Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
ISSUE INFORMATION
ORIGINAL RESEARCH
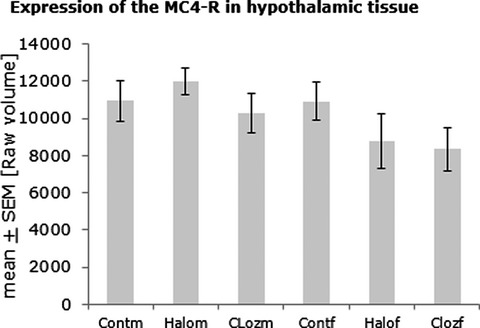
Sex-dependent alterations of dopamine receptor and glucose transporter density in rat hypothalamus under long-term clozapine and haloperidol medication
- First Published: 11 June 2020
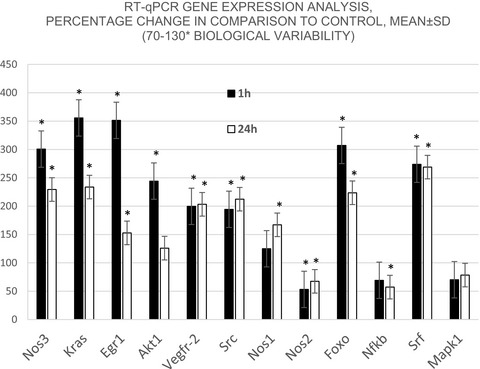
bFGF promotes neurological recovery from neonatal hypoxic–ischemic encephalopathy by IL-1β signaling pathway-mediated axon regeneration
- First Published: 11 June 2020
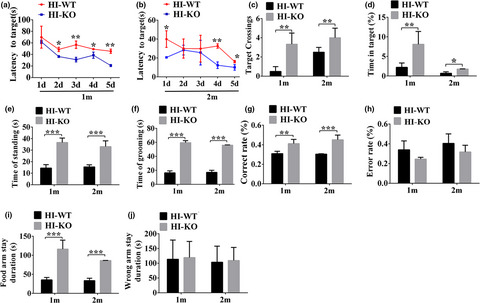
Hypoxic-ischemic brain damage (HIBD) can lead to serious neuron damage and dysfunction, and cause serious world health problems. BFGF has been reported as a protective agent to promote neuronal repair under hypoxia/ischemia (HI). We found that the axon regeneration mediated by IL-1 β is one of the mechanisms of bFGF in the treatment of hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy. The results of this study will provide theoretical and molecular basis for the future treatment of HIBD.
DATA PAPER
Parkinson's disease or atypical parkinsonism? The importance of acoustic voice analysis in differential diagnosis of speech disorders
- First Published: 11 June 2020
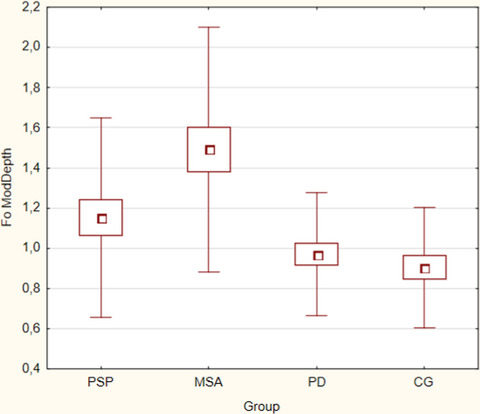
The aim of the study was to assess objectively by parametric measurements, speech, and voice disorders in hypokinetic, ataxic, and spastic dysarthria in PD and APS patients. Acoustic analysis can be diagnostically helpful in differential diagnosis of speech disorders in parkinsonian syndromes and may provide objective measures of treatment response and disease progression.
ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Gepants for abortive treatment of migraine: A network meta-analysis
- First Published: 11 June 2020
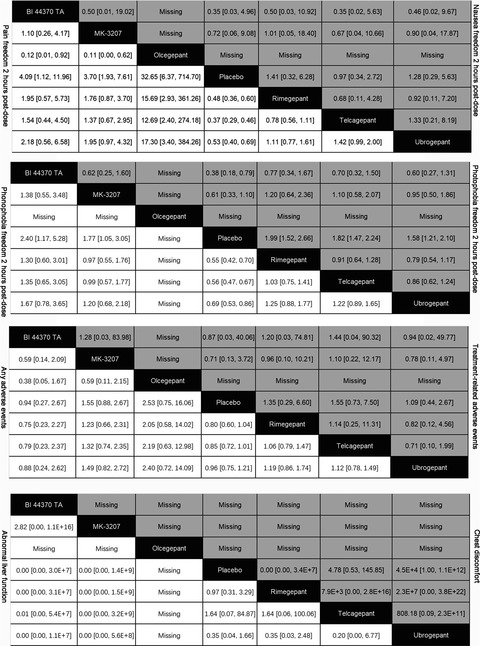
All gepants were superior to placebo in achieving pain freedom 2 hr postdose and only rimegepant and telcagepant were higher than placebo in incidence of any adverse events.In network meta-analysis, the rank best 3 drugs were olcegepant, BI 44370 TA, and MK-3207 for efficacy outcomes. And the rank best 3 drugs were BI 44370 TA, placebo, and ubrogepant for safety outcomes.
Multi-voxel pattern analysis of amygdala functional connectivity at rest predicts variability in posttraumatic stress severity
- First Published: 11 June 2020
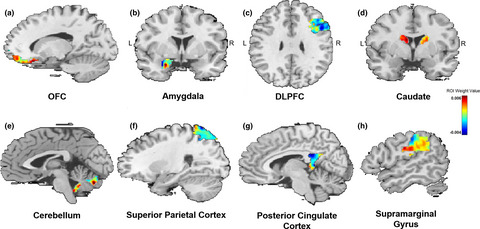
We examined patterns of whole-brain connectivity with the amygdala as a predictor of posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD) severity using a machine-learning approach. A total of n = 90 civilian trauma survivors completed a functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) resting state scan and provided stress severity symptoms. Results showed that multi-voxel patterns of amygdala connectivity accurately predicted severity of PTSD symptoms, while amygdala connectivity with regions involved in regulation (prefrontal cortex) contributed highly to accurate prediction.
Effects of oxiracetam combined with ginkgo biloba extract in the treatment of acute intracerebral hemorrhage: A clinical study
- First Published: 12 June 2020

The combination of oxiracetam and ginkgo biloba extract in patients with acute intracerebral hemorrhage has potential in term of significantly improving the therapeutic effect and alleviating neurological deficit, reducing the absorption of hematoma and edema, and it is safe and beneficial to the rehabilitation of patients.
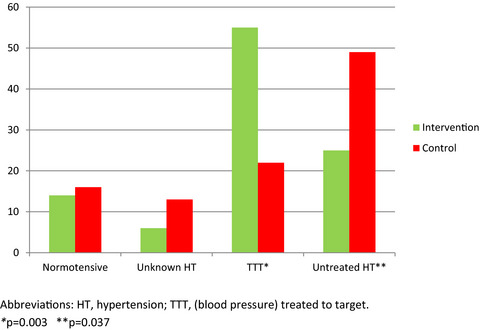
Blood pressure after follow-up in a stroke prevention clinic
- First Published: 12 June 2020
Altered gut bacterial–fungal interkingdom networks in patients with current depressive episode
- First Published: 12 June 2020
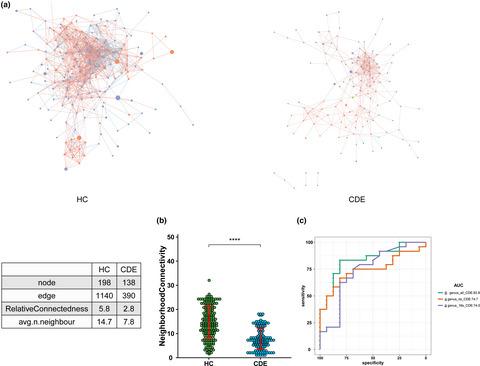
Patients with current depressive episode (CDE) display bacterial and fungal gut dysbiosis. Fungal gut dysbiosis in CDE is characterized by an altered composition and reduced biodiversity. In patients with CDE, the correlation network between bacteria and fungi is disrupted. Our findings suggest that the gut mycobiota contributes to the pathogenesis of CDE and should be considered as a new target for therapeutic intervention.
