Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Original Article
Establishment of a novel gene panel as a biomarker of immune checkpoint inhibitor response
- First Published: 30 June 2020
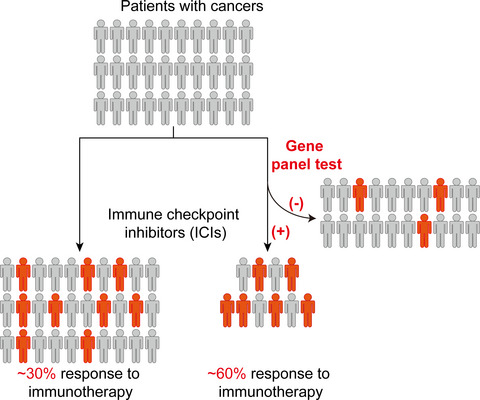
Immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs) have been widely used to treat various cancers and have achieved impressive success, resulting in a new era of anticancer therapy. However, only a subset of patients experienced lasting responses; therefore, exploring predictive biomarkers is critical to identify the patients who have benefit from ICIs. This gene panel using liquid biopsy is one of the best predictive biomarkers presently available and can help physicians to predict the response to ICIs and judge the utility of ICIs in clinical practice.
Original Articles
Development and characterisation of NKp44-based chimeric antigen receptors that confer T cells with NK cell-like specificity
- First Published: 08 July 2020
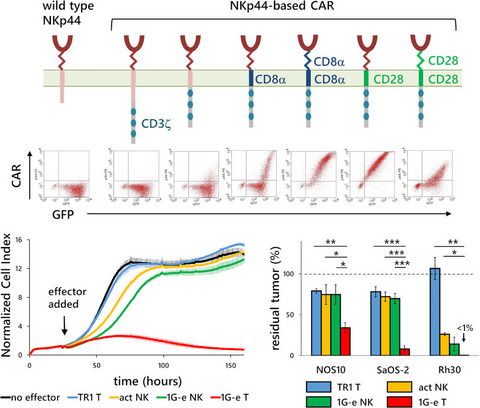
A challenge in the development of effective chimeric antigen receptor transduced T (CAR-T) cell therapy is to identify an appropriate target on tumor cells. We created a series of novel CAR constructs with the extracellular immunoglobulin-like domain of NKp44, one of the activating receptors expressed on activated natural killer cells. Human T cells transduced with optimised NKp44-based CAR constructs exerted specific cytotoxic effects and cytokine secretion upon encountering multiple types of neoplastic cells, including those associated with acute myeloid leukaemia, T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukaemia, osteosarcoma, rhabdomyosarcoma, Ewing sarcoma, neuroblastoma and glioblastoma cells.
Novel pathogenic mutations identified in the first Chinese pedigree of complete C6 deficiency
- First Published: 08 July 2020
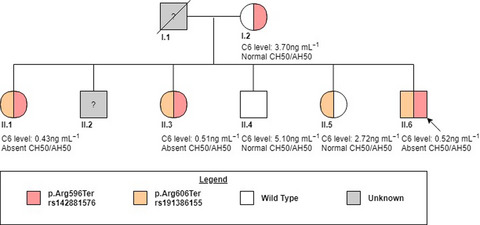
We report on two compound heterozygous mutations in C6 (p.Arg596Ter and p.Arg606Ter) in the first recorded Chinese pedigree of complete C6 deficiency. We demonstrate that heterozygous family members with subtotal C6 levels had preserved complement hemolytic function and demonstrate a threshold effect of C6 protein level.
