Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Original Article
Bromodomain and extraterminal (BET) protein inhibition of IgG/IgE production in murine B cells is counter-balanced by a strong Th2 bias
- First Published: 30 May 2021
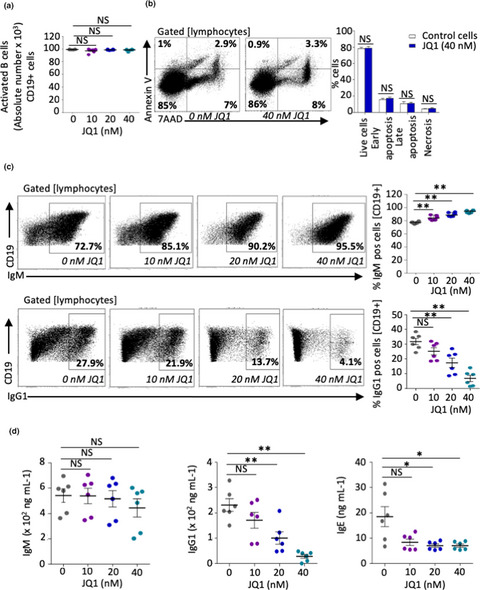
While bromodomain and extra terminal domain inhibition reduces class switching, antibody secretion and T follicular helper cell number, this treatment increases the proportion of GATA3+ T helper 2 cells and the secretion of corresponding cytokines. In a mouse model of lung inflammation, JQ1 thus aggravates rather than improves clinical manifestations.
Genetic risk for severe COVID-19 correlates with lower inflammatory marker levels in a SARS-CoV-2-negative cohort
- First Published: 06 June 2021
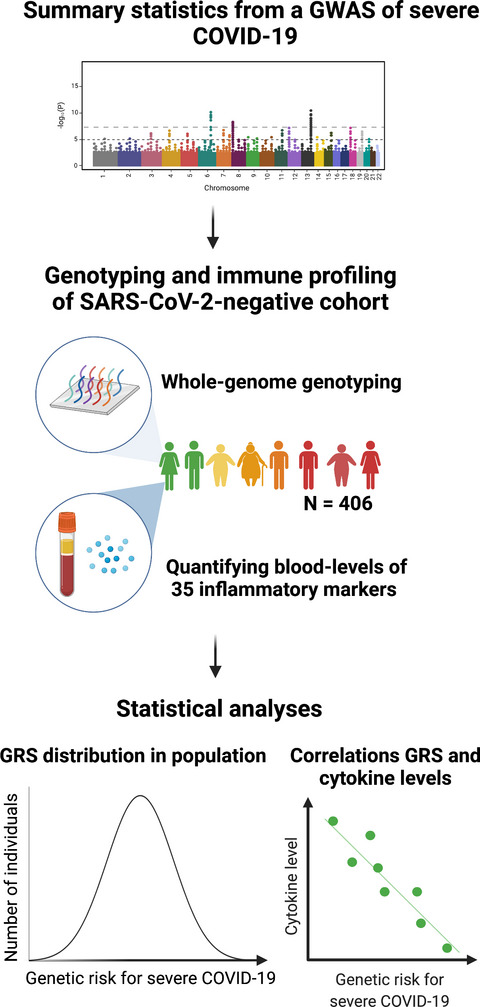
We used genetic risk scores to model how susceptibility to severe COVID-19 correlates with baseline levels of 35 inflammatory markers, by testing their impact in a SARS-CoV-2-negative population cohort. Higher genetic risk for severe COVID-19 was associated with lower blood levels of interferon gamma (IFN-γ), vascular endothelial growth factor D (VEGF-D) and tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-α). Inflammatory profiles of those with high genetic risk increasingly diverge from the norm in association with age and obesity.
