Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
ISSUE INFORMATION
RESEARCH ARTICLE
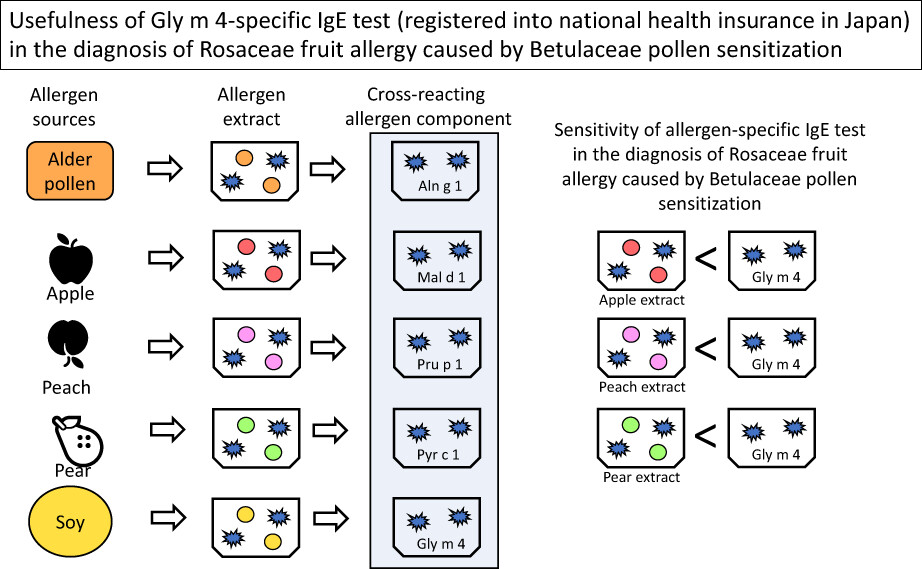
Usefulness of Gly m 4-specific IgE test in the diagnosis of Rosaceae fruit-oral allergy syndrome caused by Betulaceae pollen sensitization
- Pages: 42-48
- First Published: 09 December 2022
CASE STUDY
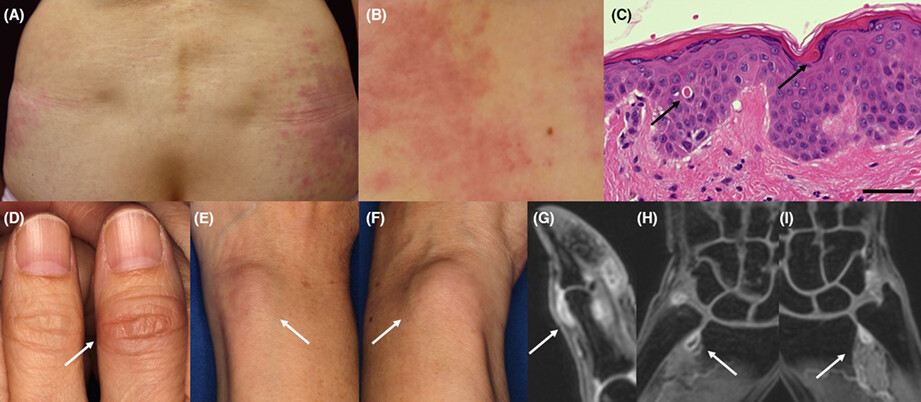
Neutrophilic dermatosis with necrobiotic changes as an unusual manifestation after the first shot of a COVID-19 mRNA vaccine together with a high fever and liver injury
- Pages: 49-54
- First Published: 02 September 2022
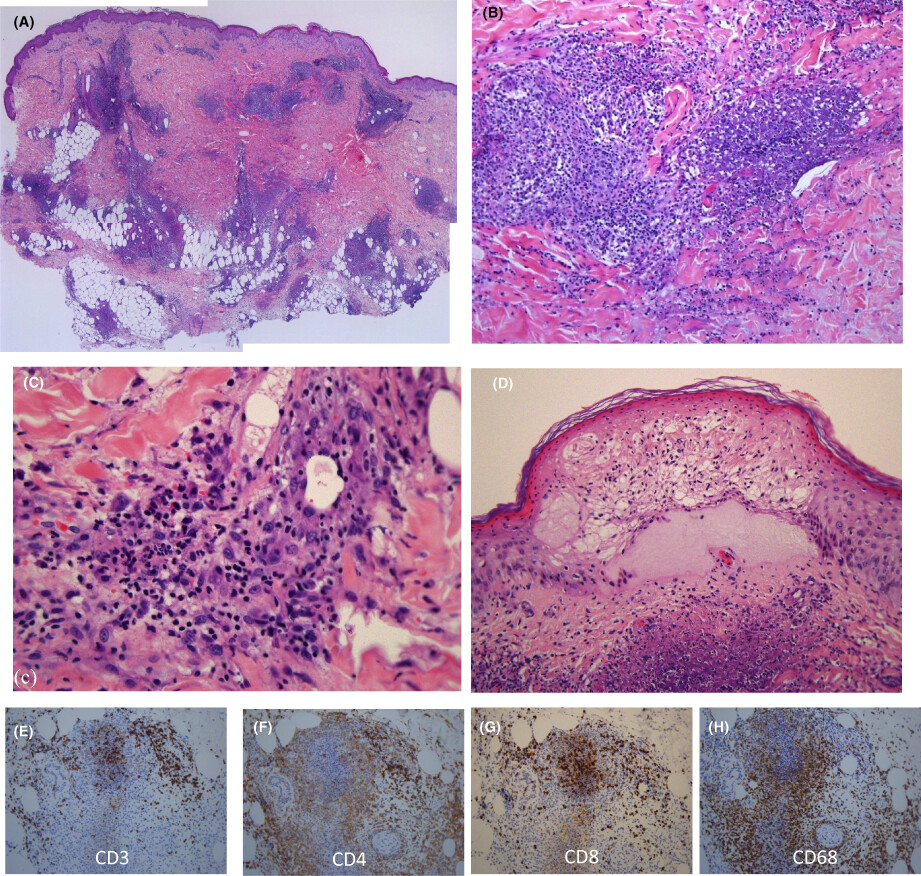
A histopathological examination of an EN-like lesion with a few pustules revealed dense perivascular and periglandular infiltrates throughout the dermis and subcutis, which were composed of neutrophils, histiocytes, lymphocytes, and a lot of cell debris with marked necrobiotic changes. Immunohistochemically, cytotoxic CD8+ cells were much more common than CD4+ cells in the dense neutrophilic infiltrates. Many CD68+ macrophages were present around the CD8+ cells.
CORRESPONDENCES
A case of COVID-19 with pernio-like skin lesions and increased red blood cell distribution width
- Pages: 55-56
- First Published: 15 August 2022
Heparin resistance has been observed in patients with active severe COVID-19 infection. The red blood cell distribution (RDW), a component of the complete blood count that reflects cellular volume variation, has been shown to be associated with elevated risk for morbidity and mortality in a wide range of diseases. Cutaneous manifestations, RDW, and levels of LD and D-dimer might be useful biomarkers in triage of patients with COVID-19.
Erythema annulare centrifugum in the setting of COVID-19 infection: A case report and literature review
- Pages: 57-58
- First Published: 30 August 2022
Hydroxyzine-induced fixed drug eruption and cross-reaction with oxatomide
- Pages: 59-60
- First Published: 15 September 2022
There are a few reports in the literature implicating them in causing fixed drug eruption, the piperazine derivatives. In this case, although eszopiclone for insomnia medicinehas a piperazine ring, no eruption appeared so far. Oxatomide and hydroxyzine not only shared a piperazine ring but also shared two benzene rings via a methine group (=CH–). It was suspected that this shared structural group became an antigenic determinant and resulted in cross-reactivity. Such a unique case has not been reported before.
