Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
ISSUE INFORMATION
ORIGINAL RESEARCH
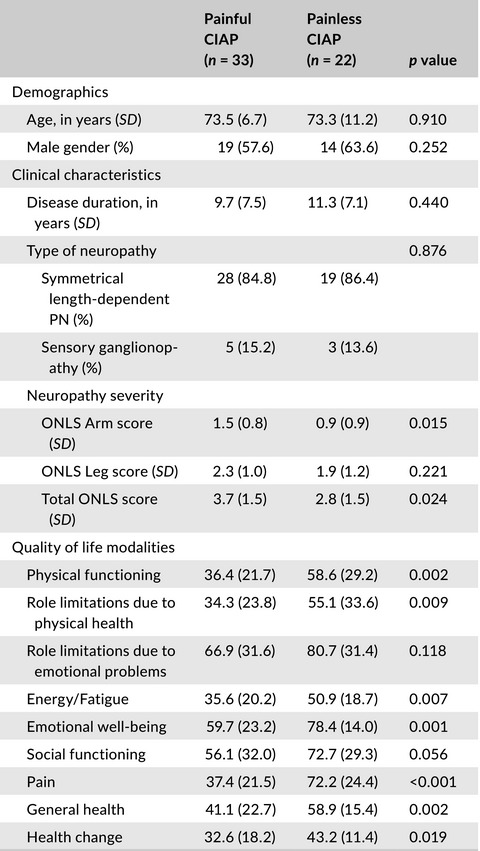
Chronic idiopathic axonal polyneuropathy: Prevalence of pain and impact on quality of life
- First Published: 25 November 2018
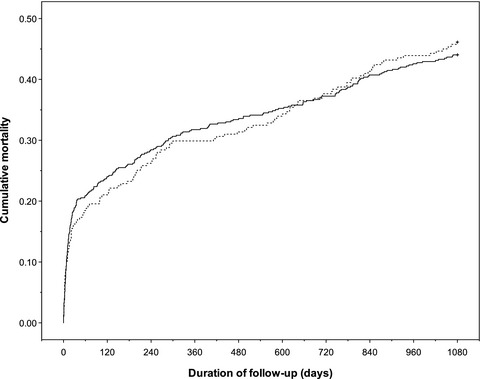
Changes in survival and characteristics among older stroke unit patients—1994 versus 2012
- First Published: 25 November 2018
Limbic encephalitis: Experience of a moroccan center
- First Published: 25 November 2018
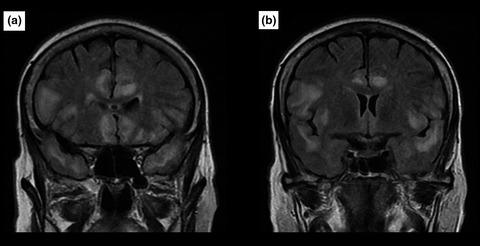
We describe in this study the demographic, clinical, paraclinical, and etiological features of limbic encephalitis, as well as its medium-term prognosis in Moroccan patients. We found a wide diversity of etiologies of this disease in Morocco with essentially an acute mode of onset of symptoms. 45% of patients had sequelae including temporal lobe epilepsy, anterograde amnesia, and severe cognitive impairment.
Incidence rate and sex ratio in multiple sclerosis in Lithuania
- First Published: 28 November 2018
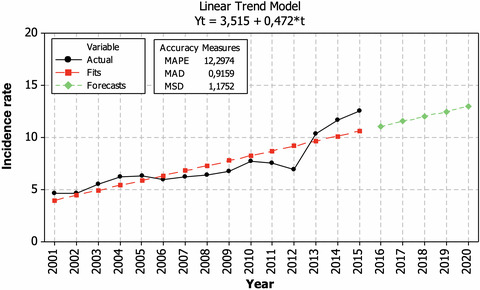
We show a substantial growth of the incidence rate of multiple sclerosis (MS) in Lithuania during the period of 2001–2015. Female-to-male sex ratio had also a tendency to increase over the period. In 2020, the incidence rate of MS is estimated to reach 13 cases per 100,000 persons and females are expected to be diagnosed with MS two times more often than males.