A lymphodepleted non-human primate model for the assessment of acute on-target and off-tumor toxicity of human chimeric antigen receptor-T cells
- First Published: 03 June 2021
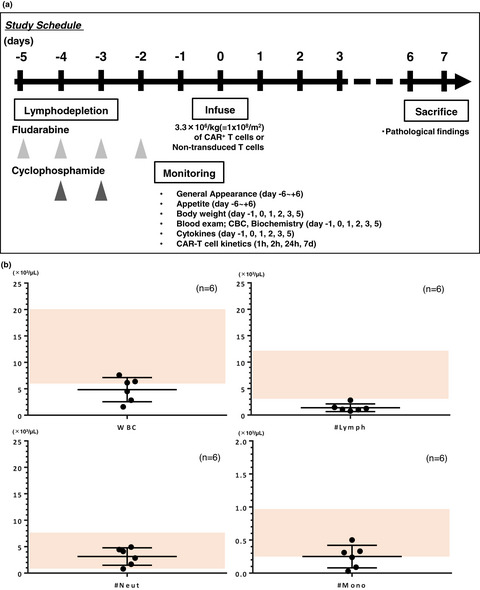
We have investigated the on-target/off-target toxicity of CAR-T cells using a lymphodepleted non-human primate (NHP) model. We followed the most widely accepted non-myeloablative lymphodepletion protocol in clinical use for CAR-T therapy to deplete the lymphocyte counts in the macaques, and lymphodepletion allowed CAR-T cells to transiently expand and become detectable in the peripheral blood. Our lymphodepleted NHP model could provide new insights into the safety assessment of immune effector cell-based therapy as the investigational new intervention.
Sustained low-dose interleukin-2 therapy alleviates pathogenic humoral immunity via elevating the Tfr/Tfh ratio in lupus
- First Published: 01 June 2021
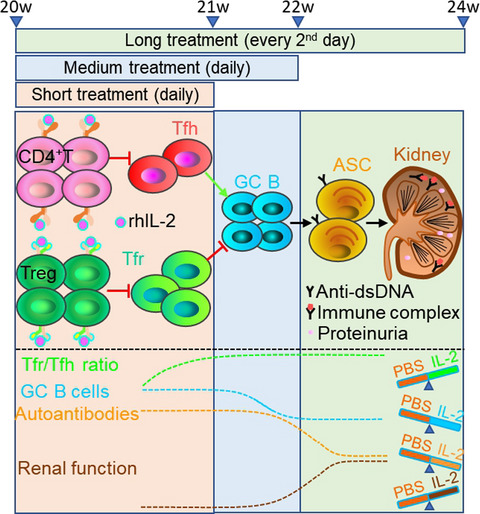
We designed and examined three treatment regimens of low-dose interleukin-2 (IL-2) therapy in lupus-prone NZB/W F1 mice and characterised the immune responses in detail. Low-dose IL-2 therapy increases the Tfr/Tfh ratio and a less frequent and prolonged treatment can alleviate pathogenic humoral immunity and improve renal function, which provide necessary rationale and new insights in optimising low-dose IL-2 therapy.
Quantification and role of innate lymphoid cell subsets in Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease
- First Published: 05 June 2021
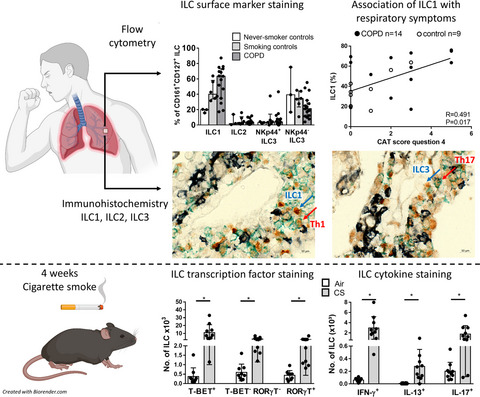
In this article, we investigated the role of pulmonary innate lymphoid cells (ILCs) in the pathogenesis of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). We found that the ILC1 subset is increased in COPD patients and correlates with smoking and severity of respiratory symptoms. In C57BL/6 mice, ILCs increase upon cigarette smoke (CS) exposure. In the absence of adaptive immunity, ILCs contribute to CS-induced pro-inflammatory mediator release, but they are redundant in CS-induced innate inflammation.
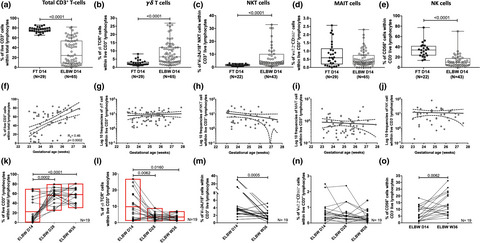
Extreme prematurity and sepsis strongly influence frequencies and functional characteristics of circulating γδ T and natural killer cells
- First Published: 10 June 2021
Repeated influenza vaccination provides cumulative protection from distinct H3N2 viruses
- First Published: 13 June 2021
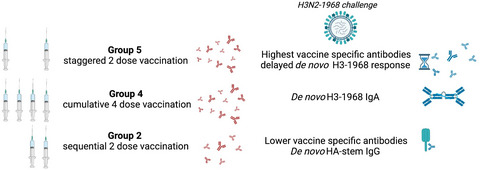
In this study, we found that cumulative and staggered influenza vaccination generates high titre antibody responses, which protect upon infection despite limited de novo responses. While broadly reactive, HA-stem antibodies are made by less-developed vaccine responders. Therefore, influenza vaccination should be considered for its benefits for immediate protection and future virus encounters.
