Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
ISSUE INFORMATION
REVIEW
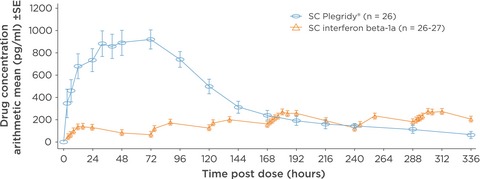
The innovative development in interferon beta treatments of relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis
- First Published: 08 May 2017
ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Frontal assessment battery and frontal atrophy in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis
- First Published: 12 April 2017
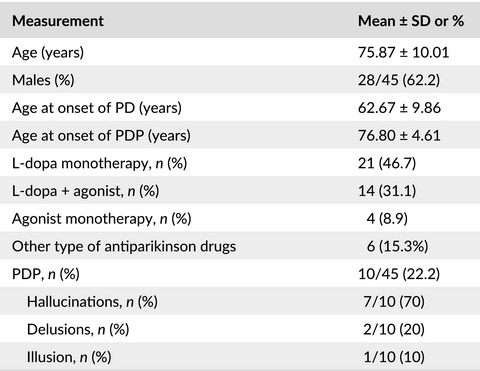
Atypical antipsychotic therapy in Parkinson's disease psychosis: A retrospective study
- First Published: 14 April 2017
Sexual dysfunction in female patients with relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis
- First Published: 14 April 2017
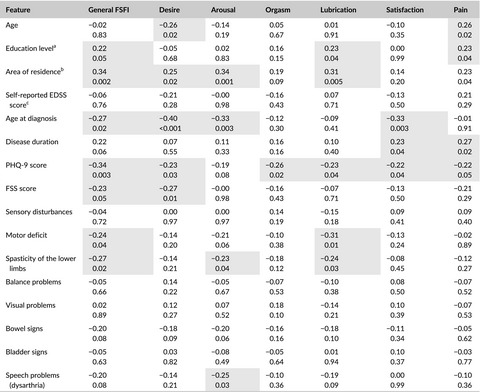
Sexual dysfunction is one of the common symptoms of multiple sclerosis (MS) and is often underdiagnosed, especially in women. Relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis is the most widespread form of the disease, but the data on SD occurrence in this particular group of patients is limited. Presented study analyzes this topic on the highly-selected group of patients.
Citation classics in central nervous system inflammatory demyelinating disease
- First Published: 19 April 2017
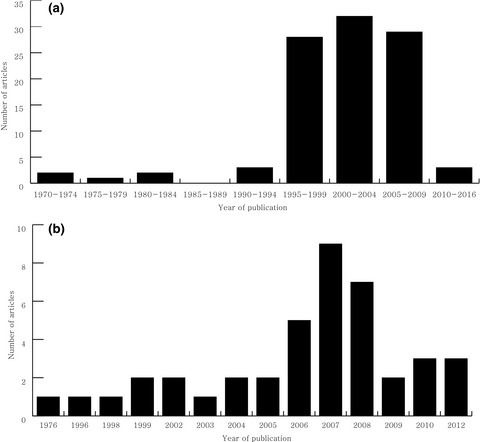
We identified and characterized the top 100 cited articles concerning central nervous system (CNS) inflammatory demyelinating disease in global level. The detailed list of citation classics on neuromyelitis optica were presented separately. This study provides a historical perspective on the research progress on CNS inflammatory demyelinating disease and may serve as a guide for important advances and trends in the field for associated researchers.
Decrease in brain-derived neurotrophic factor at plasma level but not in serum concentrations in suicide behavior: A systematic review and meta-analysis
- First Published: 19 April 2017
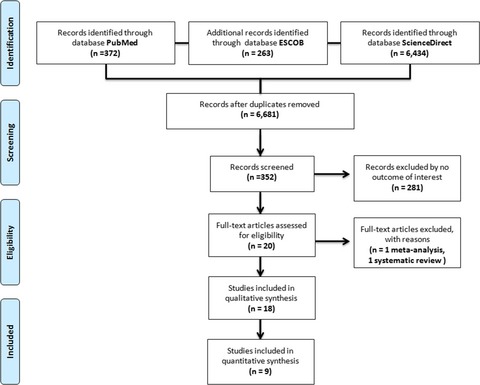
Levels of brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) has become in an attractive biomarker for suicide behavior. Using a meta-analysis approach, we assess BDNF levels in blood plasma, serum to see whether there is a difference in concentrations in patients with suicide behavior when compared to those in controls. The meta-analysis showed that plasma BDNF level could be used as a potential biomarker in suicide behavior.
