Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
News and Commentary
Interleukin-22 in urinary tract disease – new experimental directions
- First Published: 07 June 2020
Original Articles
Synovial fluid CD69+CD8+ T cells with tissue-resident phenotype mediate perforin-dependent citrullination in rheumatoid arthritis
- First Published: 08 June 2020
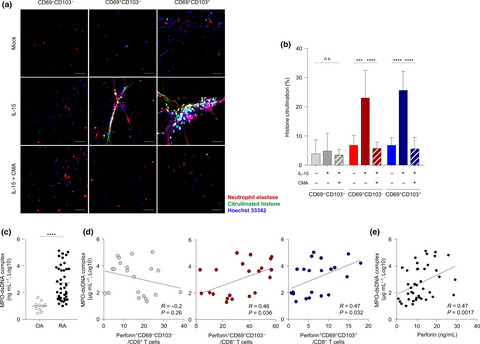
In this study, CD8+ T cells from the synovial fluid of patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA) were analysed. A significant proportion of memory CD8+ T cells expressed canonical markers (CD69 and/or CD103) of tissue-resident memory T (TRM) cells. These TRM-like CD8+ T cells induced histone citrullination in a perforin-mediated manner, contributing anti-citrulline immunity in RA.
Original Article
Immune microenvironment composition in non-small cell lung cancer and its association with survival
- First Published: 12 June 2020
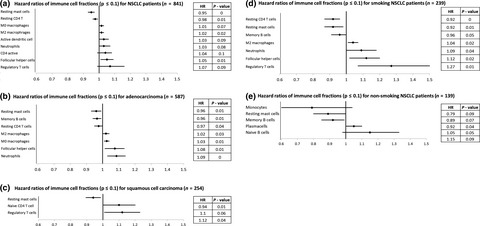
Because of small populations, it is difficult to assess differences in the immunocomposition and their associated survival depending on smoking behaviour and tumor subtype for non-small cell lung cancer patients. Here, we used an in silico approach of all available material to identify these differences and the associations with survival. Immune cell fractions showed different, sometimes opposing associations depending on the tumor subtype and smoking status.
Case Reports
Bioactivity and safety of B7-H3-targeted chimeric antigen receptor T cells against anaplastic meningioma
- First Published: 12 June 2020
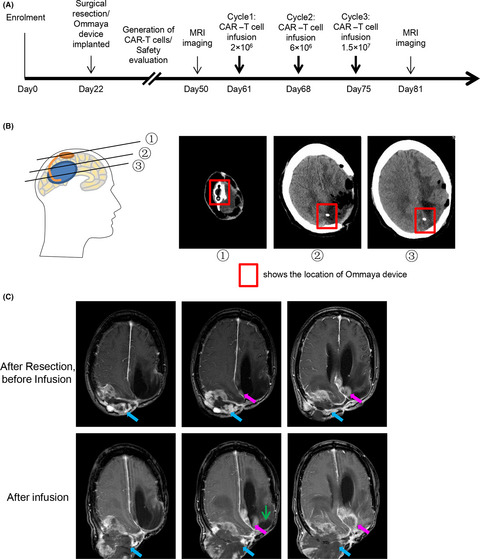
We present a first-in-human B7-H3 (CD276)-targeted CAR-T-cell pilot study for the treatment of recurrent anaplastic meningioma and evaluated the bioactivity and safety of this approach. We provide the evidence of safety and anti-tumor response of local administration autologous B7-H3-targeted CAR-T cells and have established the foundation for further development of B7-H3-targeted CAR-T-cell therapy.
Original Article
Human CLEC9A antibodies deliver Wilms' tumor 1 (WT1) antigen to CD141+ dendritic cells to activate naïve and memory WT1-specific CD8+ T cells
- First Published: 12 June 2020
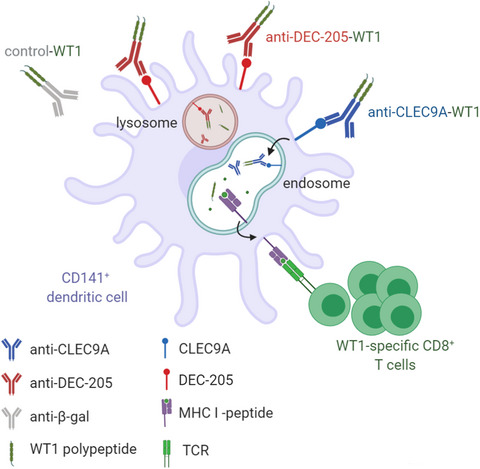
This project developed a new vaccine comprising a human anti-CLEC9A antibody fused to the immunogenic, broadly expressed tumor antigen, WT1. This vaccine specifically delivered WT1 to human CD141+ (cDC1) dendritic cells, for efficient cross-presentation and activation of naïve and memory WT1-specific CD8+ T cells. The anti-CLEC9A-WT1 antibody is a promising new vaccine candidate for malignancies that express WT1.
Reviews
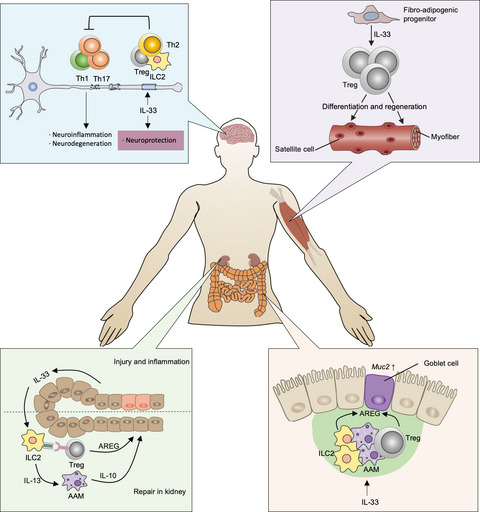
Interleukin (IL)-33: an orchestrator of immunity from host defence to tissue homeostasis
- First Published: 17 June 2020
Original Articles
Transcriptional profiling and immunophenotyping show sustained activation of blood monocytes in subpatent Plasmodium falciparum infection
- First Published: 18 June 2020
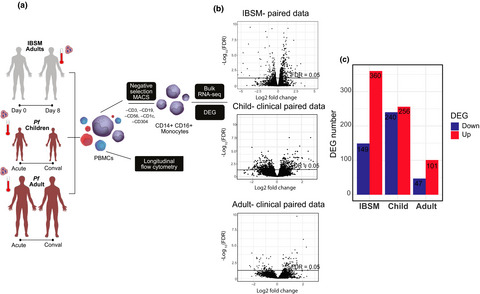
We investigate the transcriptional, functional and phenotypic changes in monocytes during an experimental blood-stage P. falciparum infection in malaria naive healthy subjects and during an episode of clinical malaria in children and adults residing in a malaria-endemic region. We specifically isolated monocytes for transcriptome analysis by RNA sequencing, to determine monocyte gene expression during subpatent and clinical malaria. Monocyte activation during subpatent malaria is driven by an inflammatory molecular signature and a greater magnitude of transcriptional changes in children with acute malaria suggest monocyte phenotypes may change with age or exposure.