Mass cytometry reveals immune signatures associated with cytomegalovirus (CMV) control in recipients of allogeneic haemopoietic stem cell transplant and CMV-specific T cells
- First Published: 02 July 2020
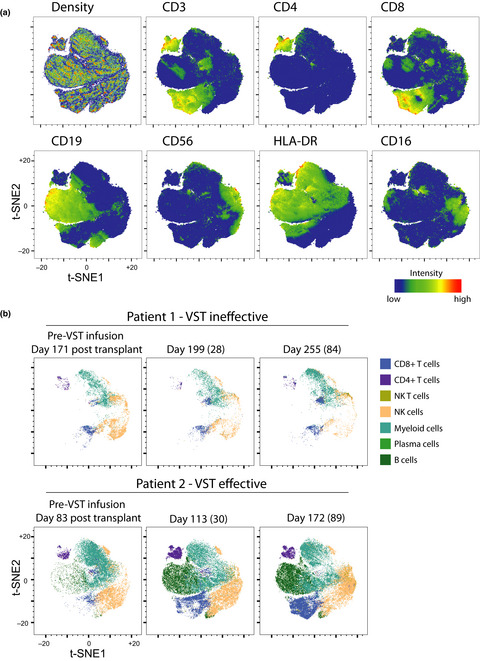
In this study, immune profiling with mass cytometry identified immune signatures associated with cytomegalovirus (CMV) reactivation after allogeneic stem cell transplant in patients undergoing natural immune recovery. Failure to control CMV was associated with failure to develop an adaptive immune signature that could be reversed with third-party CMV virus-specific T cells in some recipients.
Deficits in the IgG+ memory B-cell recovery after anthracycline treatment is confined to the spleen of rhesus macaques
- First Published: 02 July 2020
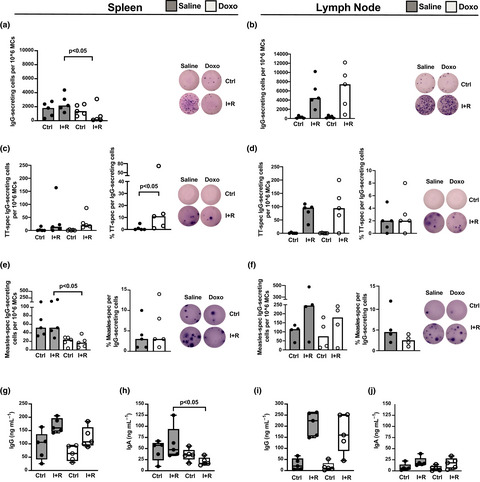
In this study, we found that the recovery of IgG-producing memory B cells in the spleen lags behind after cessation of anthracycline treatment, a widely used drug in acute lymphoblastic leukaemia protocols. This finding was accompanied by impaired splenic B-cell response to booster antigen, raising the possibility of residual damage to serological memory after treatment of blood cancers.
Identifying the optimal donor for natural killer cell adoptive therapy to treat paediatric B- and T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukaemia
- First Published: 16 July 2020
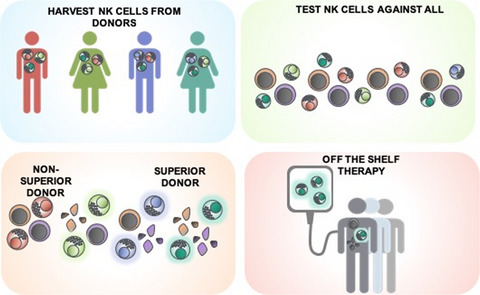
Natural killer (NK) cells are an attractive source of cells for an ‘off the shelf’ cellular therapy; however, since not all NK cells are equally effective at targeting cancer, selecting the right donor for cellular therapy is critical for the success of the treatment. We identified a group of donors who exhibited superior responses against multiple acute lymphoblastic leukaemia (ALL) cells, representing a potential pool of donors that could be used to develop an adoptive NK cell therapy capable of treating a range of ALL subtypes.
CD8+ tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes within the primary tumor of patients with synchronous de novo metastatic colorectal carcinoma do not track with survival
- First Published: 17 July 2020
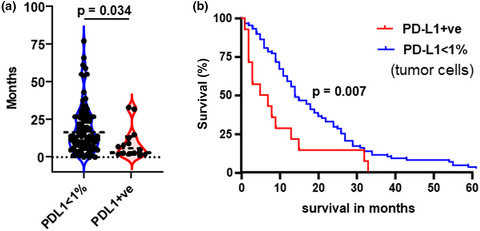
Unlike early-stage colorectal cancer (CRC), the immune response in primary tumors of patients with de novo mCRC does not appear to influence survival despite MSI-H tumors having higher tumor infiltrating lymphocytes (TILs). This unique cohort of patients with synchronous mCRC by definition represents the breakdown of immune containment of the primary tumor. Despite this, we also identified a subgroup of MSS tumors with a high TILs comparable to MSI-H tumors and this group traditionally would not be considered for immune checkpoint blockade, and perhaps should be.
