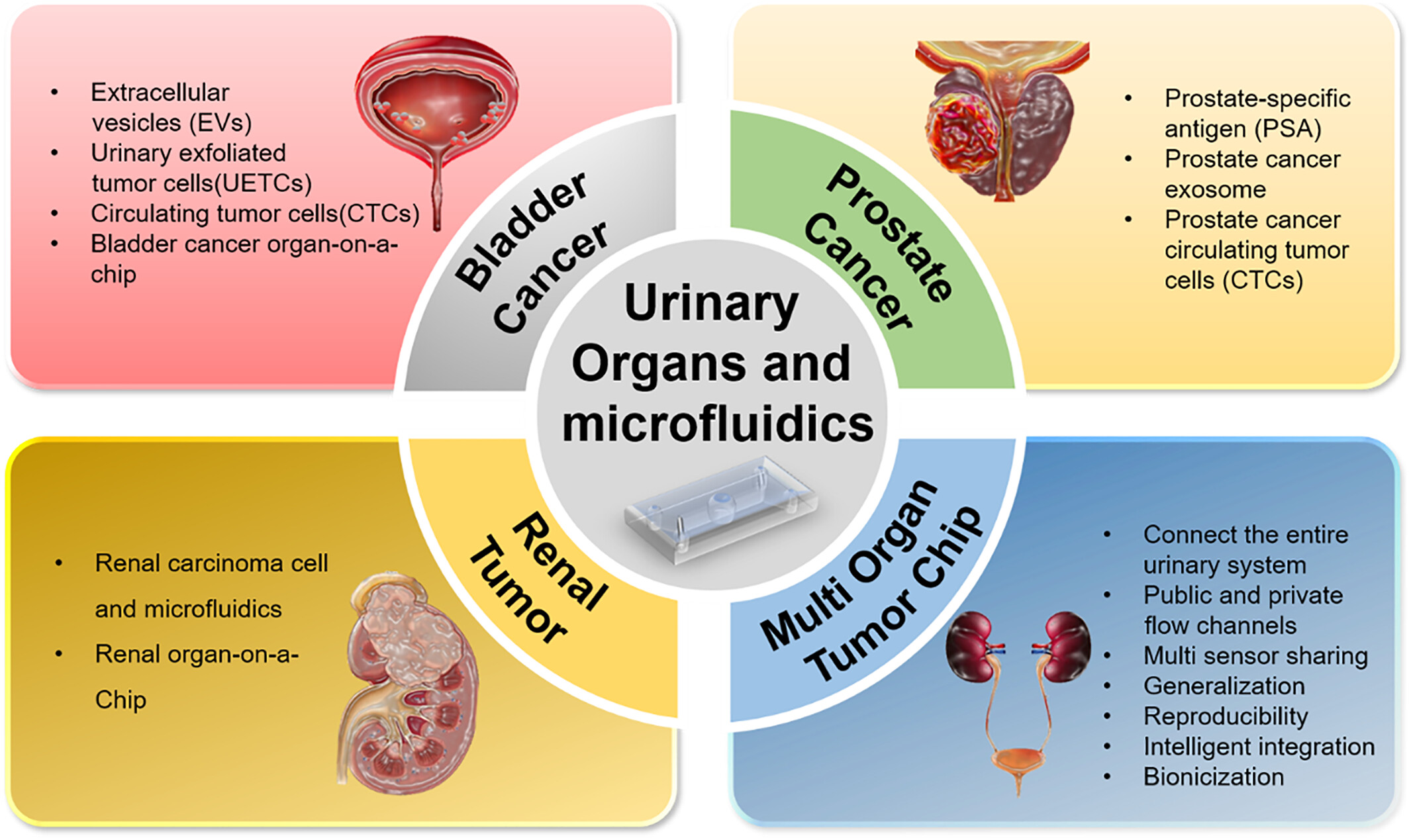
The researches of primary urological cancer include bladder cancer (BCa), prostate cancer (PCa), and renal cancer (RCa) developed rapidly but with many drawbacks. Compared to the heterogeneity of animal models and the ethical issues of human study, microfluidic technology provides various benefits. Microfluidic technology and its application with cell culture (organ-on-a-chip, OOC) have been extensively applied to study urological oncology in preclinical and clinical settings. These studies have broadened the diagnostic and therapeutic approaches for urological diseases, especially for evaluating biomarkers for urinary malignancies. In the future, microfluidic and OOC are expected to extensively complement animal models and clinical research. For the prospection of urological microfluidic studies, how to reduce costs and improve intelligent integration reproducibility and bionics are wanted.
