Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
ISSUE INFORMATION
ORIGINAL ARTICLES
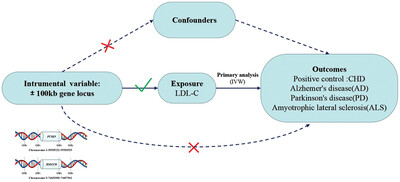
Causal relationship between PCSK9 inhibitor and common neurodegenerative diseases: A drug target Mendelian randomization study
- First Published: 05 June 2024
Rapid eye movement dependency is associated with increased inflammatory activity in obstructive sleep apnea syndrome
- First Published: 06 June 2024
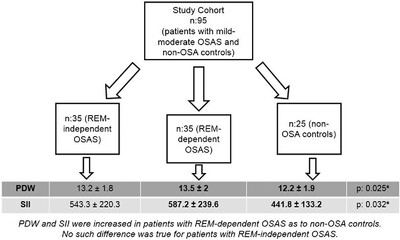
REM-dependent OSAS has some typical characteristics that distinguish it from stage-independent OSAS. These include a preference for younger age, female gender, and milder disease severity. Although these features suggest a benign course for this phenotype, recent literature shows that it is also associated with various cardiometabolic consequences. In our retrospective study, we found that PDW and SII, two accessible blood parameters, indicate an increased inflammatory status in this subtype. Our results highlight the need for close follow-up in patients with REM-dependent OSAS, as increased systemic inflammation can have negative consequences.
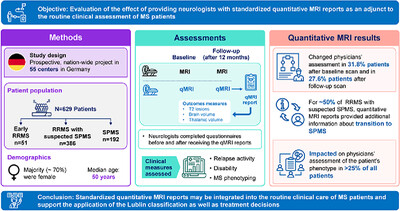
Addition of quantitative MRI to the routine clinical care of patients with multiple sclerosis—Results from the MAGNON project
- First Published: 06 June 2024
ORIGINAL ARTICLE
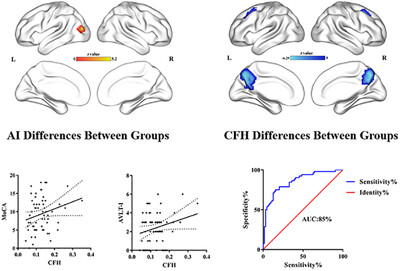
Brain functional specialization and cooperation in Alzheimer's disease
- First Published: 06 June 2024
Assistive tools for classifying neurological disorders using fMRI and deep learning: A guide and example
- First Published: 06 June 2024
ORIGINAL ARTICLES
Visual search for real-world scenes in patients with Alzheimer's disease and amnestic mild cognitive impairment
- First Published: 06 June 2024
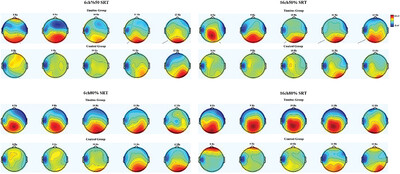
Investigation of the behavior of tinnitus patients under varying listening conditions with simultaneous electroencephalography and pupillometry
- First Published: 06 June 2024
Olfactory dysfunction as an early predictor for post-COVID condition at 1-year follow-up
- First Published: 06 June 2024
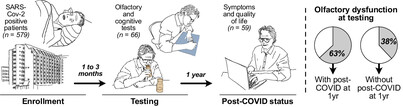
Objectively assessed olfactory dysfunction at one to three months after COVID-19, but not subjective olfactory symptoms, predicted post-COVID condition (PCC) at one year. We propose that olfactory screening in the early post-acute phase of COVID-19 infection might identify individuals that are at higher risk of developing long-term health sequalae.
