Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
ISSUE INFORMATION
RESEARCH ARTICLES
An intelligent SDN-enabled CCN routing mechanism with community division
- First Published: 29 July 2019
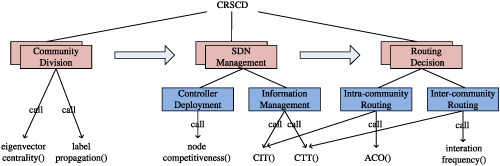
The proposed CRSCD consists of three kernel modules, i.e., community division, SDN management, and routing decision. Among them, the first one is for dividing CCN mesh topology into some communities according to eigenvector centrality and label propagation; the second one selects a node from each community and assigns an SDN controller at this node according to node competitiveness; the last one designs a routing mechanism based on ACO with the help of CIT and CTT.
The role of caching in next generation cellular networks: A survey and research outlook
- First Published: 02 August 2019
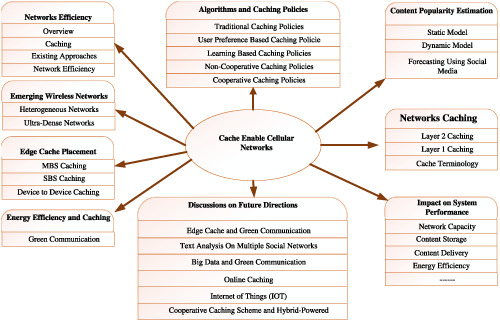
To address the expeditious growing demand for data services in 5G cellular networks, it is important to develop distribution techniques and an efficient content caching, aiming to significantly reduce redundant data transmission and thus improve the efficiency of the networks. In modern communication systems Caching has emerged as a vital tool for reducing peak data rates. It is anticipated that energy harvesting and self-powered small base stations are the fundamental part of next-generation cellular networks.
Dynamic network service deployment across multiple SDN domains
- First Published: 02 August 2019
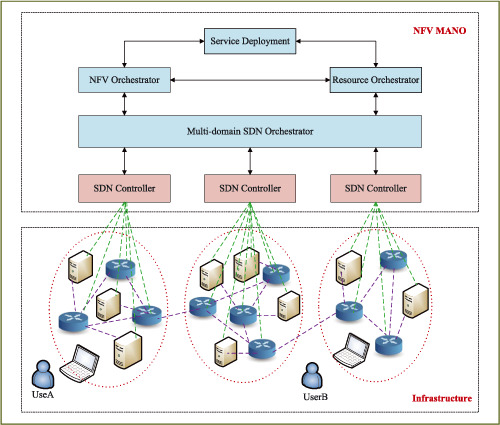
- (1) We first design a novel service deployment framework to support dynamic deployment and optimization of virtual network function in multidomain SDN networks.
- (2) We formulate the problem as a multiobjective optimization problem with the target of jointly minimizing resource consumption cost and operating cost.
- (3) We transform the multiobjective optimization problem into a single objective optimization model and present an efficient heuristic service deployment approach to solve it by leveraging Dijkstra algorithm.
A matching game for tasks offloading in integrated edge-fog computing systems
- First Published: 04 August 2019
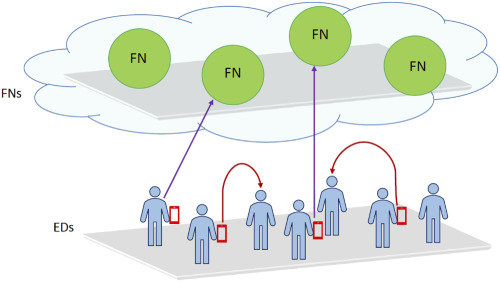
Edge and fog computing paradigms have recently emerged as promising approaches to overcome latency and network congestion drawbacks of the cloud network architecture alternative. In this direction, the paper deals with an integrated edge-fog computing system to provide computational offloading capabilities to end-devices. In particular, this paper proposes a suitable tasks allocation strategy based on the matching theory in order to minimize both the system energy consumption and the worst overall task completion time.
