Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Issue Information
Short Research Letters
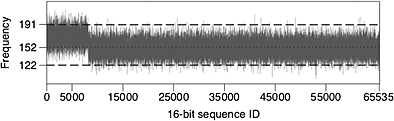
On the similarity of commercial EPC Gen2 pseudorandom number generators
- Pages: 151-154
- First Published: 06 December 2012
Blind timing synchronization in OFDM systems by exploiting cyclic structure
- Pages: 155-160
- First Published: 28 August 2012
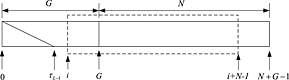
In order to eliminate the intersymbol interference as well as the intercarrier interference, a cyclic prefix (CP) is appended to each orthogonal frequency division multiplexing symbol. By using the frequency domain equivalence of the time domain circular convolution in the CP interval, we propose a novel method to estimate the timing offset blindly.
Research Articles
Nonlinear backward ADPCM speech coding using kernel methods and online sparsification
- Pages: 161-172
- First Published: 20 June 2012
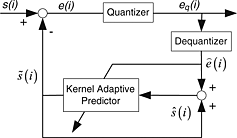
The problems encountered in nonlinear adaptive coding are addressed by employing, for the first time, several kernel adaptive algorithms in the framework of speech coding using backward adaptive differential pulse code modulation technique. Particular attention is focused on the effect of various sparsification techniques on the performance of the resultant algorithms. Results show an average improvement of up to 3.4 dB in the signal-to-noise ratio criterion of the reconstructed speech utilizing kernel methods.
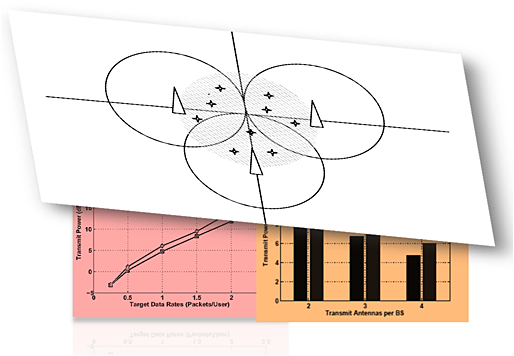
Downlink beamforming and resource allocation in multicell MISO-OFDMA systems
- Pages: 173-182
- First Published: 03 July 2012
Performance analysis of reliable flooding in duty-cycle wireless sensor networks
- Pages: 183-198
- First Published: 25 July 2012
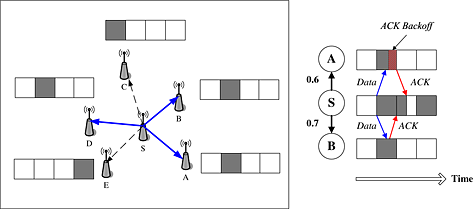
In this work, a theoretical performance analysis of acknowledgement (ACK)-based and non-acknowledgement (NoACK)-based transmission mechanisms is presented. The evaluation considers both point-to-point and point-to-multipoint models. Extensive simulations show that ACK-based and NoACK-based implementations produce a similar performance on the flooding delay, but with significantly different costs on the energy consumption.
Using body sensor networks for motion detection: a cluster-based approach for green radio
- Pages: 199-216
- First Published: 13 August 2012
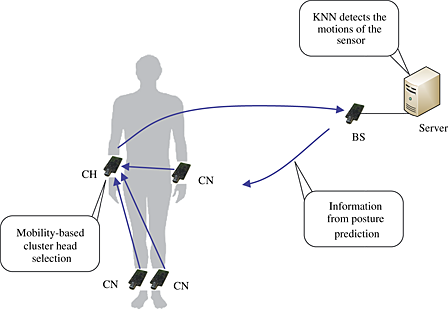
We discuss the amount of energy that can be saved using a cluster-based approach. We propose a novel cluster head selection algorithm by considering the required power level for sending a packet from the cluster node to the cluster head, which is complemented by a prediction mechanism to reduce the number of data transmissions. We implement our cluster-based algorithm on a test bed using the k-nearest-neighbor algorithm and show that it can achieve high accuracy (above 90%).
On the capacity of the binary-symmetric parallel-relay network
- Pages: 217-230
- First Published: 13 August 2012
Joint spectrum sensing and transmit power adaptation in interference-aware cognitive radio networks
- Pages: 231-238
- First Published: 05 October 2012

In this article, the limitations of conventional spectrum sensing at discovering spatial spectrum hole are highlighted and an interference-aware sensing metric is adopted to maximize the spectrum hole utilization for a secondary user. Specifically, we introduce a new degree of freedom, transmit power adaptation, into the issue of interference-aware spectrum sensing and develop a joint optimization problem to maximize the interference-free throughput of the secondary user while satisfying the quality of service constraints of both the primary and secondary transmissions.
Dynamic semantic-based adaptation of multimedia documents
- Pages: 239-258
- First Published: 28 June 2013
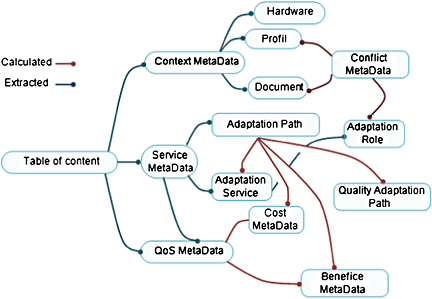
We propose the tool support based on the ontology adaptation service quality, and we propose a new approach to automatically assemble dynamic quality and semantic adaptation services. We show by a case study how to easily govern the response time and the quality assembly of mobile applications at runtime.
On sparse sensing and sparse sampling of coded signals at sub-Landau rates
- Pages: 259-272
- First Published: 15 November 2013
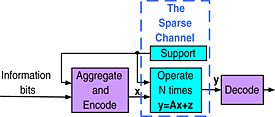
Sparse sampling of uncoded signals at sampling rates exceeding the Landau rate is well established. We examine sampling of coded signals at sub-Landau rates. Then the Landau condition may be relaxed, and the sampling rate can be lower than the effective bandwidth. Tight bounds on information rates and on signal recovery are derived. When the system is high-dimensional, the required SNR is finite but high, it can be lowered by concentrating the frequency support into a finite number of subbands.
On the tweet arrival process at Twitter: analysis and applications
- Pages: 273-282
- First Published: 06 February 2014
This work provides a novel measurement-based analysis of the tweet arrival traffic process at Twitter. The analysis considers more than one million total tweets collected at 48 different times of the day. We observe a 3.5-tweet/ms average rate with a valley of 2.5 tweets/ms at 10 AM (GMT+1) and a peak at 3 PM (GMT+1) of about 5 tweets/ms. We further model the traffic pattern as a Gaussian process, and we validate such an assumption with multiple normality tests.
Call for Papers
Enabling 5G: Energy and Spectrally Efficient Communication Systems
- Pages: 283-288
- First Published: 24 September 2013