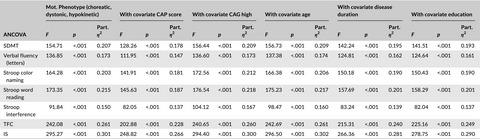
Functional and cognitive capacity differ in dystonic motor subtypes when compared to choreatic and hypokinetic-rigid motor subtypes in Huntington's disease
- First Published: 12 June 2020
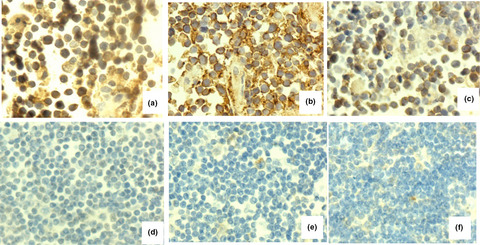
Expression of hypoxia-inducible factor 1α, glucose transporter 1, and hexokinase 2 in primary central nervous system lymphoma and the correlation with the biological behaviors
- First Published: 12 June 2020
Effective connectivity during autobiographical memory search
- First Published: 15 June 2020
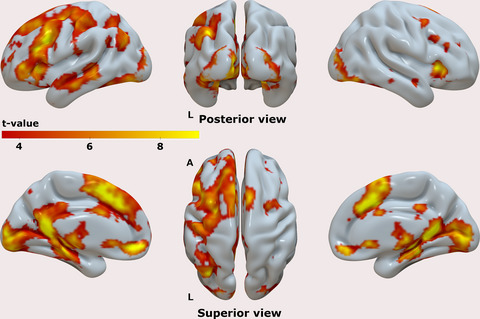
Autobiographical memory (AM) processes are known to recruit a large ensemble of brain regions. We used dynamic causal modeling to estimate effective connectivity among 6 of these regions based on fMRI data collected while participants performed an AM search task. Results were consistent with the notion that midline cortical regions are crucial in supporting the retrieval of AMs, and highlighted the interplay between the prefrontal and posterior midline regions during AM search.
Prognostic factors in children with head and neck rhabdomyosarcoma: A 12-year retrospective study
- First Published: 16 June 2020
Altered white matter integrity in patients with monocular blindness: A diffusion tensor imaging and tract-based spatial statistics study
- First Published: 17 June 2020
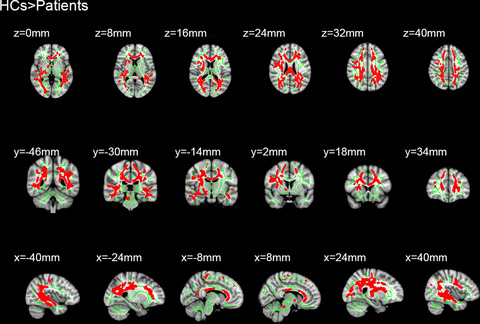
Diffusion tensor imaging and tract-based spatial statistics may be useful in examining abnormal spontaneous alterations in the white matter of monocular blindness patients. The observed changes in fractional anisotropy and radial diffusivity values may imply the larvaceous neurological mechanism involved in patients with monocular blindness.
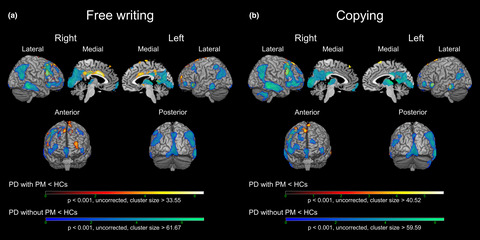
Neural substrates underlying progressive micrographia in Parkinson's disease
- First Published: 18 June 2020
Performance of healthy persons under pain in different cognitive load tasks: An event-related potential study on experimental pain individuals
- First Published: 18 June 2020
Functional network activity during errorless and trial-and-error color-name association learning
- First Published: 18 June 2020
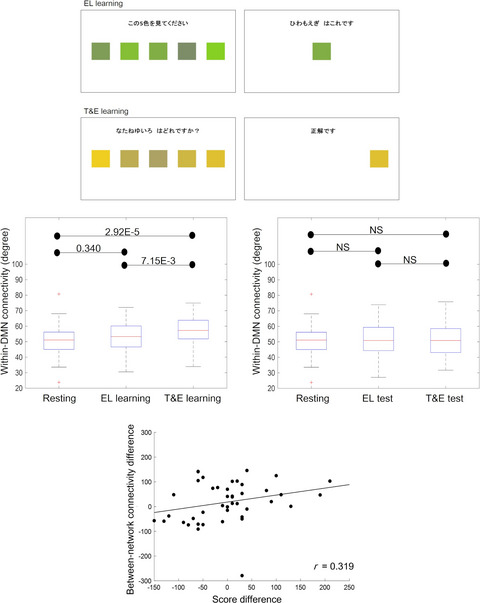
Participants memorised colour-name associations in errorless(EL) and trial-and-error(T&E) methods using Japanese traditional colours which were unfamiliar to study participants. We focused on the default mode network (DMN) and the fronto-parietal network (FPN), and conducted functional network analysis by applying graph theory. Our results suggest that within-DMN connectivity is important in T&E learning and that the learning benefit differences between EL and T&E approaches possibly relate to the functional integration strength between the DMN and FPN.
