Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
ISSUE INFORMATION
ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Altered resting-state functional connectivity of the putamen and internal globus pallidus is related to speech impairment in Parkinson's disease
- First Published: 25 July 2018
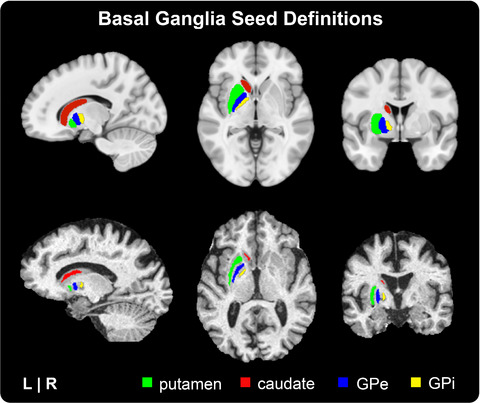
This study uses resting-state fMRI to investigate whether individuals with Parkinson's disease who present with speech impairment (PDSI) exhibit differences in functional connectivity between the cortex and basal ganglia when compared to older healthy controls (OHC) and individuals with Parkinson's disease who do not present with speech impairment (PDN). Our findings suggest that generalized speech impairment in Parkinson's disease may involve abnormal functional connectivity of the left putamen and left GPI to regions of the cerebral cortex.
Obstetric anesthesia/analgesia does not affect disease course in multiple sclerosis: 10-year retrospective cohort study
- First Published: 25 July 2018
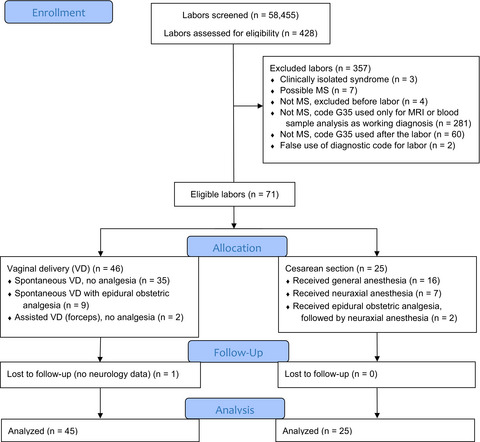
We aimed to describe occurrence or absence of relapses in 6-month postpartum period in multiple sclerosis parturients with and without obstetric anesthesia/analgesia. The most important finding of our study was that relapse occurrence (RO) after labor does not depend on either type of delivery or type of anesthesia for C-section (CS). There was also no impact of epidural obstetric analgesia on presence of RO.
Similar changes in neuropsychological functioning in english and spanish speaking HIV patients
- First Published: 25 July 2018
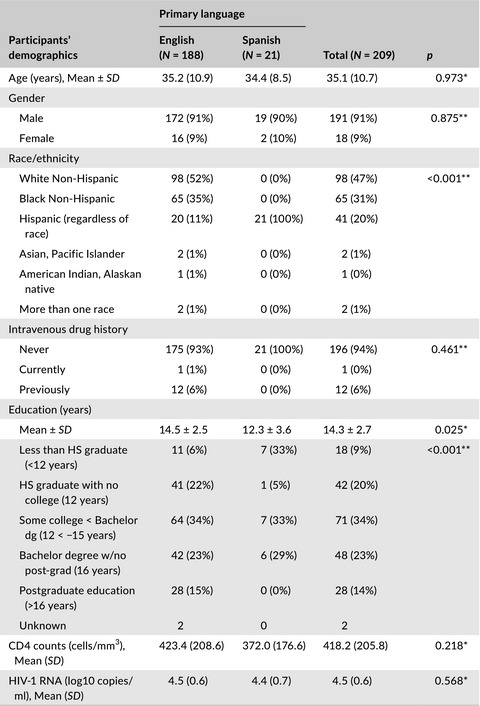
We sought to determine whether being a primary Spanish versus English speaker affects changes in neuropsychological evaluations in persons living with HIV. Data from 212 (190 English speakers and 22 Spanish speakers) ART-naïve HIV-infected adults were extracted from ACTG A5303, a 48-week randomized clinical trial of two HIV treatment regimens and analyzed. Changes in NP during ART were similar between English and Spanish speaking HIV-infected individuals for all NP measures.