The neurological phenotype of developmental motor patterns during early childhood
- First Published: 28 November 2018
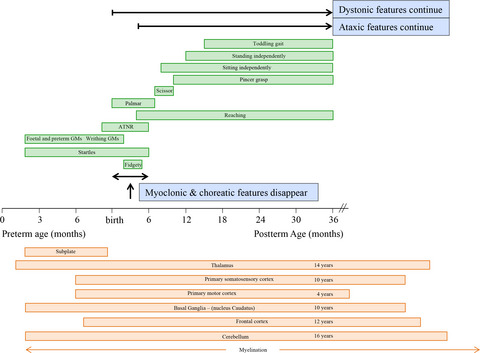
In healthy infants and toddlers (0–3 years), typical developmental motor patterns reveal choreatic-, myoclonic-, dystonic- and ataxic-like features. The transient character of these neurologic phenotypes is placed in perspective of the physiologic shaping of the underlying motor centers. Neurologic phenotypic insight into developmental motor patterns can contribute to adequate discrimination between ontogenetic and initiating pathologic movement features and to adequate interpretation of therapeutic interactions.
Short-term Sahaja Yoga meditation training modulates brain structure and spontaneous activity in the executive control network
- First Published: 28 November 2018
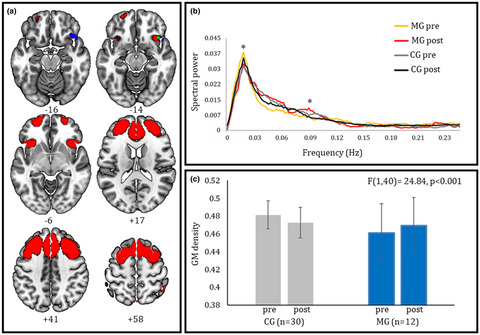
We assessed the effects of a 4-week Sahaja Yoga meditation training on gray matter volume and spontaneous resting-state brain activity in a group of 12 meditation-naïve healthy adults compared with 30 control subjects. The participants to meditation training showed increased gray matter density and a change in coherent brain activity in two adjacent regions of the right inferior frontal gyrus encompassing the anterior component of the executive control network. The significant impact of a brief meditation training on brain regions associated with self-control and self-awareness may reflect the engagement of cognitive control skills in searching for a state of mental silence, a distinctive feature of Sahaja Yoga meditation.
Accelerated age-related cortical thinning in mild traumatic brain injury
- First Published: 28 November 2018
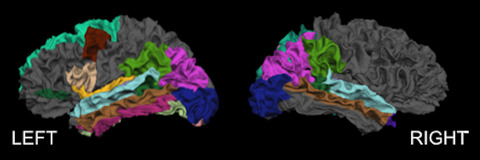
Cortical thinning can occur with normal aging and brain injury. This study reports an apparent accelerated age-related cortical thinning in those with a history of mild traumatic brain injury. Specifically, regional cortical thinning patterns were observed in bilateral parietal and left frontal and temporal cortices, and were similar regardless of gender.
Resting-state functional brain networks in adults with a new diagnosis of focal epilepsy
- First Published: 28 November 2018
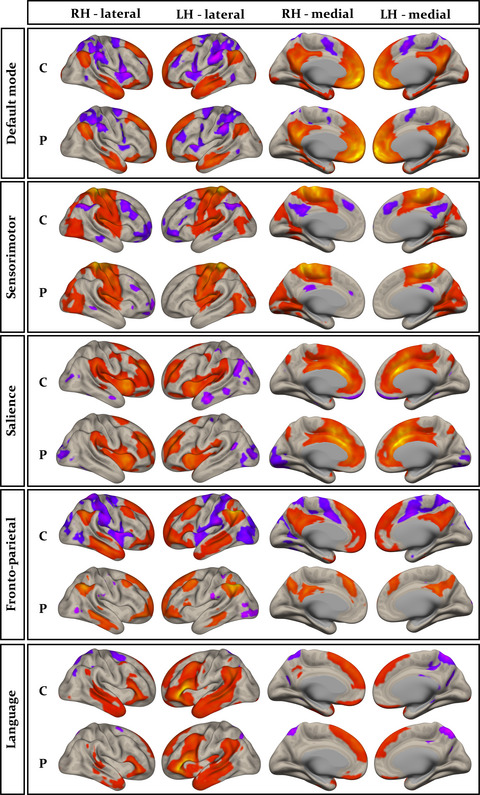
Virtually nothing is known about functional brain networks in adults with a new diagnosis of focal epilepsy (NDfE). Alonazi and colleagues show abnormalities in the fronto-parietal attentional network in patients with NDfE. Abnormalities of this network may relate to the previously demonstrated cognitive impairments patients with NDfE experience.