Special Feature Review
Original Articles
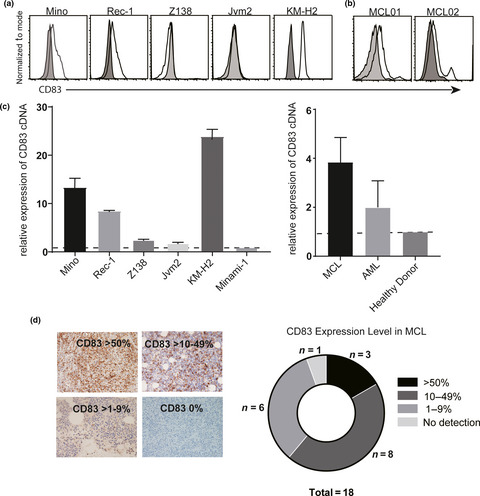
Targeting CD83 in mantle cell lymphoma with anti-human CD83 antibody
- First Published: 15 July 2020
Short Communication
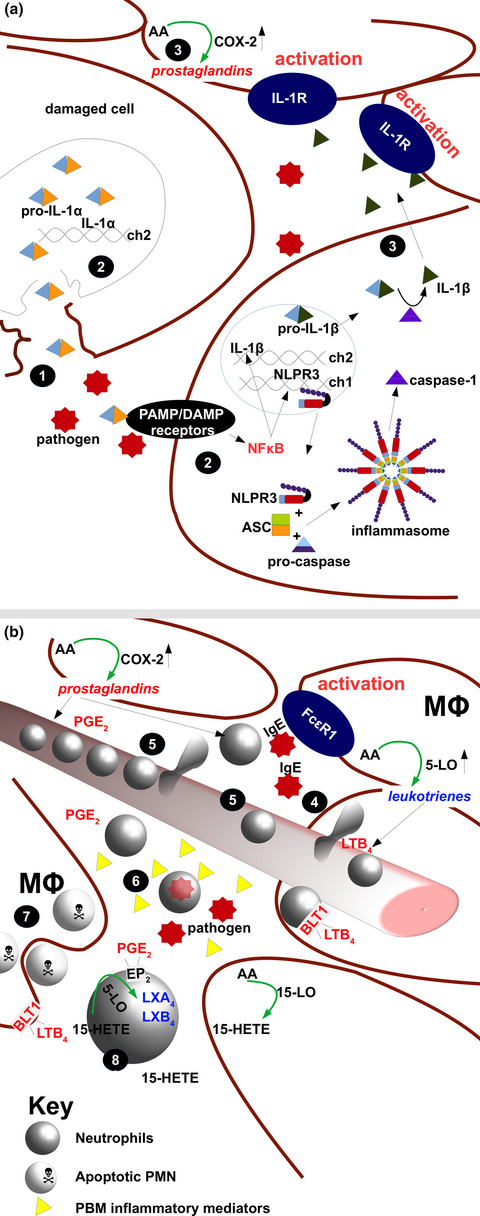
Safety and potential efficacy of cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitors in coronavirus disease 2019
- First Published: 26 July 2020

We conducted a retrospective study of 168 COVID-19 patients aged ≥ 50 years with pneumonia, 22 (13.1%) of whom received cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) inhibitor treatment. Patients receiving COX-2 inhibitors had a lower rate of adverse outcomes: 4 (18.2%) versus 57 (39.0%), P = 0.062. Measurement of cytokine levels in following treatment, measurements of cytokine levels, five of six patients (83.3%) from the treatment group had a reduction in interleukin-6 after treatment, which was not seen in the control group.
