Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
ISSUE INFORMATION
EDITORIAL
Hypnotherapy and IBS: Time to take control of the Asian gut
- Pages: 445-446
- First Published: 07 July 2022
LEADING ARTICLE
Experience and clinical efficacy of gut-directed hypnotherapy in an Asian population with refractory irritable bowel syndrome
- Pages: 447-453
- First Published: 19 May 2022
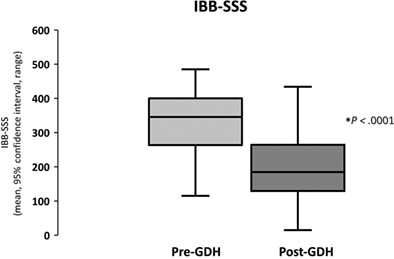
This study suggests that hypnotherapy is a highly effective treatment approach in an Asian population with refractory irritable bowel syndrome. Hypnotherapy significantly improves gastrointestinal, extra-intestinal, psychological symptoms, and quality of life. These data have highlighted the need for developing hypnotherapy services and population-specific clinical studies to confirm these findings in Asian countries.
REVIEW ARTICLE
Brain–immune–gut benefits with early life supplementation of milk fat globule membrane
- Pages: 454-461
- First Published: 01 June 2022
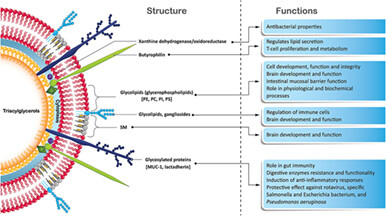
The milk fat globule membrane (MFGM) has been recognized as a milk component for more than 60 years, but its exact benefits remain unknown. Research on human MFGM has revealed that the membrane holds a host of bioactive components with potential benefits for the brain–immune–gut axis in early life. Evidence indicates the potential benefits of MFGM in early life supplementation, including better cognitive development, reduction of infection risks, and modulation of the gut microbiome.
ORIGINAL ARTICLES
Characteristics of hepatocellular carcinoma in patients with hepatitis C virus who received direct-acting antiviral therapy and achieved sustained virological response: The impact of a hepatologist on surveillance
- Pages: 462-469
- First Published: 06 June 2022
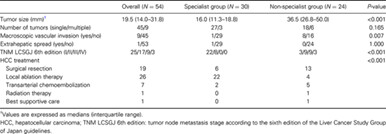
- The relationship between the characteristics of HCC diagnosed after SVR with DAA therapy and surveillance status has not been sufficiently investigated.
- This study investigated the clinical risk factors for HCC development and HCC characteristics according to which type of physician performed follow-up after SVR in Japan.
- Follow-up physician type (non-specialist) (HR, 39.100) was independently associated with HCC stage progression.
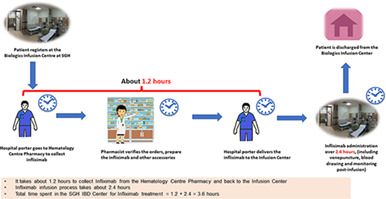
A quality improvement project reduces time spent at an inflammatory bowel disease infusion center with accelerated infliximab infusion protocol
- Pages: 470-476
- First Published: 01 June 2022
Comparison of the prognostic effect of sarcopenia on atezolizumab plus bevacizumab and lenvatinib therapy in hepatocellular carcinoma patients
- Pages: 477-486
- First Published: 08 June 2022
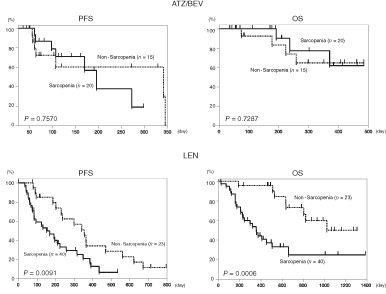
We compared the effect of sarcopenia on the prognosis of unresectable-hepatocellular carcinoma patients treated with atezolizumab plus bevacizumab and lenvatinib. In patients treated with lenvatinib, sarcopenia was the significant prognostic factor, whereas in patients treated with atezolizumab plus bevacizumab, sarcopenia does not determine prognosis.
General evaluation score for predicting the development of hepatocellular carcinoma in patients with advanced liver fibrosis associated with hepatitis C virus genotype 1 or 2 after direct-acting antiviral therapy
- Pages: 487-495
- First Published: 08 June 2022
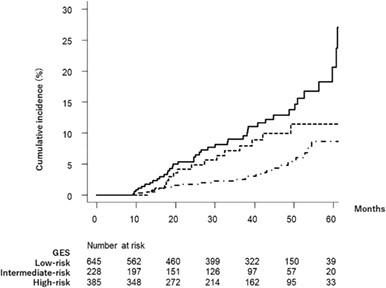
To validate the utility of the general evaluation score (GES) for predicting the development of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) in patients with advanced liver fibrosis associated with hepatitis C virus genotype 1 or 2 who have received direct-acting antiviral. The incidence of HCC differed significantly by GES-based risk groups in this patient population. GES had higher predictive power for HCC development than FIB-4 index according to time-dependent receiver operating characteristic analysis.
Analysis of the albumin-bilirubin score as an indicator of improved liver function among hepatitis C virus patients with sustained viral response after direct-acting antiviral therapy
- Pages: 496-502
- First Published: 16 June 2022
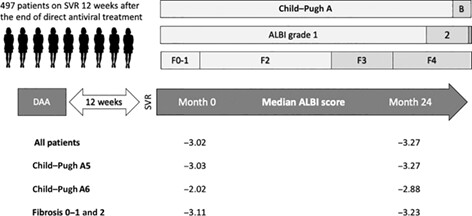
A cohort of 497 patients with chronic hepatitis C (97% in Child–Pugh (CTP) class A and 53% with fibrosis grades 0–2) who achieved sustained virological response after direct antiviral therapy were followed for at least 24 months; albumin-bilirubin (ALBI) score improved significantly over time, including patients with ALBI grade 1 or CTP A5 at baseline. A significant improvement in ALBI was also observed across stages of fibrosis at baseline.
Efficacy and safety of oral semaglutide in patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease complicated by type 2 diabetes mellitus: A pilot study
- Pages: 503-511
- First Published: 16 June 2022
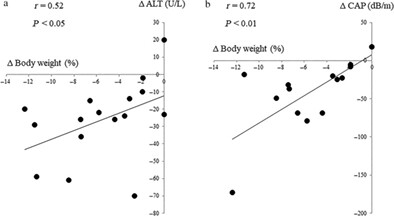
This is a single-arm, open-label pilot study. Oral semaglutide treatment for 24 weeks in patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease complicated by type 2 diabetes improved impaired liver function, hypertriglyceridemia, insulin resistance, and hepatic steatosis, as well as improving diabetic status and reducing body weight.
CASE REPORT
Nausea and vomiting caused by candida esophagitis in an elderly frail patient
- Pages: 512-513
- First Published: 03 June 2022