Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
ISSUE INFORMATION
ORIGINAL RESEARCH
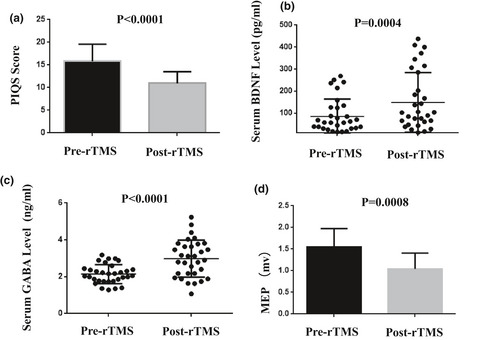
The Effect of sequential bilateral low-frequency rTMS over dorsolateral prefrontal cortex on serum level of BDNF and GABA in patients with primary insomnia
- First Published: 04 January 2019
Effects of time delays on the therapeutic outcomes of intravenous thrombolysis for acute ischemic stroke in the posterior circulation: An observational study
- First Published: 06 January 2019
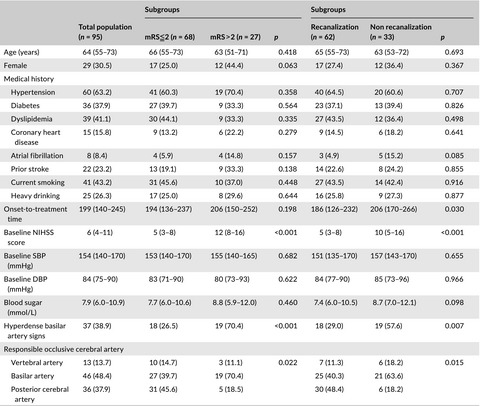
Our result showed that irrespective of stroke severity, a linear trend between onset-to-treatment time and recanalization was found in posterior circulation stroke with intravenous thrombolysis. That is, despite a greater ischemic tolerance and safer profile in bleeding complications when compared with anterior circulation stroke, the recanalization after intravenous thrombolysis was still time-dependent for posterior circulation stroke, which was not investigated in previous studies.
Abnormalities of white matter microstructure in unmedicated patients with obsessive–compulsive disorder: Changes after cognitive behavioral therapy
- First Published: 09 January 2019
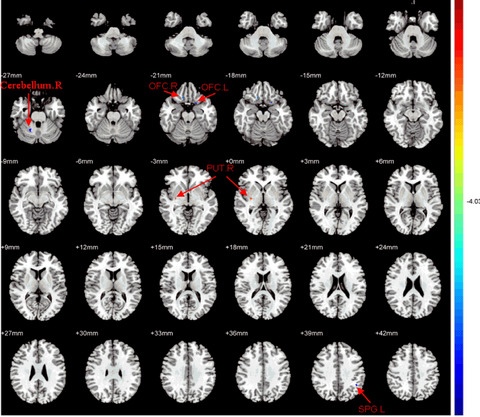
Little is known about the effects of CBT on white matter in OCD patients. We investigated white matter changes and the effect of CBT on white matter in unmedicated OCD patients using diffusion tensor tractography. OCD patients showed significant abnormalities of white matter microstructure in some brain areas, and these abnormalities may be partly reversed by CBT. The recovery of white matter fiber connections was correlated with an improvement in obsessive–compulsive symptoms. CBT inversion of partial white matter microstructure abnormalities can be used as an imaging index to predict the efficacy of CBT in the treatment of OCD.
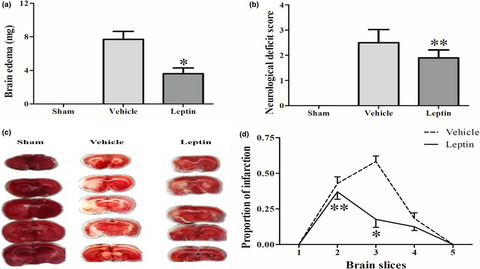
Leptin attenuates cerebral ischemic injury in rats by modulating the mitochondrial electron transport chain via the mitochondrial STAT3 pathway
- First Published: 10 January 2019
The rate of early neurological deterioration occurring after thrombolytic therapy: A meta-analysis
- First Published: 10 January 2019
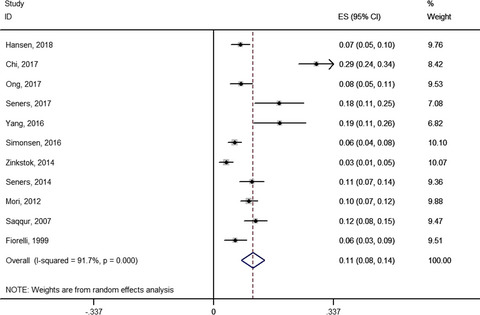
Eleven studies with a total of 3,539 subjects, including 373 patients with END and 3,166 patients without END, met the eligibility criteria. The pooled analysis showed that the rate of END occurring after thrombolytic therapy of the 11 studies was about 11.0% (95% CI: 7.8%–14.3%). This finding may provide a scientific reference for researchers to evaluate the efficacy and safety of thrombolytic therapy.