The Recent Development in the Diagnosis of Mycobacterium tuberculosis
- First Published: 25 April 2025
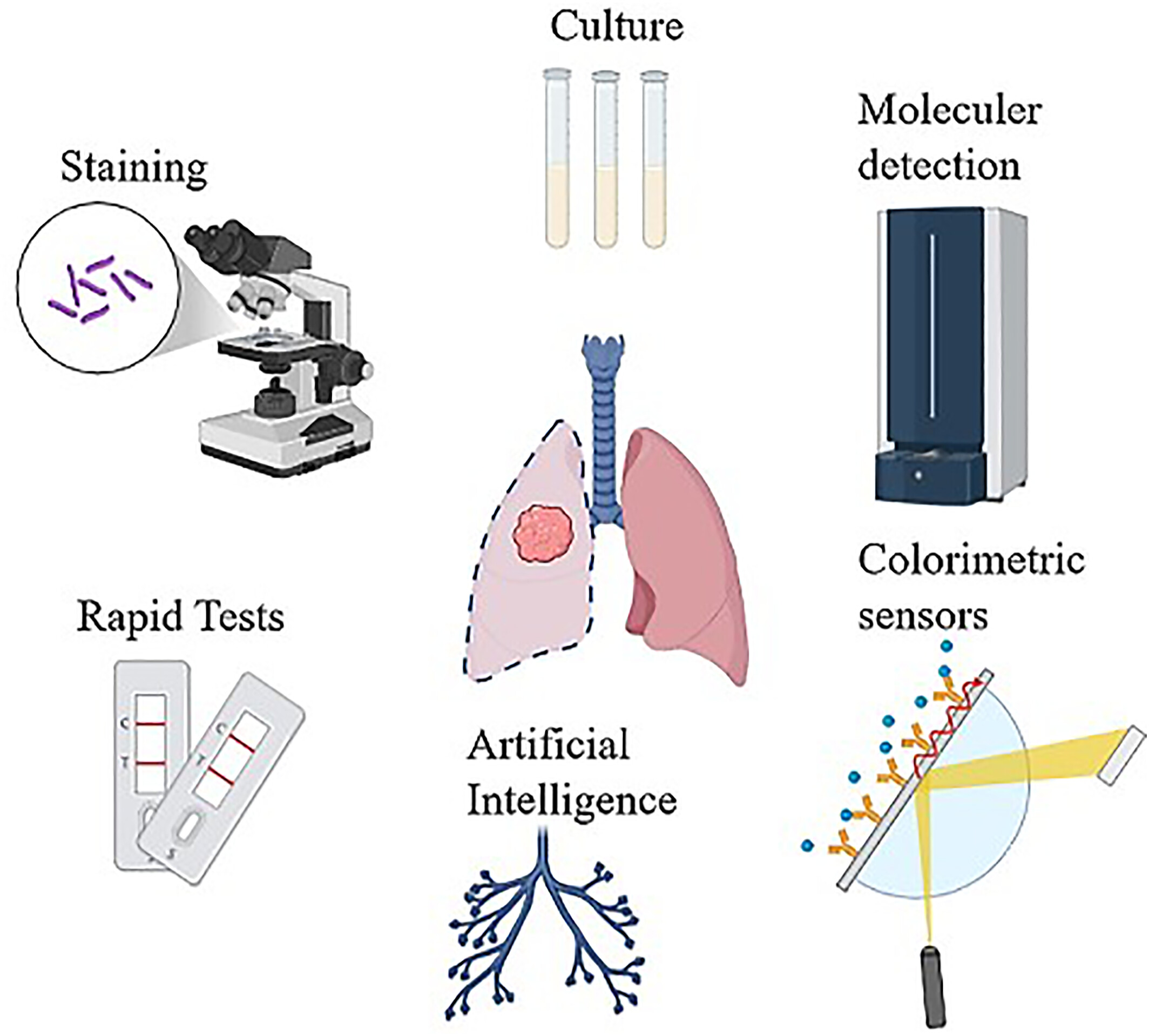
Mycobacterium tuberculosis (MTB) remains a major global health challenge due to slow, low-sensitivity traditional diagnostics. Rapid, highly sensitive point-of-care tests are critical for timely diagnosis and treatment, reducing transmission. This study reviews the evolution of MTB diagnostic tests, emphasizing advancements and addressing accessibility and efficiency challenges.