Altered functional connectivity of brain regions based on a meta-analysis in patients with T2DM: A resting-state fMRI study
- First Published: 18 June 2020
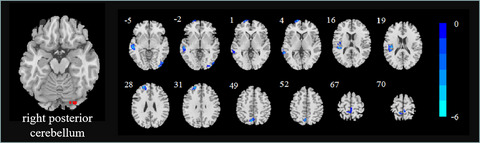
The posterior cerebellum is involved in a variety of brain function impairments in T2DM patients.It is suggested that the cerebellar–cerebral circuit may be involved in the neuropathological basis of brain dysfunction in patients with T2DM, which provides new insight into the neural mechanisms of brain dysfunction in patients with T2DM from the perspective of the cerebellum.
The effect of pentadecapeptide BPC 157 on hippocampal ischemia/reperfusion injuries in rats
- First Published: 18 June 2020
The functional networks of a novel environment: Neural activity mapping in awake unrestrained rats using positron emission tomography
- First Published: 20 June 2020
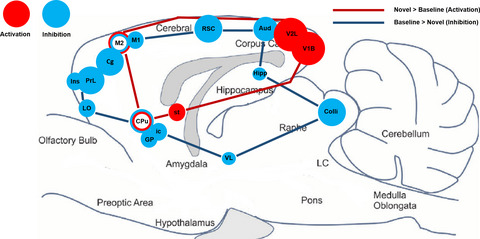
The widespread inhibition of brain activity in regions associated with exploratory behavior suggest that the novel cage is a stressful environment, a result which supports the elevated corticosterone levels in a novel environment reported by other groups. Additionally, patterns of inhibition in the novel environment are consistent with proposed rat Default Mode Network models, indicating that the animals were more cognitively engaged in this environment. Our results demonstrate the capability of FDG PET to identify cognitive changes in response to novelty and stress.
Proteins of the Lectin Pathway of complement activation at the site of injury in subarachnoid hemorrhage compared with peripheral blood
- First Published: 21 June 2020
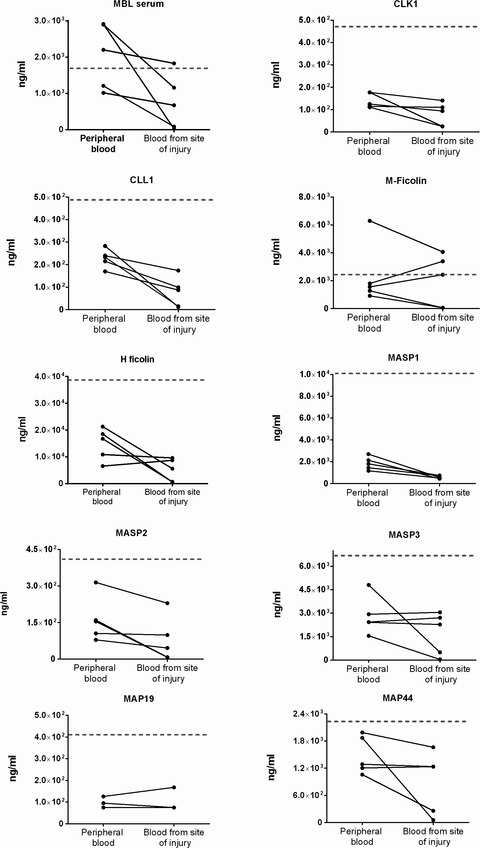
A subarachnoid hemorrhage is a debilitating stroke and activation of the lectin pathway could partially explain the poor prognosis. Conflicting results have been reported regarding the activation of the lectin pathway, which potentially reflects that changes at the site of injury are not reflected in peripheral blood. We found that the concentrations of lectin pathway proteins in peripheral blood do not always reflect changes at the site of injury.
