Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
ISSUE INFORMATION
ORIGINAL RESEARCH
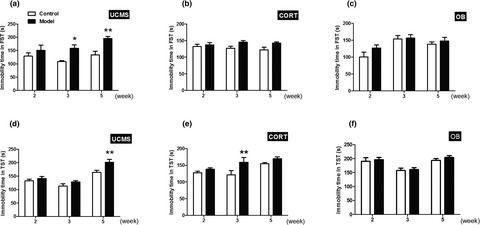
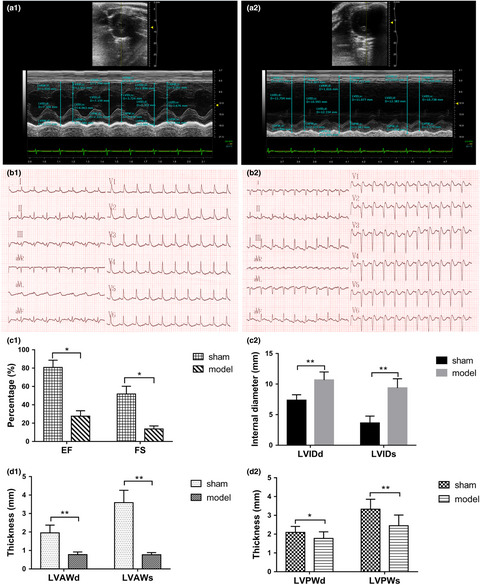
Long-term stability and characteristics of behavioral, biochemical, and molecular markers of three different rodent models for depression
- First Published: 22 December 2019
The association analysis between CYP24A1 genetic polymorphisms and the risk of ischemic stroke in Chinese Han population
- First Published: 24 December 2019
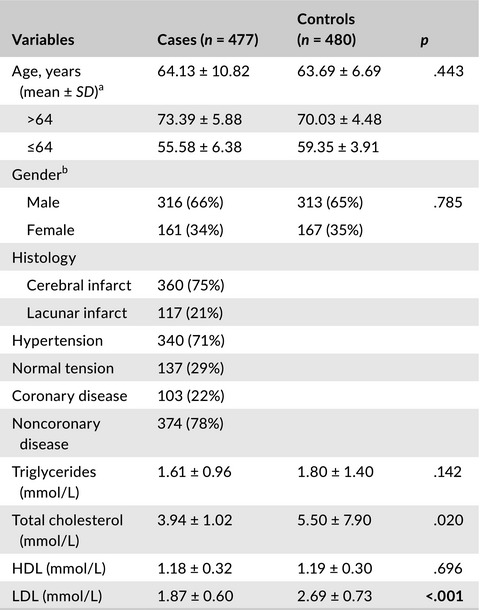
The results indicated that CYP24A1 rs1570669 was significantly association with stroke risk. Stratification analysis found that rs6068816 could enhance the stroke risk by 1.64 times at age >64 years, and rs2762934 had an increased stroke susceptibility in age ≤64 years. We observed that CYP24A1 rs2296241was associated with the increased stroke risk in males than in females.
Test–retest reliability of the Italian version of the M-BACK questionnaire to assess the barriers, attitudes, confidence, and knowledge of mental health staff regarding metabolic health of psychiatric patients
- First Published: 25 December 2019

This study aimed to validate the Italian version of M-BACK questionnaire (M-BACK-IT) and to determine the test–retest reliability. Thirty mental health professionals (4 psychiatrists, 9 psychologists, 12 nurses, and 5 exercise specialists) completed the M-BACK-IT, intraclass correlation coefficients (ICC) were calculated for the total score, and each of the four M-BACK domains, ICCs, ranged from 0.58 to 0.94.