A survey on access control mechanisms for cloud computing
- First Published: 14 August 2019
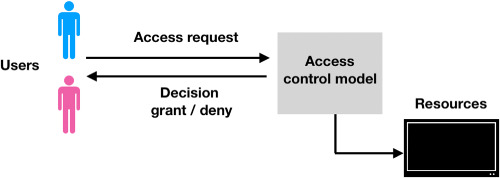
1- We presented a survey of existing access control mechanisms, especially, for Cloud-based systems. 2- We presented an analysis of the advantages and disadvantages of the presented access control models. 3- We performed, based on a literature review, a study for the requirements for access control mechanisms in Cloud computing, and we evaluate existing access control models against these requirements.
SDN-based failure detection and recovery mechanism for 5G core networks
- First Published: 12 August 2019
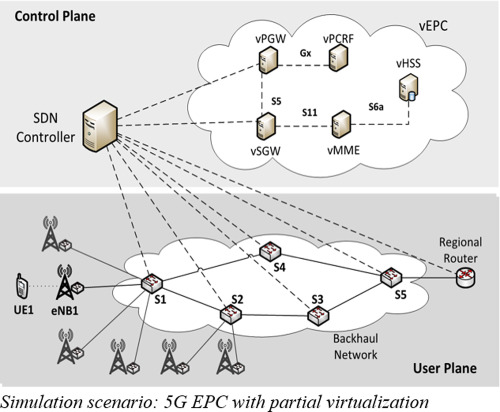
Panev and Latkoski introduce a fault detection and recovery algorithm that is suitable for SDN-based 5G Core networks. They make a clear relation of the fault recovery time with the 5G stringent latency requirements and, via simulations in Mininet, prove the validity and applicability of the proposed mechanism. Results show that the proposed solution implemented in the user plane can achieve carrier-grade fast fault recovery times (< 20 ms).
Resilient placement of SDN controllers exploiting disjoint paths
- First Published: 14 August 2019
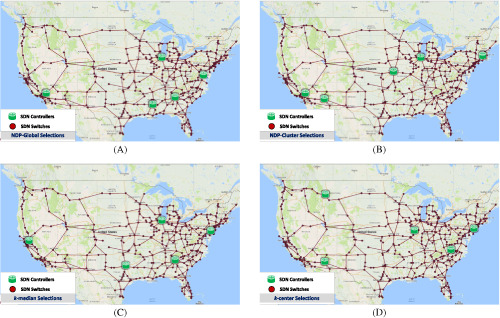
In this paper, we introduce two algorithms NDP-global and NDP-cluster to select k SDN controllers. We compare our algorithms to the k-center and k-median selection algorithms and apply them to four US-based fiber-level networks. The evaluation results show that our algorithms provide better network resilience in the face of centrality-based attacks and random failures.
Leveraging mobility and content caching for proactive load balancing in heterogeneous cellular networks
- First Published: 03 September 2019
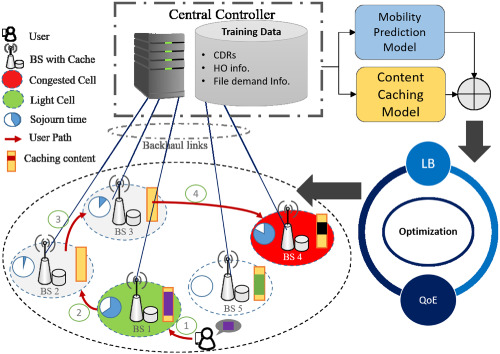
A novel proactive load balancing framework is proposed, which leverages user mobility and content demand statistics jointly to maximize downlink throughput and minimize cell loads. This framework models user mobility patterns through Semi-Markov renewal process and exploits content demand history for proactive content caching.
Techno-economic analysis of 5G immersive media services in cloud-enabled small cell networks: The neutral host business model: Providing techno-economic guidelines for the successful provision of 5G innovative services in small cell networks
- First Published: 10 September 2019
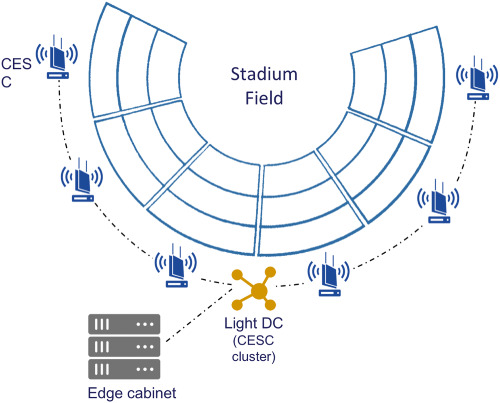
The paper studies a 5G network offering Immersive Video Services in Crowded Events, and performs a techno-economic analysis to assess the viability of such an investment. It shows that servers, small cells, and GPUs are the main factors contributing to CAPEX, while the most crucial parameter affecting the Net Present Value is the services tariffs. This study can be a useful tool for Small Cell Network Operators and venue owners.