Transcranial Doppler to detect right-to-left shunt in cryptogenic acute ischemic stroke
- First Published: 01 December 2018
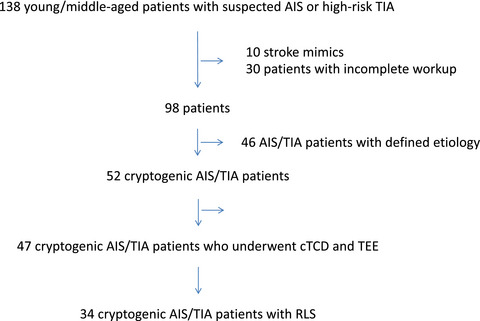
Contrast transcranial Doppler (cTCD) showed 100% sensitivity and specificity in the detection of right-to-left shunt (RLS) compared to the current reference standard (i.e., transesophageal echocardiography—TEE) in consecutive patients aged <55 years with a cryptogenic acute ischemic stroke or high-risk transient ischemic attack. Median delays from symptom onset to examination were 2 (min–max 1–10) and 21 (min–max 1–60) days, respectively, for cTCD and TEE. Transcranial Doppler with “bubble test” appears as the best screening test for the detection of RLS in young and middle-aged adults with cryptogenic acute cerebral ischemic events to select patients potentially suitable for closure procedure after TEE confirmation.
Edaravone acts as a potential therapeutic drug against pentylenetetrazole-induced epilepsy in male albino rats by downregulating cyclooxygenase-II
- First Published: 01 December 2018
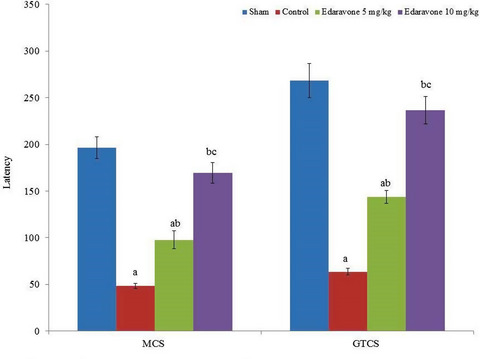
Edaravone supplementation significantly normalized altered lipid peroxidation and antioxidant biochemical markers. Apoptosis and NO levels were reduced compared to their respective controls. mRNA and protein expression of COX-II was substantially reduced following edaravone supplementation. Taken together, our results suggest that edaravone is a potential candidate for the treatment of PTZ-induced epilepsy and functions by downregulating the levels of COX-II and NO.
EDITORIAL
Improving transparency and scientific rigor in academic publishing
- First Published: 02 December 2018
ORIGINAL RESEARCH
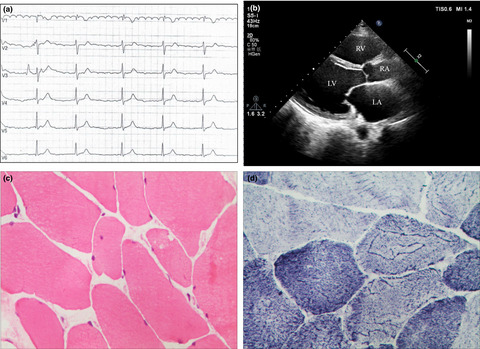
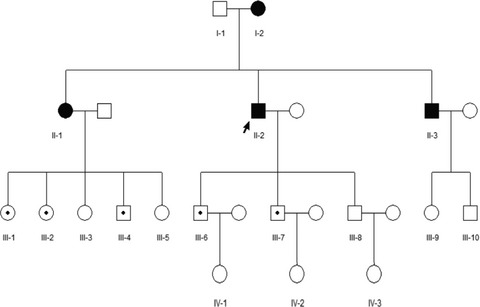
A novel EMD mutation in a Chinese family with initial diagnosis of conduction cardiomyopathy
- First Published: 03 December 2018
Total MRI burden of cerebral vessel disease correlates with the progression in patients with acute single small subcortical strokes
- First Published: 03 December 2018
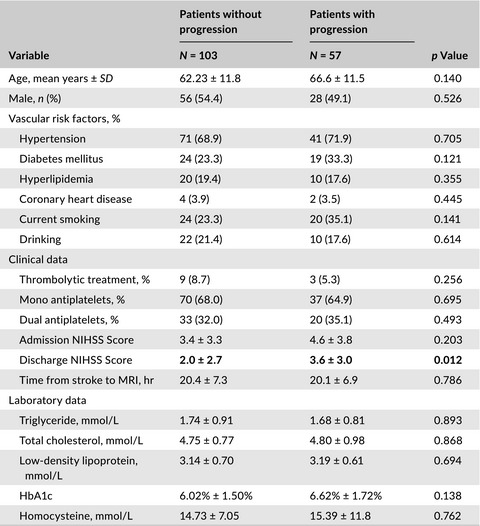
In our study, 35.6% of patients with subcortical stroke showed progression in the first 72 hr after stroke onset. Severe WMHs and moderate- and high-grade basal ganglia EPVS were associated with increased odds of progression in subcortical stroke patients. Total burden of cSVD was accompanied by neurological deterioration in single subcortical stroke patients.