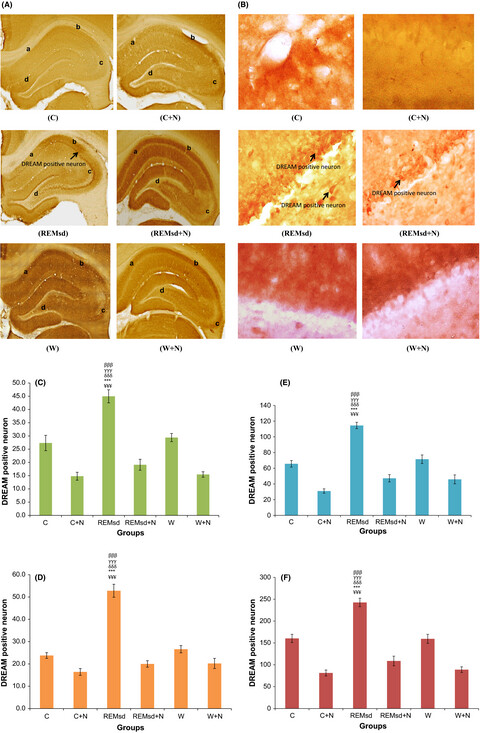
Nicotine-prevented learning and memory impairment in REM sleep-deprived rat is modulated by DREAM protein in the hippocampus
- First Published: 20 April 2017
The behavioral and physiological effects of high-fat diet and alcohol consumption: Sex differences in C57BL6/J mice
- First Published: 20 April 2017
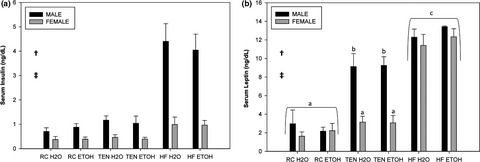
Sex differences in C57BL6/J mice were observed for both behavior and overall health when consuming high-fat diet and alcohol. Female mice were more resistant to changes in behavior and health when consuming high-fat diet as they exhibited reduced body weight gain, reduced insulin levels, and had increased locomotion in the open field compared to males. While female mice consumed more ethanol, ethanol was able to equally improve glucose tolerance and worsen anxiety in both sexes.
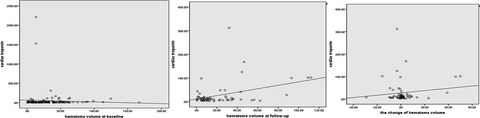
Cardiac troponin and cerebral herniation in acute intracerebral hemorrhage
- First Published: 21 April 2017
Swallowing safety in Parkinson's disease after zona incerta deep brain stimulation
- First Published: 21 April 2017
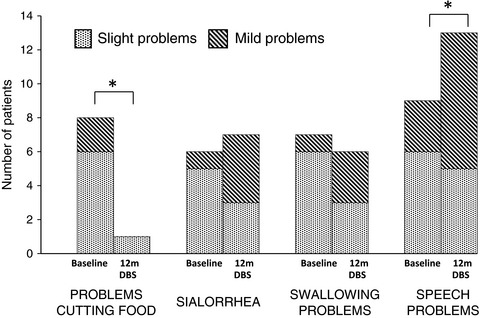
The purpose of the present report was to examine how different aspects of swallowing and eating are affected by caudal zona incerta deep brain stimulation. The actual study also includes an analysis of weight change after deep brain stimulation and specific items from the second part of Unified Parkinson's Disease Rating Scale. Caudal zona incerta deep brain stimulation does not seem to have a negative impact on swallowing safety in this extended sample.
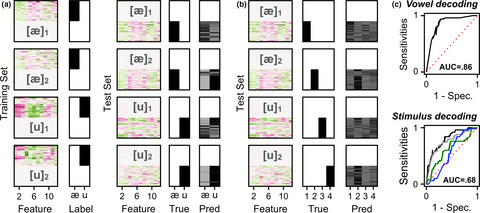
Vowel decoding from single-trial speech-evoked electrophysiological responses: A feature-based machine learning approach
- First Published: 26 April 2017
Plantar Exteroceptive Inefficiency causes an asynergic use of plantar and visual afferents for postural control: Best means of remediation
- First Published: 01 May 2017
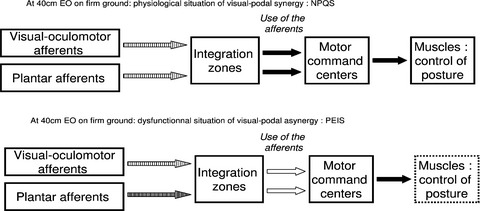
The purpose of the experiment is to characterize the Plantar Exteroceptive Inefficiency (PEI) better and see if a synergy in the use of plantar and visual afferents can be objectified. We assessed the sensorial preferences for postural control in quiet stance of 48 young and healthy subjects. The main results are that there normally exists a synergy in the use of plantar and visual afferents, but only at 40 cm and in the absence of PEI; the latter interferes with the role of vision in postural control.