Neural activity patterns between different executive tasks are more similar in adulthood than in adolescence
- First Published: 26 July 2018
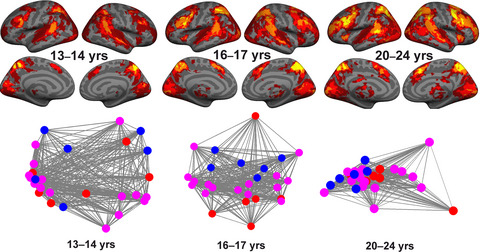
In the current study, age-related differences in the neural correlates of executive functioning were tracked by comparing three age groups consisting of adolescents and young adults. The results demonstrate that the similarity between different executive processes in terms of both neural recruitment and functional connectivity seems to increase with age from adolescence to early adulthood, possibly contributing to the age-related behavioral improvements in executive functioning.
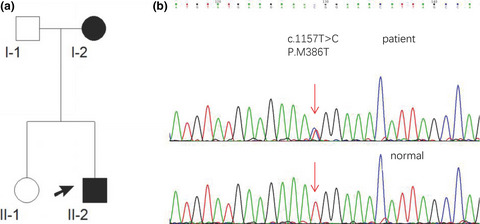
A novel SETX gene mutation associated with Juvenile amyotrophic lateral sclerosis
- First Published: 27 July 2018
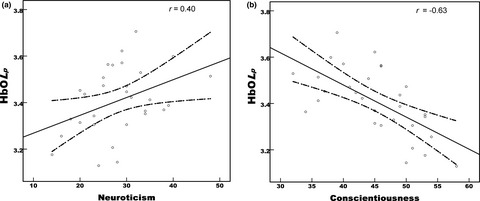
Neuroticism and conscientiousness respectively positively and negatively correlated with the network characteristic path length in dorsal lateral prefrontal cortex: A resting-state fNIRS study
- First Published: 27 July 2018
MRI in predicting conversion to multiple sclerosis within 1 year
- First Published: 02 August 2018
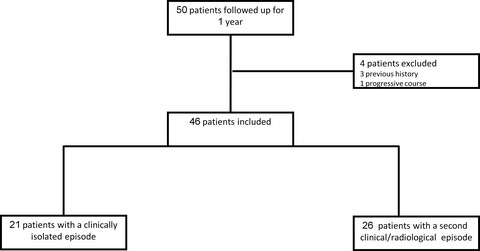
We tried to developed assessment tool in order to predict which parameter in CIS patient who come to the MS clinic in the first time has the highest risk of predicting conversion to multiple sclerosis within 1 year. We found out combination of lesions perpendicular to corpus callosum, more than 13 lesion and max diameter lesion more than 0.75 cm has 19 times higher risk for another clinical episode or to show dynamic change at the MRI scan in the first year after CIS.
Prehospital stroke scale (FAST PLUS Test) predicts patients with intracranial large vessel occlusion
- First Published: 07 August 2018

We performed prehospital, multicenter, prospective cohort observational study with large number of patients to define sensitivity, specificity, NPV a PPV our prehospital test (FAST PLUS test) to predict large vessel occlusion stroke. Our results are very important for triage of suspected acute stroke patients and prehospital stroke care. Any incorrect triage could delay the start of intravenous thrombolysis treatment or mechanical thrombectomy.
Most calbindin-immunoreactive neurons, but few calretinin-immunoreactive neurons, express the m1 acetylcholine receptor in the middle temporal visual area of the macaque monkey
- First Published: 09 August 2018
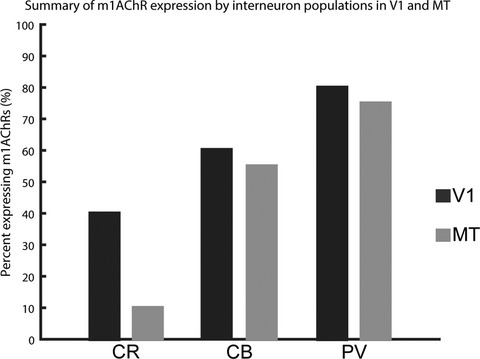
Using dual-immunofluorescence in extrastriate area MT of the macaque, we find most neurons immunoreactive for calbindin express the m1 acetylcholine receptor. In contrast, we find few neurons immunoreactive for calretinin express this receptor. In comparing these results with data from macaque visual area V1, we show m1 acetylcholine receptor expression by the calretinin-immunoreactive populations differs profoundly, supporting the idea that cholinergic modulation in cortex is tuned such that different compartments may respond to acetylcholine release in different ways.