Analyzing the genes and pathways related to major depressive disorder via a systems biology approach
- First Published: 25 December 2019
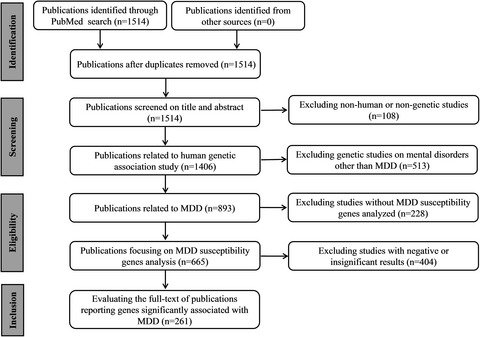
In this study, a systems biology approach focusing on the function correlation and interaction of the candidate genes related to major depressive disorder was adopted to explore the molecular mechanisms underlying the disease. Major pathways and the cross talks among them were detected, and novel genes potentially related to the disease were also identified.
Retinal sublayer defect is independently associated with the severity of hypertensive white matter hyperintensity
- First Published: 25 December 2019
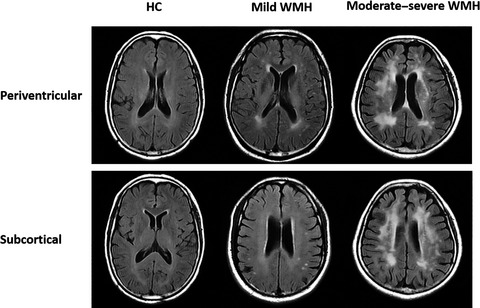
In our current study, we conducted an observational study to investigate the association of the retinal sublayer thickness on OCT with focal markers of brain tissue on MRI in participants with WMH using the Fazekas scale. Retinal degeneration in the RNFL and GCIP was independently associated with focal lesions in the white matter of the brain and deteriorates with the severity of the lesions. We suggest that imaging and measurement of the retinal sublayers using the OCT may provide evidence on neurodegeneration in WMH.
Adaptation and validation of a scale of self-efficacy and social support for physical activity in Spanish patients with severe mental disorders
- First Published: 26 December 2019
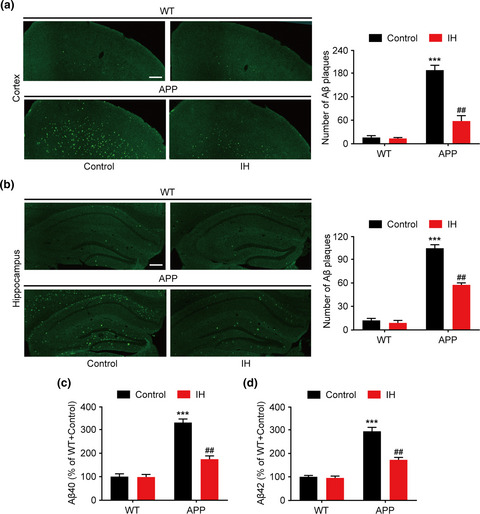
Intermittent hypoxia improves cognition and reduces anxiety-related behavior in APP/PS1 mice
- First Published: 26 December 2019
The relationships among MAOA, COMT Val158Met, and 5-HTTLPR polymorphisms, newborn stress reactivity, and infant temperament
- First Published: 29 December 2019
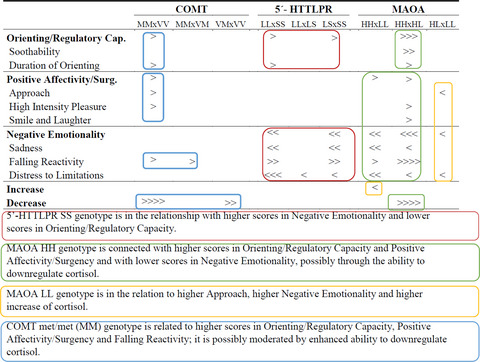
The rapidity of cortisol elimination after the stress event (a heel stick blood draw) was important in determining infant early temperament. The 5-HTTLPR short allele and the MAOA low expressing allele predisposed their carriers to negative emotions proneness and lower regulatory capacity, the Met allele of COMT predisposed their carriers to more extraverted and regulated behavior.