Device-centric communication in IoT: An energy efficiency perspective
- First Published: 23 October 2019
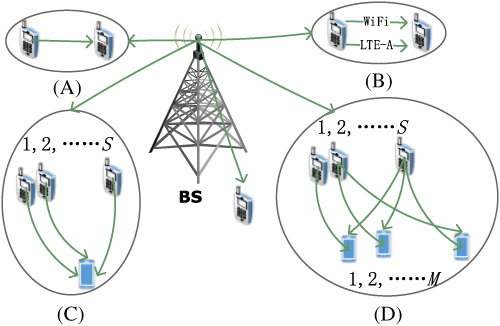
In this article, a new method for device-centric communication in IoT system is introduced, where multiple source IoT devices(SIDs) can send data to multiple destination IoT devices (DIDs) using multiple radio resource blocks. This method is called devices to devices (Ds2Ds)communication. The simulation results show the superiority of Ds2Ds over exiting devices to device (Ds2D) and multi-homing-D2D (MH-D2D) communication in terms of energy efficiency, which in turn implies better throughput
Heuristic approaches for the reliable SDN controller placement problem
- First Published: 23 October 2019
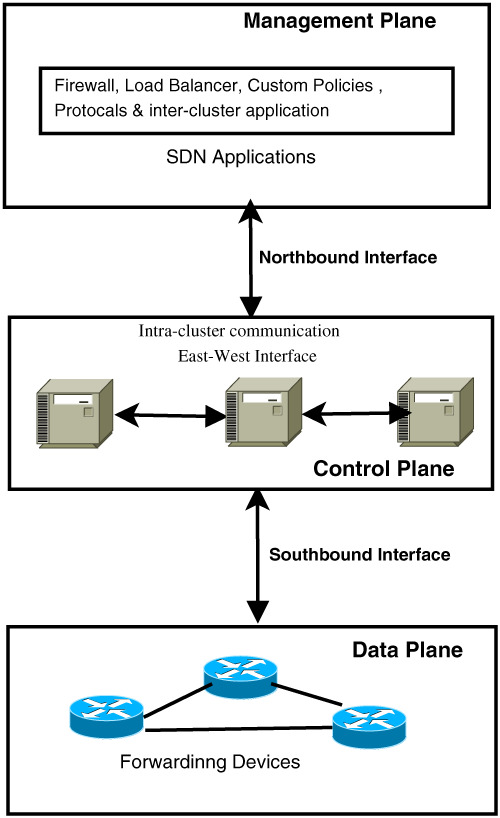
This paper proposes a Varna-based optimization (VBO) for a reliable CPP that minimizes the total average latency of SDN. The experimental results show that VBO gives better performance than teacher learning-based optimization, PSO, and Jaya algorithms for the popular topologies that are publicly available.
A semi-oblivious approach for robust segment routing in software-defined wide area networks
- First Published: 21 October 2019
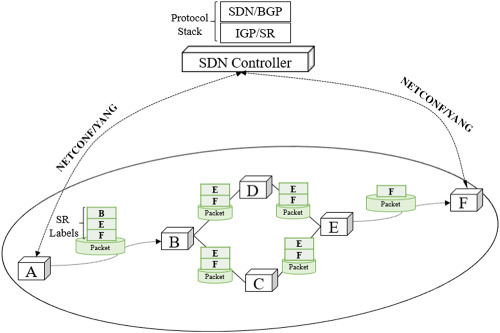
In this paper, we propose a semi-oblivious segment routing method that optimizes routing for a predicted probable traffic matrix, while ensuring its robustness by guarantying the worst-case performance under the fluctuations. We envision to apply this scheme in software-defined networks where the controller is responsible to compute robust segment routing paths and to configure the edge routers accordingly.