RESEARCH ARTICLE
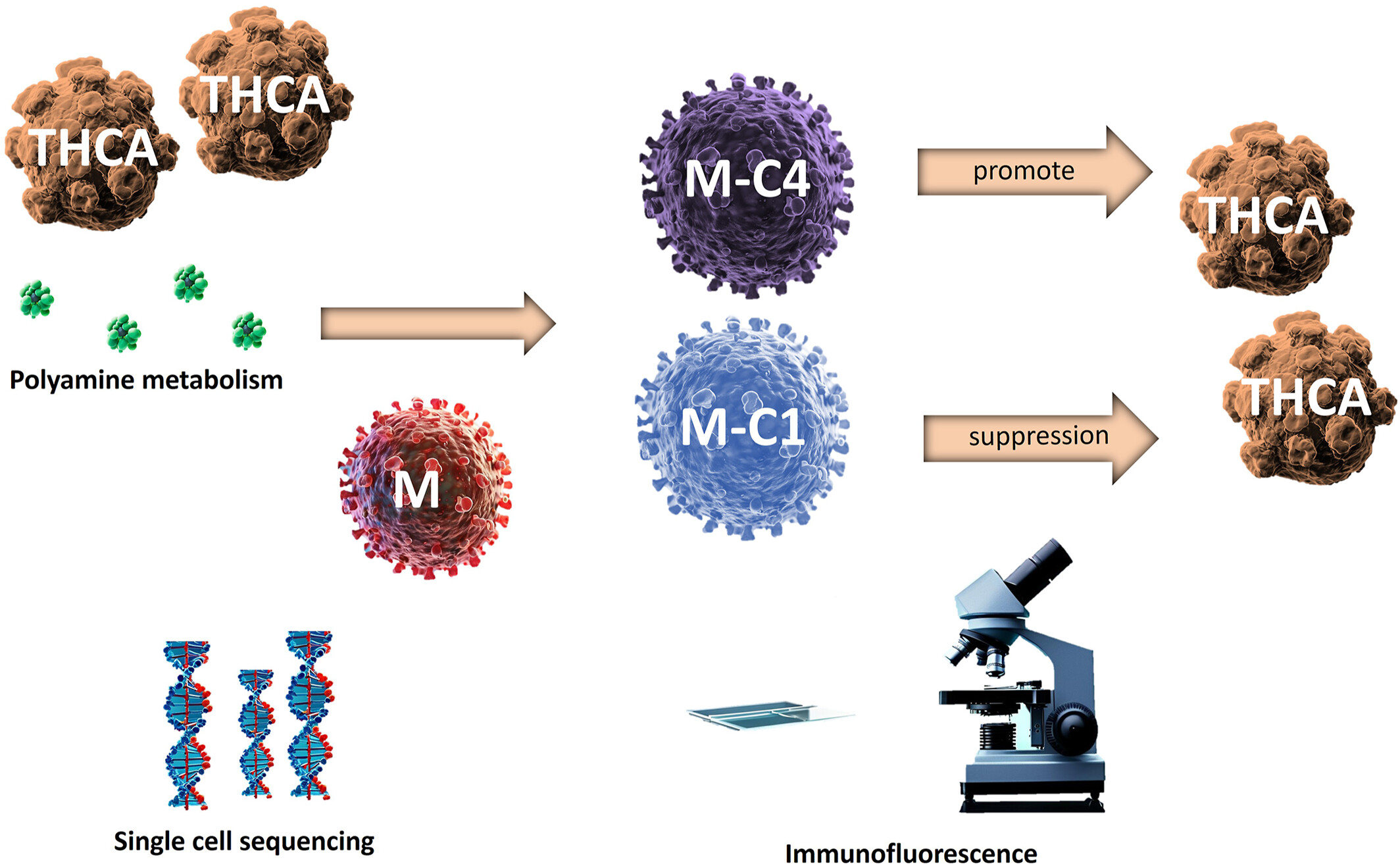
Polyamine Metabolism Promotes the Progression of Thyroid Carcinoma by Regulating the Immune Phenotype of Tumor Associated Macrophages
- First Published: 16 May 2025
MXene-Based Photothermal-Responsive Injectable Hydrogel Microsphere Modulates Physicochemical Microenvironment to Alleviate Osteoarthritis
- First Published: 13 April 2025
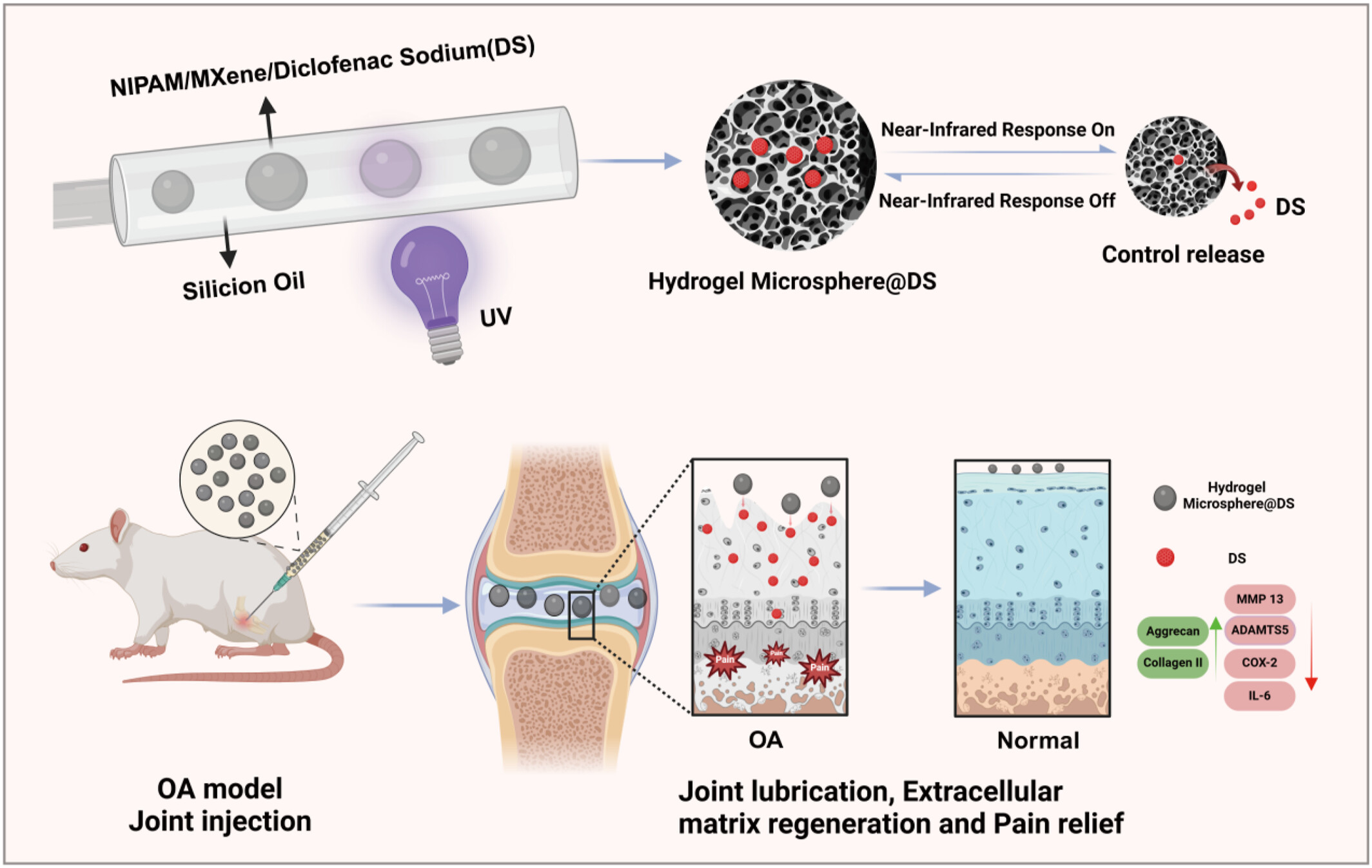
Photothermo-responsive hydrogel microspheres were synthesized using microfluidic technology, demonstrating controlled drug release under NIR laser irradiation and enhanced joint lubrication. The anti-inflammatory efficacy, reduction in cartilage degradation, and effective management of osteoarthritis in rat models were confirmed, highlighting their therapeutic potential for clinical applications.
