Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Issue Information
Review
Platelets and Platelet-Derived Extracellular Vesicles in Liver Physiology and Disease
- Pages: 855-866
- First Published: 22 April 2019
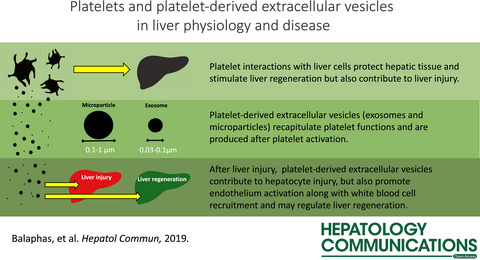
Platelets are proposed as key mediators of several physiological and pathophysiological processes of the liver such as liver regeneration, toxic or viral acute liver injury, liver fibrosis, and carcinogenesis. Platelets are the major source of circulating extracellular vesicles, which are suggested to play key roles in platelet interactions with endothelial cells in several clinical disorders. In the present review, we discuss the implications of platelet-derived extracellular vesicles in physiological and pathophysiological processes of the liver.
Original Articles
Deficient IL-6/Stat3 Signaling, High TLR7, and Type I Interferons in Early Human Alcoholic Liver Disease: A Triad for Liver Damage and Fibrosis
- Pages: 867-882
- First Published: 10 May 2019
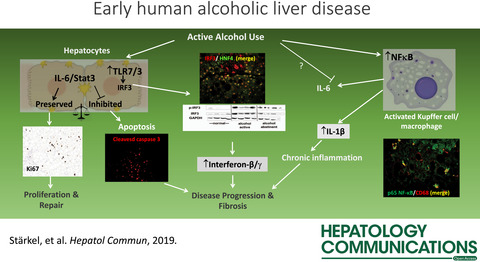
Why some patients with alcohol dependence develop progressive liver disease remains largely unknown. Here we describe inflammatory and immune mechanisms that increase liver damage and impair liver regeneration and repair. These changes already operate at early stages of alcoholic liver disease in humans. They likely prepare an environment that favors progression of liver disease if drinking habits persist and could constitute a future target for therapy.
Nocturnal Hypoxia Activation of the Hedgehog Signaling Pathway Affects Pediatric Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Severity
- Pages: 883-893
- First Published: 17 April 2019
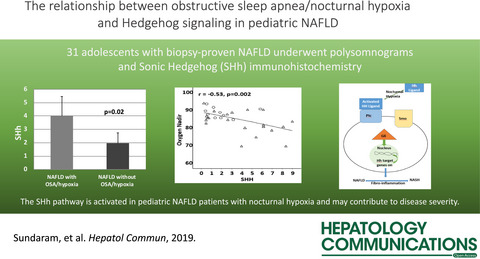
Chronic intermittent hypoxia and dysregulation of the Hedgehog (Hh) pathway are associated with NAFLD progression. In adolescents with biopsy proven NASH and sleep apnea, the severity of their obstructive sleep apnea correlated with SHh (r = 0.31, P = 0.09) and Gli2 positively (r = 0.37, P = 0.04). The severity of hypoxia was also associated with increasing SHh (r = −0.53), GLI2 (r = −0.52), α-SMA (r = −0.61), and K7(r = −0.42), P < 0.02. The Hh pathway is activated in pediatric NAFLD patients with nocturnal hypoxia and relates to disease severity.
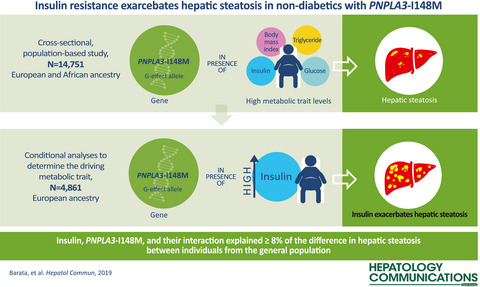
Insulin Resistance Exacerbates Genetic Predisposition to Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in Individuals Without Diabetes
- Pages: 894-907
- First Published: 18 April 2019
Selective Liver Estrogen Receptor α Modulation Prevents Steatosis, Diabetes, and Obesity Through the Anorectic Growth Differentiation Factor 15 Hepatokine in Mice
- Pages: 908-924
- First Published: 29 April 2019
Influence of Fat on Differential Receptor Interacting Serine/Threonine Protein Kinase 1 Activity Leading to Apoptotic Cell Death in Murine Liver Ischemia Reperfusion Injury Through Caspase 8
- Pages: 925-942
- First Published: 25 April 2019
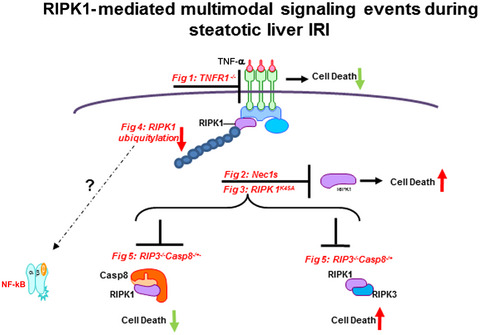
Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease is increasingly prevalent and markedly complicates an affected individual’s capacity to tolerate ischemia reperfusion injury (IRI) by resulting in cell death. In this study, we demonstrate that blockade of RIP1 kinase activity leads to exacerbated cell death in steatotic liver undergoing hepatic IRI via a caspase 8 mediated apoptotic-cell death mechanism. These are clinically relevant, novel findings with a broad applicability. This study also presents new targets for drug therapy to prevent hepatocellular injury in NAFLD.