Modeling essential connections in obsessive–compulsive disorder patients using functional MRI
- First Published: 01 January 2020
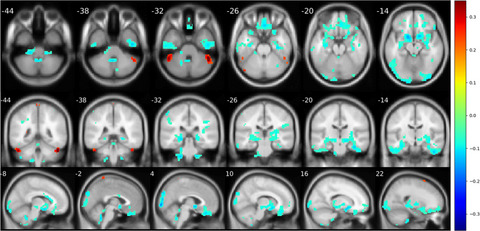
This paper proposed a method based on kernel PCA and Riemann manifold to characterize patients with OCD from healthy controls, whose performance reaches 90%. Furthermore, by feature reconstruction, our algorithm could generate decisive features from the classification model. Results demonstrate the possible affect of cerebellum in the etiology of OCD.
Increased muscle tone and contracture late after ischemic stroke
- First Published: 01 January 2020
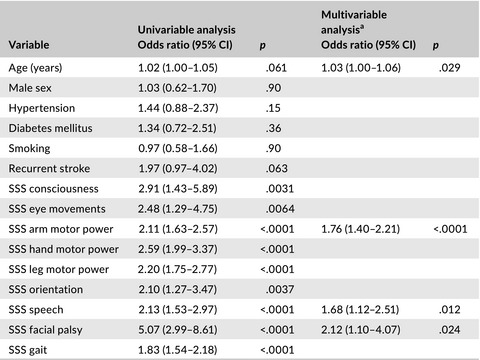
One-third of patients with ischaemic stroke before 70 years of age showed increased muscle tone at 7-year follow-up. Half of them also had classical spasticity, and almost every tenth had one or more contractures. Increased muscle tone was predicted by age, arm paresis, aphasia, and facial palsy at index stroke.
Associations between personality and whole-brain functional connectivity at rest: Evidence across the adult lifespan
- First Published: 05 January 2020
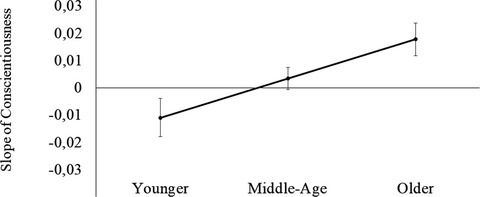
We investigated the associations between personality and resting-state functional MRI data from 365 individuals across the adult lifespan (20–80 years). We found that openness was positively associated with connectivity in the default mode network, neuroticism was negatively associated with both the ventral and dorsal attention networks, and agreeableness was negatively associated with the dorsal attention network. In addition, age moderated the association between conscientiousness and the frontoparietal network, indicating that this association becomes stronger in older age.
Sex differences in the association between prenatal exposure to maternal obesity and hippocampal volume in children
- First Published: 05 January 2020
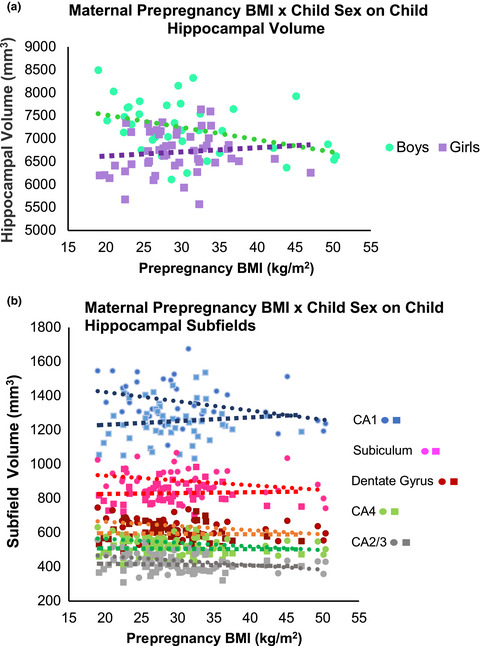
We provide novel evidence in support of findings in rodent models suggesting that in utero exposure to maternal obesity differentially impacts the hippocampus of boys compared to girls during childhood. This is the first study in humans to show changes to the hippocampus in association with in utero exposure to maternal obesity.