REVIEW ARTICLE
Anesthesia for endovascular treatment in anterior circulation stroke: A systematic review and meta-analysis
- First Published: 03 December 2018
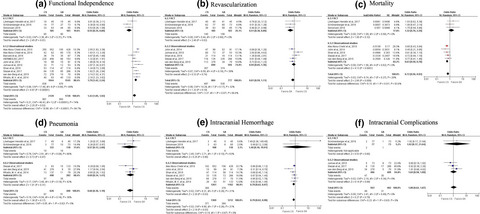
This study conducted a meta-analysis comparing general anesthesia (GA) with conscious sedation (CS) during endovascular treatment for acute anterior circulation ischemic stroke. In the overall analysis and observational studies, CS was associated with improved functional outcomes and relatively safe for anterior ischemic stroke compared with GA. While the pooled data from RCTs suggested that GA was associated with improved outcomes.
ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Implicit but not explicit extinction to threat-conditioned stimulus prevents spontaneous recovery of threat-potentiated startle responses in humans
- First Published: 04 December 2018
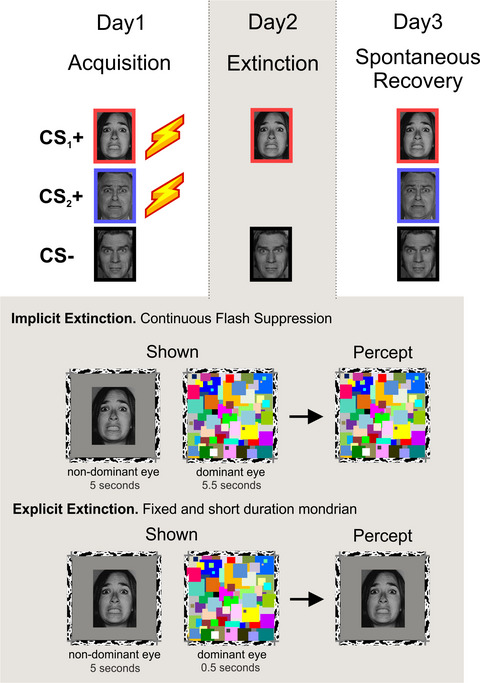
Exposure-based therapies often fail when higher order structures are unable to inhibit the activity in the threat defensive circuit. Here, we show that implicit exposure of a threat conditioned stimulus can reduce the recovery of defensive responses in the startle reflex index. These results suggest that implicit extinction might facilitate the modulation of the affective component of fearful memories, representing an important therapeutic target to further advance exposure-based psychotherapies.
Objective and subjective measures of prior sleep–wake behavior predict functional connectivity in the default mode network during NREM sleep
- First Published: 04 December 2018
This study establishes an association between intersubject variability in habitual sleep behaviours and the strength of functional connectivity (FC) within the regions of the default mode network during non-rapid eye movement sleep. In several cases, FC was related to sleep measures independently of sleep stage, suggesting that previous sleep history effects sleep FC globally across the stages. This highlights the need to consider a subject's prior sleep history in studies utilising FC analysis during wakefulness and sleep, and indicates the complexity of the impact of sleep on the brain both in the short and long term.
