Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Original Articles
C-reactive protein flare-response predicts long-term efficacy to first-line anti-PD-1-based combination therapy in metastatic renal cell carcinoma
- First Published: 06 December 2021
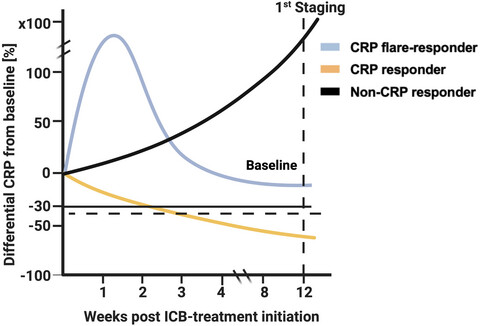
In this multicentre study, we investigated the predictive potential of early serum C-reactive protein (CRP) kinetics during 1st-line immunotherapy in metastatic renal cell carcinoma (mRCC). Out of 95 patients with mRCC, those with significant CRP flare-response or decrease in CRP levels had superior outcomes. This potential biomarker could improve therapy monitoring of mRCC and eventually also treatment stratification.
Short Communications
Blunted sFasL signalling exacerbates TNF-driven neutrophil necroptosis in critically ill COVID-19 patients
- First Published: 11 December 2021
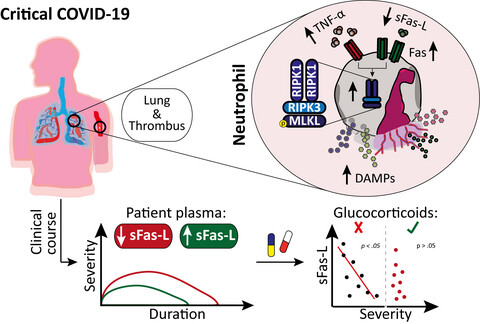
This work highlights the role of cell death ambiguity in neutrophils and its contribution to pathophysiology during critical COVID-19. The inflammatory COVID-19 environment provoked a TNF-α-induced necroptosis-sensitive neutrophil subpopulation, characterised by elevated release of DAMPs, increased RIPK1 levels and a pivotal role for MLKL. Neutrophil necroptosis through the RIPK1-RIPK3-MLKL axis was further confirmed in COVID-19 thrombus and lung biopsies. Blunted Fas engagement by sFasL was identified to drive elevated RIPK1 levels upon TNF-α-induced necroptosis, while decreased sFasL plasma levels in critically ill COVID-19 patients correlated to elevated disease severity, which was masked by glucocorticoid treatment.