Original Article
Enhancing chimeric antigen receptor T-cell immunotherapy against cancer using a nanoemulsion-based vaccine targeting cross-presenting dendritic cells
- First Published: 22 July 2020
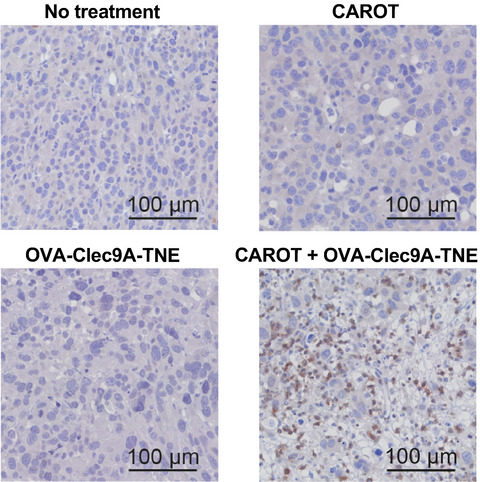
Clec9A-targeting tailored nanoemulsion (Clec9A-TNE) induced extensive proliferation, persistence and activation of chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T cells, leading to the eradication of solid tumours in murine models. This novel approach could lead to the development of new CAR T-cell therapies against some common solid tumour types in patients.
Review
What lies beneath the airway mucosal barrier? Throwing the spotlight on antigen-presenting cell function in the lower respiratory tract
- First Published: 23 July 2020
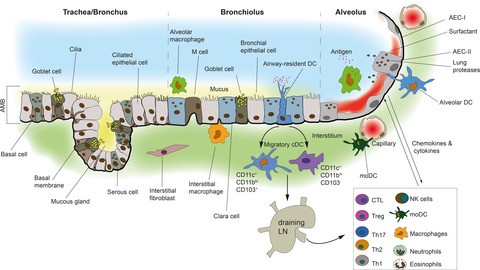
We review the role of different antigen-presenting cells (APC) in the lower airways and the mechanisms used by pathogens to modulate APC function during infectious disease. We discuss features of APC that are unique to the airways and their influence on uptake and presentation of antigen to T cells directly in situ in the airways. We summarize current information on the crucial role that airway APC play in regulating respiratory infection.
Original Articles
Associations of viral ribonucleic acid (RNA) shedding patterns with clinical illness and immune responses in Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) infection
- First Published: 27 July 2020
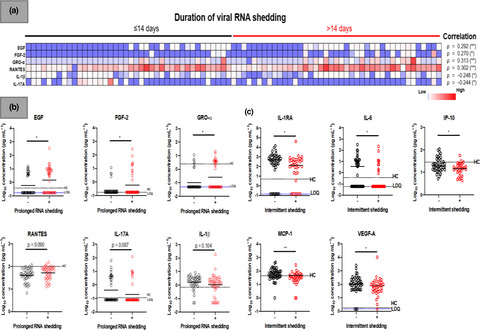
We studied 201 patients with PCR-confirmed COVID-19 infection. We found median RNA shedding was 14 days and intermittent RNA shedding was observed in 38.3%. The only associated clinical factor with prolonged RNA shedding was invasive mechanical ventilation. Importantly, we observed in a subset of patients with cytokine analysis, that prolonged RNA shedding was associated with EGF, FGF-2, GRO-α and RANTES at the initial phase of infection. Intermittent RNA shedding was associated with lower levels of pro-inflammatory cytokines.
Special Feature Review
The contribution of animal models to understanding the role of the immune system in human idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis
- First Published: 27 July 2020
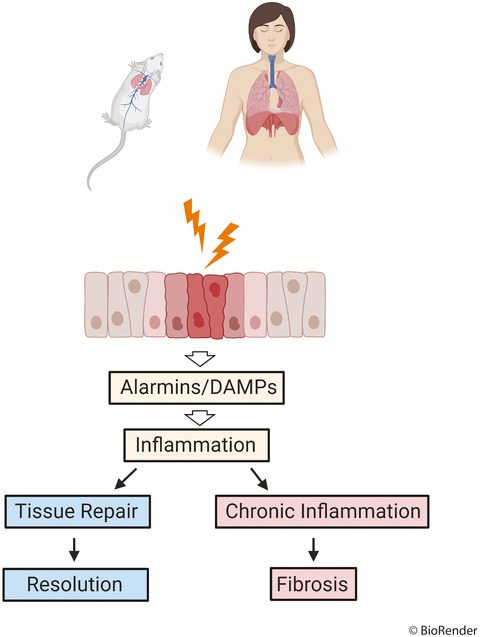
This review will compare some of the models used to investigate the pathogenesis and treatment of pulmonary fibrosis, in particular those used to study immune cell pathogenicity in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis, highlighting their advantages, disadvantages and suitability in representing the human disease.