Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
ISSUE INFORMATION
RESEARCH ARTICLES
Daylight integrated indoor VLC architecture: An energy-efficient solution
- First Published: 18 November 2019
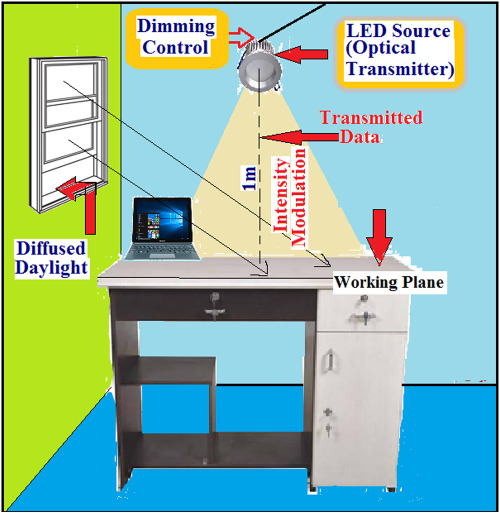
We propose novel daylight integrated indoor VLC architecture through a suitable dimming control mechanism adopted in transmitter section of the system. Maximum 37.29% energy can be saved at utmost daylight condition while fulfilling both communication and lighting requirements. Furthermore, measured short term flicker severity at the time of data transmission complies with IEC guidelines. The wide-range dimming mechanism has the provision to integrate ambient daylight up to 500 lux depending upon the daylight availability & system requirement.
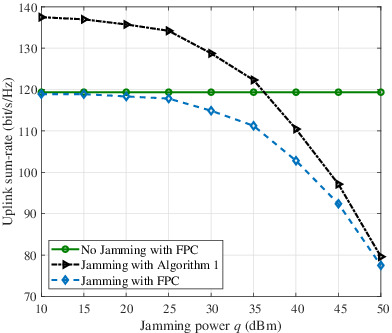
Sum-rate maximization in uplink cell-free massive multiinput multioutput system with jamming
- First Published: 20 August 2020
Game theoretic application for energy efficient mobility handling in wireless sensor network
- First Published: 12 August 2020
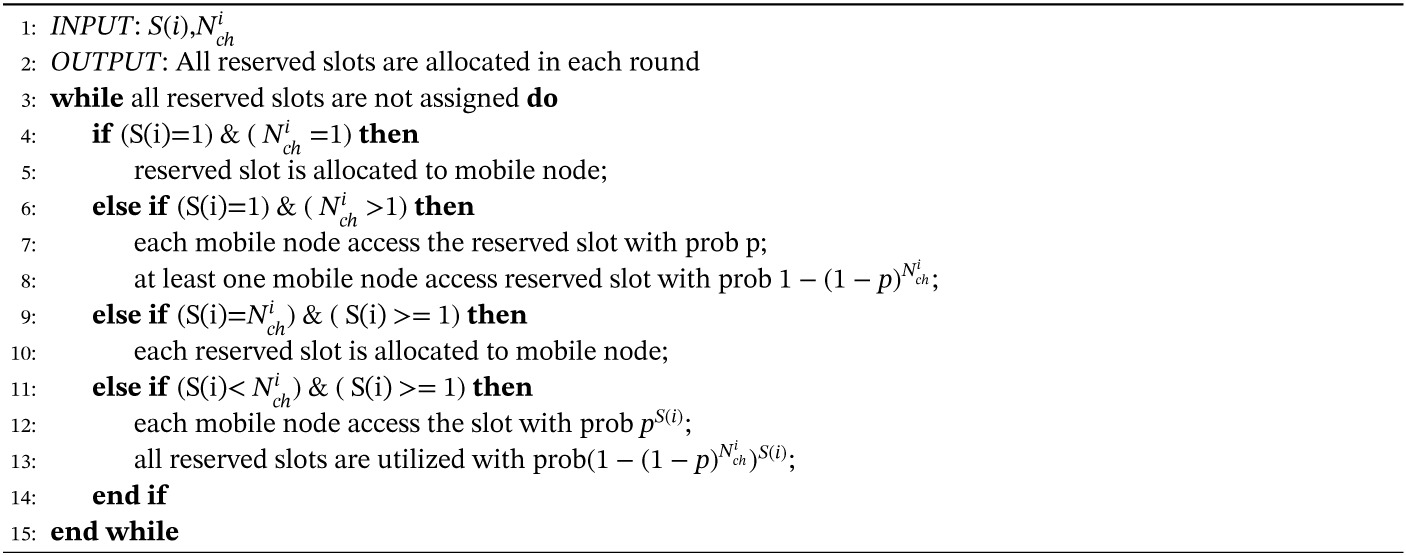
- 1.
Cooperative Coordination scheme (CCS) is used to provide reserved TDMA slots to occasional mobile nodes to allow them to send data packets in current TDMA schedule.
- 2.
Calculation of probability p used by occasional mobile nodes to send data packets to avoid congestion and packet loss in network is done.
- 3.
This scheme can achieve efficient delivery of packets and avoid discarded messages due to buffer overflows.
A review of industrial wireless communications, challenges, and solutions: A cognitive radio approach
- First Published: 15 July 2020
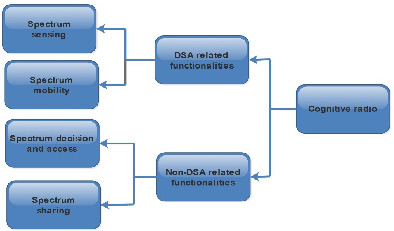
For IWSNs nodes to enjoy the benefits of CR technology as anticipated, DSA capabilities developed for CR nodes have to be integrated into IWSN nodes functionalities. Moreover, DSA provides individual sensor nodes in IWSN with CR ability. As a result, the nodes are able to detect unused frequency spectrum in congested ISM band as well as to opportunistically utilize the channel for their communications. However, the realization of DSA capabilities for IWSN nodes involves executing spectrum sensing and spectrum mobility requirements which are two important CR functionalities. We illustrate the two-level implementation in Figure below.