“Cure” for multiple sclerosis (MS)—Evolving views of therapy goals in patients on different stages of the disease: A pilot study in a cohort of Polish MS patients
- First Published: 02 May 2017

In this study, which was designed as a prospective nonanonymous online questionnaire, we analyzed patients’ acceptance for risks connected with the MS treatment. The patients with faster progression of the disease were likely to accept risky “curative” treatments. Over 81% of patients accepted mortality rates over 1% for the treatment that achieves self-defined cure.
Long noncoding RNA expression in peripheral blood mononuclear cells and suicide risk in Chinese patients with major depressive disorder
- First Published: 02 May 2017
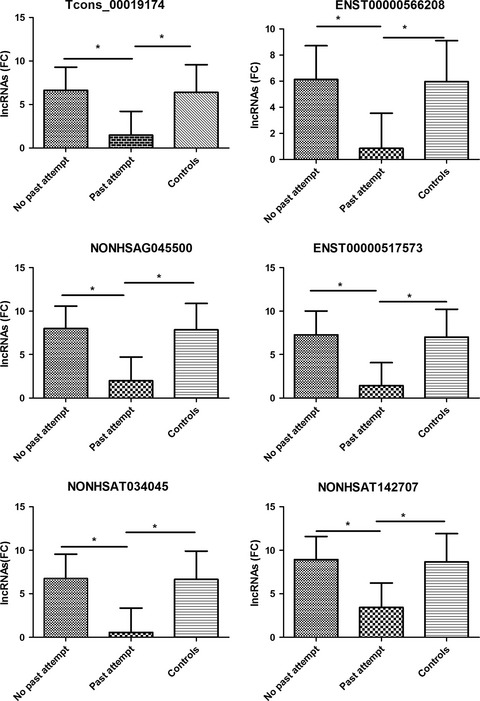
Epigenetics is the beginning of a new frontier in studies of complex diseases. Epigenetic modifications are reversible, and in a sense this modification is a dynamic process, allowing the cell to become more responsive to environment stimuli. Suicidal behavior includes a broad spectrum and many risk and protective factors. Suicide risk assessment is challenging for several reasons, so an objective and quantitative method is urgently needed. This study tried to explore the association between lncRNA expression in peripheral blood mononuclear cells with suicide risk level, and obtain a prediction equation.
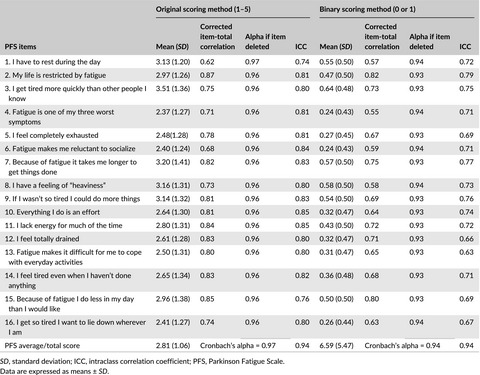
Validation of the Parkinson Fatigue Scale in Chinese Parkinson's disease patients
- First Published: 02 May 2017
Substance P NK1 receptor in the rat corpus callosum during postnatal development
- First Published: 02 May 2017
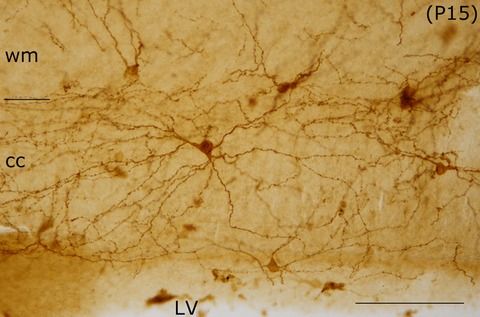
(1) Intracallosal neurons expressing NK1, the principal SP receptor, are visible since P5; (2) at P5, their distribution is already similar to that seen in the adult; (3) their number increase between P5 and P10, then declines, but unlike other intracallosal neurons, NK1IP-n make up a significant population in the adult cc; (4) intracallosal NK1IP-n size increase with age; (5) starting at P20, intracallosal NK1IP-n form a heterogeneous population.