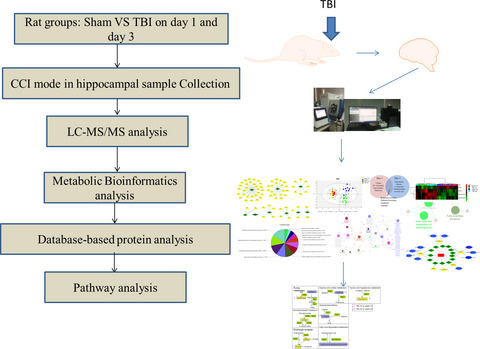
Metabolomics analysis of the hippocampus in a rat model of traumatic brain injury during the acute phase
- First Published: 06 January 2020
Early and very early-onset schizophrenia compared with adult-onset schizophrenia: French FACE-SZ database
- First Published: 07 January 2020
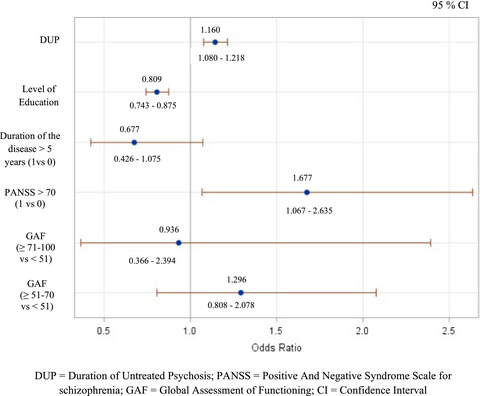
To describe schizophrenia from childhood to adulthood is complex and patients with early-onset schizophrenia (EOS) remain undiagnosed or misclassified, especially the subgroup with very early-onset schizophrenia (VEOS). In patients with VEOS, the DUP which exceeds 8 years, almost eight times higher than in patients with AOS, objective the problem of early diagnosis and the need to develop diagnostic programs and management cares.
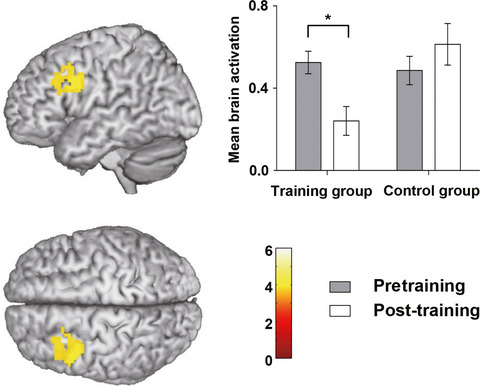
Evidence for the contribution of COMT gene Val158/108Met polymorphism (rs4680) to working memory training-related prefrontal plasticity
- First Published: 09 January 2020
Changes in resting-state functional connectivity in nonacute sciatica with acupuncture modulation: A preliminary study
- First Published: 10 January 2020
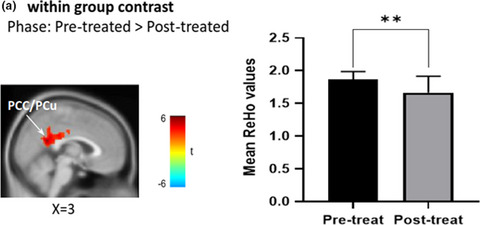
Acupuncture modulation elicited a bidirectionally regulated effect on default mode network (DMN) in chronic sciatica patients. The changes in subclinical endophenotype of brain FC after acupuncture treatment may provide clues for understanding the mechanism of acupuncture-mediated analgesia in chronic pain.