Detecting peripersonal space: The promising role of ultrasonics
- First Published: 09 August 2018
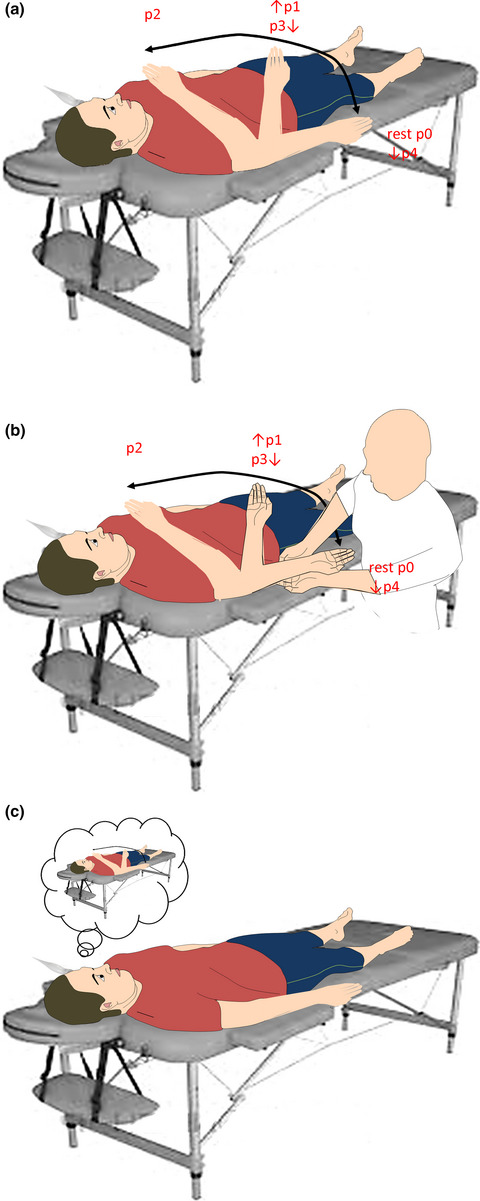
We evaluated CBF and HR changes in 15 healthy participants using transcranial Doppler during a motor task approaching peripersonal space. We found that the modulation of PPS-related brain responses (CBS and HR) depends on specific sensory-motor integration processes related to the location and the final position of a target in the peripersonal and extrapersonal spaces.
Hand selection in a preferential reaching task: The effects of object location, orientation, and task intention in preadolescent children
- First Published: 11 August 2018
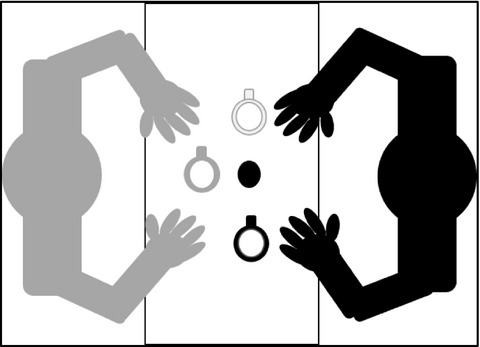
Hand selection was assessed in preadolescent children (ages 9–11) within a preferential reaching task to delineate the effects of object location, orientation, and task intention on the assessment procedure and compared to data previously acquired from young adults. The observed differences support the notion that children are still in a process of refining their movements in attempt to discern the most efficient and effective patterns of behaviour.
Clinical and laboratory factors related to acute isolated vertigo or dizziness and cerebral infarction
- First Published: 11 August 2018
Hippocampal amino-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-4-isoxazolepropionic acid GluA1 (AMPA GluA1) receptor subunit involves in learning and memory improvement following treatment with Centella asiatica extract in adolescent rats
- First Published: 14 August 2018

The effect of Centella asiatica has been evaluated in adult animals until today. This work is investigated centell asiatica in adolescent rats also analysis expression of AMPA and GABA receptors in hippocampus in rats. Adolescent age is considered to be critical developmental stage of animals as well as humans.
Functional connectivity changes in the entorhinal cortex of taxi drivers
- First Published: 15 August 2018
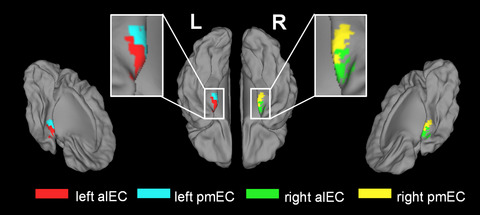
Extensive navigational behaviors changed functional pattern of the EC. Altered resting-state functional connectivity of EC significantly influenced the encoding of spatial information. Navigation-related functional connectivity changes in EC negatively correlated to the time spent on intensive navigational training.