The maturation of the P1m component in response to voice from infancy to 3 years of age: A longitudinal study in young children
- First Published: 23 June 2020
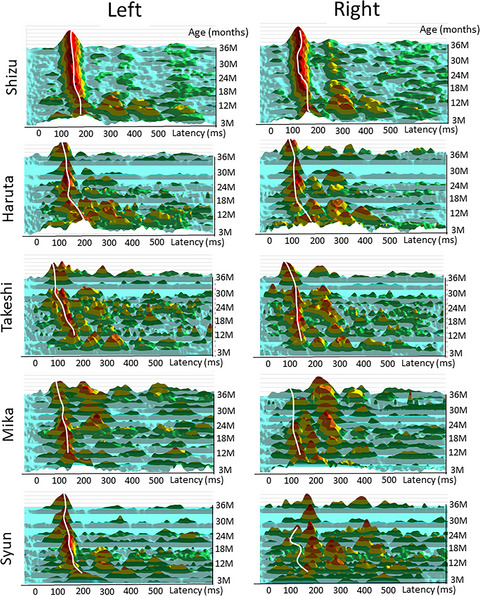
We performed a longitudinal magnetoencephalography (MEG) study that focused on auditory early component. The maturational changes over three years starting from age 0 were examined. Our result revealed that the early prominent component in infants aged 3 month corresponded to the auditory P1m component in young children over 2 years old, which we had previously reported to be related to language development and/or autism spectrum disorders.
Differences of connectivity between ESRD patients with PD and HD
- First Published: 24 June 2020
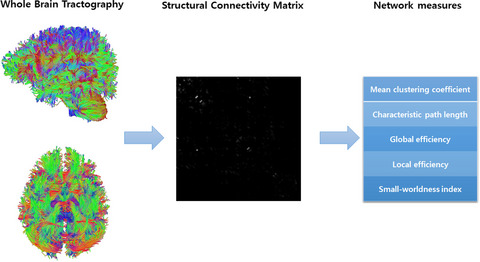
Alterations in structural and functional connectivity in ESRD patients who were undergoing PD and HD were different than those in healthy controls. The measures of global structural connectivity were significantly different between the patients with ESRD who were undergoing PD and healthy subjects. In the global functional connectivity, the network measures in patients with HD were different from those of the healthy controls.
Mental health status of the general population, healthcare professionals, and university students during 2019 coronavirus disease outbreak in Jordan: A cross-sectional study
- First Published: 24 June 2020

The prevalence of depression and anxiety among the entire study participants was 23.8% and 13.1%, respectively. Anxiety and depression were most prevalent across university students, followed by healthcare professionals, and general population. Females, university students, divorced individuals, healthcare professionals at front-line, and those who are with underlying chronic conditions are at a higher risk of these mental health problems.