Original Articles
Next-generation Bruton's tyrosine kinase inhibitor BIIB091 selectively and potently inhibits B cell and Fc receptor signaling and downstream functions in B cells and myeloid cells
- First Published: 14 June 2021
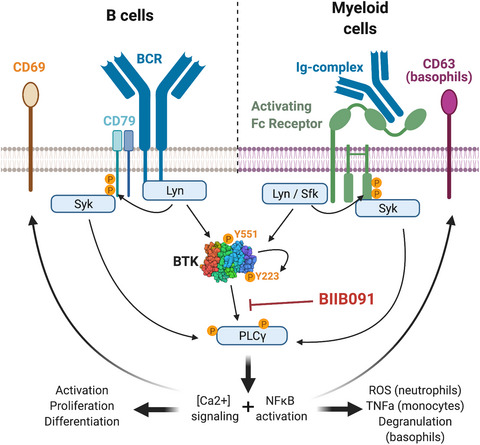
In this study, we characterise BIIB091, a novel, potent, selective and reversible small-molecule inhibitor of Bruton's Tyrosine Kinase (BTK). In vitro, BIIB091-inhibited BTK-dependent proximal signaling and distal functional responses in both B cells and myeloid cells, including antigen presentation to T cells, a key mechanism of action thought to be underlying the efficacy of B cell-targeted therapeutics in MS. In vivo, BIIB091 blocked B-cell activation, antibody production and germinal center differentiation, however in phase 1 healthy volunteer study, BIIB091 inhibited B-cell receptor-mediated activation of naïve and unswitched memory B cells.
Theoretical Articles
Hypothesis: Febrile infection-related epilepsy syndrome is a microglial NLRP3 inflammasome/IL-1 axis-driven autoinflammatory syndrome
- First Published: 14 June 2021
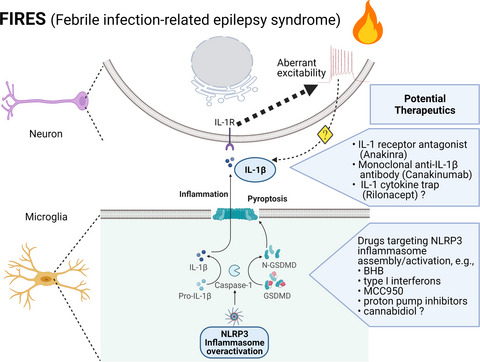
Febrile infection-related epilepsy syndrome (FIRES) is a protracted and difficult-to-treat neuroinflammatory condition of obscure cause. Converging evidence implicates that FIRES is a microglial NLRP3 inflammasome/IL-1 axis-driven autoinflammatory syndrome, in which the reverberation between inflammation and seizure forms vicious cycles that sustain smoldering neuroinflammation. Further research in the light of this theoretical framework may lead to better care of patients afflicted by FIRES.
Original Article
IL-33/ST2 axis deficiency exacerbates neutrophil-dominant allergic airway inflammation
- First Published: 16 June 2021
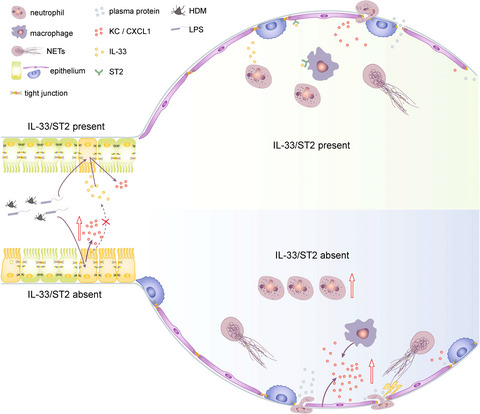
Most research on the IL-33/ST2 axis has been conducted in type 2 immunity-mediated eosinophilic asthma, but less research has focused on neutrophilic asthma. In this study, we found that IL-33/ST2 axis deficiency aggravated neutrophil-dominant allergic airway inflammation induced by house-dust mite and lipopolysaccharide coexposure, which may account for the more proinflammatory status of IL-33/ST2 axis-deficient macrophages and lung epithelial cells.