Altered physiological brain variation in drug-resistant epilepsy
- First Published: 15 August 2018
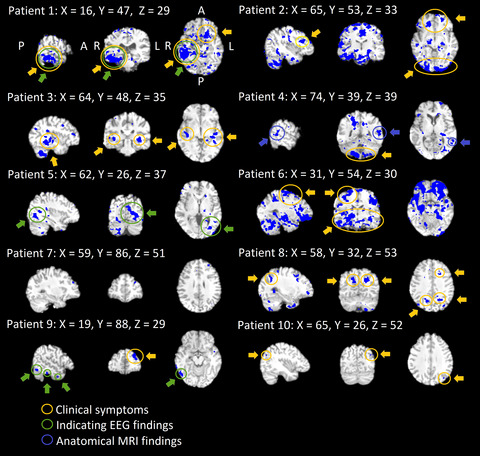
We used coefficient of variation (CV) of critically sampled 10 Hz ultra-fast fMRI signal to compare physiological variance between healthy controls (n = 10) and patients (n = 10) with drug-resistant epilepsy (DRE). We showed highly significant voxel-level (p < 0.01, TFCE-corrected) increase in the physiological variance in DRE patients. At individual level, the elevations range over three standard deviations (σ) above the control mean (μ) CV values solely in DRE patients, enabling patient-specific mapping of elevated physiological variance.
Voxel-based meta-analysis of gray and white matter volume abnormalities in spinocerebellar ataxia type 2
- First Published: 20 August 2018
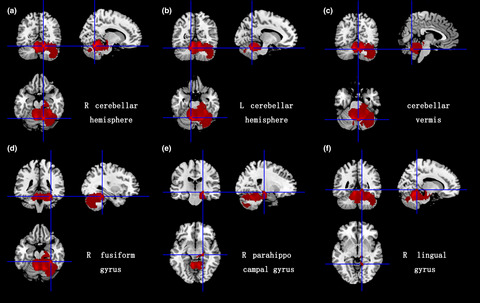
The consistent findings from the present voxel-based meta-analysis showed that GM volume reductions in SCA2 patients were mainly focused on cerebellum and a part of cortex in supratentorial regions related to several networks regulating cognitive functions and emotions. The significant WM volume reductions widely existed in cerebellum along with its afferent pathways and pyramidal system.
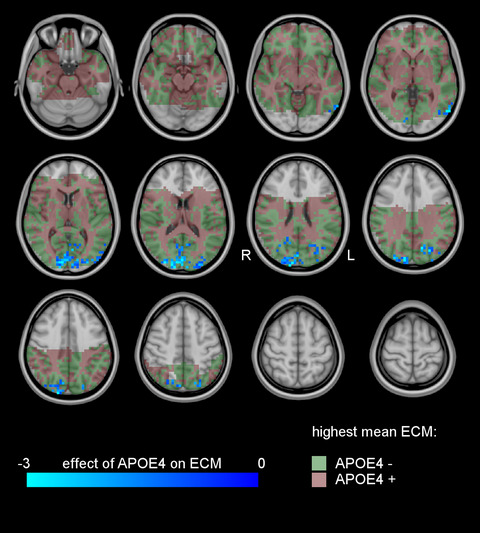
Functional brain network centrality is related to APOE genotype in cognitively normal elderly
- First Published: 22 August 2018
Patient-reported and performance-based measures of walking in mild–moderate Parkinson's disease
- First Published: 22 August 2018
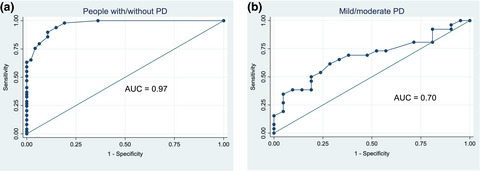
Knowledge of the relationships between patient-reported and performance-based walking measures in Parkinson's disease (PD) should inform clinical decision-making. We investigated the relationship between patient-reported walking difficulties (Walk-12G) and performance-based walking in laboratory and free-living conditions. The strongest associations were observed for step velocity and walking behavior so targeting these specific gait aspects could improve perceived walking difficulties in daily life
The feasibility of an augment reality system to study the psychophysiological correlates of fear-related responses
- First Published: 22 August 2018
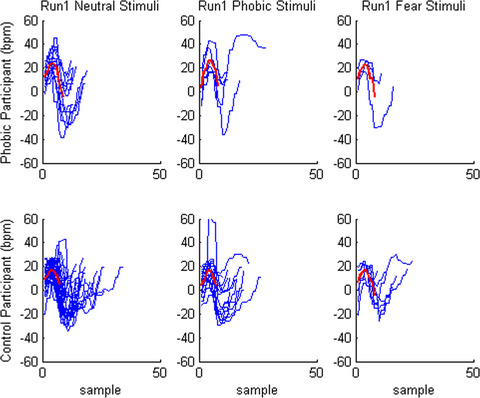
We tested the feasibility of an AR system integrated in a mobile and wearable device for assessing the psychophysiological mechanisms involved in fear responses in real-life contexts. The stimuli were able to induce physiological alterations in the participants, which were specific depending on the stimulus type (fear or neutral) and on the participants’ level of spider fear (phobic and control group), arguing in favor of the system's feasibility at capturing and quantifying the physiological dimension of fear-related responses.