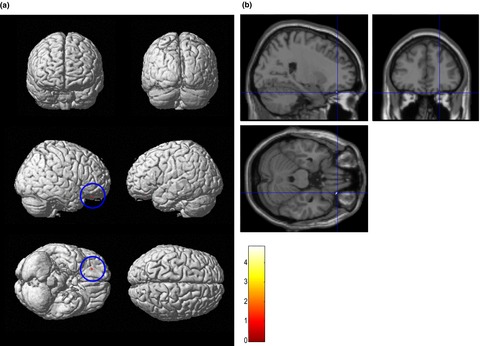
Abnormal amplitude of low-frequency fluctuations and functional connectivity of resting-state functional magnetic resonance imaging in patients with leukoaraiosis
- First Published: 02 May 2017
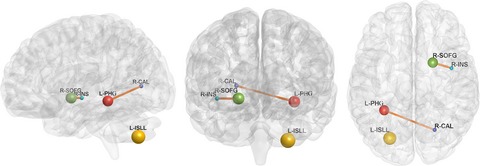
Brain areas with significant differences between the patients with leukoaraiosis (LA) and the controls in their amplitude of low frequency fluctuations (ALFF) and functional connectivity. Compared with normal controls, the LA group exhibited significantly decreased ALFF in the left parahippocampal gyrus (PHR) and increased ALFF in the left inferior semi-lunar lobule and right frontal superior orbital gyrus (SOFG). The LA patients showed an increasing connectivity between the right insular region and the right SOFG and between the right calcarine cortex and the left PHR.
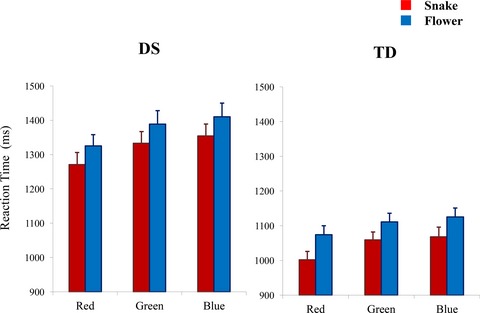
Negative emotion evoked by viewing snakes has a motivating effect on cognitive processing in human children with or without intellectual disability
- First Published: 02 May 2017
Rat intersubjective decisions are encoded by frequency-specific oscillatory contexts
- First Published: 05 May 2017
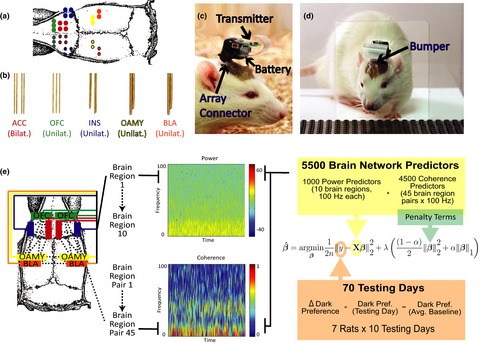
We show that the brain regions that encode rats’ decisions to prevent other rats from being shocked overlap with those involved in self-reports of human empathy. Furthermore, we demonstrate that these rat intersubjective decisions are encoded by frequency-specific oscillations across brain regions in addition to isolated activity occurring within brain regions. These results show the promise of using rodent models to understand the neural mechanisms mediating decisions to alleviate others’ pain, and highlight the importance of studying neural context in the social brain.
Reinnervation of denervated muscle by implantation of nerve-muscle-endplate band graft to the native motor zone of the target muscle
- First Published: 03 May 2017
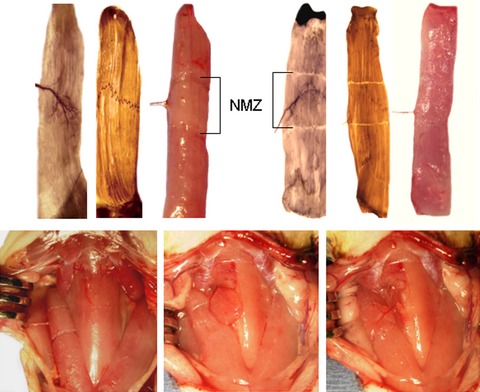
We developed a novel surgical technique called nerve-muscle-endplate band grafting (NMEG) for muscle reinnervation. Experimentally denervated sternomastoid muscle in the rat was reinnervated by transferring a NMEG from the ipsilateral sternohyoid muscle to the native motor zone (NMZ) of the target muscle. Our findings suggest that the NMZ of the denervated muscle is an ideal site for NMEG implantation and for the development of new procedures to achieve sufficient axonal regeneration, rapid endplate reinnervation, and optimal functional recovery.