Isoliquiritigenin Promotes the Repair of High Uric Acid-Induced Vascular Injuries
- First Published: 04 April 2025
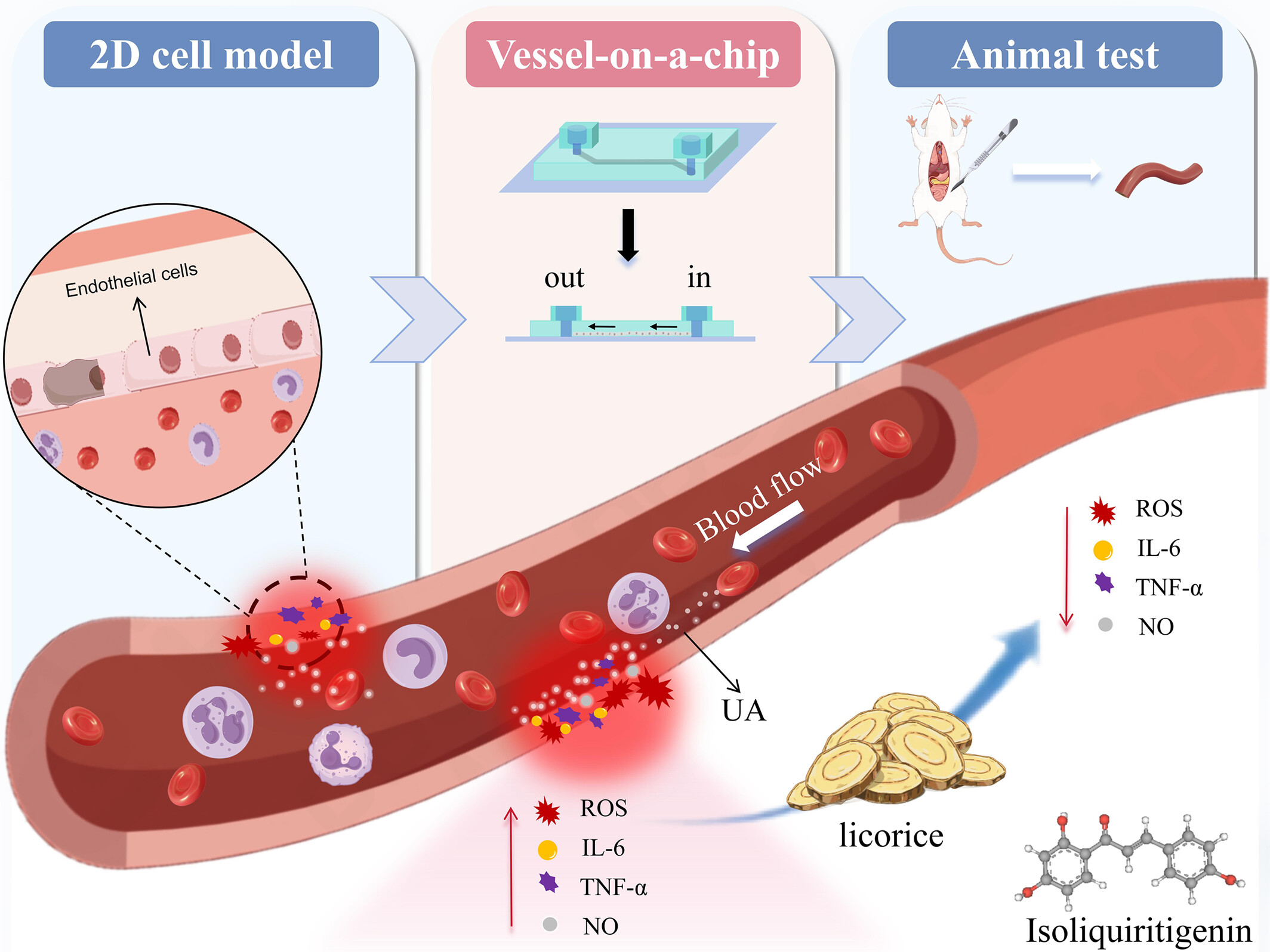
High uric acid-induced vascular injuries are always accompanied with hyperuricemia, for which seeking for effective safety drugs is an urgent and crucial problem that needs to be solved. Here, we have successfully screened isoliquiritigenin out from multiplex traditional Chinese medicine monomers in promoting the repair of high uric acid-induced vascular injuries based on our established injury indexes mini-library for the first time. This result has been identified, validated and efficiency evaluated following subsequent blood vessel-on-a-chip and animal tests. The potential mechanism has also been explored with network pharmacology, molecular docking and experimental demonstration. This work provides a new drug candidate for hyperuricemia and an important scientific reference for the clinical application of traditional Chinese medicines.