Postoperative complications influencing the long-term outcome of head-injured patients after decompressive craniectomy
- First Published: 04 December 2018
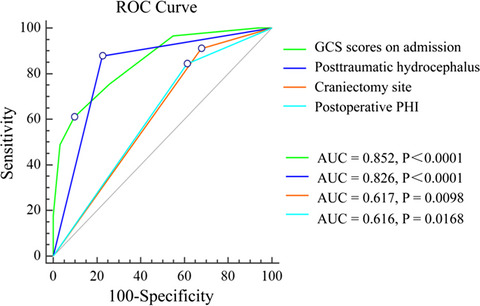
The results suggest that PTH and postoperative PHI were found to be independently associated with unfavorable long-term outcome after DC in patients with TBI. Early prevention and treatment of PTH and postoperative PHI may be beneficial to improve the long-term outcome, especially in patients with lower admission GCS scores or bilateral DC.
Individual optimal attentional strategy during implicit motor learning boosts frontoparietal neural processing efficiency: A functional near-infrared spectroscopy study
- First Published: 05 December 2018

The attentional focus is an important cognitive factor influencing motor control. The right dorsolateral prefrontal cortex and the right somatosensory association cortex showed relatively lower activities under the attentional condition with higher motor learning effect. These results suggest that the individual optimal attentional strategy is associated with more efficient neural processing in the frontoparietal network.
REVIEW ARTICLE
Social capital: Implications for neurology
- First Published: 08 December 2018
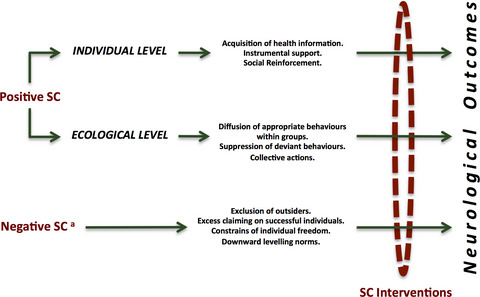
Social capital (SC) refers to the resources derived from the cooperation between individuals and groups that partially explain how social conditions influence health and mortality. The role of SC in neurological disease is just beginning to be explored. Concerted efforts are needed to ensure that empirical evidence on SC could be properly translated into interventions for health-promoting purposes.
ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Brain iron deposition in primary insomnia—An in vivo susceptibility-weighted imaging study
- First Published: 11 December 2018
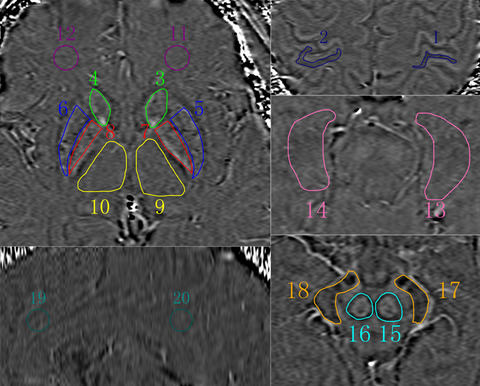
The cognitive impairment of primary insomnia is related to increased iron deposition in the left hippocampus. The sleep quality and disturbances have no correlation with the brain iron deposition. The iron concentration of the left HP is a biomarker of cognitive impairment and may play an important role in the pathophysiological mechanism.