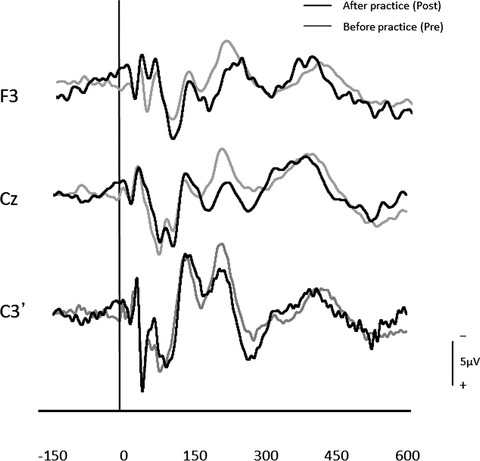
Altered somatosensory evoked potentials associated with improved reaction time in a simple sensorimotor response task following repetitive practice
- First Published: 25 June 2020
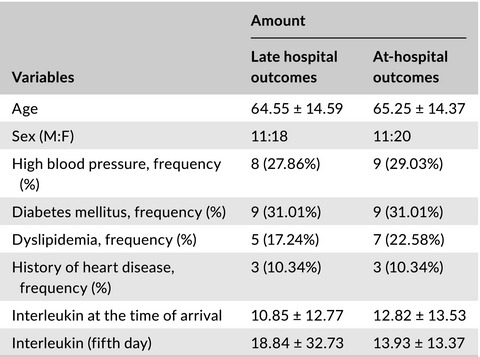
Investigating the relationship between interleukin-6 serum levels and outcome in acute ischemic CVA
- First Published: 25 June 2020
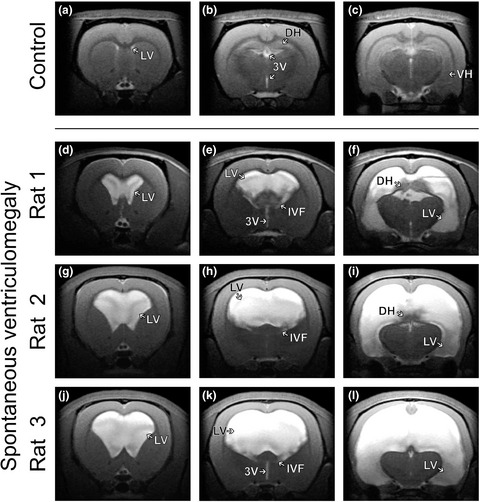
Memory deficits in Sprague Dawley rats with spontaneous ventriculomegaly
- First Published: 25 June 2020
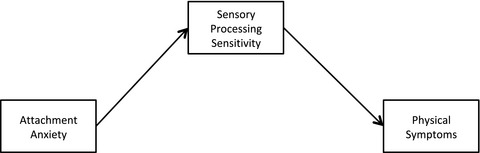
Relationship between insecure attachment and physical symptom severity is mediated by sensory sensitivity
- First Published: 26 June 2020
A qualitative exploration of the sociology of poststroke visual impairments and the associated health inequalities
- First Published: 26 June 2020
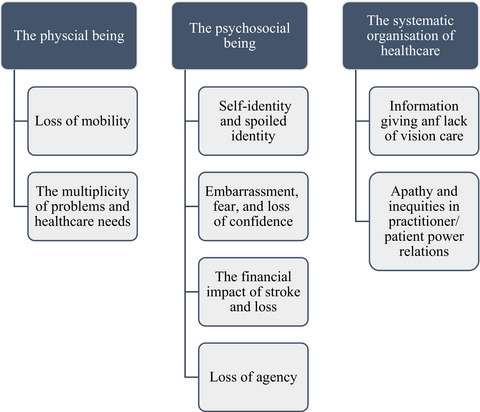
The long-term impact of living with poststroke visual impairments has been explored using focus groups and individual interviews, in order to identify health inequalities and potential means of addressing these. The findings emphasize a need to educate clinicians and patients of the bigger picture of life after stroke, highlighting all available support.
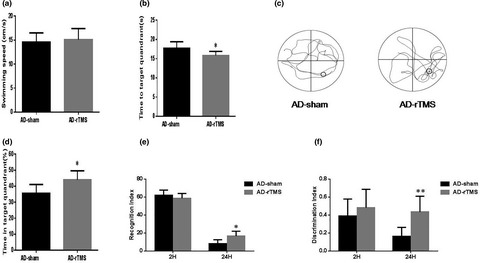
High-frequency transcranial magnetic stimulation protects APP/PS1 mice against Alzheimer’s disease progress by reducing APOE and enhancing autophagy
- First Published: 26 June 2020
REVIEW ARTICLE
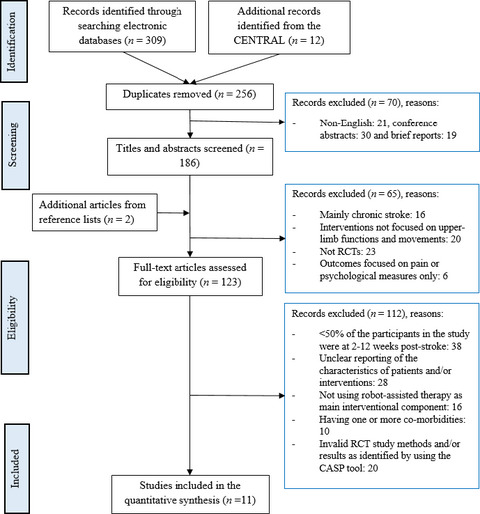
Robot-assisted therapy for upper-limb rehabilitation in subacute stroke patients: A systematic review and meta-analysis
- First Published: 26 June 2020
ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Identifying interactive biological pathways associated with reading disability
- First Published: 28 June 2020
Effects of environmental tobacco smoke exposure on brain functioning in never-smoking adolescents
- First Published: 01 July 2020
Fetal eye movements in response to a visual stimulus
- First Published: 01 July 2020
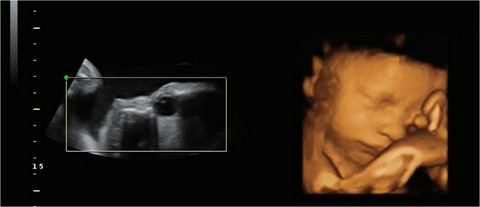