Targeting KRAS Sensitizes Ferroptosis by Coordinately Regulating the TCA Cycle and Nrf2-SLC7A11-GPX4 Signaling in Hepatocellular Carcinoma
- First Published: 06 May 2025
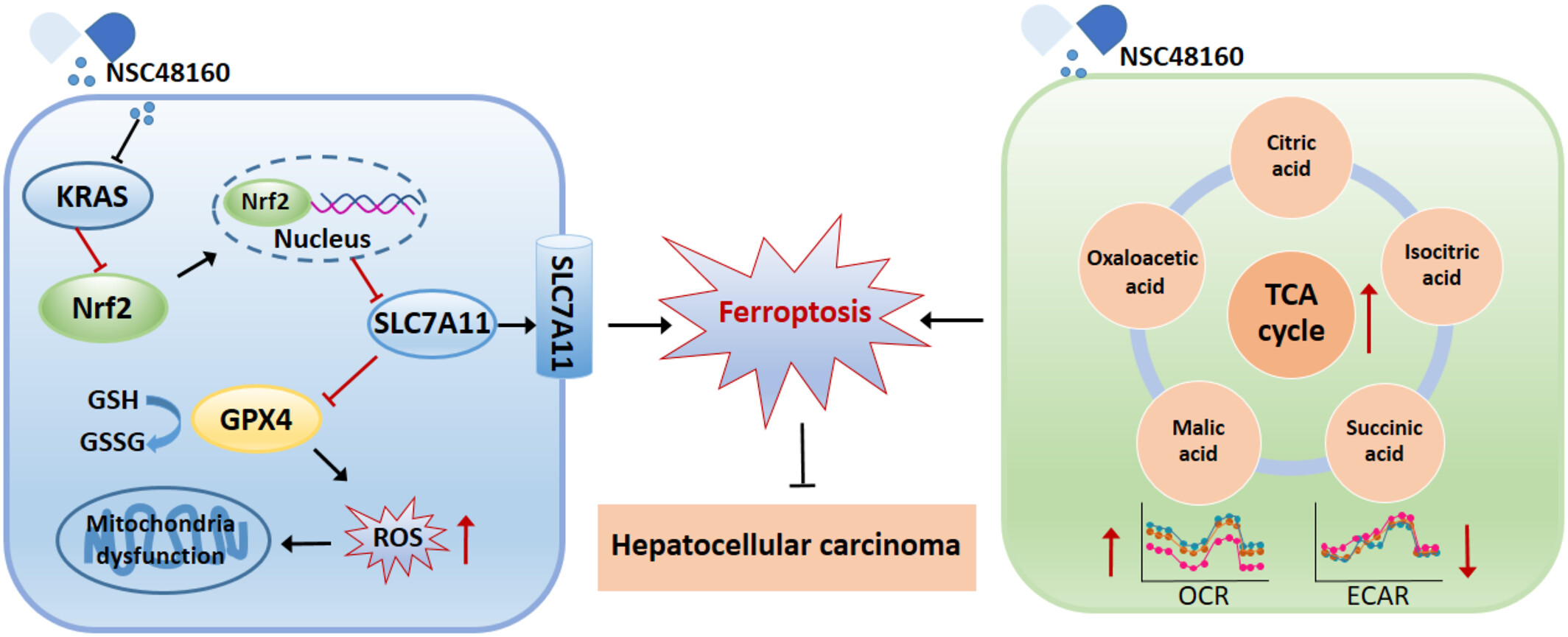
Molecular target engagements and metabolic changes reveal that NSC48160 inhibits the progression of HCC through ferroptosis. NSC48160 elucidates the ferroptosis mechanism whereby it impedes KRAS and instigates the downregulation of Nrf2/SLC7A11/GPX4. Meanwhile, NSC48160 inhibits HCC by promoting the TCA cycle, elevating the OCR, and an augmented generation of ROS.