An efficient task scheduling approach using moth-flame optimization algorithm for cyber-physical system applications in fog computing
- First Published: 23 October 2019
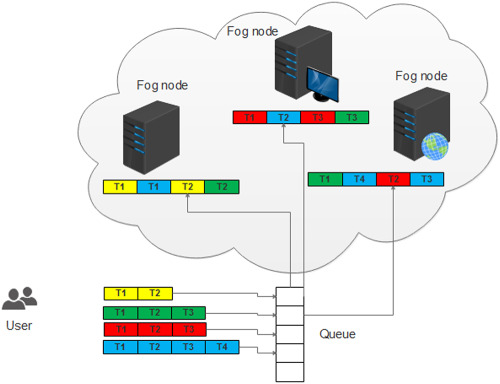
This paper presents a task scheduling algorithm based on MFO algorithm to assign an optimal set of tasks to fog nodes to meet the satisfaction of QoS requirements of CPS applications in such a way that the total execution time of tasks is minimized. The minimization of task execution and transfer time in the proposed algorithm are considered as objective functions. The experimental testing of the proposed solution is carried out in iFogSim toolkit.
A systematic literature review on formal verification of software-defined networks
- First Published: 11 November 2019
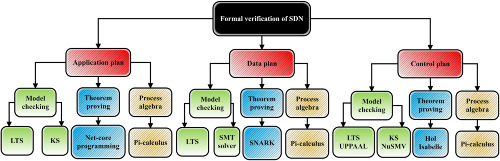
This paper provides an analytical review for the formal verification methods in the software-defined network (SDN) in form of the SDN plans to recognize the state of the art of the open challenges. The presented review is classified into three main fields: application plan, data plan, and control plan approaches. The verification mechanisms are compared with each other according to the important factors such as structural properties, quality-of-service metrics, applied algorithms, and measurement tools.
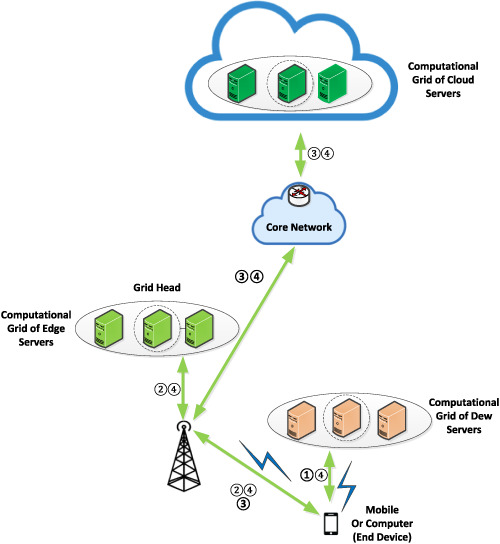
A proposed computation, which benefits from the cooperation of dew, edge, and cloud computations
- First Published: 19 November 2019
Joint optimization of computation cost and delay for task offloading in vehicular fog networks
- First Published: 17 December 2019
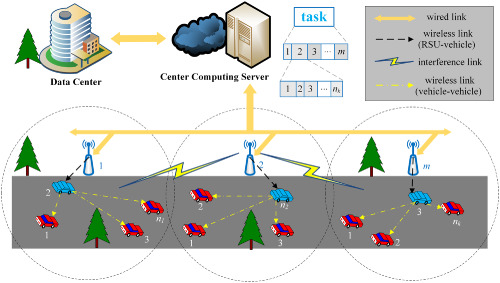
Based on the system model, the problem of task offloading in vehicular fog networks is formulated and analyzed. And an efficient resource allocation scheme based on Lagrange method is presented. The analysis and simulation results validate the high efficiency of the proposed scheme compared with other algorithms.
An adaptive resource placement policy by optimizing live VM migration for ITS applications in vehicular cloud network
- First Published: 26 December 2019
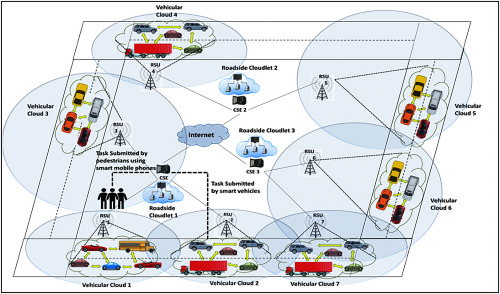
The problem of selecting the optimized destination physical host in vehicular cloud environment is addressed. The problem is mathematically formulated considering several quality-of-service parameters making the algorithm adaptive in nature. A mobility prediction model for a vehicular network is also developed. The problem is solved using the proposed hybrid optimization algorithm, which is the combination of particle swarm optimization (PSO) and genetic algorithm (GA). The algorithm combines the exploitative feature of PSO and the exploratory feature of GA, helping it to reach the true global optima at an accelerated rate.