Altered functional connectivity in binge eating disorder and bulimia nervosa: A resting-state fMRI study
- First Published: 15 January 2019
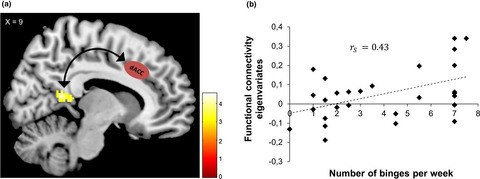
The present study investigated functional as well as seed-based connectivity of the default mode network, salience network, and executive network in individuals with bulimic-type eating disorders (BTE) such as binge eating disorder and bulimia nervosa (BN). Individuals with BTE exhibit aberrant functional connectivity in these networks. The BN group exhibited increased connectivity between the dorsal anterior cingulate cortex and the retrosplenial cortex which was also positively related to frequency of binges experiences by individuals with BN.
A diffusion tensor imaging study of brain microstructural changes related to religion and spirituality in families at high risk for depression
- First Published: 15 January 2019
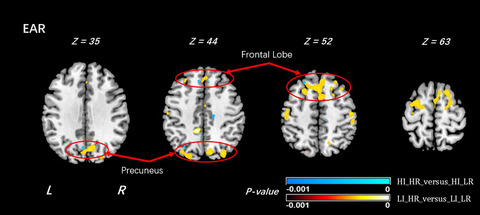
The present study examined brain microstructural differences associated with risk for major depressive disorder (MDD) and tested whether these are normalized in at-risk offspring who report high importance of religion/spirituality (R/S). The analyses suggested that R/S beliefs may affect microstructure in brain regions associated with R/S, potentially conferring resilience to depression among individuals at high familial risk for the disorder.
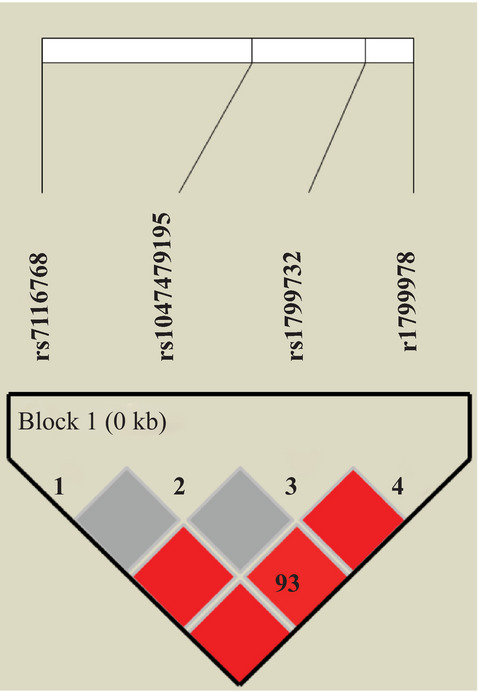
Dysmorphic contribution of neurotransmitter and neuroendocrine system polymorphisms to subtherapeutic mood states
- First Published: 17 January 2019
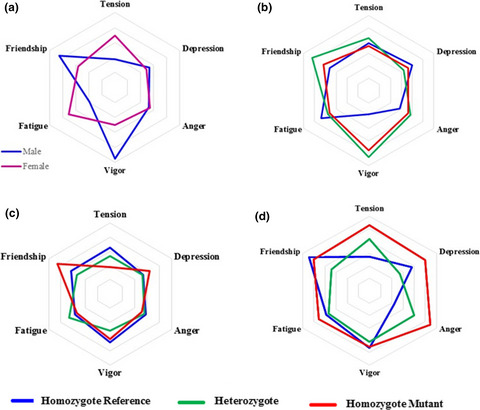
We show how genetic changes affecting neuroendocrine and neurotransmission pathways affect subtherapeutical mood states in a gender-dependent manner. MAOA-rs3788862 correlates with decreasing levels of tension among females while correlating with lower GHQ-28 depression score among males. Equivalently, SLC18A1 and HTR2A variants correlated with anger and vigor scores only among males. From the neuroendocrine system, OPRM1-rs1799971 correlated increasing levels of female’s Anxiety, depression and Social Dysfunction scores. Our findings suggest that these polymorphisms contribute to define general population mood levels, although exhibiting a clear sexual dimorphism.