Relation of postoperative serum S100A12 levels to delirium and cognitive dysfunction occurring after hip fracture surgery in elderly patients
- First Published: 11 December 2018
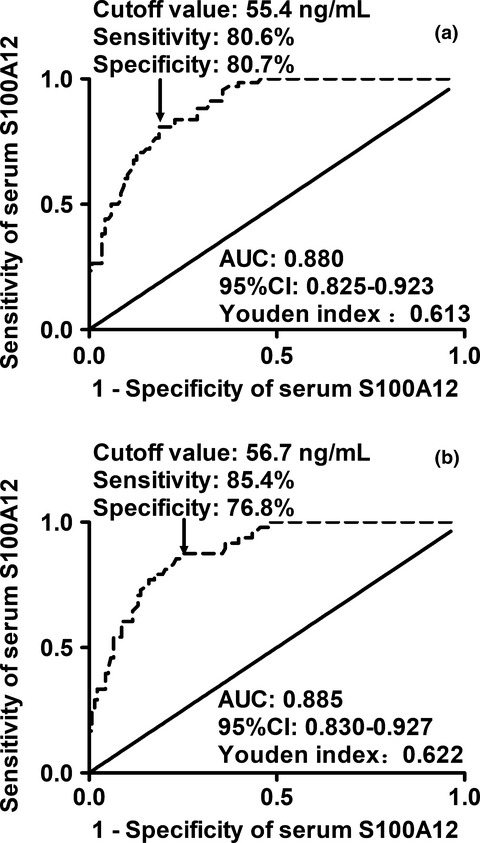
Elevated S100A12 levels in serum after hip fracture surgery in elderly patients. Independent relation of postoperative serum S100A12 to delirium and cognitive dysfunction after hip fracture surgery. High discriminatory ability of postoperative serum S100A12 for delirium and cognitive dysfunction after hip fracture surgery.
Unilateral neglect post stroke: Eye movement frequencies indicate directional hypokinesia while fixation distributions suggest compensational mechanism
- First Published: 12 December 2018
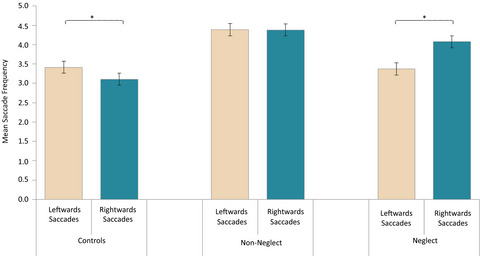
Our study investigated attention pathology in right hemisphere stroke patients with and without neglect. Patients had higher fixation frequencies compared to controls, suggesting they were less efficient in their visual processing. Neglect patients showed a spatial bias in their distribution of fixations that depended on neglect severity. This bias shifted from a rightward bias to a leftward bias as neglect symptoms decreased. This suggested that patients with less severe neglect were able to use compensational mechanisms in their contralesional space. The relation between direction of eye-movements and their frequency in the neglect patients suggests that directional hypokinesia can be a relevant component in this syndrome.
Gene mutations in a Han Chinese Alzheimer's disease cohort
- First Published: 14 December 2018
Vibrotactile sensitivity of patients with HIV-related sensory neuropathy: An exploratory study
- First Published: 18 December 2018
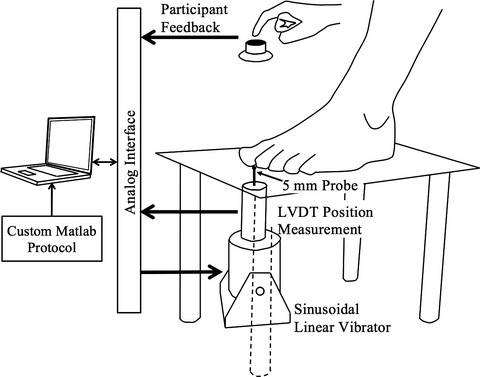
HIV-associated distal polyneuropathy (HIV-PN) affects large and small sensory nerve fibers and can cause tactile insensitivity. We report a detailed description of the vibrotactile sensitivity of individuals with HIV-PN and compare the commonly used clinical vibration testing and scoring grades with a more robust double-blinded quantitative vibration perception thresholds (VPTs) protocol. The results indicate that patients with HIV-PN have reduced vibration sensitivity at all tested vibration frequencies and that the pathology may not affect all mechanoreceptors similarly.