A comprehensive study on managing strategies in the fog environments
- First Published: 11 December 2019
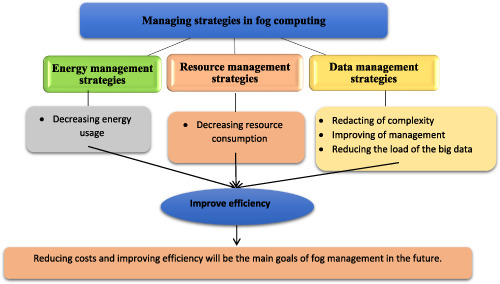
The management strategies have a great impact on the FC, such as monitoring and optimizing the correlated components. However, the complete and systematic review in this field is very rare. In this paper, three categories to study these mechanisms are considered such as data management, energy, and resource. Results showed the fog management strategies in computing environments still need improvements in the variety of its setting to convert to an on-request method, decrease the associated overhead, and improve the performance.
Virtual network embedding on massive substrate networks
- First Published: 14 January 2020
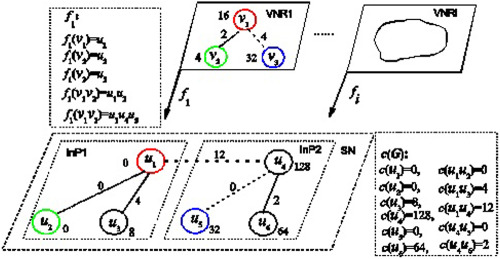
This paper proposes an efficient node ranking strategy that considers both global and local topological characteristics of the substrate network in mapping virtual nodes to physical nodes. This method ranks the substrate network nodes globally at first. Then, extracts a connected subset of the ranked substrate nodes forming the H-admissible embedding subgraph, and the subgraph nodes are ranked according to a local node ranking vector derived from a random-walking scheme.
A probability distribution function for investigating node infection and removal times
- First Published: 02 October 2019
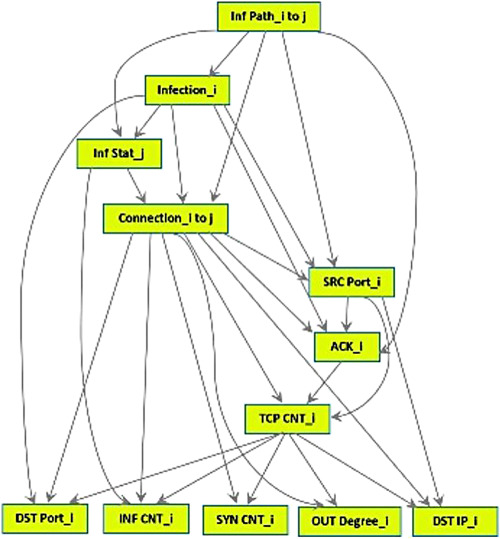
In this paper, we tackle the problem of investigating node infection and removal times, when the spread of a preferential scanning worm happens. To achieve this, we develop a new probabilistic model based on Bayesian networks, using historical data and features extracted from the network and application layers. For model building, we propose a four-step method and also a training and test dataset using simulations of Code Red II worm.
Fake news detection using deep learning models: A novel approach
- First Published: 05 November 2019
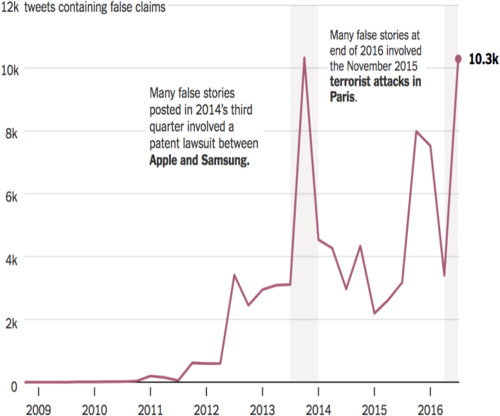
With the ever increase in social media usage, it has become necessary to combat the spread of false information and decrease the reliance of information retrieval from such sources. Social platforms are under constant pressure to come up with efficient methods to solve this problem. We tackled the fake news identification problem and achieved a detection rate of 88.78%.