Functional connectivity predicts the dispositional use of expressive suppression but not cognitive reappraisal
- First Published: 13 January 2020
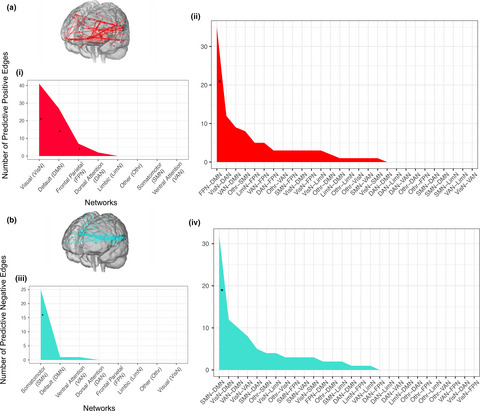
Here, we used a data-driven approach to investigate how individual differences in distributed intrinsic functional brain connectivity predict emotion regulation tendency. We found a significant neuromarker of dispositional use of suppression, but not reappraisal. These findings help inform how whole-brain networks of functional connectivity characterize how people tend to regulate emotion outside the laboratory.
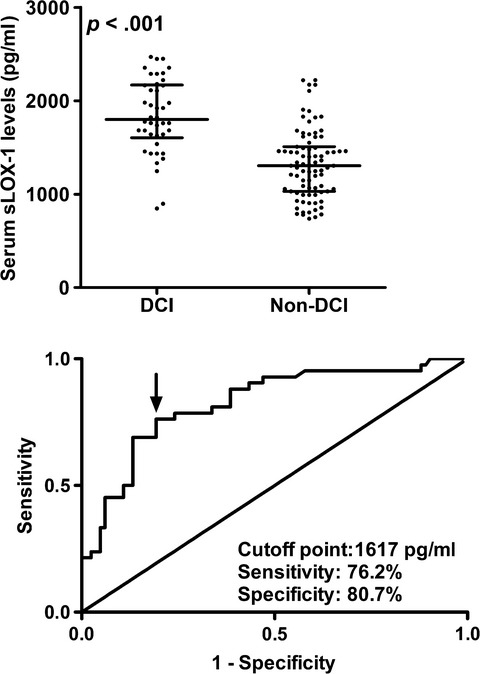
Serum soluble lectin-like oxidized low-density lipoprotein receptor-1 as a biomarker of delayed cerebral ischemia after aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage
- First Published: 14 January 2020
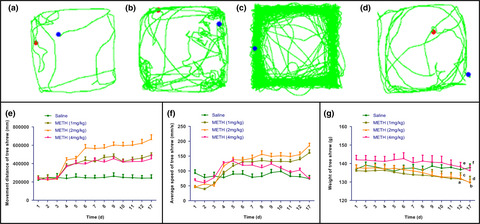
Involvement of dopamine D3 receptor and dopamine transporter in methamphetamine-induced behavioral sensitization in tree shrews
- First Published: 14 January 2020
Comparison of different protocols of Morris water maze in cognitive impairment with heart failure
- First Published: 16 January 2020
Operation spinal cord regeneration: Patterning information residing in extracellular matrix glycosaminoglycans
- First Published: 16 January 2020
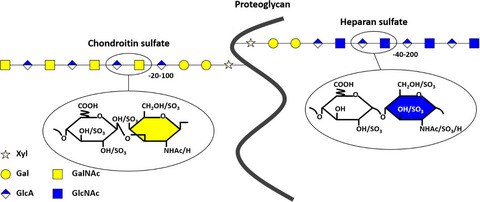
Spinal cord injuries are devastating, with many complications beyond paralysis and loss of sensory function. A recommended solution is to take advantages of the regenerative mechanism of axolotls and the current knowledge about the pattern-forming glycosaminoglycans for successful spinal cord regeneration and clinical applications.