Sex differences in correlates of suicide attempts in Chinese Han first-episode and drug-naïve major depressive disorder with comorbid subclinical hypothyroidism: A cross-sectional study
- First Published: 06 June 2024
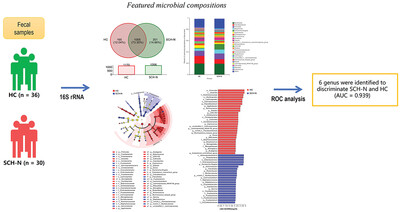
16S rRNA gene sequencing reveals altered gut microbiota in young adults with schizophrenia and prominent negative symptoms
- First Published: 06 June 2024
ORIGINAL ARTICLE
Rationale for issuing neuroimaging requests for patients with primary headaches in China
- First Published: 06 June 2024
ORIGINAL ARTICLES
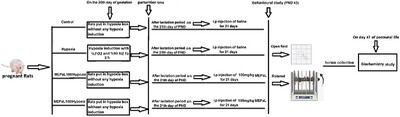
The effects of MEPaL on oxidative stress and motor function in the rats affected by prenatal hypoxia
- First Published: 07 June 2024
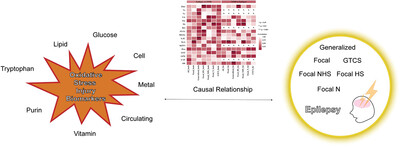
Causal link between oxidative stress and epilepsy: A two-sample Mendelian randomization study
- First Published: 07 June 2024
Depression and risk of arthritis: A Mendelian randomization study
- First Published: 07 June 2024
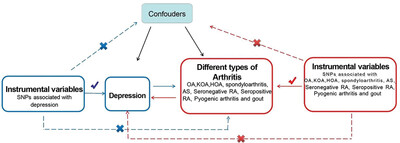
This study investigated A two-sample two-way Mendelian randomization (MR) analysis was performed to determine whether there is a relationship between depression and multiple types of arthritis. The present study found a bidirectional causal relationship between depression and OA. The depression only increased the risk of KOA.
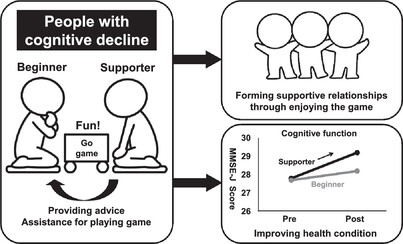
“GO” to move toward dementia-friendly communities: A pilot study
- First Published: 07 June 2024
Topological differences of striato-thalamo-cortical circuit in functional brain network between premature ejaculation patients with and without depression
- First Published: 07 June 2024
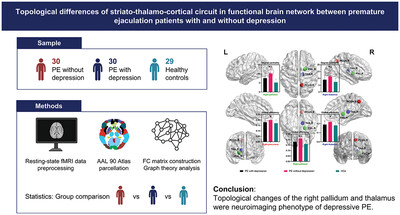
Premature ejaculation (PE) is often accompanied by abnormal psychological factors, such as depression. We collected resting-state fMRI data of PE patients with and without depression, as well as healthy controls. Graph theory analysis of functional brain networks underlined the topological changes of pallidum and thalamus as a neuroimaging phenotype for depressive PE.
REVIEW
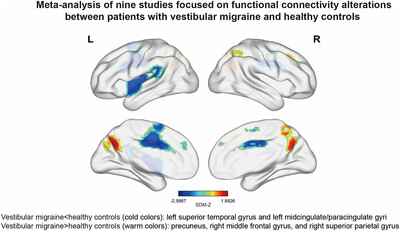
The altered functional status in vestibular migraine: A meta-analysis
- First Published: 07 June 2024
ORIGINAL ARTICLE
Associations between atypical intracortical myelin content and neuropsychological functions in middle to older aged adults with ASD
- First Published: 07 June 2024
ORIGINAL ARTICLES
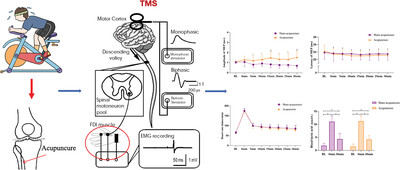