Joint resource block and power allocation in heterogeneous cellular networks with different backhaul capacity limitations
- First Published: 28 July 2020
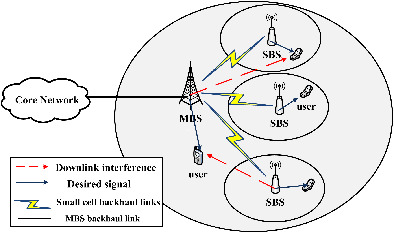
In heterogeneous cellular networks, the growing demand of small cell data traffic puts great pressure on the capacity-limited backhaul links. In this article, we investigate the joint resource block and power allocation problem under two different backhaul capacity limitations. Besides, the QoS requirements of users and the cross-tier interference mitigation are also considered. By variable substitution and constraints relaxation, we convert the original optimization problem into a convex one and obtain the optimal solutions.
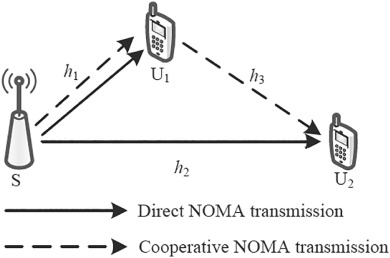
Cooperative NOMA system with incremental relaying and energy harvesting: Performance analysis and optimization
- First Published: 17 August 2020
Multipath TCP security over different attacks
- First Published: 23 August 2020
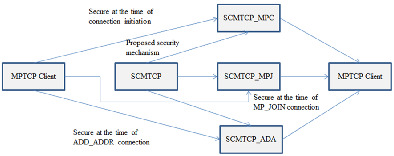
In this research paper, we proposed a security mechanism for Multipath TCP (MPTCP), named as secure connection multipath TCP (SCMTCP). The SCMTCP is an opportunistic security protocol that generates the secret keys for an MPTCP host The SCMTCP generates a unique session key for an MPTCP session using the secret keys and hash function. It also generates a unique authentication key for each new subflow during a subflow initiation using the session key. The SCMTCP security protocol has three modules according to different MPTCP options: SCMTCP with MP_CAPABLE (SCMTCP_MPC), SCMTCP with MP_JOIN (SCMTCP_MPJ), and SCMTCP with ADD_ADDR (SCMTCP_ADA). The SCMTCP_MPC generates a unique session key for an MPTCP session. It secures the Initial connection of MPTCP hosts requested through the MP_CAPABLE option that carries various secret information such as session information. After establishing the first subflow, the remaining all available connections are requested through the MP_JOIN option. The SCMTCP_MPJ generates a unique authentication key for each new requesting connection and exchanges the key information like the nonce and authentication keys using the MP_JOIN option. It protects the MPTCP from DoS attack. If a new connection of a host becomes available during the MPTCP session, then it is requested to connect using the ADD_ADDR option. The SCMTCP_ADA generates a unique authentication key for each such connection that is requested through the ADD_ADDR option. It protects the MPTCP from the ADD_ADDR attack by putting an authentication key into the ADD_ADDR packet.
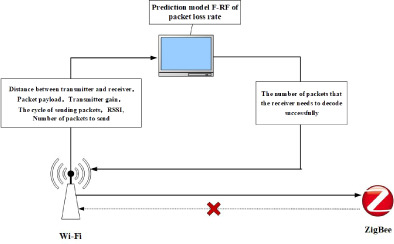
A reliable nonfeedback transmission mechanism for asymmetric channels based on machine learning
- First Published: 21 August 2020
Combining partial transmit sequences and selective mapping to reduce computational complexity of selective mapping techniques
- First Published: 19 August 2020
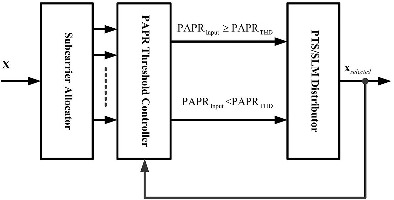
This study proposes an improved SLM scheme, which divides available subcarriers into two parts, with one part used in PTS and the other in SLM. The proposed method determines whether PTS or SLM is to be used by input signals by setting an adaptive threshold, which can reduce the number of IDFTs accumulated over the implementation of SLM following a large number of OFDM signal transmissions.
Stochastic channel models for massive and extreme large multiple-input multiple-output systems
- First Published: 24 August 2020
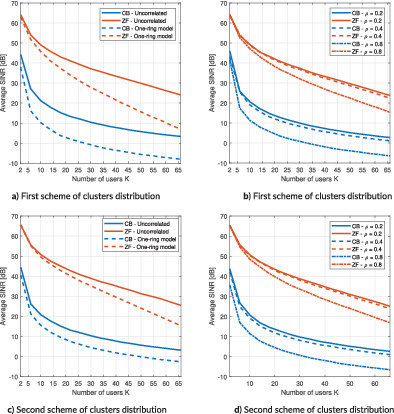
Attainable SINR as a function of number of users K for two schemes of clusters distribution: a) Correlation matrix R is modelled by Uncorrelated and One-ring models; b) R is modelled by Exponential channel model. c) Second scheme of clusters distribution: R is modelled by Uncorrelated and One-ring model; d) R is modelled by Exponential channel model.