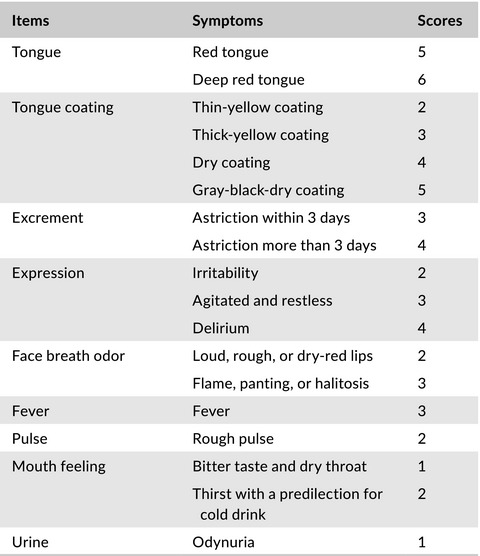
Sanhuang Xiexin decoction promotes good functional outcome in acute ischemic stroke
- First Published: 19 December 2018
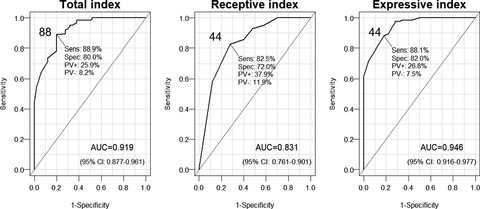
Adaption and validation of the Mississippi Aphasia Screening Test to Estonian speakers with aphasia
- First Published: 19 December 2018
Positive affective priming decreases the middle late positive potential response to negative images
- First Published: 19 December 2018
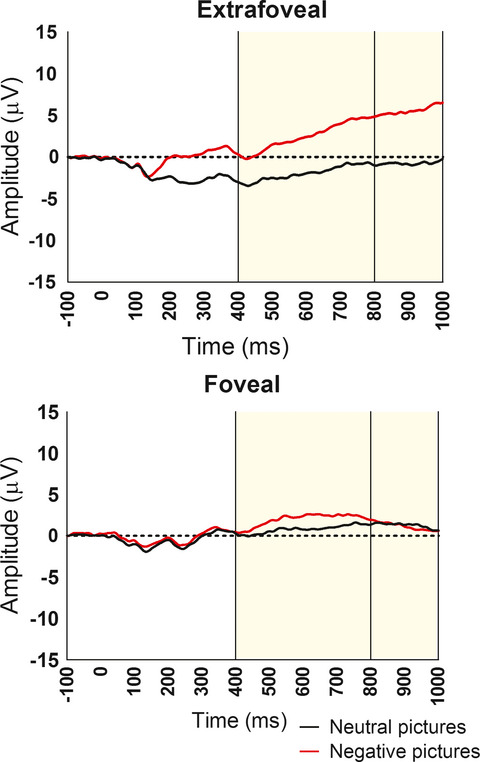
Late positive potential ERP recordings show that priming with a happy-inducing video decreases the response to emotionally negative pictures in both the foveal and extrafoveal visual field. These results suggest that incidental happy states can have a protective effect when viewing aversive stimuli. Additionally, the LPP showed greater sensitivity to negative stimuli when presented extrafoveally compared to foveally.
Diffusion tensor imaging and disability progression in multiple sclerosis: A 4-year follow-up study
- First Published: 26 December 2018
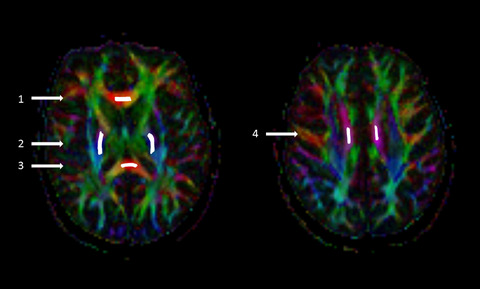
Baseline DTI indices in the CC splenium were associated with 4-year disability progression in MS. One-year DTI changes were not linked to 4-year disability progression. Dynamic change in DTI over time is different with respect to anatomical location. Disease progression showed heterogeneity and temporal DTI changes in the brain regions seem to occur with individual rate. DTI is sensitive to diffusivity abnormalities in the specific brain regions responsible for disability accumulation and to longitudinal changes in diffusivity.