Transcranial magnetic stimulation in the assessment of acupuncture effect on exercise-induced fatigue
- First Published: 12 June 2024
REVIEW
Use of lecanemab for the treatment of Alzheimer's disease: A systematic review
- First Published: 12 June 2024
ORIGINAL ARTICLES
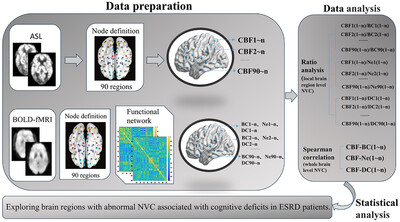
Multiparameter neuroimaging study of neurovascular coupling changes in patients with end-stage renal disease
- First Published: 24 June 2024
ORIGINAL ARTICLE
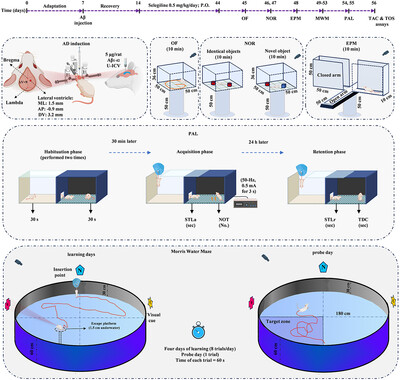
Protective effects of selegiline against amyloid beta-induced anxiety-like behavior and memory impairment
- First Published: 14 June 2024
Modulation of habenular and nucleus accumbens functional connectivity by ketamine in major depression
- First Published: 19 June 2024
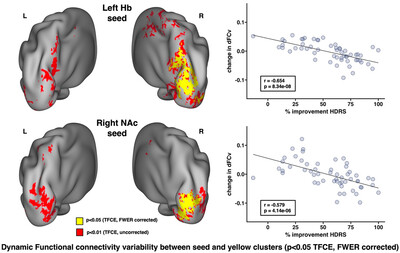
We investigated how ketamine treatment perturbs static and dynamic functional connectivity from reward circuitry in treatment resistant depression. We found that ketamine produces functional connectivity changes between the habenula and visual cortex, and changes in dynamic functional connectivity between the habenula, nucleus accumbens, visual cortex, and posterior cingulate cortex were associated with greater treatment response.
ORIGINAL ARTICLES
Task-induced deactivation dysfunction during reward processing is associated with low self-esteem in a possible subtype of major depression
- First Published: 14 June 2024
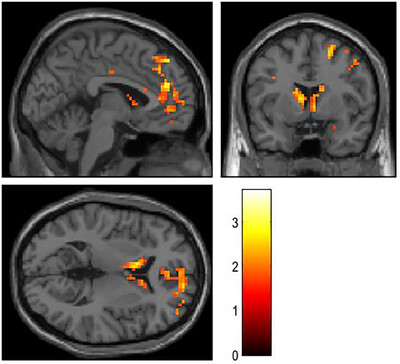
Self-esteem in patients with major depressive disorder (MDD) correlated negatively with reward-related activity changes in the pregenual anterior cingulate cortex (pgACC) and the ventral striatum. This suggests that a previously described MDD subtype with reward-related overactivations in pgACC and ventral striatum is clinically characterized by low self-esteem.
REVIEWS
A systematic review and meta-analysis of the linkage between low vitamin D and the risk as well as the prognosis of stroke
- First Published: 14 June 2024
ORIGINAL ARTICLE
The relationships between the multidimensional planned behavior model, green brand awareness, green marketing activities, and purchase intention
- First Published: 14 June 2024

This study investigates the mediating role of green marketing activities in the effect of green brand awareness on consumer purchase intention. A survey was conducted with university students in the Generation Z consumer class for empirical research. A total of 638 feedbacks were provided in the online survey application. The analyses were conducted on 590 valid survey data.