Repression of MicroRNA-30e by Hepatitis C Virus Enhances Fatty Acid Synthesis
- Pages: 943-953
- First Published: 25 April 2019
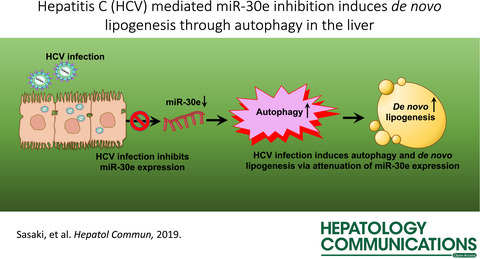
HCV infection inhibited miR-30e expression. Exogenous expression of miR-30e targets ATG5 and inhibits HCV induced autophagy and lipid synthesis. These results provide new mechanistic insights into the interactions between autophagy and lipid synthesis via inhibition of miR-30e in HCV infected hepatocytes.
OLFM4 Enhances STAT3 Activation and Promotes Tumor Progression by Inhibiting GRIM19 Expression in Human Hepatocellular Carcinoma
- Pages: 954-970
- First Published: 02 May 2019
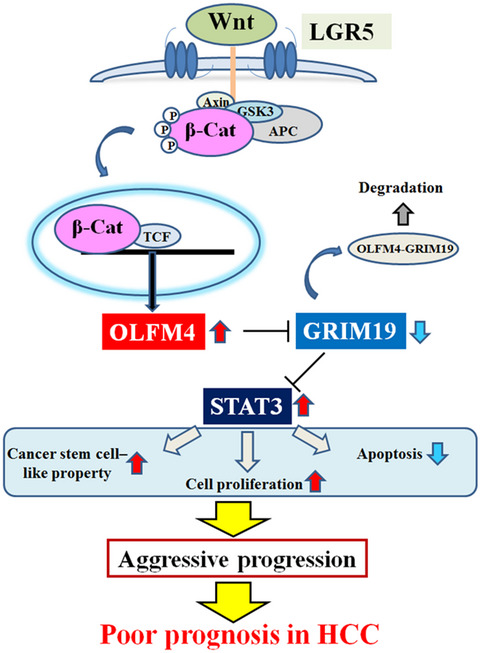
OLFM4 is induced by the LGR5-Wnt signaling pathway and strongly associated with aggressive tumor progression and poor prognosis in HCC, by regulating STAT3-induced tumor cell proliferation and cancer stem cell–like property. OLFM4 is a novel prognostic predictor and a potential therapeutic target for patients with HCC.
Hepatocellular Carcinoma Xenografts Established From Needle Biopsies Preserve the Characteristics of the Originating Tumors
- Pages: 971-986
- First Published: 06 May 2019
Emricasan Ameliorates Portal Hypertension and Liver Fibrosis in Cirrhotic Rats Through a Hepatocyte-Mediated Paracrine Mechanism
- Pages: 987-1000
- First Published: 22 April 2019
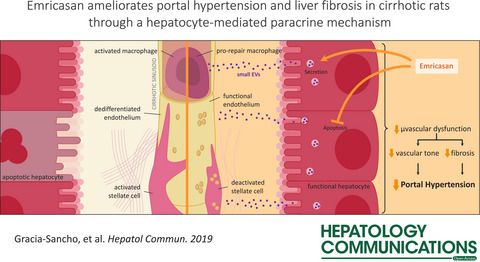
One-week emricasan promoted a significant amelioration in portal hypertension and hepatic microcirculation in experimental cirrhosis. Underlying mechanisms included direct improvement in hepatocytes phenotype, which paracrinally leads to fibrosis improvement, better endothelial function, and less inflammation.
A Single-Center Experience on Outcomes of Complementary and Alternative Medicine Use Among Patients With Cirrhosis
- Pages: 1001-1012
- First Published: 12 April 2019
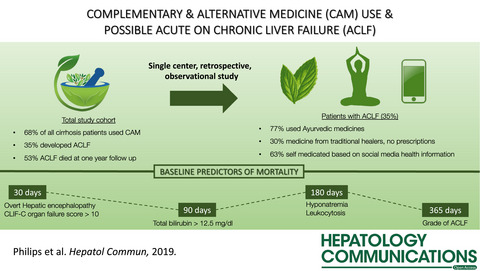
Data on complementary and alternative medicine (CAM) related drug induced liver injury leading to acute on chronic liver failure (ACLF) is lacking. Our study describes predictors of patient outcomes in the short, intermediate and long-term in possible CAM related ACLF. Self-treatment with un-labelled Ayurvedic multi-herb drugs and consultations with traditional healers is common among cirrhotics . Baseline clinical, investigational and ACLF grades help predict liver related death. CAM use among cirrhosis is a modifiable risk factor to ease liver disease burden and resource utilization.
Correspondence
Prothrombin Complex Concentrates Only After Thromboelastography
- Page: 1013
- First Published: 16 April 2019
Correspondence regarding a recent article involving the use of prothrombin complex concentrates.