A network covert timing channel detection method based on threshold secret sharing
- First Published: 11 December 2019
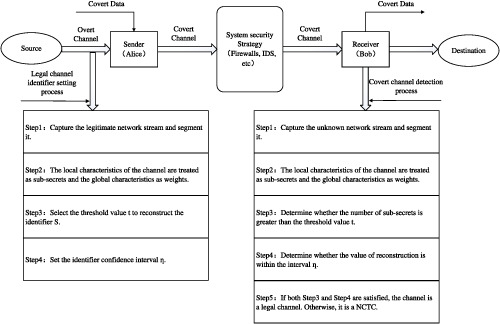
This paper proposes a network covert timing channel detection method based on threshold secret sharing. The new approach utilizes the principle of threshold secret sharing to tolerate the loss or the destruction of partial subsecrets, improves the robustness of the detection method, and solves the problem that the current detection method cannot resist environment changes. We compared our algorithm with some other methods, and our findings clearly suggest that the algorithm perform better in detection range and robustness.
BEAcM-DP: A broadcast encryption anti-censorship mechanism based on directory proxy
- First Published: 25 November 2019
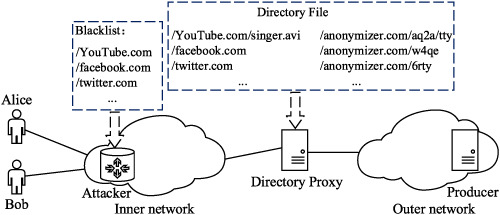
To defend the name censorship attack in NDN, this paper proposed a broadcast encryption anti-censorship mechanism which is based on directory proxy (BEAcM-DP). In BEAcM-DP, a directory proxy to camouflage the real content name is set to evade censorship, the broadcast encryption is adopted to ensure that the censored content can be reused in the network for the users within a broadcast group.
CSI-based authentication: Extracting stable features using deep neural networks
- First Published: 26 November 2019
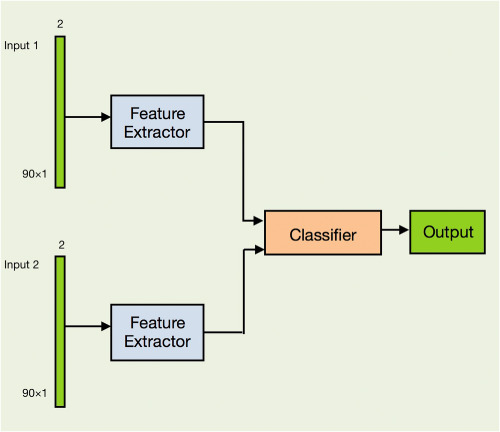
Despite the high accuracy of CSI-Based user authenticating schemes, these approaches lack the stability authentication when the users rotate in their positions. In this paper, we have proposed a method that gets raw CSI and use a deep neural network to extract a few rotation-invariant features. We also present an algorithm in which users can be efficiently authenticated while they are at specific locations in an environment (even if they rotate) and will be rejected if they change their location.
Mitigation of DIS flooding attacks in RPL-based 6LoWPAN networks
- First Published: 13 December 2019
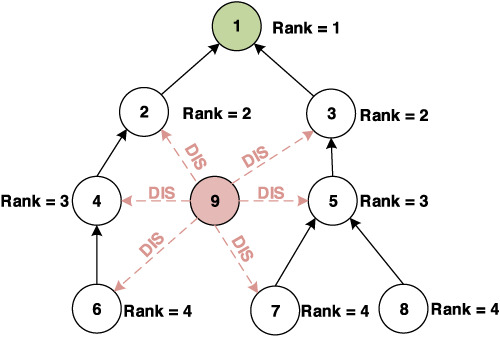
In this paper, it is observed that the DIS flooding attack increases the control packet overhead of the network, which significantly degrades the networks performance. To address this problem, a mitigation scheme named Secure-RPL is proposed. Secure-RPL mitigates significantly the effects of DIS flooding attack on the network's performance. The experimental results show that Secure-RPL detects and mitigates DIS flooding attack quickly and efficiently in both static and dynamic network scenarios, without adding any significant overhead to the nodes.