ORIGINAL ARTICLES
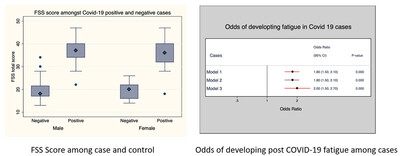
Assessment of post-SARS-CoV-2 fatigue among physicians working in COVID-designated hospitals in Dhaka, Bangladesh
- First Published: 14 June 2024
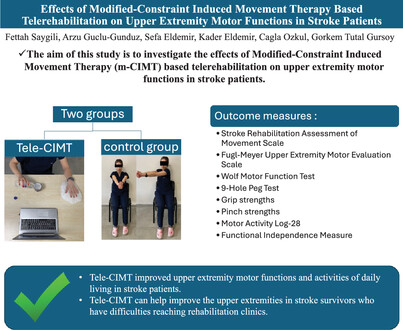
Effects of modified-constraint induced movement therapy based telerehabilitation on upper extremity motor functions in stroke patients
- First Published: 14 June 2024
REVIEW
Elucidating the pivotal molecular mechanisms, therapeutic and neuroprotective effects of lithium in traumatic brain injury
- First Published: 14 June 2024
ORIGINAL ARTICLES
Comparative analysis of brain language templates with primary language areas detected from presurgical fMRI of brain tumor patients
- First Published: 19 June 2024
REGISTERED REPORT STAGE 1
Assessing midbrain neuromelanin and its relationship to reward learning in anorexia nervosa: Stage 1 of a registered report
- First Published: 19 June 2024
ORIGINAL ARTICLES
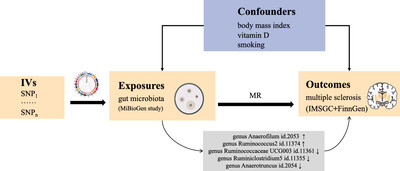
Causal effects of gut microbiota on multiple sclerosis: A two-sample Mendelian randomization study
- First Published: 19 June 2024
Episodic memory network characteristics in patients with amnestic mild cognitive impairment accompanied by executive function impairment
- First Published: 19 June 2024
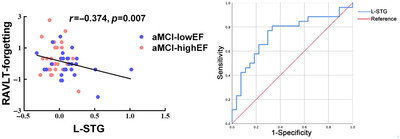
The study found that amnestic mild cognitive impairment (aMCI) patients with lower executive function (aMCI-lowEF) exhibit more severe cognitive impairment, decreased cerebral glucose metabolism, and elevated AV45 levels compared to those with higher executive function (aMCI-highEF). Significant increased functional connectivity in the left superior temporal gyrus of the episodic memory network (EMN) were observed in aMCI-lowEF group. These findings underscore the impact of executive function on EMN alterations in aMCI patients.
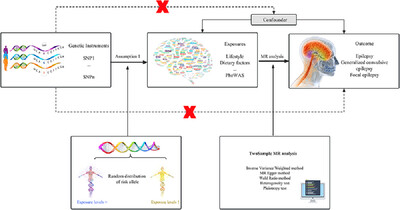
A Mendelian randomization study of the entire phenome to explore the causal links between epilepsy
- First Published: 19 June 2024
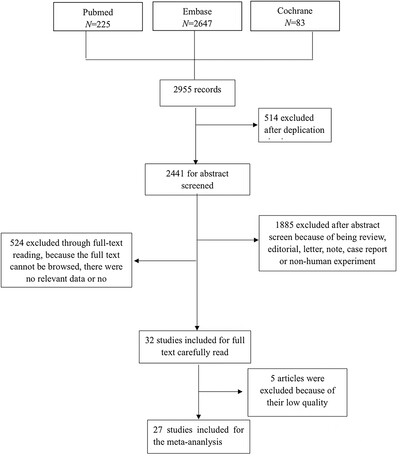
Low triiodothyronine (T3) levels predict worse outcomes in autoimmune encephalitis—A meta-analysis of current literature
- First Published: 19 June 2024

The findings of our study suggest that low fT3 levels might be related to a more severe disease state, implying the significance of thyroid hormones in Autoimmune Encephalitis pathogenesis. This finding is crucial in not only improving the early diagnosis of severe autoimmune encephalitis but also in the efficient management of the disease.
BRIEF REPORT
The potential significance of hepcidin evaluation in progressive supranuclear palsy
- First Published: 21 June 2024
ORIGINAL ARTICLES
Contrast-enhanced transcranial Doppler for the detection of right-to-left shunt: A new provocation method with a syringe-modified Valsalva maneuver
- First Published: 17 May 2024
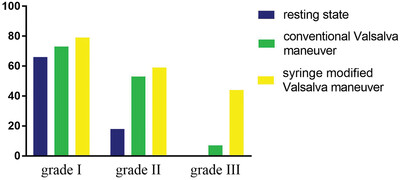
A new provocation method with a syringe-modified Valsalva maneuver (sm-VM) during Contrast-enhanced transcranial Doppler (cTCD) was proposed in this study. Compared to cTCD detected at resting state and with conventional Valsalva maneuver, cTCD with sm-VM could further increase the positive detection rate of RLS. These findings support the use of this method in clinical practice.