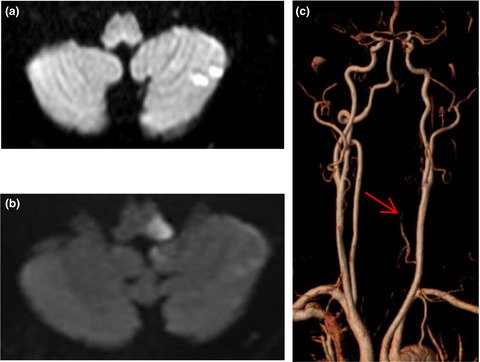
Circulating endothelial progenitor cells and endothelial cells in moyamoya disease
- First Published: 23 August 2018

This study is the first to investigate the presence of CECs in the plasma of patients with MMD. We found a negative correlation between CEC count and concomitant disease such as hypertension, diabetes mellitus, and coronary heart disease. This may indicate that as vascular injury exists in hypertension, DM, and coronary heart disease, MMD concomitant with these diseases may lead to superimposed damage to the endothelium. Our results may be useful to further understanding of the pathogenesis of MMD.
Botulinum toxin A modifies nociceptive withdrawal reflex in subacute stroke patients
- First Published: 23 August 2018
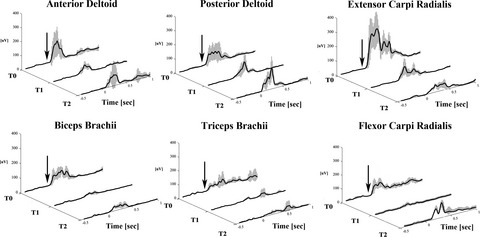
Injection of BoNT-A in the subacute phase of stroke can modify the baseline EMG activity. Injection of BoNT-A in the subacute phase of stroke can modify NWR-related EMG responses in the upper limb muscles. Injection of BoNT-A in the subacute phase of stroke can modify the reflex-mediated defensive mechanical responses.
Transient topographical disorientation due to right-sided hippocampal hemorrhage
- First Published: 23 August 2018
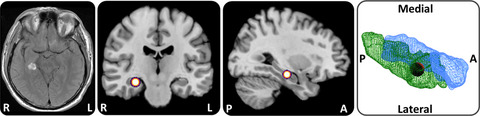
The paper reports detailed measurements of spatial orientation abilities of a patient with the rare presentation of a topographic disorientation as an isolated symptom of a focal right hippocampal hemorrhage. Severe deficits in allo- and egocentric navigation in the acute stage resolved completely within 4 month. This case exemplifies that acute topographical disorientation should be recognized in clinical practice as a distinct and focal symptom indicating right-sided lesions of the hippocampal formation.