We have developed a light source for delivering visual stimuli to be seen by the fetal eye, and the 2D component of 94 fetal scans was coded to determine whether the eyes moved in response to the stimuli independent of any head movement. The light stimulus significantly provoked head and eye movements, but after the light was withdrawn the head stopped moving, yet the eyes continued to move. This provides evidence for visual attention mechanisms that can be controlled through eye movements that are independent of head movements prior to birth.
Effects of mirror neuron system-based training on rehabilitation of stroke patients
- First Published: 01 July 2020

After 8 consecutive weeks’ training, both groups showed significant improvements on the upper extremity motor function, cognitive function, and daily life ability score after training (p < .05). The MNS group showed significantly improved upper extremity motor function and cognitive function (p < .05) compared with control group.Combining MNS-based and conventional training can improve upper extremity motor function and cognitive function in stroke patients.
Reproducibility of graph measures at the subject level using resting-state fMRI
- Pages: 2336-2351
- First Published: 02 July 2020
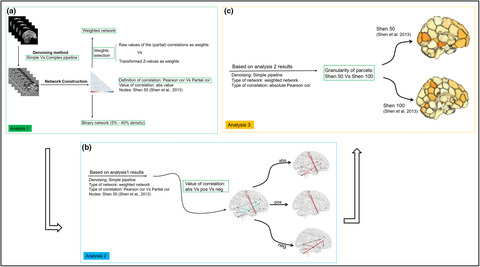
We used the multi-session fMRI dataset from the Brain Genomics Superstruct Project consisting of 69 healthy young adults. Our results demonstrated that normalized global graph measures based on a weighted network using the absolute (partial) correlation as weight were reproducible. The denoising pipeline and the granularity of the whole-brain parcellation used to define the nodes were not critical for the reproducibility of normalized graph measures.
Interaction between catechol-O-methyltransferase polymorphism and childhood trauma in suicidal ideation of patients with post-traumatic stress disorder
- First Published: 02 July 2020
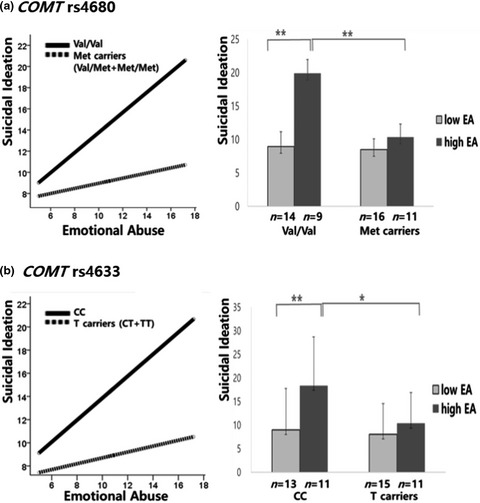
Our study demonstrated that the interaction of COMT polymorphism and childhood emotional abuse predicted suicidal ideation in patients with PTSD. Our results suggest that vulnerability to suicide could be increased in the Val/Val genotype of rs4680 and the CC genotype of rs4633 in patients with PTSD.