A case of cutaneous Mycobacterium chelonae infection requiring a differential diagnosis of Mycobacterium stephanolepidis infection
- Pages: 61-62
- First Published: 08 September 2022
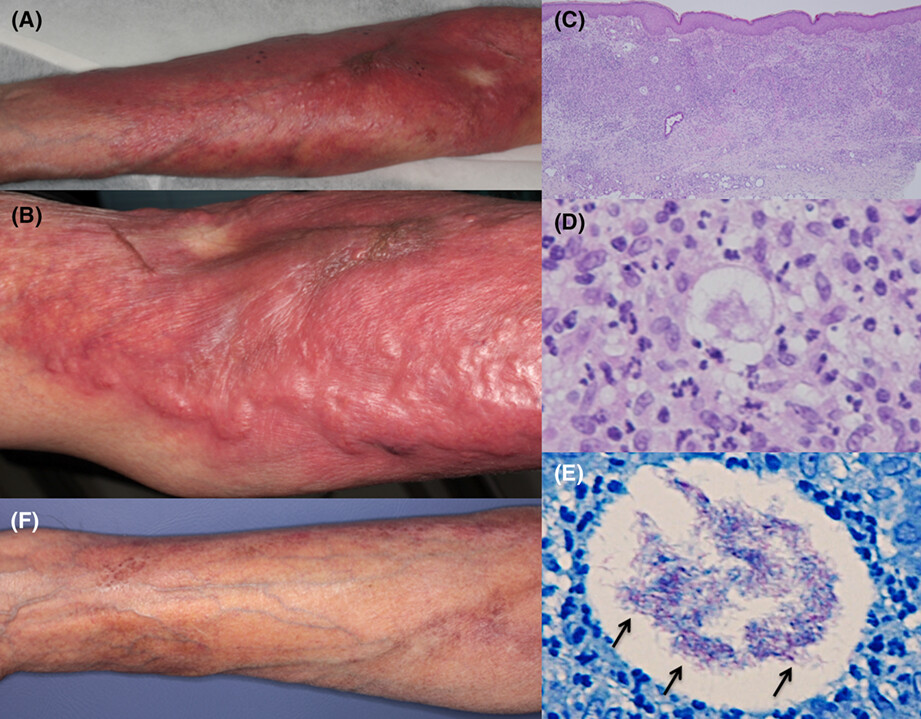
Mycobacterium stephanolepidis is a rapidly growing mycobacterium, closely related to Mycobacterium chelonae. It was first reported in 2017, and whether it is infectious to humans is unknown. Here, we report a rare case of cutaneous M. chelonae infection requiring a differential diagnosis of M. stephanolepidis infection.
A case of refractory hypertrophic lupus erythematosus on the face whose irreversible skin fibrosis was treated by local full-thickness skin graft under disease control with a combined use of topical and systemic immunosuppressants, and hydroxychloroquine
- Pages: 63-65
- First Published: 26 August 2022
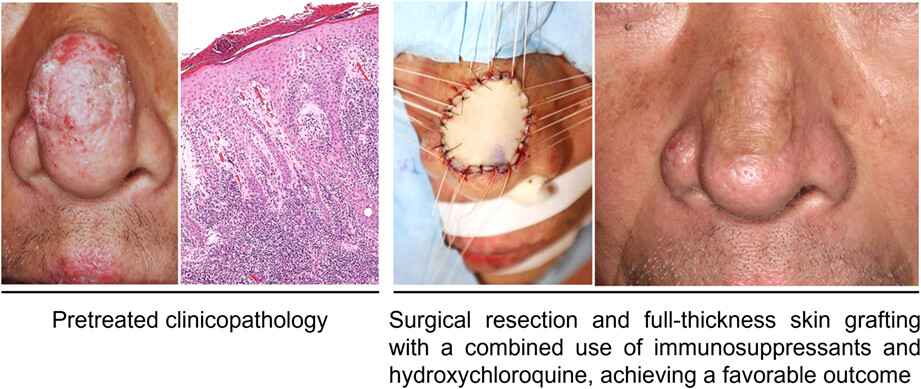
Hypertrophic lupus erythematosus (HLE) remains pose a treatment challenge, and often displays disfiguring scar with cosmetic and/or functional impairment. We report a male case of refractory hypertrophic lupus erythematosus on the face, whose disease activity was controlled with a combined use of topical and systemic immunosuppressants, and hydroxychloroquine. The persisted, irreversible fibrotic skin mass was finally treated with surgical approach using full-thickness skin graft, achieving a favorable cosmetic result.
Adult-onset Still's disease following mRNA-1273 Moderna COVID-19 vaccination: A case report
- Pages: 66-67
- First Published: 19 October 2022