High sensitivity and specificity of a 5-analyte protein and microRNA biosignature for identification of active tuberculosis
- First Published: 22 June 2021
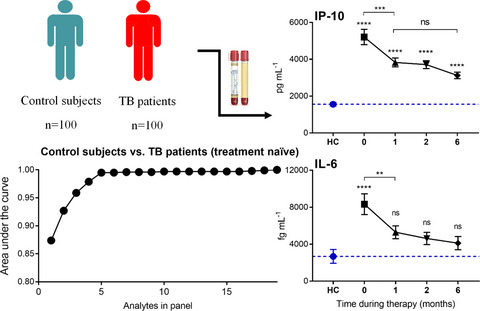
The biomarker potential of plasma proteins to identify tuberculosis (TB) patients was examined. Six proteins were significantly elevated in TB patients with IP-10 and IL-6 declining with treatment. In conjunction with miRNA previously detected, a five analyte biosignature could identify TB patients with an AUC = 0.995, sensitivity of 96% and specificity of 97%. IP-10 was the best single biomarker candidate, showing utility as a triage tool, to quickly and easily identify potential TB patients and monitor their response to therapy.
Review
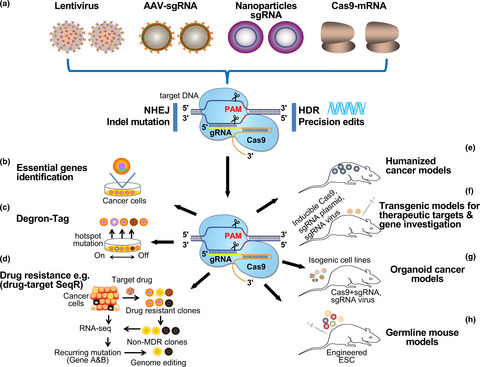
Exploiting the CRISPR-Cas9 gene-editing system for human cancers and immunotherapy
- First Published: 22 June 2021
Original Articles
Interleukin-18, IL-18 binding protein and IL-18 receptor expression in asthma: a hypothesis showing IL-18 promotes epithelial cell differentiation
- First Published: 26 June 2021
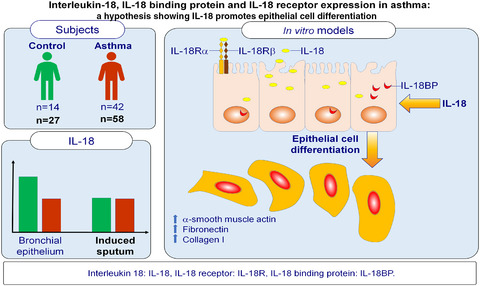
In this study, we demonstrated that the expression of IL-18 was significantly lower in bronchial epithelium in subjects with asthma than in healthy controls. IL-18 treatment of human epithelial cells induced metabolic activity, wound repair and epithelial cell differentiation, which could potentially contribute to airway remodelling.
Pervasive inflammatory activation in patients with deficiency in very-long-chain acyl-coA dehydrogenase (VLCADD)
- First Published: 27 June 2021
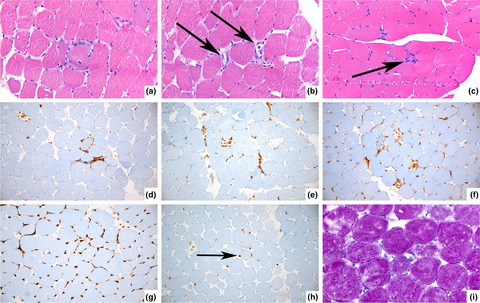
Very-long-chain acyl-CoA dehydrogenase deficiency (VLCADD), an incurable inborn error of fatty acid oxidation, is traditionally considered a disease of energy deficit. Symptoms are managed by dietary supplementation of medium-chain fatty acids, but patients remain vulnerable to hospitalisations because of recurrent rhabdomyolysis. This study shows for the first time that chronic inflammation is a novel physiologic dimension of VLCADD, which provide rationale for personalised adoption of anti-inflammatory intervention(s) in disease management.