Association between miRNAs expression and cognitive performances of Pediatric Multiple Sclerosis patients: A pilot study
- First Published: 17 January 2019
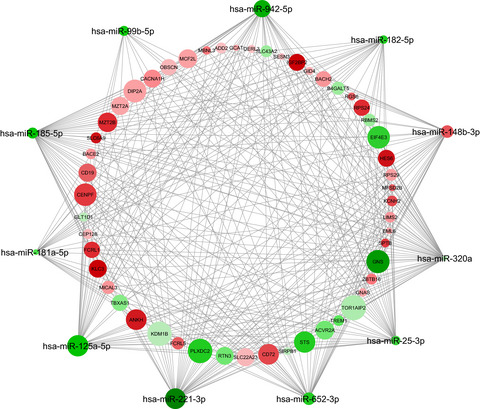
Based on several published evidences on the occurrence of cognitive impairment during MS, the main aim of this investigation was to suggest novel molecular hypothesis that may sustain the onset of these disabling symptoms, as well as they may cause changes in the regional brain volumes of MS patients. We believe that the potential of our research will be useful also for the clinical practice.
No association between polymorphisms in the promoter region of dopamine receptor D2 gene and schizophrenia in the northern Chinese Han population: A case–control study
- First Published: 18 January 2019
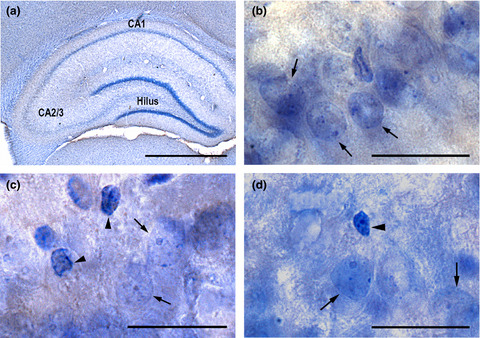
Electroconvulsive treatment prevents chronic restraint stress-induced atrophy of the hippocampal formation—A stereological study
- First Published: 18 January 2019
CGRP monoclonal antibody for preventive treatment of chronic migraine: An update of meta-analysis
- First Published: 18 January 2019
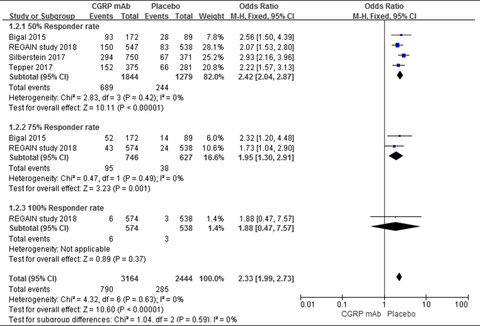
Calcitonin gene-related peptide monoclonal antibody (CGRP mAb) is a promising preventive treatment for migraine. And erenumab is approved by U.S. Food and Drug Administration in preventing episodic migraine recently. And the present meta-analysis shown that CGRP mAb is an effective and safety treatment for chronic migraine, of which preventive treatments are rarely.
Is it worth turning a trigger into a joke? Humor as an emotion regulation strategy in remitted depression
- First Published: 21 January 2019
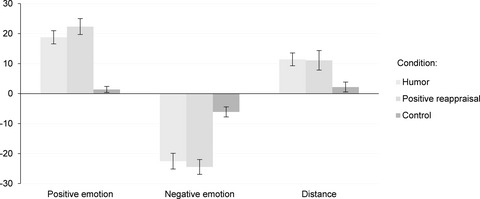
We examined the effects of humor as an emotion regulation strategy in remitted depression; fifty-five previously depressed outpatients took part in a laboratory computer experiment. The obtained findings provided support for an idea that for remitted depressed patients, humor can be a beneficial tool in dealing with negative, potentially triggering, experiences. Humor was found to down-regulate negative emotions, up-regulate positive emotions, and increase the distance from adversity; it was more beneficial than spontaneous emotion regulation and similarly advantageous to positive reappraisal.
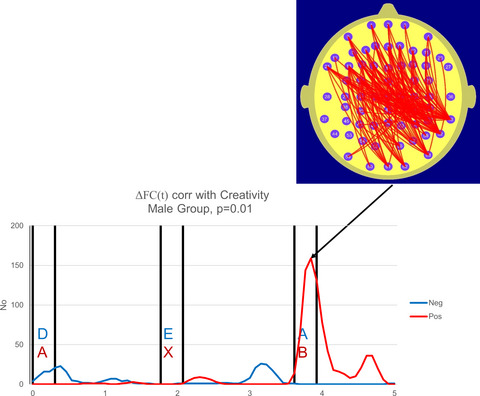
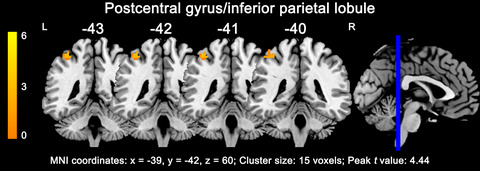
Gender differences in parieto-frontal brain functional connectivity correlates of creativity
- First Published: 27 January 2019
Prediction of early response to overall treatment for schizophrenia: A functional magnetic resonance imaging study
- First Published: 30 January 2019
CORRIGENDUM
Muscle training-induced bilateral brachial plexopathy in an adolescent with sporadic hereditary neuropathy with liability to pressure palsies
- First Published: 18 February 2019
Beauty-related perceptual bias: Who captures the mind of the beholder?
- First Published: 18 February 2019