MINI REVIEW
Droplet Microfluidics for Advanced Single-Cell Analysis
- First Published: 04 April 2025
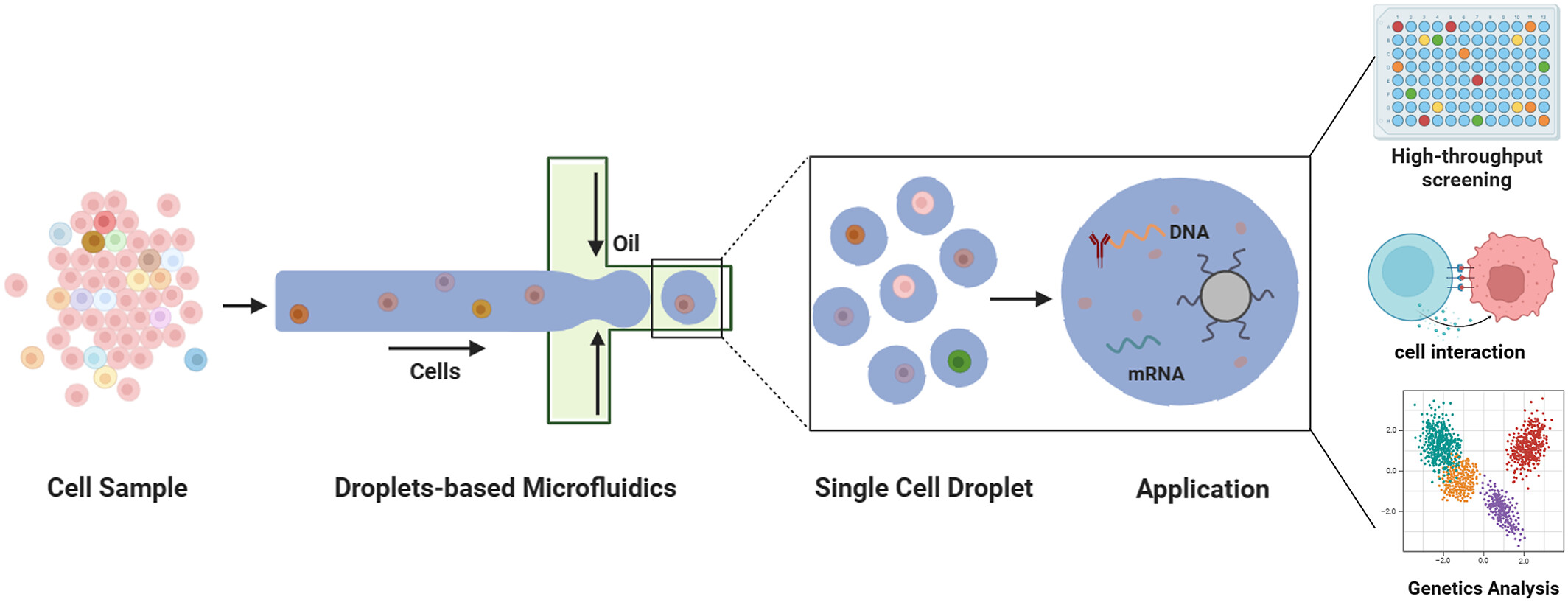
This paper reviews the transformative impact of droplet microfluidics on single-cell research. It highlights current advancements in encapsulation techniques, applications in high-throughput screening, and the study of intercellular and cell-microorganism interactions. The discussion includes the advantages, limitations, and future research directions of this innovative technology in biological investigations.