Perilesional and homotopic area activation during proverb comprehension after stroke
- First Published: 26 December 2018
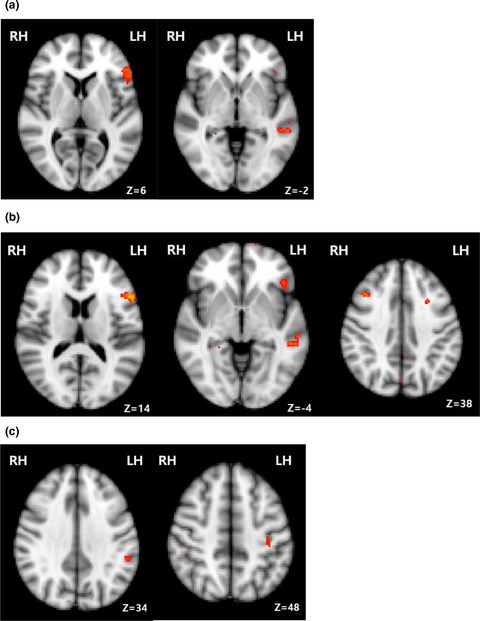
This study compared the brain regions activated by literal sentences and by opaque or transparent proverbs in right middle cerebral artery (MCA) infarction patients and a normal population using functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI). Fifteen normal adults and 17 right MCA infraction patients participated in the study. In right hemispheric stroke patients, the areas of the brain involved in understanding a proverb compared with a literal sentence include the left IFG, left MTG, right MFG, and frontal pole. The activation areas in right hemispheric stroke patients can be explained by the homotopic area and perilesional activation of the infarction area of these patients compared with normal subjects.
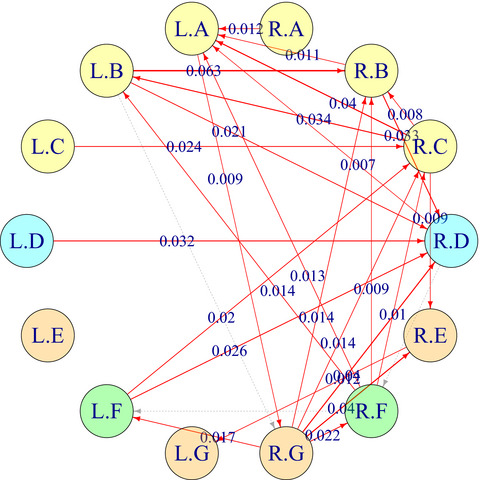
Copula directional dependence for inference and statistical analysis of whole-brain connectivity from fMRI data
- First Published: 27 December 2018
Neuroimaging markers of global cognition in early Alzheimer's disease: A magnetic resonance imaging–electroencephalography study
- First Published: 27 December 2018
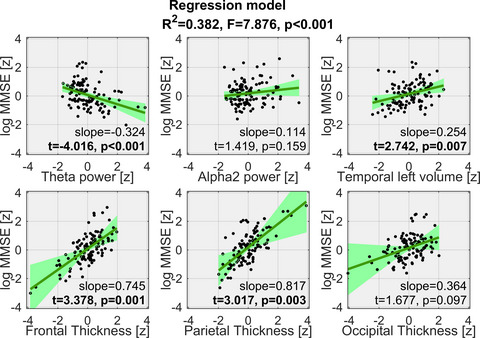
Measures from MRI and EEG have shown potential as markers of Alzheimer's disease but, individually, these modalities tend to lack precision in both diagnosis and disease staging. Here, we systematically investigated the capability of a joint MRI–EEG approach to identify the global cognitive status in early Alzheimer's disease. The observed accuracy of 84.7% suggests that including joint MRI–EEG markers may be beneficial in the current diagnostic workup.
Resting-state connectivity within and across neural circuits in anorexia nervosa
- First Published: 27 December 2018
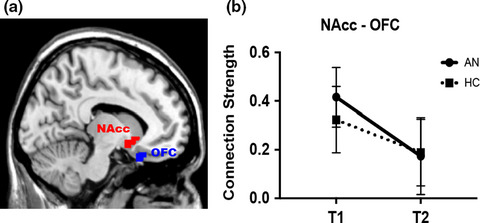
Obsessional thoughts and ritualized eating behaviors are characteristic of Anorexia Nervosa (AN), leading to the common suggestion that the illness shares neurobiology with obsessive–compulsive disorder (OCD). Based on findings of abnormal limbic cortico-striato-thalamo-cortical (CSTC) loop functional connectivity among individuals with OCD, this longitudinal study examined limbic CSTC functional connectivity in AN, as well as in the salience network, the default mode network, and the executive control network (components of the triple network model of psychopathology). There was no significant association between limbic CSTC connectivity and obsessive–compulsive symptoms or prognosis in AN; exploratory analyses of functional network connectivity within the triple network model showed weaker inter-network connectivity among AN relative to HC between the salience network and left executive control network that persisted following weight restoration.