TAMU-RPL: Thompson sampling-based multichannel RPL
- First Published: 28 November 2019
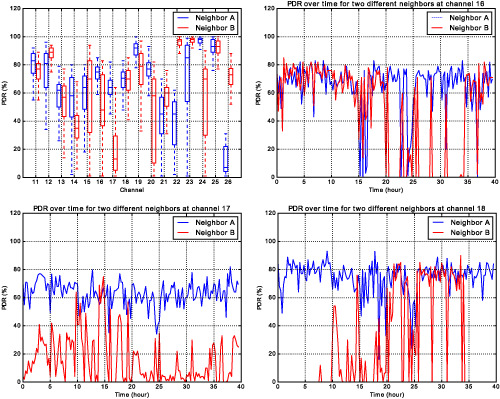
We executed an experiment to show the variation of connectivity over time and over channels from a particular sensor node to two different neighbors. The experiment employs 40 sensor nodes in an indoor test bed. In the experiment, every node broadcast 100 packets, each with of 100 bytes size. When one particular node is transmitting, all others listen and record whether the packets are received. This sequence is repeated for all 16 channels available in the 2.4-GHz band specified by the IEEE 802.15.4 standard. The experiment is rerun every 30 minutes during a 40-hour period. The figure plots a subset of data collected in the experiment. It shows the packet delivery ratio (PDR) between one node and two different neighbors, one of which located approximately at 5 m (neighbor A) and the other (neighbor B) approximately at 8 m of distance. The graph on the top left shows the PDR statistics over channels. It can be seen that both neighbors have similar statistics in some channels (eg, channels 11, 18 and 25), but very different in others (eg, channels 16, 27, and 20). The other three graphs show the PDR over time for channels 16, 17, and 18. Surprisingly, although these three channels are close to each other in the frequency domain and some of them have similar overall statistics (eg, channel 18), their performance is very different for each neighbor. What can be concluded from this small data set extracted from the experiment is that the performance of links can vary largely over both frequency and time, which makes difficult to successfully exploit diversity if the quality of individual channels is not continuously learned and routing decisions only account aggregated statistics.
LCPPA: Lattice-based conditional privacy preserving authentication in vehicular communication
- First Published: 22 November 2019
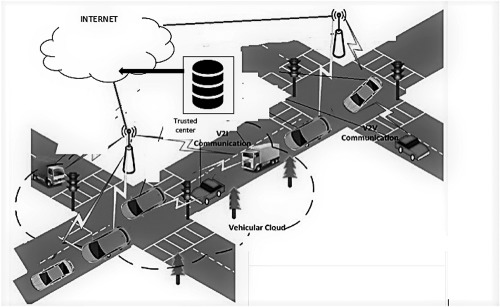
Vehicular ad-hoc network (VANET) plays an extremely important role in intelligent transportation systems. It enables vehicles equipped with smart devices to communicate with vehicles or available roadside units or infrastructure. It has been observed that the security of data and privacy of user are two key challenges for vehicular communication to enable sharing of resources among unfamiliar vehicles. The existing classical cryptography-based schemes are not secure in the quantum computing world due to Shor's algorithm. To address the challenges in post-quantum era, we have presented a framework based on short integer solution (SIS) problem in some lattice, attains all effective identification and authenticity of the user to get authorized access, along with revocation to services. The integrity of proposed framework ensures that information is accurate and can be trusted. This paper ensures conditional autonomous driving as well as efficient vehicular traffic flow in a vehicular ad hoc network. As a result, the presented protocol is suitable for practical applications even in the post-quantum environment, can be utilized for reliable vehicular communication.
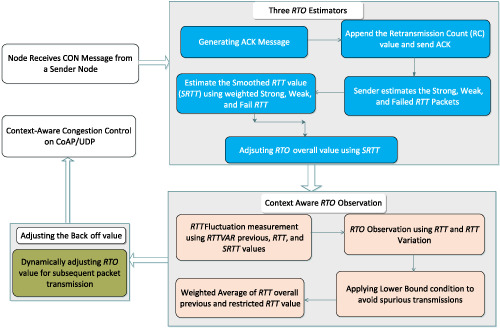
CACC: Context-aware congestion control approach for lightweight CoAP/UDP-based Internet of Things traffic
- First Published: 10 December 2019