Diagnostic accuracy of cognitive screening tools under different neuropsychological definitions for poststroke cognitive impairment
- First Published: 03 July 2020
Transient effects of multi-infusion ketamine augmentation on treatment-resistant depressive symptoms in patients with treatment-resistant bipolar depression – An open-label three-week pilot study
- First Published: 03 July 2020
Time course of pupillary response to threat words before and after attention bias modification for transdiagnostic anxiety disorders: A randomized controlled trial
- First Published: 07 July 2020
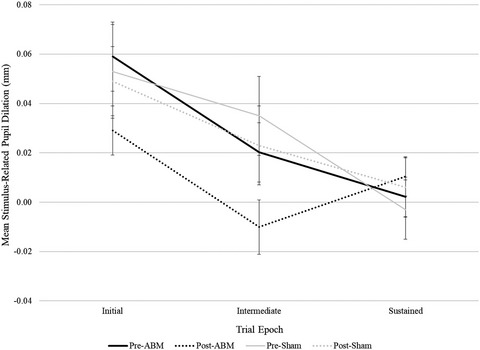
Altered attention to threatening stimuli at initial and sustained stages of processing may be dissociable dimensions that influence symptoms of anxiety and require distinct intervention; therefore, the current study utilized pupillary response as a temporally sensitive and cost-effective peripheral marker of neurocognitive response to attention bias modification (ABM) treatment. Results demonstrate that ABM is associated with reductions in pupillary response to threat words during initial and intermediate stages of processing, which were related to top-down cognitive control processes, and that pre- to post-training reductions in intermediate and late pupillary response to threat were positively correlated with ABM-related reductions in patient-reported anxious arousal. Findings suggest that pupillometry may be well suited to measure both target engagement and treatment outcome following ABM.
Corticomotor reorganization during short-term visuomotor training in the lower back: A randomized controlled study
- First Published: 07 July 2020
Accumulating evidence suggests that motor skill training is associated with structural and functional reorganization of the primary motor cortex. However, previous studies have focussed primarily upon the upper limb, and it is unclear whether comparable reorganization occurs following training of other regions, such as the lower back. The aims of this study were therefore to (a) determine whether a lumbopelvic tilt motor training task induced reorganization of the corticomotor representations of lower back muscles, (b) quantify the variability of corticomotor responses to motor training, and (c) determine whether any improvements in task performance were correlated with corticomotor reorganization. No relationship between corticomotor reorganization and improvements in task performance was identified, suggesting that short-term improvements in lower back performance may be driven by changes in remote subcortical and/or spinal networks rather than adaptations in corticomotor pathways.
Adults with spina bifida: A cross-sectional study of health issues and living conditions
- First Published: 07 July 2020
The aim was to describe health issues and living conditions of adults with Spina bifida. Today, persons who have survived to the age of >46 years had less complex medical conditions, better physical and cognitive functions, and had attained a higher level of education, leading to better prerequisites for living independently and participating in society. The future generations of older adults may need more attention in many ways, since they at a younger age do have more complex medical conditions, lower physical and cognitive functions, and lower prerequisites for independent living and participation in society than those> 46 years today. This elucidates that adults with Spina bifida need systematic follow-up services and social support throughout life.
Evaluation of the recovery outcome of poststroke cognitive impairment after cluster needling of scalp acupuncture therapy based on functional near-infrared spectroscopy
- First Published: 08 July 2020
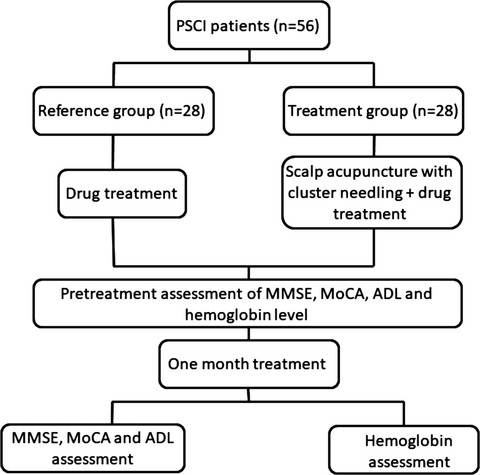
In the present study, we reveal that applying cluster needling of scalp acupuncture on top of drug treatment can significantly improve the cognitive function and elevate the cerebral hemoglobin levels compared to patients treated with drug only. Our results suggest that cluster needling of scalp acupuncture is an effective treatment against PSCI and shed light on its application on other neurological disorders.
Improving timely treatment with a stroke emergency map: The case of northern China
- First Published: 11 July 2020