Long-term cost of spouses’ informal support for dependent midlife stroke survivors
- First Published: 03 May 2017
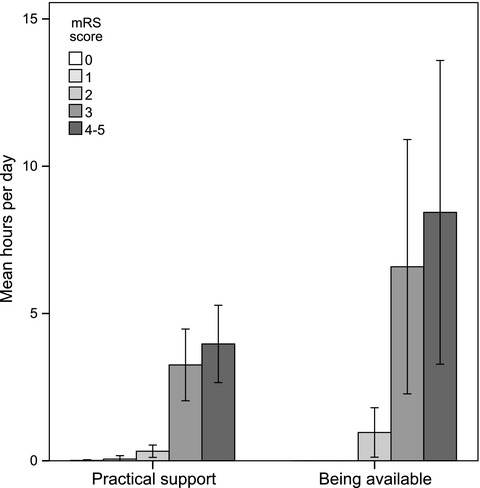
In this article, we provide novel information about the quantity and content of long-term informal support provided by spouses of midlife stroke survivors. The main finding is that the cost of informal support provided to midlife stroke survivors is of a major magnitude, even 7 years after stroke onset. We also show that the cost of the informal support is highly associated with the dependency (modified Rankin Scale 3–5) of the stroke survivors, more than 7 years after stroke. The mean annual cost of informal support provided for independent stroke survivors was estimated at €991 and €25,127 for dependent stroke survivor.
Childhood trauma and negative memory bias as shared risk factors for psychopathology and comorbidity in a naturalistic psychiatric patient sample
- First Published: 09 May 2017

Childhood trauma and negative memory bias have been associated with depression and anxiety disorders. We examined the quantitative relationship between the frequency and diversity of traumatic childhood events, strength of memory bias, and presence and number of comorbid psychiatric disorders in a large naturalistic psychiatric patient sample. Both childhood trauma and negative memory bias may be risk factors for a broader spectrum of psychiatric diagnoses as well as for comorbidity between disorders.
Lipid and hyperglycemia factors in first-ever penetrating artery infarction, a comparison between different subtypes
- First Published: 10 May 2017
Associations between cognitive impairment and motor dysfunction in Parkinson's disease
- First Published: 12 May 2017
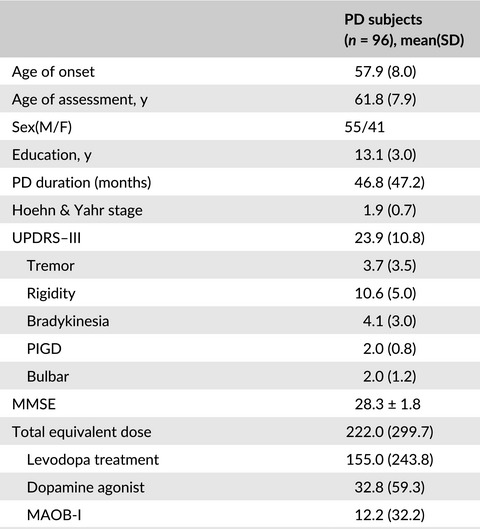
In this manuscript, we investigated the association between impairments in cognitive subdomains and motor features in 96 Chinese PD patients. Overall, executive function and attention was associated with bradykinesia and rigidity, while visuospatial function was associated with bradykinesia and tremor. Of which, the correlation between visuospatial memory reservation and tremor was not reported previously, probably reflecting the involvement of other non-dopaminergic transmitter systems like acetylcholine underlying these functions.
METHODS
Cerebral blood flow evaluation of intensive rosuvastatin therapy in stroke/transient ischemic attack patients with intracranial arterial atherosclerotic stenosis study: Rationale and design
- First Published: 28 April 2017
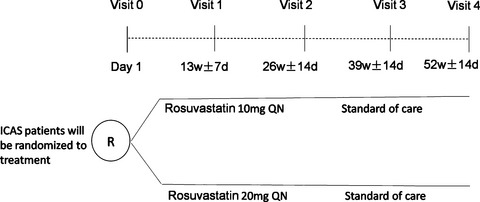
With the use of computed tomography perfusion, we aim to evaluate the impact of Rosuvastatin on cerebral hemodynamic changes, as well as the downstream perfusion. This trial concerning the effects of statin on the temporal hemodynamic progression of intracranial atherosclerotic stenosis (ICAS) may extend our understanding of the basic pathophysiology and mechanisms of stroke in ICAS patients.