Computed tomography provides enhanced techniques for longitudinal monitoring of progressive intracranial volume loss associated with regional neurodegeneration in ovine neuronal ceroid lipofuscinoses
- First Published: 23 August 2018
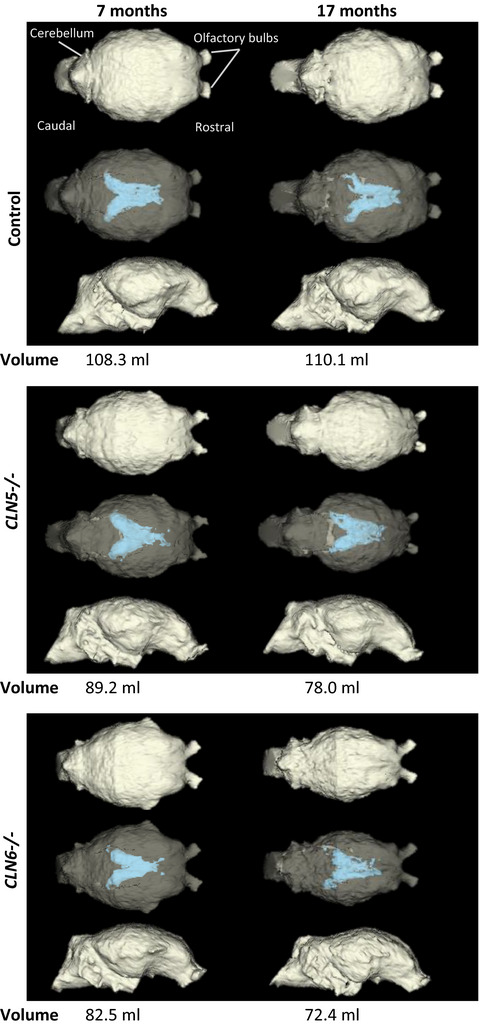
Neuroimaging is a fast developing field for monitoring of neurodegeneration. Longitudinal CT scanning allows the assessment of disease progression and therapeutic efficacy for fast, reliable, and cost-effective monitoring of neurodegeneration in ovine NCL. The relationship between brain atrophy and intracranial volume is poorly described in most species, and there are conflicting reports in the pathology of many human brain wasting diseases, where most observations are based on postmortem findings.
Estriol-mediated neuroprotection in multiple sclerosis localized by voxel-based morphometry
- First Published: 24 August 2018
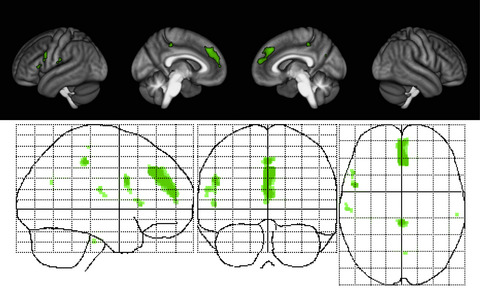
We explored the relationship between the gray matter (GM) sparing and paced auditory serial addition test (PASAT) improvement in the context of traditional magnetic resonance imaging measures and other clinical outcomes in a recent phase 2 trial of estriol treatment in women with relapsing–remitting multiple sclerosis (MS). Using voxel-based morphometry, we discovered a region of cortical GM in the medial frontal lobe that was both associated with PASAT performance and preserved with estriol treatment. These findings indicate that localized GM sparing during estriol treatment was associated with improvement in cognitive testing, suggesting a clinically relevant, disability-specific biomarker for clinical trials of candidate neuroprotective treatments in MS.
The essential neurological examination of the unconscious patient in the emergency room
- First Published: 28 August 2018
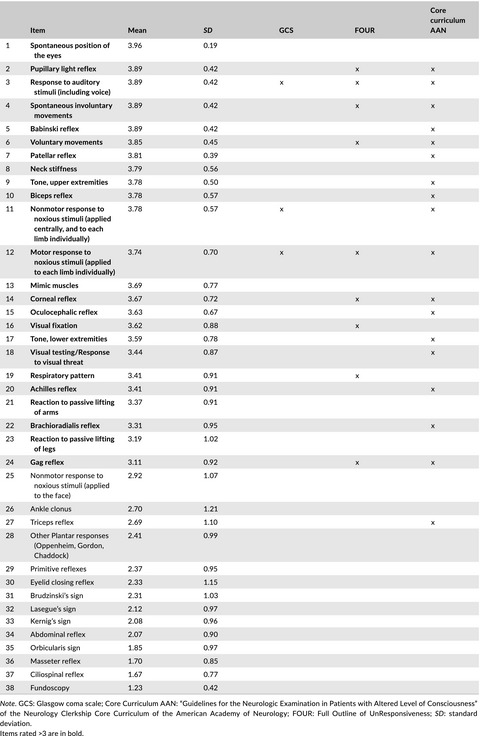
Our study is a survey among board-certified practicing neurologists who regularly examine unconscious patients in the emergency room about the specific components of the NE that they would normally choose to apply. They rated 24 of 38 items as essential steps of the neurological examination of the unconscious patient, with a high level of agreement among survey participants. These findings provide an important source of validation for teaching this particular NE to medical students, as well as non-neurologists working in an emergency setting.
CORRIGENDUM
Investigation of the COMT Val158Met variant association with age of onset of psychosis, adjusting for cannabis use
- First Published: 27 September 2018